Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), often categorized as C, B, or U codes, absolutely exist and are crucial for diagnosing issues within these sophisticated vehicle systems. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert insight and tools to accurately identify and address these codes, ensuring optimal ADAS performance and safety. Let’s explore the specifics of these codes and how they relate to your Mercedes-Benz’s ADAS, so you can understand diagnostic procedures, ADAS troubleshooting, and Mercedes-Benz diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in ADAS
- 2. The Significance of C, B, and U Codes in ADAS Diagnostics
- 3. Common ADAS Components and Their Associated DTCs
- 4. Diagnostic Tools for Reading ADAS DTCs
- 5. Interpreting ADAS DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 6. Common ADAS DTCs and Their Potential Causes
- 7. The Role of Calibration in ADAS Repairs
- 8. Using Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Tools for ADAS DTCs
- 9. The Importance of Staying Updated with ADAS Technology
- 10. Preventing ADAS Issues Through Regular Maintenance
- 11. How ADAS DTCs Impact Vehicle Safety
- 12. DIY vs. Professional ADAS Diagnostics and Repairs
- 13. ADAS DTCs and Their Relationship to Insurance Claims
- 14. Future Trends in ADAS Diagnostics and DTCs
- 15. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ADAS DTCs
- 16. The Costs Associated with ADAS Diagnostics and Repairs
- 17. Resources for Learning More About ADAS DTCs
- 18. Legal and Ethical Considerations in ADAS Repairs
- 19. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist with ADAS DTCs
- 20. Proactive Measures to Minimize ADAS DTCs
- FAQ: Understanding ADAS DTCs
1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in ADAS
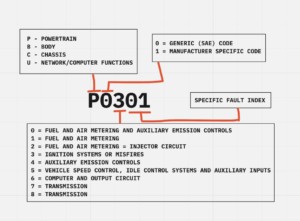
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes used to identify potential problems within a vehicle’s systems, including its Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). These codes are generated by the vehicle’s onboard computer when it detects a malfunction. Understanding how DTCs work is essential for effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
- Definition of DTCs: DTCs are standardized codes that provide a snapshot of a system’s health at the moment an issue is detected.
- Role of DTCs in ADAS: In ADAS, DTCs can pinpoint issues ranging from sensor malfunctions to communication errors between different ADAS components.
2. The Significance of C, B, and U Codes in ADAS Diagnostics
Within the spectrum of DTCs, C, B, and U codes hold specific relevance to ADAS, indicating the area of the vehicle where the fault lies.
- C Codes (Chassis): These codes often relate to systems affecting vehicle handling and stability, such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), ESC (Electronic Stability Control), and steering systems.
- B Codes (Body): B codes typically indicate problems within the vehicle’s body systems, including components like airbags, seatbelts, and central locking, which can interface with ADAS features.
- U Codes (Network & Communication): U codes point to issues in the vehicle’s communication network, which is critical for ADAS functions that rely on data sharing between various modules.
3. Common ADAS Components and Their Associated DTCs
ADAS encompasses a wide range of technologies. Here are some common components and the types of DTCs that might be associated with them:
| ADAS Component | Potential DTC Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Cruise Control | U, C | U codes may indicate communication issues between the ACC module and other vehicle systems. C codes can point to problems with the radar or sensors used by ACC to maintain distance. |
| Lane Keeping Assist | U, C | U codes can signify communication failures between the lane-keeping assist module and the steering system. C codes could indicate issues with the camera or sensors that detect lane markings. |
| Blind Spot Monitoring | U, B | U codes may relate to network communication problems affecting the blind spot monitoring system. B codes could signal malfunctions in the sensors located in the side mirrors or bumpers. |
| Automatic Emergency Braking | U, C | U codes might point to communication issues between the AEB system and the braking system. C codes can indicate problems with the radar, lidar, or camera systems used by AEB to detect potential collisions. |
| Parking Assist Systems | U, B | U codes can relate to communication failures affecting the parking assist system. B codes may indicate malfunctions in the parking sensors located in the bumpers. |
4. Diagnostic Tools for Reading ADAS DTCs
To read ADAS DTCs, specialized diagnostic tools are required that can access the vehicle’s various electronic control units (ECUs).
- OBD-II Scanners: Basic OBD-II scanners can read some ADAS-related codes, particularly those related to engine and emission systems.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: More advanced scan tools, like those offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, can access the specific modules that control ADAS functions, providing a more detailed diagnosis.
- Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Software: For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, software like XENTRY or Vediamo offers in-depth diagnostic capabilities, allowing technicians to pinpoint ADAS issues with greater accuracy.
 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
5. Interpreting ADAS DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
Interpreting ADAS DTCs involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem.
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Read the DTCs: Use the tool to scan for and retrieve any stored DTCs.
- Record the Codes: Note down all the DTCs, including the code type (C, B, or U) and the specific number.
- Consult a Repair Manual: Look up the DTCs in a Mercedes-specific repair manual or database to understand their meaning and potential causes.
- Perform Diagnostic Tests: Follow the diagnostic procedures outlined in the repair manual to further investigate the issue.
- Verify the Repair: After performing the necessary repairs, clear the DTCs and test the system to ensure the problem is resolved.
6. Common ADAS DTCs and Their Potential Causes
Here are some common ADAS DTCs and their potential causes:
| DTC | Description | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C15100 | Steering angle sensor malfunction | Misalignment of the steering angle sensor, faulty sensor wiring, or a defective sensor. |
| B22170 | Radar sensor blocked | Dirt, snow, or other obstructions blocking the radar sensor, misaligned sensor, or a defective sensor. |
| U01000 | Lost communication with the engine control module | Wiring issues, a faulty engine control module, or a problem with the vehicle’s CAN bus network. |
| C11000 | ABS malfunction | Faulty ABS wheel speed sensor, malfunctioning ABS pump, or wiring issues. |
| B10100 | Airbag malfunction | Defective airbag sensor, wiring issues, or a problem with the airbag control module. |
7. The Role of Calibration in ADAS Repairs
ADAS components often require calibration after repairs or replacements to ensure they function correctly.
- Why Calibration is Necessary: Calibration ensures that sensors and cameras are properly aligned and that the system accurately interprets data.
- Calibration Procedures: Calibration typically involves using specialized equipment to align the sensors and cameras according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Post-Calibration Verification: After calibration, it’s essential to verify that the system is functioning correctly through road tests and diagnostic scans.
8. Using Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Tools for ADAS DTCs
Mercedes-Benz vehicles require specialized diagnostic tools to accurately diagnose and repair ADAS issues.
- XENTRY: XENTRY is the official Mercedes-Benz diagnostic software, offering comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for all Mercedes models.
- Vediamo: Vediamo is a more advanced diagnostic tool used by experienced technicians to perform in-depth diagnostics and programming.
- Benefits of Using Mercedes-Specific Tools: These tools provide access to specific ADAS modules, detailed diagnostic information, and guided repair procedures, ensuring accurate and effective repairs.
9. The Importance of Staying Updated with ADAS Technology
ADAS technology is constantly evolving, so staying updated with the latest advancements is crucial for technicians and vehicle owners alike.
- Training and Certification: Technicians should undergo regular training and certification programs to stay proficient in ADAS diagnostics and repair.
- Access to Information: Subscribing to industry publications, attending workshops, and utilizing online resources can help you stay informed about the latest ADAS technology.
- Utilizing Online Resources: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides valuable resources, including articles, guides, and videos, to help you understand and troubleshoot ADAS issues.
10. Preventing ADAS Issues Through Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance can help prevent ADAS issues and ensure optimal performance.
- Sensor Cleaning: Keep sensors and cameras clean and free from obstructions to ensure accurate data collection.
- Wheel Alignment: Maintain proper wheel alignment to ensure that ADAS features like lane keeping assist function correctly.
- Software Updates: Install software updates promptly to address any known issues and improve system performance.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections with a qualified technician to identify and address potential ADAS issues before they escalate.
11. How ADAS DTCs Impact Vehicle Safety
ADAS DTCs can have a significant impact on vehicle safety if left unaddressed.
- Compromised Safety Features: Malfunctioning ADAS components can compromise the effectiveness of safety features like automatic emergency braking and lane keeping assist, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: If ADAS features are not functioning correctly, drivers may not receive timely warnings or assistance, leading to accidents.
- Importance of Prompt Repairs: Addressing ADAS DTCs promptly is crucial to ensure that safety features are functioning as intended and to minimize the risk of accidents.
12. DIY vs. Professional ADAS Diagnostics and Repairs
While some basic ADAS diagnostics can be performed by vehicle owners, professional diagnostics and repairs are often necessary for complex issues.
- DIY Diagnostics: Vehicle owners can use basic OBD-II scanners to read ADAS-related DTCs and perform simple troubleshooting steps.
- Professional Diagnostics: Complex ADAS issues require specialized diagnostic tools, expertise, and calibration procedures that are best handled by trained technicians.
- When to Seek Professional Help: If you encounter ADAS DTCs that you cannot resolve yourself, or if the system requires calibration, it’s essential to seek professional help from a qualified technician.
13. ADAS DTCs and Their Relationship to Insurance Claims
ADAS DTCs can play a role in insurance claims, particularly in cases involving accidents.
- Evidence of Malfunction: ADAS DTCs can provide evidence of a malfunction that may have contributed to an accident.
- Liability: If an accident occurs due to a malfunctioning ADAS component, the vehicle owner or manufacturer may be held liable.
- Importance of Documentation: Documenting ADAS DTCs and repairs can be helpful in insurance claims and legal proceedings.
14. Future Trends in ADAS Diagnostics and DTCs
ADAS technology is rapidly evolving, and future trends in diagnostics and DTCs are likely to include:
- Increased Complexity: As ADAS systems become more complex, diagnostics and DTCs will become more sophisticated.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Over-the-air updates may be used to address software issues and improve ADAS performance.
- Predictive Diagnostics: Predictive diagnostics may be used to identify potential ADAS issues before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Integration with Telematics: ADAS diagnostics may be integrated with telematics systems, allowing for remote monitoring and diagnostics.
15. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ADAS DTCs
Here are some case studies illustrating real-world examples of ADAS DTCs:
- Case Study 1: A Mercedes-Benz C-Class exhibits a C15100 DTC indicating a steering angle sensor malfunction. The technician discovers that the sensor is misaligned due to a recent wheel alignment. After calibrating the sensor, the DTC is cleared, and the lane keeping assist system functions correctly.
- Case Study 2: A Mercedes-Benz E-Class displays a B22170 DTC indicating a blocked radar sensor. The technician finds that the sensor is covered in dirt and snow. After cleaning the sensor, the DTC is cleared, and the adaptive cruise control system functions normally.
- Case Study 3: A Mercedes-Benz S-Class exhibits a U01000 DTC indicating a loss of communication with the engine control module. The technician discovers a wiring issue in the CAN bus network. After repairing the wiring, the DTC is cleared, and the ADAS features function correctly.
16. The Costs Associated with ADAS Diagnostics and Repairs
ADAS diagnostics and repairs can be costly due to the specialized tools, expertise, and calibration procedures required.
- Diagnostic Fees: Diagnostic fees can range from $100 to $300, depending on the complexity of the issue.
- Repair Costs: Repair costs can vary widely depending on the specific ADAS component that needs to be repaired or replaced.
- Calibration Costs: Calibration costs can range from $200 to $500, depending on the number of sensors and cameras that need to be calibrated.
17. Resources for Learning More About ADAS DTCs
There are many resources available for learning more about ADAS DTCs, including:
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles can provide valuable information and insights from other owners and technicians.
- Industry Publications: Industry publications like Automotive Engineering International and SAE International offer technical articles and research papers on ADAS technology.
- Training Courses: Training courses offered by organizations like ASE and I-CAR can provide in-depth knowledge and hands-on experience in ADAS diagnostics and repair.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on ADAS DTCs, including articles, guides, and videos.
18. Legal and Ethical Considerations in ADAS Repairs
ADAS repairs raise several legal and ethical considerations.
- Liability: Technicians and repair shops can be held liable for damages if ADAS repairs are not performed correctly.
- Disclosure: Repair shops have a responsibility to disclose any ADAS malfunctions or repairs to the vehicle owner.
- Calibration: It is unethical to perform ADAS repairs without properly calibrating the system.
19. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist with ADAS DTCs
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of services to assist with ADAS DTCs, including:
- Diagnostic Tools: Providing advanced diagnostic tools that can accurately read and interpret ADAS DTCs.
- Repair Information: Offering detailed repair information and guided procedures for addressing ADAS issues.
- Calibration Services: Providing calibration services to ensure that ADAS components are functioning correctly after repairs.
- Training and Support: Offering training and support to help technicians and vehicle owners understand and troubleshoot ADAS issues.
20. Proactive Measures to Minimize ADAS DTCs
Taking proactive measures can help minimize the occurrence of ADAS DTCs.
- Regular Maintenance: Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule can help prevent ADAS issues.
- Sensor Cleaning: Keeping sensors and cameras clean and free from obstructions can ensure accurate data collection.
- Software Updates: Installing software updates promptly can address any known issues and improve system performance.
- Careful Driving: Avoiding collisions and other incidents that could damage ADAS components can help prevent DTCs.
By understanding ADAS DTCs and taking proactive measures, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz’s safety features are functioning as intended and minimize the risk of accidents.
Facing persistent ADAS DTCs or unsure how to proceed with diagnostics and repairs? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance and support. Our team of experienced technicians can provide accurate diagnostics, reliable repairs, and professional calibration services to ensure your Mercedes-Benz’s ADAS is functioning optimally.
Contact us today:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in maintaining the safety and performance of your Mercedes-Benz. Unlock hidden features, diagnose issues accurately, and receive expert guidance for all your Mercedes-Benz needs.
FAQ: Understanding ADAS DTCs
1. What are ADAS DTCs?
ADAS DTCs (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems Diagnostic Trouble Codes) are codes generated by a vehicle’s onboard computer to indicate malfunctions or issues within its ADAS.
2. What do C, B, and U codes signify in ADAS DTCs?
C codes relate to chassis systems (e.g., ABS, ESC), B codes indicate body system issues (e.g., airbags, seatbelts), and U codes point to network and communication problems.
3. How can I read ADAS DTCs?
You can read ADAS DTCs using an OBD-II scanner or a more advanced diagnostic tool that can access specific ADAS modules.
4. What is the importance of calibrating ADAS components after repairs?
Calibration ensures that sensors and cameras are properly aligned and that the ADAS system accurately interprets data, which is crucial for its correct functioning.
5. Can I perform ADAS diagnostics and repairs myself?
While basic diagnostics can be done by vehicle owners, complex issues require specialized tools and expertise, necessitating professional help.
6. How do ADAS DTCs impact vehicle safety?
If left unaddressed, ADAS DTCs can compromise the effectiveness of safety features like automatic emergency braking and lane keeping assist, increasing the risk of accidents.
7. What are some common causes of ADAS DTCs?
Common causes include sensor malfunctions, wiring issues, communication problems, and obstructions blocking sensors.
8. How can I prevent ADAS issues and DTCs?
Regular maintenance, sensor cleaning, software updates, and careful driving can help prevent ADAS issues and DTCs.
9. What is the role of Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools in addressing ADAS DTCs?
Mercedes-specific tools like XENTRY and Vediamo offer in-depth diagnostic capabilities, allowing technicians to pinpoint ADAS issues with greater accuracy.
10. Where can I find more information about ADAS DTCs?
You can find more information on online forums, industry publications, training courses, and resources like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
This comprehensive guide should provide you with a solid understanding of ADAS DTCs and their significance in maintaining the safety and performance of your Mercedes-Benz.