The 2003 Ford F150 Obd2 Fuse Location is generally within the interior fuse panel, often situated under the dashboard on the driver’s side; identifying its precise location is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues and maintaining your vehicle’s performance, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides and tools to assist you. By using the right diagnostic equipment, understanding fuse box diagrams, and seeking expert guidance, you can efficiently troubleshoot your Ford F150. Key terms include OBD2 scanner, Ford F150 repair, and automotive diagnostics.
Contents
- 1: Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2003 Ford F150
- 1.1: The Role of the OBD2 Port
- 1.2: Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 1.3: Why the OBD2 Fuse Blows
- 2: Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2003 Ford F150
- 2.1: Accessing the Interior Fuse Panel
- 2.2: Using the Owner’s Manual
- 2.3: Common Locations and Markings
- 3: Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the OBD2 Fuse
- 3.1: Safety Precautions
- 3.2: Tools You’ll Need
- 3.3: The Replacement Process
- 4: Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Fuse Issues
- 4.1: Identifying the Root Cause
- 4.2: Checking for Short Circuits
- 4.3: When to Seek Professional Help
- 5: Understanding Fuse Types and Amperage for Your 2003 Ford F150
- 5.1: Identifying the Correct Fuse Type
- 5.2: Understanding Amperage
- 5.3: Risks of Using the Wrong Fuse
- 6: Maintaining Your 2003 Ford F150’s Electrical System
- 6.1: Regular Inspections
- 6.2: Preventing Overloads
- 6.3: Keeping the System Clean
- 7: Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Your 2003 Ford F150
- 7.1: Multimeters
- 7.2: OBD2 Scanners
- 7.3: Oscilloscopes
- 8: Common Electrical Problems in the 2003 Ford F150
- 8.1: GEM Module Issues
- 8.2: Wiring Harness Problems
- 8.3: Sensor Failures
- 9: Upgrading Your 2003 Ford F150’s Electrical System
- 9.1: High-Output Alternators
- 9.2: Enhanced Wiring Harnesses
- 9.3: Auxiliary Fuse Boxes
- 10: The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and the OBD2 Port
- 10.1: Wireless Diagnostics
- 10.2: Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 10.3: AI and Machine Learning
- 11: OBD2 Fuse Location and its Impact on Vehicle Performance
- 11.1: Optimal Fuse Placement
- 11.2: Accessibility for Technicians
- 11.3: User-Friendly Maintenance
- 12: Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Ford F150 Diagnostics
- 12.1: Expert Diagnostic Support
- 12.2: Comprehensive Tool Selection
- 12.3: Step-by-Step Guides
- 13: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Fuse Issues in Ford F150 Vehicles
- 13.1: Case Study 1: Intermittent Scanner Connection
- 13.2: Case Study 2: Check Engine Light Reset Failure
- 13.3: Case Study 3: Repeated Fuse Blows
- 14: How to Use a Multimeter to Test Your 2003 Ford F150 Fuses
- 14.1: Setting Up the Multimeter
- 14.2: Testing the Fuse
- 14.3: Interpreting the Results
- 15: Advanced Tips for Diagnosing Electrical Issues in Your 2003 Ford F150
- 15.1: Voltage Drop Testing
- 15.2: Reading Wiring Diagrams
- 15.3: Using a Scan Tool for Live Data
- 16: What to Do When Your Ford F150 OBD2 Port Isn’t Working
- 16.1: Checking the Connector
- 16.2: Testing the Power and Ground
- 16.3: Checking for Communication Issues
- 17: Identifying the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2003 Ford F150
- 17.1: Basic Code Readers
- 17.2: Advanced Scan Tools
- 17.3: Compatibility and Features
- 18: How Regular Maintenance Can Prevent Electrical Problems in Your Ford F150
- 18.1: Battery Maintenance
- 18.2: Checking and Replacing Fuses
- 18.3: Inspecting Wiring
- 19: Understanding Ford F150 Electrical System Terminology
- 19.1: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
- 19.2: Grounding
- 19.3: Short Circuits and Open Circuits
- 20: Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
- 20.1: How to Reach Us
- 20.2: Services Offered
- 20.3: Why Choose Us?
- FAQ: 2003 Ford F150 OBD2 Fuse Location
1: Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2003 Ford F150
What makes the OBD2 fuse so important in your 2003 Ford F150? The OBD2 fuse is crucial because it powers the diagnostic port, allowing mechanics and vehicle owners to access vital data about the engine and other systems. Without a functioning OBD2 port, diagnosing problems becomes significantly harder, leading to potential delays and increased repair costs.
1.1: The Role of the OBD2 Port
How does the OBD2 port function and why is it essential for modern vehicle maintenance? The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface used to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s computer. These codes provide insights into various malfunctions, enabling targeted repairs. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics through the OBD2 port can reduce repair times by up to 40%.
1.2: Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
What are the telltale signs of a blown OBD2 fuse in your 2003 Ford F150? Common symptoms include the inability to connect an OBD2 scanner, a check engine light that won’t reset, and issues with emissions testing. A faulty OBD2 fuse can prevent you from reading diagnostic codes, leading to guesswork and potentially incorrect repairs.
1.3: Why the OBD2 Fuse Blows
What are the typical reasons for the OBD2 fuse to blow in your 2003 Ford F150? Overloads, short circuits, and faulty wiring are common causes. Connecting a malfunctioning OBD2 scanner or experiencing electrical surges can also lead to a blown fuse. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent these issues.
2: Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2003 Ford F150
Where exactly can you find the OBD2 fuse in your 2003 Ford F150? The OBD2 fuse is typically located in the interior fuse panel, often found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consulting your vehicle’s owner’s manual is the best way to confirm its exact placement.
2.1: Accessing the Interior Fuse Panel
How do you properly access the interior fuse panel to check the OBD2 fuse? Typically, the fuse panel is behind a small cover, which can be opened by hand or with a flathead screwdriver. Ensure the ignition is turned off before accessing the panel to avoid electrical shock or further damage.
2.2: Using the Owner’s Manual
Why is the owner’s manual your best resource for finding the OBD2 fuse? The owner’s manual provides a detailed fuse box diagram specific to your 2003 Ford F150. This diagram indicates the exact location of the OBD2 fuse, its amperage, and its function.
2.3: Common Locations and Markings
Are there any common locations or markings to look for when searching for the OBD2 fuse? Look for fuses labeled “OBD,” “DLC” (Data Link Connector), or “Diagnostic Port.” These markings can help you quickly identify the correct fuse in the panel.
 2003 Ford F-150 fuse box diagram Passenger compartment fuse panel
2003 Ford F-150 fuse box diagram Passenger compartment fuse panel
3: Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the OBD2 Fuse
How can you safely and effectively replace a blown OBD2 fuse in your 2003 Ford F150? Replacing a blown fuse is a straightforward process, but it’s important to follow safety precautions and use the correct replacement fuse.
3.1: Safety Precautions
What safety measures should you take before replacing the OBD2 fuse? Always turn off the ignition and any accessories to prevent electrical shock or further damage. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes, and ensure your hands are dry.
3.2: Tools You’ll Need
Which tools are necessary for replacing the OBD2 fuse in your 2003 Ford F150? You’ll need a fuse puller (often included in the fuse box), a replacement fuse with the correct amperage, and a flashlight to see clearly inside the fuse panel.
3.3: The Replacement Process
What are the steps for replacing the OBD2 fuse in your 2003 Ford F150?
- Locate the fuse panel and open it.
- Use the fuse puller to remove the blown fuse.
- Inspect the fuse to confirm it is blown (the filament will be broken).
- Insert the new fuse with the correct amperage into the slot.
- Close the fuse panel and test the OBD2 port with a scanner.
4: Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Fuse Issues
What should you do if the OBD2 fuse keeps blowing in your 2003 Ford F150? Repeatedly blown fuses indicate a more significant electrical problem that needs to be addressed.
4.1: Identifying the Root Cause
How do you diagnose the underlying cause of a repeatedly blown OBD2 fuse? Check for short circuits, damaged wiring, or a faulty OBD2 scanner. A multimeter can help you test for continuity and voltage issues in the circuit.
4.2: Checking for Short Circuits
What steps can you take to check for short circuits in the OBD2 system? Visually inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or corrosion. Use a multimeter to test for continuity between the power wire and ground.
4.3: When to Seek Professional Help
When is it necessary to consult a professional mechanic for OBD2 fuse problems? If you’re unable to identify the cause of the blown fuses or if the problem persists after troubleshooting, it’s best to seek professional help. Electrical issues can be complex and require specialized tools and knowledge. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can connect you with experienced technicians for expert diagnostics and repairs.
5: Understanding Fuse Types and Amperage for Your 2003 Ford F150
Why is it crucial to use the correct fuse type and amperage in your 2003 Ford F150? Using the wrong fuse can lead to electrical damage or even a fire. The correct fuse protects the circuit by blowing before excessive current can cause harm.
5.1: Identifying the Correct Fuse Type
How do you determine the correct fuse type for the OBD2 port in your 2003 Ford F150? Consult your owner’s manual for the specified fuse type. Common types include mini, blade, and cartridge fuses. Ensure the replacement fuse matches the original in both type and size.
5.2: Understanding Amperage
What does amperage mean, and why is it important to match the correct amperage when replacing a fuse? Amperage is the measure of electrical current a fuse can handle before blowing. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging the circuit.
5.3: Risks of Using the Wrong Fuse
What are the potential consequences of using a fuse with incorrect amperage? Using a fuse with a lower amperage can cause it to blow prematurely, while using a higher amperage fuse can lead to overheating, electrical damage, or even a fire.
6: Maintaining Your 2003 Ford F150’s Electrical System
What are the best practices for maintaining your 2003 Ford F150’s electrical system and preventing fuse-related issues? Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent electrical problems and extend the life of your vehicle.
6.1: Regular Inspections
How often should you inspect your vehicle’s electrical system and fuses? It’s recommended to inspect your vehicle’s electrical system at least once a year, or more frequently if you experience any electrical issues. Check for corroded terminals, damaged wiring, and blown fuses.
6.2: Preventing Overloads
What steps can you take to prevent electrical overloads that can cause fuses to blow? Avoid using multiple high-power accessories at the same time, and ensure that all aftermarket accessories are properly installed and fused.
6.3: Keeping the System Clean
Why is it important to keep your vehicle’s electrical system clean and free of corrosion? Corrosion can increase resistance in the electrical system, leading to overheating and blown fuses. Clean battery terminals and wiring connections regularly to ensure optimal performance.
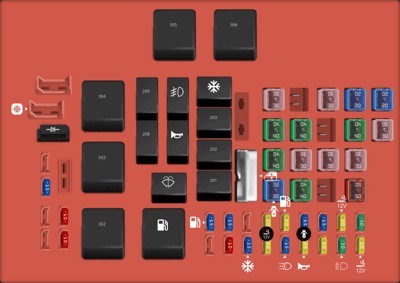 2003 Ford F-150 fuse box diagram Power distribution box
2003 Ford F-150 fuse box diagram Power distribution box
7: Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Your 2003 Ford F150
What advanced diagnostic tools can help you troubleshoot electrical issues in your 2003 Ford F150 beyond just checking the OBD2 fuse? Advanced tools can provide deeper insights into your vehicle’s systems and help identify complex problems.
7.1: Multimeters
How can a multimeter help you diagnose electrical problems in your 2003 Ford F150? A multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance, allowing you to test for continuity, short circuits, and voltage drops in the electrical system.
7.2: OBD2 Scanners
What are the benefits of using an advanced OBD2 scanner compared to a basic code reader? Advanced OBD2 scanners can provide real-time data, perform diagnostic tests, and reset trouble codes. They often include features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bidirectional control.
7.3: Oscilloscopes
How can an oscilloscope help diagnose intermittent electrical issues? An oscilloscope can display electrical signals over time, allowing you to identify intermittent problems that may not be apparent with a multimeter or OBD2 scanner.
8: Common Electrical Problems in the 2003 Ford F150
What are some common electrical problems specific to the 2003 Ford F150 that might lead to OBD2 fuse issues? Understanding these common issues can help you troubleshoot more effectively.
8.1: GEM Module Issues
How can problems with the Generic Electronic Module (GEM) affect the OBD2 system? The GEM controls various electrical functions, and a faulty GEM can cause a range of issues, including blown fuses and communication problems with the OBD2 port.
8.2: Wiring Harness Problems
What are the common wiring harness problems in the 2003 Ford F150, and how do they impact fuse integrity? Over time, the wiring harness can become damaged due to wear and tear, corrosion, or rodent damage. Damaged wiring can lead to short circuits and blown fuses.
8.3: Sensor Failures
How can failing sensors contribute to electrical problems and blown fuses? Faulty sensors can send incorrect signals to the vehicle’s computer, leading to electrical overloads and blown fuses. Regularly testing and replacing sensors can help prevent these issues.
9: Upgrading Your 2003 Ford F150’s Electrical System
What upgrades can you make to your 2003 Ford F150’s electrical system to improve reliability and performance? Upgrading certain components can enhance the system’s durability and functionality.
9.1: High-Output Alternators
What are the benefits of upgrading to a high-output alternator? A high-output alternator can provide more power for aftermarket accessories and prevent voltage drops, reducing the risk of blown fuses and electrical problems.
9.2: Enhanced Wiring Harnesses
How can replacing the factory wiring harness improve electrical system reliability? Upgrading to a higher-quality wiring harness can reduce the risk of corrosion, damage, and short circuits, improving the overall reliability of the electrical system.
9.3: Auxiliary Fuse Boxes
What are auxiliary fuse boxes, and why might you need one? Auxiliary fuse boxes provide additional circuits for aftermarket accessories, preventing overloads on the factory fuse panel.
10: The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and the OBD2 Port
How is automotive diagnostics evolving, and what role will the OBD2 port play in the future? The OBD2 port remains a crucial interface, but new technologies are enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
10.1: Wireless Diagnostics
What are the advantages of wireless OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools? Wireless scanners allow for greater flexibility and convenience, enabling technicians to diagnose problems from anywhere around the vehicle.
10.2: Cloud-Based Diagnostics
How is cloud technology improving automotive diagnostics? Cloud-based diagnostic platforms provide access to vast databases of repair information, diagnostic codes, and troubleshooting guides, improving the accuracy and efficiency of repairs.
10.3: AI and Machine Learning
How are AI and machine learning transforming automotive diagnostics? AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze data from multiple sources to identify complex problems and predict potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance.
11: OBD2 Fuse Location and its Impact on Vehicle Performance
How does the location of the OBD2 fuse specifically affect the overall performance and diagnostic capabilities of your 2003 Ford F150? The strategic placement of the OBD2 fuse ensures the diagnostic port receives consistent power, which is crucial for accurate and timely vehicle maintenance.
11.1: Optimal Fuse Placement
Why is the interior fuse panel the most common and effective location for the OBD2 fuse? The interior fuse panel is easily accessible and protected from the elements, making it an ideal location for the OBD2 fuse. This placement ensures that the fuse can be quickly checked and replaced if needed.
11.2: Accessibility for Technicians
How does the location of the OBD2 fuse enhance the efficiency of automotive technicians? The OBD2 fuse’s accessible location allows technicians to quickly diagnose issues by ensuring the diagnostic port is functioning correctly. This saves time and reduces labor costs.
11.3: User-Friendly Maintenance
In what ways does the OBD2 fuse location support DIY maintenance for vehicle owners? The easy-to-find location of the OBD2 fuse empowers vehicle owners to perform basic diagnostic checks and maintenance, enhancing their ability to keep their vehicles running smoothly.
12: Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Ford F150 Diagnostics
Why should you choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for your Ford F150 diagnostic needs? We provide comprehensive guides, expert advice, and top-quality diagnostic tools to help you maintain and repair your vehicle.
12.1: Expert Diagnostic Support
How does MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer expert diagnostic support for Ford F150 owners? Our website features detailed guides, troubleshooting tips, and expert advice to help you diagnose and resolve electrical issues in your Ford F150.
12.2: Comprehensive Tool Selection
What types of diagnostic tools are available through MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN? We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, from basic code readers to advanced OBD2 scanners and multimeters, ensuring you have the right equipment for your needs.
12.3: Step-by-Step Guides
How do the step-by-step guides on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN assist with diagnosing and repairing your Ford F150? Our step-by-step guides provide clear, easy-to-follow instructions for diagnosing and repairing common electrical issues, including OBD2 fuse problems.
13: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Fuse Issues in Ford F150 Vehicles
Can you share some real-world examples of how OBD2 fuse issues have affected Ford F150 owners and how these problems were resolved? Sharing these examples provides practical insights into diagnosing and fixing OBD2 fuse-related problems.
13.1: Case Study 1: Intermittent Scanner Connection
How did one Ford F150 owner resolve an issue with an intermittent OBD2 scanner connection? The owner found that the OBD2 fuse was loose in its slot, causing an intermittent connection. By securing the fuse, the connection was stabilized and the scanner worked correctly.
13.2: Case Study 2: Check Engine Light Reset Failure
What steps did a technician take to address a Ford F150 with a check engine light that wouldn’t reset? The technician discovered a blown OBD2 fuse. After replacing the fuse, the check engine light could be successfully reset, and diagnostic codes could be read.
13.3: Case Study 3: Repeated Fuse Blows
How did a mechanic diagnose and fix the problem of a repeatedly blown OBD2 fuse in a Ford F150? The mechanic traced the issue to a short circuit in the wiring harness connected to the OBD2 port. Repairing the harness resolved the short circuit and prevented further fuse failures.
14: How to Use a Multimeter to Test Your 2003 Ford F150 Fuses
Why is a multimeter a valuable tool for testing fuses in your 2003 Ford F150? A multimeter provides a reliable way to check the continuity of a fuse, ensuring it is functioning correctly.
14.1: Setting Up the Multimeter
What are the initial steps for setting up a multimeter to test a fuse? Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a diode symbol or a sound wave). Ensure the multimeter is properly calibrated and the battery is charged.
14.2: Testing the Fuse
How do you properly test a fuse using a multimeter?
- Remove the fuse from the fuse panel.
- Touch one probe of the multimeter to each end of the fuse.
- If the multimeter shows continuity (usually indicated by a beep or a reading of 0 ohms), the fuse is good. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown.
14.3: Interpreting the Results
How do you interpret the readings on the multimeter to determine the condition of the fuse? A reading of continuity indicates a functional fuse, while a lack of continuity indicates a blown fuse that needs replacement.
15: Advanced Tips for Diagnosing Electrical Issues in Your 2003 Ford F150
What advanced techniques can you use to diagnose complex electrical issues beyond just checking fuses? These tips can help you tackle more challenging problems in your Ford F150’s electrical system.
15.1: Voltage Drop Testing
How can voltage drop testing help identify problems in your 2003 Ford F150’s electrical circuits? Voltage drop testing measures the amount of voltage lost across a circuit, indicating areas of high resistance or poor connections.
15.2: Reading Wiring Diagrams
Why is understanding wiring diagrams essential for advanced electrical diagnostics? Wiring diagrams provide a detailed map of the vehicle’s electrical system, allowing you to trace circuits, identify components, and troubleshoot problems effectively.
15.3: Using a Scan Tool for Live Data
How can a scan tool with live data capabilities assist in diagnosing electrical issues? Live data from sensors and modules can provide valuable insights into the operation of the electrical system, helping you identify faulty components and diagnose intermittent problems.
16: What to Do When Your Ford F150 OBD2 Port Isn’t Working
What steps should you take if your Ford F150’s OBD2 port is not functioning, even after checking the fuse? A non-functional OBD2 port can be caused by several factors, requiring a systematic approach to diagnosis.
16.1: Checking the Connector
How do you inspect the OBD2 port connector for damage or corrosion? Visually inspect the OBD2 port for bent pins, corrosion, or other damage. Clean the connector with electrical contact cleaner if necessary.
16.2: Testing the Power and Ground
What steps can you take to test the power and ground connections at the OBD2 port? Use a multimeter to check for 12V power and a good ground connection at the OBD2 port. Lack of power or ground can prevent the port from functioning correctly.
16.3: Checking for Communication Issues
How do you diagnose communication issues between the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer? Use an advanced OBD2 scanner to check for communication errors. If the scanner cannot establish a connection, there may be a problem with the vehicle’s computer or the wiring between the port and the computer.
17: Identifying the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 2003 Ford F150
What factors should you consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner for your 2003 Ford F150? Selecting the right scanner ensures you can accurately diagnose and address issues.
17.1: Basic Code Readers
What are the capabilities of basic OBD2 code readers, and who are they best suited for? Basic code readers can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and provide a brief description of the problem. They are best suited for DIYers who need to diagnose simple issues.
17.2: Advanced Scan Tools
What features do advanced OBD2 scan tools offer, and when are they necessary? Advanced scan tools offer features like live data streaming, bidirectional control, and enhanced diagnostic tests. They are necessary for diagnosing complex problems and performing advanced repairs.
17.3: Compatibility and Features
How do you ensure that an OBD2 scanner is compatible with your 2003 Ford F150 and offers the necessary features? Check the scanner’s compatibility list to ensure it supports your vehicle’s make and model. Look for features like ABS, SRS, and transmission diagnostics.
18: How Regular Maintenance Can Prevent Electrical Problems in Your Ford F150
Why is regular maintenance essential for preventing electrical problems in your Ford F150? Proactive maintenance can help identify and address potential issues before they lead to costly repairs.
18.1: Battery Maintenance
How can proper battery maintenance prevent electrical issues in your Ford F150? Regularly clean battery terminals, check the battery’s voltage, and ensure the battery is securely mounted. A weak or corroded battery can cause a range of electrical problems.
18.2: Checking and Replacing Fuses
How often should you check and replace fuses in your Ford F150? Check fuses regularly for signs of damage or corrosion. Replace any blown or damaged fuses with the correct amperage.
18.3: Inspecting Wiring
Why is it important to regularly inspect wiring for damage or wear? Regularly inspect wiring for frayed insulation, corrosion, or damage. Repair or replace any damaged wiring to prevent short circuits and electrical problems.
19: Understanding Ford F150 Electrical System Terminology
What are some key electrical system terms that Ford F150 owners should understand? Familiarizing yourself with these terms will help you better understand your vehicle’s electrical system and diagnose problems effectively.
19.1: Voltage, Current, and Resistance
What do voltage, current, and resistance mean in the context of your vehicle’s electrical system?
- Voltage: The electrical potential difference that drives current through a circuit.
- Current: The flow of electrical charge through a circuit.
- Resistance: The opposition to the flow of current in a circuit.
19.2: Grounding
Why is proper grounding essential in a vehicle’s electrical system? Grounding provides a return path for electrical current, ensuring that circuits function correctly and preventing electrical shocks.
19.3: Short Circuits and Open Circuits
What is the difference between a short circuit and an open circuit, and how do they affect your vehicle?
- Short Circuit: An unintended path for current to flow, often resulting in excessive current and blown fuses.
- Open Circuit: A break in the circuit, preventing current from flowing and causing components to malfunction.
20: Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Need further assistance with your 2003 Ford F150’s OBD2 fuse or other diagnostic needs? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance and support.
20.1: How to Reach Us
What is the best way to contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for diagnostic support? You can reach us at our address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Call or message us on Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
20.2: Services Offered
What types of diagnostic services does MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for Ford F150 vehicles? We offer expert diagnostic support, comprehensive guides, and a wide selection of diagnostic tools to help you maintain and repair your Ford F150.
20.3: Why Choose Us?
Why should you choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for your Ford F150 diagnostic needs? We provide expert advice, comprehensive resources, and top-quality tools to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us today for all your diagnostic needs.
Don’t let electrical issues keep you off the road. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance with your 2003 Ford F150! Our team is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any electrical problems you may be experiencing. Reach us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
FAQ: 2003 Ford F150 OBD2 Fuse Location
1. Where is the OBD2 fuse located in a 2003 Ford F150?
The OBD2 fuse is typically located in the interior fuse panel, often found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
2. What does the OBD2 fuse do?
The OBD2 fuse powers the diagnostic port, allowing mechanics and vehicle owners to access vital data about the engine and other systems.
3. What are the symptoms of a blown OBD2 fuse?
Symptoms include the inability to connect an OBD2 scanner, a check engine light that won’t reset, and issues with emissions testing.
4. How do I replace the OBD2 fuse in my 2003 Ford F150?
Locate the fuse panel, remove the blown fuse with a fuse puller, and insert a new fuse with the correct amperage into the slot.
5. What if the OBD2 fuse keeps blowing?
Repeatedly blown fuses indicate a more significant electrical problem, such as a short circuit or damaged wiring, that needs to be addressed.
6. What type of fuse does the OBD2 port use?
Consult your owner’s manual for the specified fuse type, as it can vary. Common types include mini, blade, and cartridge fuses.
7. Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage?
No, using a fuse with a higher amperage can allow too much current to flow, potentially damaging the circuit.
8. How often should I inspect my vehicle’s electrical system?
It’s recommended to inspect your vehicle’s electrical system at least once a year, or more frequently if you experience any electrical issues.
9. What tools do I need to replace a fuse?
You’ll need a fuse puller, a replacement fuse with the correct amperage, and a flashlight to see clearly inside the fuse panel.
10. Where can I find expert diagnostic support for my Ford F150?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides, troubleshooting tips, and expert advice to help you diagnose and resolve electrical issues in your Ford F150.