Mitsubishi OBD2 pinout provides access to your vehicle’s diagnostic data, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you understand and utilize this information effectively. By understanding the pinout, you can accurately diagnose issues and potentially perform maintenance tasks yourself. Learn about OBD2 connector, diagnostic protocols, and ECU information.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and Mitsubishi Vehicles
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. Why is OBD2 Important for Mitsubishi Vehicles?
- 1.3. Common Mitsubishi Models and OBD2 Compatibility
- 2. Decoding the OBD2 Connector Pinout for Mitsubishi
- 2.1. Standard OBD2 Connector Pin Layout
- 2.2. Mitsubishi Specific Pin Assignments
- 2.3. Identifying Diagnostic Protocols Used by Mitsubishi
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using the OBD2 Pinout for Diagnostics
- 3.1. Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
- 3.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Mitsubishi Vehicle
- 3.3. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.4. Using the Pinout to Test Specific Components
- 4. Common Issues Diagnosed Using the Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
- 4.1. Engine Performance Problems
- 4.2. Transmission Issues
- 4.3. ABS and Traction Control Problems
- 4.4. Electrical System Faults
- 5. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Pinouts
- 5.1. Disconnecting the Battery
- 5.2. Using Proper Grounding Techniques
- 5.3. Avoiding Short Circuits
- 5.4. Consulting the Vehicle’s Service Manual
- 6. Advanced Diagnostics with Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
- 6.1. Reprogramming the ECU
- 6.2. Data Logging and Analysis
- 6.3. Customizing Vehicle Parameters
- 7. OBD2 Pinout for Specific Mitsubishi Models
- 7.1. Mitsubishi Lancer (2008-2015)
- 7.2. Mitsubishi Outlander XL (2007-2012)
- 7.3. Mitsubishi ASX (2011+)
- 7.4. Mitsubishi Outlander (2013+)
- 7.5. Key Considerations
- 8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Mitsubishi
- 8.1. Compatibility with Mitsubishi Protocols
- 8.2. Features and Functionality
- 8.3. User Interface and Ease of Use
- 8.4. Scanner Updates and Support
- 8.5. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mitsubishi Vehicles
- 9. Resources for Mitsubishi OBD2 Diagnostics
- 9.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 9.2. Vehicle-Specific Service Manuals
- 9.3. Diagnostic Code Databases
- 9.4. Professional Training Courses
- 10. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Connection Problems
- 10.1. Scanner Not Powering On
- 10.2. Scanner Unable to Connect to the Vehicle
- 10.3. Intermittent Connection Issues
- 11. OBD2 Compatibility List for Mitsubishi Vehicles
- 12. Understanding Diagnostic Protocols Used by Mitsubishi
- 13. Where to Find Reliable OBD-II Cables and Adapters
- 13.1. Trusted Suppliers
- 13.2. Key Considerations When Purchasing Cables
- 14. FAQ: Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
- 14.1. Which OBD2 scanner is best for Mitsubishi?
- 14.2. How do I find the OBD2 port in my Mitsubishi?
- 14.3. Can I use a generic OBD2 scanner with my Mitsubishi?
- 14.4. What does a specific DTC code mean?
- 14.5. How do I clear DTCs from my Mitsubishi ECU?
- 14.6. What safety precautions should I take when working with OBD2 pinouts?
- 14.7. Where can I find a reliable OBD2 pinout diagram for my Mitsubishi?
- 14.8. What is the CAN bus, and why is it important?
- 14.9. Can I reprogram my Mitsubishi ECU using the OBD2 port?
- 14.10. How often should I scan my Mitsubishi for DTCs?
- 15. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and Mitsubishi Vehicles
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a standardized system used in most vehicles, including Mitsubishi models, to provide access to engine and vehicle data for diagnostics and monitoring. It’s crucial for technicians and car owners alike. OBD2 enhances vehicle maintenance and performance.
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2, short for On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system implemented in vehicles to monitor and report on their performance. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated in the United States for all cars manufactured after 1996 to monitor emission-related components. This system helps in diagnosing issues related to the engine, transmission, and other parts of the vehicle. It provides a standardized way to access vehicle health data.
1.2. Why is OBD2 Important for Mitsubishi Vehicles?
For Mitsubishi vehicles, OBD2 offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Quickly identify issues, reducing diagnostic time.
- Emission Control: Monitor emission-related components to ensure compliance with environmental standards.
- Performance Monitoring: Track vehicle performance metrics for proactive maintenance.
- Cost Savings: Diagnose and fix minor issues early, avoiding costly repairs.
1.3. Common Mitsubishi Models and OBD2 Compatibility
Most Mitsubishi models manufactured from the late 1990s onward are OBD2 compliant. Here’s a quick compatibility list:
- Mitsubishi Lancer: 1996 and newer.
- Mitsubishi Outlander: 2003 and newer.
- Mitsubishi Pajero: 1996 and newer.
- Mitsubishi Mirage: 1997 and newer.
- Mitsubishi Montero: 1996 and newer.
Always verify your specific model year to confirm OBD2 compliance.
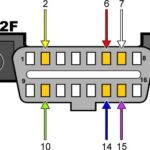
2. Decoding the OBD2 Connector Pinout for Mitsubishi
Understanding the OBD2 connector pinout is crucial for performing accurate diagnostics on your Mitsubishi vehicle. Each pin serves a specific function, enabling communication between diagnostic tools and the vehicle’s computer.
2.1. Standard OBD2 Connector Pin Layout
The OBD2 connector has a standardized 16-pin layout. Key pins include:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (Controller Area Network)
- Pin 7: K-Line (ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4)
- Pin 14: CAN Low
- Pin 16: Battery Power (+12V)
These pins are essential for power, grounding, and communication.
2.2. Mitsubishi Specific Pin Assignments
While the OBD2 connector is standardized, Mitsubishi may have specific assignments for certain pins. Here’s a general overview:
| Pin | Signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Control | Diagnostic control |
| 4 | CGND | Chassis ground |
| 5 | SGND | Signal ground |
| 6 | CAN High | CAN communication line |
| 7 | K-Line | MPI, CVT, SRS, Immobilizer |
| 14 | CAN Low | CAN communication line |
| 16 | +12v | Battery power supply (+12V) |
Consult your vehicle’s service manual for precise pin assignments.
2.3. Identifying Diagnostic Protocols Used by Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi vehicles typically use several OBD2 protocols:
- ISO 9141-2: Older models.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Intermediate models.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Newer models.
Using the correct protocol ensures successful communication with the vehicle’s ECU.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using the OBD2 Pinout for Diagnostics
Using the OBD2 pinout effectively requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you diagnose your Mitsubishi vehicle.
3.1. Gathering Necessary Tools and Equipment
Before starting, gather the following:
- OBD2 Scanner: A reliable scanner compatible with Mitsubishi vehicles.
- OBD2 Connector Pinout Diagram: Specific to your Mitsubishi model.
- Multimeter: For testing voltage and continuity.
- Vehicle Service Manual: Provides detailed information about your vehicle.
Having these tools ensures you can perform thorough diagnostics.
3.2. Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Mitsubishi Vehicle
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Ensure a secure connection.
- Turn on the Ignition: But do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to connect to the vehicle.
A proper connection is crucial for accurate data retrieval.
3.3. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Retrieve DTCs: Use the scanner to read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU.
- Record the Codes: Note down all DTCs for reference.
- Interpret the Codes: Consult your service manual or a reliable online database to understand what each code means.
DTCs provide valuable clues about the nature and location of the problem.
3.4. Using the Pinout to Test Specific Components
- Identify the Component: Determine which component you want to test.
- Locate Relevant Pins: Use the pinout diagram to find the pins associated with that component.
- Perform Tests: Use a multimeter to check voltage, continuity, or resistance as specified in the service manual.
This allows you to verify the electrical integrity of the component and its connections.
4. Common Issues Diagnosed Using the Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
The OBD2 pinout can help diagnose a wide range of issues in Mitsubishi vehicles. Here are some common problems and how the pinout aids in their diagnosis.
4.1. Engine Performance Problems
- Symptoms: Poor fuel economy, rough idling, stalling.
- DTCs: P0300 (random misfire), P0171 (system too lean).
- Pinout Use: Check the fuel injector circuits (if applicable) and O2 sensor signals.
4.2. Transmission Issues
- Symptoms: Erratic shifting, failure to shift, slipping.
- DTCs: P0700 (transmission control system malfunction), P0740 (torque converter circuit).
- Pinout Use: Verify the integrity of the transmission control module (TCM) communication lines and sensor signals.
4.3. ABS and Traction Control Problems
- Symptoms: ABS light on, traction control malfunction.
- DTCs: C0031 (left front wheel speed sensor), C1210 (pressure sensor malfunction).
- Pinout Use: Check the wheel speed sensor circuits and ABS module communication lines.
4.4. Electrical System Faults
- Symptoms: Battery drain, starting problems, malfunctioning lights.
- DTCs: U0100 (lost communication with ECM/PCM), B1000 (ECU malfunction).
- Pinout Use: Verify power and ground connections to the ECU and other modules.
5. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Pinouts
Working with OBD2 pinouts involves electrical testing, so safety should be your top priority.
5.1. Disconnecting the Battery
Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before performing any electrical tests. This prevents accidental shorts and protects you and the vehicle.
5.2. Using Proper Grounding Techniques
Ensure your multimeter and other testing equipment are properly grounded. This prevents inaccurate readings and potential electrical damage.
5.3. Avoiding Short Circuits
Be careful not to create short circuits when probing the OBD2 connector. Use insulated test leads and avoid touching multiple pins simultaneously.
5.4. Consulting the Vehicle’s Service Manual
Always refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific safety procedures and diagnostic information. This ensures you follow the correct procedures and avoid causing further damage.
6. Advanced Diagnostics with Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
For advanced users, the OBD2 pinout can be used for more sophisticated diagnostics and customization.
6.1. Reprogramming the ECU
Some advanced users reprogram the ECU to improve performance or customize vehicle settings. This requires specialized software and hardware.
6.2. Data Logging and Analysis
The OBD2 port can be used to log real-time data from the vehicle, which can be analyzed to identify performance issues or optimize tuning.
6.3. Customizing Vehicle Parameters
Certain parameters, such as idle speed and fuel mixture, can be adjusted via the OBD2 port with the right tools and knowledge.
Disclaimer: Modifying ECU settings can void warranties and may not be legal in all areas. Perform these modifications at your own risk.
7. OBD2 Pinout for Specific Mitsubishi Models
Understanding the OBD2 pinout can vary slightly depending on the Mitsubishi model. Here are some specific pinout details for popular models like the Lancer, Outlander, and ASX.
7.1. Mitsubishi Lancer (2008-2015)
| Pin | Signal | Description | Wire Colors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 4 | CGND | Chassis ground | Black |
| 5 | SGND | Signal ground | Pink or White/Black |
| 6 | CAN High | CAN communication line | Yellow/Green |
| 7 | K-Line | MPI, CVT, SRS air bags | Yellow/Blue |
| 8 | MPI Power | Power for EP-ROM Flash | Green |
| 9-13 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 14 | CAN Low | CAN communication line | Violet |
| 16 | +12v | Battery power supply | Red |
7.2. Mitsubishi Outlander XL (2007-2012)
| Pin | Signal | Description | Wire Colors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 4 | CGND | Chassis ground | Black |
| 5 | SGND | Signal ground | Black |
| 6 | CAN High | CAN communication line | Yellow/Green |
| 7 | K-Line | MPI, CVT, SRS air bags | Yellow/Blue |
| 8 | MPI Power | Power for EP-ROM Flash | Green |
| 9-13 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 14 | CAN Low | CAN communication line | Violet |
| 16 | +12v | Battery power supply | Red |
7.3. Mitsubishi ASX (2011+)
| Pin | Signal | Description | Wire Colors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 4 | CGND | Chassis ground | Black |
| 5 | SGND | Signal ground | Black |
| 6 | CAN High | CAN communication line | Blue |
| 7 | K-Line | MPI, CVT, SRS air bags | Brown |
| 8 | MPI Power | Power for EP-ROM Flash | Green |
| 9-13 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 14 | CAN Low | CAN communication line | Violet |
| 16 | +12v | Battery power supply | Red |
7.4. Mitsubishi Outlander (2013+)
| Pin | Signal | Description | Wire Colors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 4 | CGND | Chassis ground | Black |
| 5 | SGND | Signal ground | Black |
| 6 | CAN High | CAN communication line | Yellow |
| 7 | K-Line | MPI, CVT, SRS air bags | Violet |
| 8 | MPI Power | Power for EP-ROM Flash | White/Black |
| 9-13 | n/c | Not connected | – |
| 14 | CAN Low | CAN communication line | Brown |
| 16 | +12v | Battery power supply | Red |
7.5. Key Considerations
- Color Coding: Pay attention to wire colors, as they can help you identify the correct pin.
- Model Year Variations: Always confirm the pinout for your specific model year, as there can be variations.
- Service Manual: Refer to the official service manual for the most accurate information.
8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Mitsubishi
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is vital for effective diagnostics. Here’s what to consider.
8.1. Compatibility with Mitsubishi Protocols
Ensure the scanner supports the protocols used by your Mitsubishi, such as ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4, and CAN.
8.2. Features and Functionality
Look for features like:
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Essential for basic diagnostics.
- Live Data Streaming: Monitor real-time data from the vehicle.
- Freeze Frame Data: Capture data when a DTC is triggered.
- Bi-Directional Control: Perform tests and activate components.
8.3. User Interface and Ease of Use
Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear display.
8.4. Scanner Updates and Support
Opt for a scanner that receives regular software updates and has good customer support.
8.5. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mitsubishi Vehicles
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: Comprehensive diagnostics and bi-directional control.
- Launch Creader VII+: Affordable with essential features.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Pro: Wireless scanner with a user-friendly app.
9. Resources for Mitsubishi OBD2 Diagnostics
Numerous resources are available to help you with Mitsubishi OBD2 diagnostics.
9.1. Online Forums and Communities
Engage with online communities and forums dedicated to Mitsubishi vehicles. These platforms offer valuable insights and troubleshooting tips.
9.2. Vehicle-Specific Service Manuals
The vehicle-specific service manual is your go-to resource for detailed information about your Mitsubishi.
9.3. Diagnostic Code Databases
Use online diagnostic code databases to look up DTC definitions and possible causes.
9.4. Professional Training Courses
Consider taking professional training courses to enhance your diagnostic skills.
10. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Connection Problems
Sometimes, connecting to the OBD2 port can be problematic. Here’s how to troubleshoot common connection issues.
10.1. Scanner Not Powering On
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Power Supply: Check the vehicle’s battery and fuses.
- Test the Scanner: Try the scanner on another vehicle to rule out scanner malfunction.
10.2. Scanner Unable to Connect to the Vehicle
- Confirm Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s OBD2 protocol.
- Check the OBD2 Port: Inspect the port for damage or corrosion.
- Verify Pinout: Ensure the pinout matches your vehicle’s specifications.
10.3. Intermittent Connection Issues
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring harness for damage or loose connections.
- Clean the Connector: Clean the OBD2 connector with electrical contact cleaner.
- Update Scanner Software: Ensure your scanner has the latest software updates.
11. OBD2 Compatibility List for Mitsubishi Vehicles
Ensure that your Mitsubishi vehicle is OBD2 compatible by checking the model and year. Below is a non-exhaustive compatibility list:
| Model | Engine | Year (Starting From) | OBD-2 Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitsubishi Asx | 1.8 DI-D, Diesel (150HP) | 2010 | CAN 11bit (500kb) |
| Mitsubishi Canter | 3.5, Diesel (200HP) | 2003 | CAN 29bit |
| Mitsubishi Carisma | GDI, Gasoline (124 HP) | 1998 | |
| GDI, Gasoline (121 HP) | 2000 | ||
| 1.9 did, Diesel (115HP) | 2001 | KWP SLOW | |
| Gasoline (121 HP) | 2004 | ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Colt | 1.3 twenty, Gasoline (74 HP) | 1999 | ISO 9141-2 |
| CJ4A, Gasoline (89 HP) | 1999 | ||
| CZ3, Gasoline (94 HP) | 2005 | CAN | |
| 1.3, Gasoline (95HP) | 2006 | CAN 11bit (500kb) | |
| 95 DID, Diesel (95HP) | 2006 | CAN 11bit (500kb) | |
| CZT, Gasoline (148 HP) | 2007 | ||
| Mitsubishi colt glxi | 1,6 16v, Gasoline (112 HP) | 1993 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 |
| Mitsubishi Colt Z30 | Diesel (94 HP) | 2006 | CAN |
| Mitsubishi EA0 | 2.0 , Gasoline (132 HP) | 2001 | ISO 9141-2 |
| Mitsubishi EA5A Galant | 2,5 V6 6A13, Gasoline (161 HP) | 1997 | ISO 9141-2 |
| Mitsubishi Eclipse | 1997 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Eclipse Spyder | 2002 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Galant | Gasoline (161 HP) | 1997 | |
| Gasoline (135 HP) | 1998 | ISO 9141-2 | |
| 2.4 GDI, Gasoline (148 HP) | 2000 | ||
| EA0, Gasoline (159 HP) | 2001 | ISO 9141-2 | |
| 2003 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | ||
| Mitsubishi Grandis | 2.0, Diesel (135 HP) | 2005 | CAN |
| 2.0 tdI, Diesel (136HP) | 2005 | CAN 11bit (500kb) | |
| NAW0, Gasoline (163 HP) | 2006 | ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi L200 | 2.5 TD, Diesel (178HP) | 2006 | CAN 11bit (500kb) |
| Mitsubishi Lancer | 1999 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| 2.0 Turbo, Gasoline (285HP) | 2006 | ISO 9141 | |
| 2.0 DI-D, Diesel (140HP) | 2008 | CAN 11bit (500kb) | |
| Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution | 2003 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution 9 | Gasoline (277 HP) | 2005 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 |
| Mitsubishi Mirage | 1999 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Montero | 1995 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 | |
| Mitsubishi Outlander | 2.0, Gasoline (127 HP) | 2003 | ISO 14230-4, ISO 9141-2 |
| 2.0 Turbo, Gasoline (202HP) | 2005 | ISO 9141 | |
| 2.2, Diesel (177HP) | 2011 | KWP FAST | |
| Mitsubishi Outlander Instyle | DI-D 2.2, Diesel (155 HP) | 2008 | CAN |
| Mitsubishi Pajero | Diesel (114 HP) | 2004 | |
| 3.2DID, Diesel (170HP) | 2007 | CAN 11bit (500kb) | |
| 2500, Diesel (114 HP) | 2004 | ||
| Mitsubishi Pinin | 2, Gasoline (130HP) | 2001 | ISO 9141 |
| Mitsubishi Space Star | Gasoline (117 HP) | 2000 | ISO 9141-2 |
| Diesel (101 HP) | 2001 | ||
| 1.6, Gasoline (97 HP) | 2001 | ISO 9141-2 | |
| GDI 1.6, Gasoline (114 HP) | 2001 | ||
| 1.9 DID, Diesel (102HP) | 2001 | KWP FAST | |
| DGO, Gasoline (81 HP) | 2002 | ISO 9141-2 |
Note: This list is not exhaustive; always check your vehicle’s documentation.
12. Understanding Diagnostic Protocols Used by Mitsubishi
To effectively use the OBD2 scanner with your Mitsubishi, you must understand the diagnostic protocols it supports. Different models and years use various protocols:
- ISO 9141-2: Commonly used in older Mitsubishi models. It is a serial communication protocol.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): An improvement over ISO 9141-2, offering faster communication speeds.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Predominantly used in newer Mitsubishi vehicles, offering high-speed communication and advanced diagnostics.
Using the correct protocol ensures seamless communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s ECU.
13. Where to Find Reliable OBD-II Cables and Adapters
Using the correct cables and adapters is essential for successful OBD-II diagnostics. Here are some reliable sources and types of cables:
- OBD-2 ISO 9141-2 (14230-4, KWP2000) Simple Serial Cable: Suitable for older Mitsubishi models.
- OBD-2 J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW Serial ELM327 Cable: For specific older models using J1850 protocols.
- OBD-2 Universal ISO 15765-4 CAN, SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4, and SAE J1939 Diagnostic Cable: A versatile option for various Mitsubishi models.
13.1. Trusted Suppliers
- Amazon: Offers a wide range of OBD-II cables and adapters from various brands.
- eBay: A good place to find affordable options and specialized cables.
- специализированные магазины автозапчастей: Reliable for high-quality, brand-specific cables.
13.2. Key Considerations When Purchasing Cables
- Compatibility: Ensure the cable is compatible with your Mitsubishi model and the diagnostic tool.
- Quality: Opt for cables made from durable materials to ensure longevity and reliable performance.
- Reviews: Check customer reviews to gauge the cable’s performance and reliability.
14. FAQ: Mitsubishi OBD2 Pinout
14.1. Which OBD2 scanner is best for Mitsubishi?
The Autel MaxiCOM MK808 offers comprehensive diagnostics and bi-directional control, making it a great choice for Mitsubishi vehicles.
14.2. How do I find the OBD2 port in my Mitsubishi?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
14.3. Can I use a generic OBD2 scanner with my Mitsubishi?
Yes, but ensure it supports the protocols used by your Mitsubishi model.
14.4. What does a specific DTC code mean?
Consult your vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database for DTC definitions.
14.5. How do I clear DTCs from my Mitsubishi ECU?
Use an OBD2 scanner to read and clear the DTCs.
14.6. What safety precautions should I take when working with OBD2 pinouts?
Disconnect the battery, use proper grounding techniques, and avoid short circuits.
14.7. Where can I find a reliable OBD2 pinout diagram for my Mitsubishi?
Refer to your vehicle’s service manual or trusted online resources.
14.8. What is the CAN bus, and why is it important?
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a high-speed communication protocol used in newer vehicles for advanced diagnostics and control.
14.9. Can I reprogram my Mitsubishi ECU using the OBD2 port?
Yes, but it requires specialized software, hardware, and knowledge, and it may void warranties.
14.10. How often should I scan my Mitsubishi for DTCs?
Scan your vehicle whenever you notice performance issues or when the check engine light is on. Regular scanning can help catch minor problems early.
15. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of vehicle diagnostics. Our expertise extends to Mitsubishi vehicles, offering you:
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step instructions on using the OBD2 pinout for various Mitsubishi models.
- Expert Advice: Professional insights into diagnosing and resolving common issues.
- Tool Recommendations: Guidance on selecting the right OBD2 scanner for your needs.
- Support and Training: Resources to enhance your diagnostic skills.
We are committed to providing you with the knowledge and tools necessary to keep your Mitsubishi running smoothly.
Understanding the Mitsubishi OBD2 pinout is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. With the right tools, knowledge, and resources like those available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can keep your Mitsubishi in top condition.
Ready to take control of your Mitsubishi’s diagnostics? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance and support. Our team is ready to assist you with tool recommendations, detailed instructions, and professional advice. Reach out today and let us help you keep your Mitsubishi running smoothly.
Contact Information:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t wait—empower yourself with the knowledge to diagnose and maintain your Mitsubishi effectively. Contact us now for immediate assistance.