The 18 Wheeler Obd2 Port is vital for modern truck diagnostics. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive insights into understanding, accessing, and utilizing this essential tool for maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance. Through our guidance, you can expertly navigate the complexities of commercial vehicle diagnostics, ensuring your fleet operates efficiently and compliantly with vehicle diagnostic solutions.
Contents
- 1. What is the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port and Why is it Important?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 Port Located in an 18 Wheeler?
- 3. What Types of Diagnostic Tools Can Be Used with an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- 4. How to Read and Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- 5. What are Common Issues Diagnosed Through the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- 6. How Can the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port Help with Preventative Maintenance?
- 7. What are the Benefits of Using a Telematics System with the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- 8. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 18 Wheeler?
- 9. What are the Legal and Regulatory Requirements Related to OBD2 Systems in 18 Wheelers?
- 10. Can You Reprogram or Reflash an 18 Wheeler ECU Through the OBD2 Port?
- 11. What are the Limitations of Using the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port for Diagnostics?
- 12. How to Secure Your 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port Against Hacking?
- 13. What is the Future of OBD2 Technology in 18 Wheelers?
- 14. How to Troubleshoot Common OBD2 Connection Problems?
- 15. What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Your 18 Wheeler’s OBD2 Port?
- 16. How to Interpret Freeze Frame Data from an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- 17. What Is the Role of the J1939 Protocol in 18 Wheeler OBD2 Systems?
- 18. How to Use Live Data from the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port for Advanced Diagnostics?
- 19. What Are the Differences Between OBD2 Ports in Different 18 Wheeler Brands?
- 20. How to Prepare for Emissions Testing Using Your 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
- FAQ Section
1. What is the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port and Why is it Important?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port in an 18-wheeler, also known as a Class 8 truck, is a standardized interface used to access the vehicle’s computer system for diagnostics and monitoring. It is typically a 16-pin connector found inside the cabin.
The importance of the OBD2 port lies in its ability to provide real-time data about the truck’s performance and identify potential issues before they become major problems. According to a study by the American Transportation Research Institute (ATRI), proactive maintenance based on diagnostic data can reduce breakdown costs by as much as 27%. By connecting a diagnostic tool to the OBD2 port, technicians can:
- Read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to identify the source of problems.
- Monitor engine performance parameters such as fuel consumption, engine speed, and temperature.
- Reset the check engine light after repairs.
- Ensure compliance with emissions regulations.
Understanding the 18 wheeler OBD2 port is crucial for fleet managers, owner-operators, and mechanics to maintain the health and efficiency of these heavy-duty vehicles.
2. Where is the OBD2 Port Located in an 18 Wheeler?
Finding the OBD2 port in an 18-wheeler can sometimes be a bit of a treasure hunt. Unlike passenger cars, where the port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, the location in a commercial truck can vary. However, here are some common locations to check:
- Under the Dashboard: Similar to cars, check under the dashboard, often near the steering column or in the center console area.
- Inside the Glove Compartment: Some manufacturers place the OBD2 port inside the glove compartment.
- Near the Fuse Box: Look for the port near the fuse box, which is often located on the driver’s side or in the engine compartment.
- Behind a Panel: The port may be hidden behind a removable panel, usually near the driver’s seat.
Consulting the truck’s service manual can provide the most accurate location of the OBD2 port for your specific make and model. If you are still having trouble locating the port, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and support to help you find it quickly and easily.
3. What Types of Diagnostic Tools Can Be Used with an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
Several types of diagnostic tools can be used with an 18 wheeler OBD2 port, each offering different levels of functionality and capabilities. Here are some common options:
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These are handheld devices that can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). They are typically the most affordable option and are suitable for basic troubleshooting.
- Professional Diagnostic Scanners: These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming, enhanced code definitions, and bi-directional control. They are often used by professional mechanics and technicians.
- PC-Based Diagnostic Software: This involves using a laptop or desktop computer with specialized software and an OBD2 adapter. PC-based solutions often provide the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including access to OEM-specific data and programming functions.
- Telematics Devices: These devices not only provide diagnostic information but also offer fleet management features such as GPS tracking, driver behavior monitoring, and fuel efficiency analysis.
When choosing a diagnostic tool, consider your specific needs and budget. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you select the right tool for your 18-wheeler, ensuring you have the capabilities you need to keep your truck running smoothly.
4. How to Read and Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
Reading and interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a crucial skill for anyone working with 18-wheelers. DTCs are codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system that indicate a problem has been detected. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to read and interpret DTCs:
-
Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Plug your OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool into the OBD2 port of the 18-wheeler.
-
Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
-
Read the Codes: Follow the instructions on your diagnostic tool to read the stored DTCs. The tool will display a list of codes, each with a specific meaning.
-
Interpret the Codes: Use a reference guide or online database to look up the definition of each DTC. DTCs typically consist of five characters:
-
The first character indicates the system:
- P = Powertrain
- B = Body
- C = Chassis
- U = Network
-
The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
-
The third character indicates the subsystem:
- 1 = Fuel and air metering
- 2 = Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3 = Ignition system
- 4 = Auxiliary emission controls
- 5 = Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6 = Computer output system
- 7 = Transmission
- 8 = Transmission
-
The last two characters are specific to the fault.
-
-
Take Action: Once you have identified the problem, take the necessary steps to repair the issue. This may involve replacing a faulty sensor, repairing a wiring harness, or performing other maintenance tasks.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive database of DTCs for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, as well as expert guidance on how to diagnose and repair common issues.
5. What are Common Issues Diagnosed Through the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
The 18 wheeler OBD2 port can help diagnose a wide range of issues, from minor problems to major mechanical failures. Here are some common issues that can be identified through the OBD2 port:
- Engine Problems: DTCs related to the engine can indicate issues with the fuel system, ignition system, emissions controls, or other engine components. Common codes include P0300 (random misfire detected), P0171 (system too lean), and P0420 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold).
- Transmission Problems: Transmission-related DTCs can indicate issues with shifting, gear ratios, or transmission fluid pressure.
- Brake System Problems: Some OBD2 systems can monitor the performance of the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and other brake components.
- Emissions System Problems: DTCs related to the emissions system can indicate issues with the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, or other emissions control devices. As of 2023, the EPA has been increasing scrutiny on emissions compliance, making this a critical area to monitor.
- Sensor Failures: Faulty sensors are a common cause of DTCs. The OBD2 system can detect issues with various sensors throughout the vehicle, such as oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensors, and temperature sensors.
By regularly scanning the OBD2 port and addressing any detected issues promptly, you can prevent minor problems from escalating into major repairs and keep your 18-wheeler running smoothly.
6. How Can the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port Help with Preventative Maintenance?
The 18 wheeler OBD2 port is not only useful for diagnosing problems but also for preventative maintenance. By monitoring key performance parameters and identifying potential issues early, you can take steps to prevent breakdowns and extend the life of your vehicle. Here are some ways the OBD2 port can help with preventative maintenance:
- Monitor Engine Performance: By monitoring parameters such as engine temperature, oil pressure, and fuel consumption, you can identify potential problems before they cause damage.
- Track Fuel Efficiency: The OBD2 port can provide data on fuel consumption, allowing you to identify inefficiencies and take steps to improve fuel economy.
- Identify Sensor Issues: The OBD2 system can detect failing sensors before they cause major problems. Replacing faulty sensors promptly can prevent more serious damage and improve overall performance.
- Schedule Maintenance: By tracking mileage and operating hours through the OBD2 port, you can schedule maintenance tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, and tire rotations at the appropriate intervals.
According to a study by Texas Transportation Institute, a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance can reduce overall operating costs by as much as 10%. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers customized maintenance schedules and diagnostic support to help you keep your 18-wheeler in top condition.
7. What are the Benefits of Using a Telematics System with the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
Telematics systems that connect to the 18 wheeler OBD2 port offer a wide range of benefits for fleet managers and owner-operators. These systems combine diagnostic information with GPS tracking, driver behavior monitoring, and other features to provide a comprehensive view of vehicle and driver performance. Here are some key benefits of using a telematics system:
- Real-Time Vehicle Tracking: Telematics systems allow you to track the location of your vehicles in real-time, improving security and enabling better dispatching.
- Driver Behavior Monitoring: Telematics systems can monitor driver behavior such as speeding, hard braking, and excessive idling, helping you identify risky driving habits and improve safety.
- Fuel Efficiency Analysis: Telematics systems provide detailed data on fuel consumption, allowing you to identify inefficiencies and take steps to improve fuel economy.
- Remote Diagnostics: Telematics systems can remotely monitor vehicle health and provide alerts when potential problems are detected, allowing you to schedule maintenance proactively.
- Compliance Reporting: Telematics systems can automate compliance reporting for regulations such as the Electronic Logging Device (ELD) mandate, saving time and reducing the risk of violations.
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global telematics market is expected to grow to $75.97 billion by 2027, driven by the increasing demand for fleet management solutions. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers integration support for various telematics systems, ensuring you can leverage the full potential of your vehicle data.
8. How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your 18 Wheeler?
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner for your 18-wheeler depends on your specific needs and budget. With so many options available on the market, it’s important to consider the features and capabilities that are most important to you. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an OBD2 scanner:
- Compatibility: Make sure the scanner is compatible with your 18-wheeler’s make and model. Some scanners are designed specifically for heavy-duty vehicles, while others are more generic.
- Features: Consider the features that are important to you. Do you need advanced capabilities such as live data streaming, bi-directional control, or access to OEM-specific data?
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: OBD2 scanners range in price from under $100 to several thousand dollars. Determine your budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
- Updates: Check whether the scanner receives regular software updates. Updates are important for ensuring compatibility with new vehicles and accessing the latest features.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a curated selection of OBD2 scanners that are specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ensuring you get the best possible performance and compatibility.
9. What are the Legal and Regulatory Requirements Related to OBD2 Systems in 18 Wheelers?
OBD2 systems in 18-wheelers are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, particularly regarding emissions compliance. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state agencies such as the California Air Resources Board (CARB) have implemented regulations to ensure that heavy-duty vehicles meet emissions standards and are properly maintained. Here are some key requirements:
- Emissions Testing: Many states require regular emissions testing for heavy-duty vehicles. The OBD2 system is used to verify that the vehicle’s emissions controls are functioning properly.
- Clean Truck Check Program: CARB’s Clean Truck Check program requires heavy-duty vehicles operating in California to undergo regular emissions testing and reporting. The OBD2 system plays a key role in this program.
- Electronic Logging Device (ELD) Mandate: While not directly related to OBD2, the ELD mandate requires most commercial vehicles to use electronic logging devices to track driver hours of service. Many ELDs connect to the OBD2 port to gather vehicle data.
- Tampering Regulations: It is illegal to tamper with or disable the OBD2 system or any emissions control devices. Violators may be subject to fines and penalties.
Staying compliant with these regulations is essential for avoiding costly fines and ensuring that your 18-wheeler can operate legally. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides up-to-date information and resources to help you navigate the complex landscape of OBD2 regulations.
10. Can You Reprogram or Reflash an 18 Wheeler ECU Through the OBD2 Port?
Yes, it is possible to reprogram or reflash an 18 wheeler Engine Control Unit (ECU) through the OBD2 port, but it is a complex process that should only be performed by qualified technicians with the proper equipment and training. Reflashing the ECU involves overwriting the existing software with a new version, which can be done to improve performance, fix bugs, or update the ECU to meet new emissions standards. Here are some important considerations:
- Equipment: Reflashing an ECU requires specialized software and hardware, such as a J2534 pass-thru device.
- Software: You will need the correct software for your vehicle’s make and model. This software is typically available from the vehicle manufacturer or aftermarket suppliers.
- Training: Reflashing an ECU can be risky if not done properly. It is important to have the necessary training and experience to avoid damaging the ECU.
- Compatibility: Make sure the new software is compatible with your vehicle’s ECU and other components.
- Legal Considerations: In some cases, reflashing an ECU may void the vehicle’s warranty or violate emissions regulations.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers ECU remapping services for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, performed by experienced technicians using the latest equipment and software.
11. What are the Limitations of Using the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port for Diagnostics?
While the 18 wheeler OBD2 port is a powerful tool for diagnostics, it does have some limitations. Here are some of the key limitations to keep in mind:
- Limited Data: The OBD2 system only provides access to a limited set of data parameters. More advanced diagnostics may require specialized tools or access to OEM-specific data.
- Generic Codes: Many OBD2 codes are generic, meaning they provide a general indication of the problem but not a specific diagnosis. Further troubleshooting may be required to pinpoint the exact cause of the issue.
- False Positives: The OBD2 system can sometimes generate false positive codes, particularly if there are intermittent issues or sensor problems.
- Security Concerns: The OBD2 port can be a potential entry point for hackers to access the vehicle’s computer system. It is important to take security precautions to protect against unauthorized access.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all OBD2 scanners are compatible with all 18-wheelers. It is important to choose a scanner that is specifically designed for heavy-duty vehicles.
Despite these limitations, the 18 wheeler OBD2 port remains an essential tool for diagnosing and maintaining modern commercial trucks.
12. How to Secure Your 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port Against Hacking?
The OBD2 port in an 18-wheeler can be a potential entry point for hackers to access the vehicle’s computer system, making it crucial to take security precautions. Here are some steps you can take to secure your OBD2 port:
- Physical Security: Use a locking OBD2 port cover to prevent unauthorized access to the port.
- Software Security: Install a firewall or intrusion detection system to monitor OBD2 port activity and block unauthorized access.
- Regular Updates: Keep your vehicle’s software up to date with the latest security patches.
- Authentication: Use strong passwords and authentication methods to protect access to the OBD2 port.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor your vehicle’s computer system for suspicious activity.
- Professional Services: Consider using professional cybersecurity services to assess and improve your vehicle’s security posture.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, the transportation industry is increasingly becoming a target for cyberattacks, making it essential to prioritize security.
13. What is the Future of OBD2 Technology in 18 Wheelers?
The future of OBD2 technology in 18 wheelers is likely to involve more advanced diagnostics, improved security, and greater integration with telematics systems. Here are some trends to watch for:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Future OBD2 systems will likely provide access to a wider range of data parameters and more sophisticated diagnostic capabilities.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Over-the-air (OTA) updates will become more common, allowing manufacturers to remotely update vehicle software and fix bugs without requiring a visit to the dealership.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity will become an increasingly important focus, with new technologies and regulations designed to protect against hacking and unauthorized access.
- Integration with Telematics: OBD2 systems will be more tightly integrated with telematics systems, providing a seamless flow of data between the vehicle and fleet management software.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance technologies will use data from the OBD2 system to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of breakdowns.
14. How to Troubleshoot Common OBD2 Connection Problems?
Experiencing connection problems with your OBD2 scanner can be frustrating. Here are some troubleshooting steps to resolve common issues:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the OBD2 scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port. A loose connection is a common cause of communication errors.
- Verify Power: Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on. The OBD2 port receives power from the vehicle’s battery, and the scanner needs this power to function.
- Check the Scanner’s Compatibility: Confirm that your OBD2 scanner is compatible with your 18-wheeler’s make, model, and year. Some scanners are designed for specific vehicle types.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Check the OBD2 port for any damage or corrosion. Damaged pins can prevent the scanner from establishing a connection.
- Try a Different Scanner: If possible, try using a different OBD2 scanner to see if the issue is with the scanner itself.
- Check Fuses: Consult your vehicle’s manual to locate the fuse for the OBD2 port and check if it has blown. Replace the fuse if necessary.
- Update Scanner Software: Ensure your OBD2 scanner has the latest software updates installed. Updates often include bug fixes and improved compatibility.
- Consult a Professional: If you’ve tried these steps and still can’t establish a connection, consult a professional mechanic or diagnostic specialist.
15. What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Your 18 Wheeler’s OBD2 Port?
Maintaining your 18 wheeler’s OBD2 port ensures reliable diagnostic access and prevents potential issues. Follow these best practices:
- Keep It Clean: Regularly inspect the OBD2 port for dirt, dust, and debris. Use a small brush or compressed air to clean it as needed.
- Protect It: When not in use, cover the OBD2 port with a protective cap to prevent dust and moisture from entering.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not plug multiple devices into the OBD2 port simultaneously, as this can overload the circuit and damage the port.
- Handle with Care: When plugging and unplugging devices, do so gently to avoid bending or breaking the pins inside the port.
- Regular Inspections: During routine maintenance, inspect the OBD2 port for any signs of damage or corrosion. Address any issues promptly.
- Use Quality Connectors: Use high-quality OBD2 connectors and adapters to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
- Secure Wiring: Ensure the wiring connected to the OBD2 port is properly secured and protected from damage.
- Professional Check-ups: Have a professional mechanic inspect the OBD2 port during regular check-ups to identify any potential issues early.
16. How to Interpret Freeze Frame Data from an 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is triggered. This data can provide valuable insights into the cause of the problem. Here’s how to interpret freeze frame data:
- Access Freeze Frame Data: Use your OBD2 scanner to access the freeze frame data associated with a specific DTC.
- Identify Key Parameters: Look for key parameters such as engine speed (RPM), engine load, coolant temperature, fuel trim, and vehicle speed.
- Analyze the Data: Analyze the values of these parameters in relation to the DTC that was triggered. For example, if the DTC is related to a lean fuel condition, check the fuel trim values to see if they are excessively positive.
- Consider the Context: Consider the context in which the DTC was triggered. Was the vehicle idling, accelerating, or cruising at highway speed?
- Compare to Normal Values: Compare the freeze frame data to the normal operating values for your vehicle. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or online resources for this information.
- Look for Anomalies: Look for any anomalies or unusual readings in the freeze frame data. These can provide clues to the underlying problem.
- Use Multiple Data Points: Use multiple data points from the freeze frame to get a comprehensive understanding of the conditions that led to the DTC.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure how to interpret the freeze frame data, consult a professional mechanic or diagnostic specialist.
17. What Is the Role of the J1939 Protocol in 18 Wheeler OBD2 Systems?
The J1939 protocol is a standard for communication between electronic control units (ECUs) in heavy-duty vehicles, including 18 wheelers. It plays a crucial role in OBD2 systems by defining how data is transmitted and interpreted. Here’s what you need to know:
- Standardized Communication: J1939 provides a standardized way for different ECUs in the vehicle to communicate with each other. This ensures that data is transmitted consistently and reliably.
- Data Parameters: J1939 defines a set of data parameters that can be accessed through the OBD2 port, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel consumption.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: J1939 is used to transmit Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ECUs to the OBD2 scanner.
- High-Speed Communication: J1939 uses a high-speed communication network (typically CAN bus) to transmit data quickly and efficiently.
- Compatibility: Most modern 18 wheelers use the J1939 protocol for communication between ECUs.
- Diagnostic Tools: OBD2 scanners that are designed for heavy-duty vehicles typically support the J1939 protocol.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding the J1939 protocol can help you interpret the data from the OBD2 port more accurately.
- Future Developments: The J1939 protocol is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of the heavy-duty vehicle industry.
18. How to Use Live Data from the 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port for Advanced Diagnostics?
Live data from the 18 wheeler OBD2 port provides real-time information about the vehicle’s operating conditions. This can be invaluable for advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting. Here’s how to use live data effectively:
- Access Live Data: Use your OBD2 scanner to access the live data stream from the vehicle’s ECUs.
- Select Relevant Parameters: Choose the parameters that are most relevant to the problem you’re trying to diagnose. For example, if you’re troubleshooting a misfire, select parameters such as engine speed, engine load, fuel trim, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Monitor the Data: Monitor the data as the vehicle is running. Look for any unusual patterns or anomalies.
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the live data to the manufacturer’s specifications for your vehicle.
- Look for Correlations: Look for correlations between different parameters. For example, if the engine speed is fluctuating, check to see if the throttle position sensor reading is also fluctuating.
- Use Graphs: Use the graphing feature of your OBD2 scanner to visualize the live data. This can make it easier to spot trends and anomalies.
- Record the Data: Record the live data for later analysis. This can be helpful if you need to compare the data to previous readings.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure how to interpret the live data, consult a professional mechanic or diagnostic specialist.
19. What Are the Differences Between OBD2 Ports in Different 18 Wheeler Brands?
While the OBD2 standard aims to create uniformity, there can be subtle differences between OBD2 ports in different 18 wheeler brands. These differences primarily relate to:
- Location: The physical location of the OBD2 port can vary between manufacturers.
- Accessibility: Some ports are more easily accessible than others.
- Wiring: The wiring configuration may differ slightly between brands.
- Protocols: While most 18 wheelers use the J1939 protocol, some brands may use proprietary protocols in addition to J1939.
- Data Parameters: The specific data parameters that are available through the OBD2 port may vary between brands.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Some brands may use proprietary Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in addition to the standard OBD2 codes.
- Software: The software used to access the OBD2 port may differ between brands.
- Security: The security measures implemented to protect the OBD2 port may vary between brands.
Despite these differences, the basic functionality of the OBD2 port remains the same across all 18 wheeler brands.
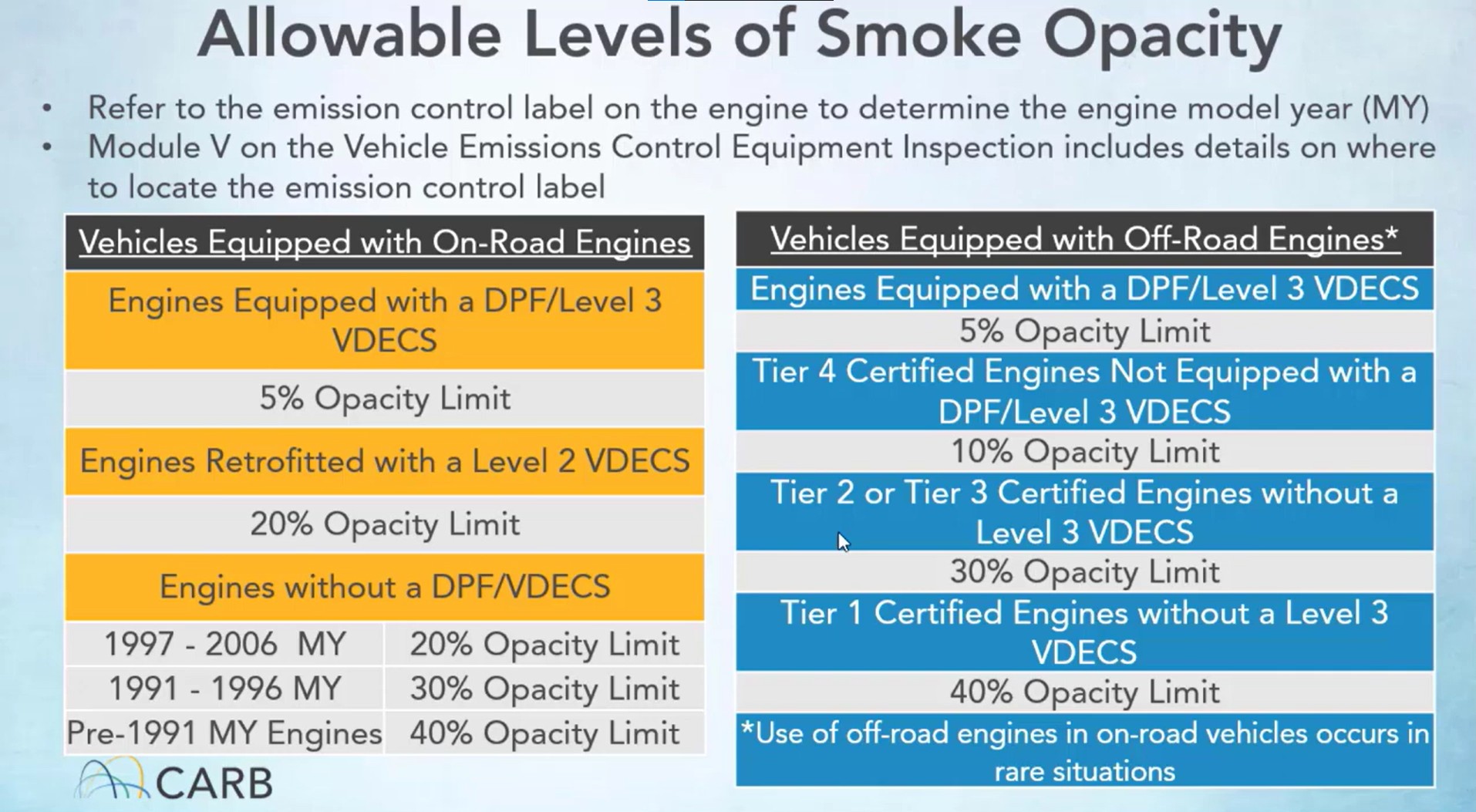
20. How to Prepare for Emissions Testing Using Your 18 Wheeler OBD2 Port?
Preparing for emissions testing using your 18 wheeler OBD2 port involves ensuring that your vehicle is in good working order and that the OBD2 system is functioning properly. Here are some steps you can take:
- Check for DTCs: Use your OBD2 scanner to check for any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). Address any issues before the emissions test.
- Review Readiness Monitors: Ensure that all of the OBD2 readiness monitors are set. These monitors indicate that the vehicle’s emissions systems have been tested and are functioning properly.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the vehicle’s emissions components, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and fuel cap.
- Check for Leaks: Check for any fuel or exhaust leaks.
- Maintain Records: Keep records of all maintenance and repairs performed on the vehicle’s emissions systems.
- Warm Up the Engine: Warm up the engine before the emissions test.
- Drive Cycle: Perform a drive cycle to ensure that all of the OBD2 readiness monitors are set.
- Professional Inspection: Have a professional mechanic inspect the vehicle before the emissions test.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the most common location for the OBD2 port in an 18-wheeler?
The OBD2 port is commonly found under the dashboard, inside the glove compartment, near the fuse box, or behind a panel near the driver’s seat.
Q2: Can I use a regular car OBD2 scanner on my 18-wheeler?
While some basic car OBD2 scanners might work, it’s best to use a scanner specifically designed for heavy-duty vehicles to ensure compatibility and access to all relevant data.
Q3: What does it mean when my OBD2 scanner shows a “Not Ready” status for some monitors?
“Not Ready” means the vehicle’s computer hasn’t completed testing certain emissions systems. You may need to drive the vehicle for a specific drive cycle to allow the monitors to complete.
Q4: Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in while driving?
It’s generally safe, but some scanners can drain the battery if left plugged in for extended periods. It’s best to unplug it when not in use, especially if the vehicle will be sitting for a while.
Q5: How often should I scan my 18-wheeler’s OBD2 port for potential issues?
Scanning the OBD2 port regularly, such as during routine maintenance or before long trips, can help catch potential issues early and prevent costly breakdowns.
Q6: Can I clear DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) myself using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can clear DTCs, but it’s important to understand the underlying issue and address it properly. Clearing the code without fixing the problem will only cause it to return.
Q7: What should I do if my 18-wheeler fails an emissions test due to OBD2 issues?
If your 18-wheeler fails an emissions test, consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the underlying problem. Retest the vehicle after the repairs are completed.
Q8: Are there any security risks associated with using the OBD2 port in my 18-wheeler?
Yes, the OBD2 port can be a potential entry point for hackers. Consider using security measures such as locking OBD2 port covers and software firewalls to protect against unauthorized access.
Q9: Can I increase my 18-wheeler’s horsepower through the OBD2 port?
While it’s possible to remap the ECU through the OBD2 port, it’s a complex process that should only be performed by qualified technicians. Modifying the ECU can also void the vehicle’s warranty and violate emissions regulations.
Q10: Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes and troubleshooting for my 18-wheeler?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources, including a database of OBD2 codes, troubleshooting guides, and expert support to help you diagnose and repair issues with your 18-wheeler.
 Mercedes diagnostic tool
Mercedes diagnostic tool
Maximize your 18-wheeler’s performance with expert OBD2 diagnostics. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or Whatsapp +1 (641) 206-8880 for comprehensive diagnostic tools, ECU remapping services, and professional guidance. Visit MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for a smoother, more efficient ride.