Aftermarket sensors can affect the accuracy of Mercedes live data; understanding the potential impact of aftermarket sensors on the accuracy of live data is crucial for proper diagnostics and repairs. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we empower you with the knowledge and tools to navigate these complexities and ensure your Mercedes-Benz performs optimally. Explore diagnostic accuracy, sensor calibration, and data interpretation for your vehicle.
Contents
- 1. What are Adaptations in Modern Vehicles?
- 1.1 ECU Learning Process
- 1.2 Examples of Adaptations
- 2. How Aftermarket Sensors Can Affect Accuracy
- 2.1 Manufacturing Quality and Calibration
- 2.2 Impact on ECU Adjustments
- 2.3 Potential for Check Engine Lights
- 3. Impact on Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Systems
- 3.1 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.2 Live Data Interpretation
- 3.3 Adaptations and Relearn Procedures
- 4. Factors Affecting Sensor Accuracy
- 4.1 Temperature Sensitivity
- 4.2 Voltage Fluctuations
- 4.3 Environmental Conditions
- 4.4 Installation Issues
- 5. Importance of OEM vs Aftermarket Sensors
- 5.1 OEM Sensor Benefits
- 5.2 Aftermarket Sensor Drawbacks
- 5.3 Case Study: Oxygen Sensors
- 6. Symptoms of Inaccurate Sensor Data
- 6.1 Reduced Engine Performance
- 6.2 Poor Fuel Economy
- 6.3 Check Engine Light Illumination
- 6.4 Diagnostic Procedures
- 7. Tools for Accurate Live Data Readings
- 7.1 OEM Diagnostic Tools
- 7.2 Aftermarket Diagnostic Tools
- 7.3 Using Diagnostic Software
- 7.4 Tips for Accurate Readings
- 8. Case Studies: Aftermarket Sensor Issues
- 8.1 Case Study 1: Oxygen Sensor Failure
- 8.2 Case Study 2: Crankshaft Position Sensor Issues
- 8.3 Case Study 3: Transmission Sensor Problems
- 9. Best Practices for Sensor Replacement
- 9.1 Use OEM Sensors When Possible
- 9.2 Follow OEM Repair Procedures
- 9.3 Calibrate Sensors After Replacement
- 9.4 Inspect Wiring and Connectors
- 9.5 Verify Sensor Data After Installation
- 10. FAQ: Aftermarket Sensors and Mercedes Live Data
Table of Contents
- What are Adaptations in Modern Vehicles?
- How Aftermarket Sensors Can Affect Accuracy
- Impact on Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Systems
- Factors Affecting Sensor Accuracy
- Importance of OEM vs Aftermarket Sensors
- Symptoms of Inaccurate Sensor Data
- Tools for Accurate Live Data Readings
- Case Studies: Aftermarket Sensor Issues
- Best Practices for Sensor Replacement
- FAQ: Aftermarket Sensors and Mercedes Live Data
1. What are Adaptations in Modern Vehicles?
Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated electronic control units (ECUs) that constantly monitor and adjust various engine parameters to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Adaptations refer to the ECU’s ability to learn and compensate for changes in sensor readings, component wear, and environmental conditions over time. This learning process ensures that the engine operates within specified parameters, even as conditions change. Adaptations involve analyzing data inputs and comparing them against pre-programmed values set by the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM).
1.1 ECU Learning Process
The ECU’s learning process involves:
- Data Input Analysis: The ECU receives data from various sensors, such as oxygen sensors, mass airflow (MAF) sensors, and crankshaft position sensors.
- Comparison: The ECU compares this live data against minimum and maximum values programmed by the OEM.
- Adjustment: Based on the comparison, the ECU makes adjustments to engine parameters like fuel trim, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture.
1.2 Examples of Adaptations
Several examples illustrate how adaptations work in modern vehicles.
- Fuel Trim: Fuel trim is the ECU’s ability to adjust the fuel mixture to compensate for changes in engine performance.
- Mercedes-Benz Transmission Adaptations: Mercedes-Benz automatic transmissions use adaptive control systems to adjust gear shifts based on real-time sensor data.
- BMW Crankshaft Position Sensor Adaptations: BMW’s Digital Motor Electronics (DME) learns crankshaft position data to monitor engine performance and detect misfires.
2. How Aftermarket Sensors Can Affect Accuracy
Aftermarket sensors, while often more affordable than OEM sensors, can introduce inaccuracies that affect the reliability of live data readings. These inaccuracies stem from variations in manufacturing quality, calibration, and material composition. When an aftermarket sensor provides incorrect data, the ECU may make inappropriate adjustments, leading to reduced performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
2.1 Manufacturing Quality and Calibration
One of the primary concerns with aftermarket sensors is the variability in manufacturing quality. OEM sensors undergo rigorous testing and calibration to ensure they meet precise specifications. Aftermarket sensors may not adhere to the same standards, resulting in:
- Inconsistent Readings: Sensors may provide readings that deviate from actual values.
- Calibration Errors: Sensors may be improperly calibrated, leading to systematic errors in data.
- Material Differences: The materials used in aftermarket sensors may not match the OEM specifications, affecting their performance and durability.
2.2 Impact on ECU Adjustments
When the ECU receives inaccurate data from aftermarket sensors, it can make incorrect adjustments to engine parameters. This can lead to:
- Incorrect Fuel Trim: The ECU may add too much or too little fuel, affecting fuel efficiency and emissions.
- Poor Shift Quality: In Mercedes-Benz transmissions, inaccurate sensor data can result in harsh or delayed gear shifts.
- Misfires: In BMW engines, incorrect crankshaft position data can cause misfires and poor engine performance.
2.3 Potential for Check Engine Lights
Inaccurate data from aftermarket sensors can trigger the Check Engine Light. The ECU monitors sensor data for deviations from expected values. If the data falls outside the acceptable range, the ECU will store a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Check Engine Light.
3. Impact on Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Systems
Mercedes-Benz vehicles rely on sophisticated diagnostic systems to monitor and control various aspects of vehicle performance. These systems depend on accurate sensor data to function correctly. When aftermarket sensors provide inaccurate data, it can compromise the effectiveness of these diagnostic systems.
3.1 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored by the ECU when it detects a problem. Inaccurate sensor data can lead to the storage of false or misleading DTCs. For example, an aftermarket oxygen sensor that consistently reads lean may cause the ECU to store a DTC related to a lean fuel condition, even if the actual problem lies with the sensor itself.
3.2 Live Data Interpretation
Live data refers to the real-time information provided by sensors, which can be accessed using a diagnostic tool. Accurate interpretation of live data is essential for diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz vehicles. However, if the sensor data is inaccurate, it can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
3.3 Adaptations and Relearn Procedures
Many Mercedes-Benz components, such as the transmission and engine control systems, require adaptations and relearn procedures after replacement. These procedures allow the ECU to learn the characteristics of the new component and adjust its operation accordingly. However, if an aftermarket sensor is used, the adaptations may not work correctly, leading to ongoing performance issues.
 Mercedes-Benz transmission
Mercedes-Benz transmission
4. Factors Affecting Sensor Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of sensors, including temperature, voltage, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring the reliability of sensor data.
4.1 Temperature Sensitivity
Many sensors are sensitive to temperature changes. Extreme temperatures can affect the sensor’s accuracy, leading to incorrect readings. For example, an aftermarket temperature sensor may provide inaccurate readings in cold weather, causing the ECU to make incorrect adjustments to the air-fuel mixture.
4.2 Voltage Fluctuations
Sensors require a stable voltage supply to operate correctly. Voltage fluctuations can affect the sensor’s output, leading to inaccurate readings. Aftermarket sensors may be more susceptible to voltage fluctuations than OEM sensors, resulting in unreliable data.
4.3 Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions, such as humidity and exposure to chemicals, can also affect sensor accuracy. Aftermarket sensors may not be as resistant to these conditions as OEM sensors, leading to premature failure and inaccurate data.
4.4 Installation Issues
Improper installation can also affect sensor accuracy. Ensure proper connections, torque specifications, and sensor placement. Poor installation can lead to mechanical stress, electrical interference, and inaccurate readings.
5. Importance of OEM vs Aftermarket Sensors
Choosing between OEM and aftermarket sensors can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems. OEM sensors are designed and tested to meet the specific requirements of the vehicle, while aftermarket sensors may vary in quality and performance.
5.1 OEM Sensor Benefits
OEM sensors offer several benefits:
- Precise Calibration: OEM sensors are calibrated to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle’s ECU.
- High Quality Materials: OEM sensors are made from high-quality materials that are resistant to temperature, voltage, and environmental conditions.
- Reliable Performance: OEM sensors are designed to provide accurate and consistent data over their lifespan.
- Warranty Coverage: OEM sensors typically come with a warranty, providing added peace of mind.
5.2 Aftermarket Sensor Drawbacks
Aftermarket sensors have potential drawbacks:
- Inconsistent Quality: Aftermarket sensors may vary in quality, leading to inaccurate readings and unreliable performance.
- Calibration Issues: Aftermarket sensors may not be calibrated to the exact specifications of the vehicle’s ECU, resulting in incorrect adjustments.
- Durability Concerns: Aftermarket sensors may not be as durable as OEM sensors, leading to premature failure and the need for frequent replacements.
- Limited Warranty: Aftermarket sensors may have a limited warranty, or no warranty at all.
5.3 Case Study: Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors are critical for monitoring the air-fuel mixture and ensuring optimal engine performance. OEM oxygen sensors are designed to provide accurate readings over a wide range of operating conditions. Aftermarket oxygen sensors may not be as accurate, leading to incorrect fuel trim adjustments and reduced fuel efficiency.
6. Symptoms of Inaccurate Sensor Data
Recognizing the symptoms of inaccurate sensor data is crucial for diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Common symptoms include reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and the illumination of the Check Engine Light.
6.1 Reduced Engine Performance
Inaccurate sensor data can lead to reduced engine performance, such as:
- Hesitation: The engine may hesitate during acceleration.
- Stalling: The engine may stall unexpectedly.
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle roughly or unevenly.
- Lack of Power: The engine may lack power, especially during acceleration.
6.2 Poor Fuel Economy
Inaccurate sensor data can affect the air-fuel mixture, leading to poor fuel economy. If the ECU adds too much fuel, the engine will run rich, resulting in wasted fuel and increased emissions.
6.3 Check Engine Light Illumination
The Check Engine Light will illuminate if the ECU detects a problem with the sensor data. Common DTCs related to inaccurate sensor data include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
- P0175: System Too Rich (Bank 2)
- P0300: Random Misfire Detected
6.4 Diagnostic Procedures
To diagnose inaccurate sensor data, perform the following steps:
- Scan for DTCs: Use a diagnostic tool to scan for any stored DTCs.
- Review Live Data: Review the live data from the sensors to identify any readings that are out of range or inconsistent.
- Perform Sensor Tests: Use the diagnostic tool to perform specific tests on the sensors, such as checking their resistance and voltage output.
- Inspect Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Compare with Specifications: Compare the sensor readings with the OEM specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
 BMW Crankshaft Position Sensor Adaptations
BMW Crankshaft Position Sensor Adaptations
7. Tools for Accurate Live Data Readings
Using the right diagnostic tools is essential for obtaining accurate live data readings from Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools allow technicians to access sensor data, perform tests, and troubleshoot problems.
7.1 OEM Diagnostic Tools
OEM diagnostic tools, such as the Mercedes-Benz XENTRY system, provide the most comprehensive access to vehicle data. These tools are designed to work specifically with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and offer advanced diagnostic capabilities.
7.2 Aftermarket Diagnostic Tools
Aftermarket diagnostic tools, such as those from Autel, Snap-on, and Bosch, can also provide accurate live data readings. However, it’s important to choose a tool that is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and offers the necessary diagnostic functions.
7.3 Using Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic software, such as XENTRY Diagnostics, can be used to access live data, perform sensor tests, and troubleshoot problems. Ensure the software is up to date and compatible with the diagnostic tool and the vehicle.
7.4 Tips for Accurate Readings
Follow these tips to ensure accurate live data readings:
- Use a reliable diagnostic tool: Choose a diagnostic tool that is known for its accuracy and reliability.
- Update the software: Keep the diagnostic software up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicle models.
- Follow the instructions: Follow the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool and the vehicle manufacturer.
- Verify the data: Verify the sensor data by comparing it with the OEM specifications.
- Check the wiring: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
8. Case Studies: Aftermarket Sensor Issues
Examining case studies of aftermarket sensor issues can provide valuable insights into the potential problems that can arise when using non-OEM sensors. These examples illustrate the importance of using high-quality sensors and following proper diagnostic procedures.
8.1 Case Study 1: Oxygen Sensor Failure
A Mercedes-Benz C-Class experienced reduced fuel economy and a Check Engine Light. The diagnostic scan revealed a DTC related to the oxygen sensor. The technician replaced the OEM oxygen sensor with an aftermarket sensor. However, the problem persisted, and the Check Engine Light remained illuminated. Further investigation revealed that the aftermarket oxygen sensor was providing inaccurate readings, causing the ECU to make incorrect fuel trim adjustments. Replacing the aftermarket sensor with an OEM sensor resolved the issue.
8.2 Case Study 2: Crankshaft Position Sensor Issues
A Mercedes-Benz E-Class exhibited rough idling and occasional stalling. The diagnostic scan indicated a problem with the crankshaft position sensor. The technician replaced the OEM sensor with an aftermarket sensor. However, the engine performance did not improve, and the vehicle continued to experience rough idling and stalling. Aftermarket sensor testing revealed that the aftermarket crankshaft position sensor was not providing accurate data. Replacing the aftermarket sensor with an OEM sensor resolved the issue.
8.3 Case Study 3: Transmission Sensor Problems
A Mercedes-Benz S-Class experienced harsh gear shifts and delayed shifting. The diagnostic scan revealed a problem with the transmission speed sensor. The technician replaced the OEM sensor with an aftermarket sensor. However, the transmission problems persisted. Further investigation revealed that the aftermarket transmission speed sensor was not providing accurate data, causing the transmission control unit to make incorrect shift decisions. Replacing the aftermarket sensor with an OEM sensor resolved the issue.
9. Best Practices for Sensor Replacement
Following best practices for sensor replacement is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems.
9.1 Use OEM Sensors When Possible
Whenever possible, use OEM sensors to ensure precise calibration, high-quality materials, and reliable performance. OEM sensors are designed and tested to meet the specific requirements of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
9.2 Follow OEM Repair Procedures
Follow the OEM repair procedures when replacing sensors. These procedures provide detailed instructions on how to properly install and calibrate the sensors.
9.3 Calibrate Sensors After Replacement
Many sensors require calibration after replacement. Use the diagnostic tool to perform the necessary calibration procedures.
9.4 Inspect Wiring and Connectors
Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion before installing the new sensor. Replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
9.5 Verify Sensor Data After Installation
Verify the sensor data after installation to ensure it is accurate and consistent with the OEM specifications. Use the diagnostic tool to review the live data and perform any necessary tests.
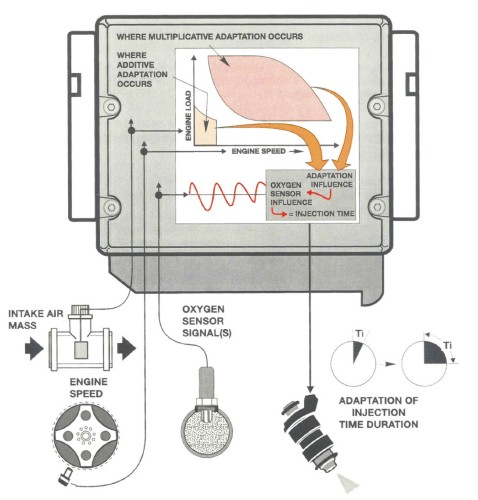 Sensor adaptation
Sensor adaptation
10. FAQ: Aftermarket Sensors and Mercedes Live Data
Here are some frequently asked questions about aftermarket sensors and Mercedes live data.
10.1 Can aftermarket sensors cause inaccurate live data readings?
Yes, aftermarket sensors can cause inaccurate live data readings due to variations in manufacturing quality, calibration, and material composition.
10.2 What are the potential symptoms of inaccurate sensor data?
Symptoms of inaccurate sensor data include reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and the illumination of the Check Engine Light.
10.3 Are OEM sensors always better than aftermarket sensors?
OEM sensors are generally better than aftermarket sensors because they are designed and tested to meet the specific requirements of the vehicle.
10.4 How can I diagnose inaccurate sensor data?
To diagnose inaccurate sensor data, scan for DTCs, review live data, perform sensor tests, inspect wiring, and compare the readings with OEM specifications.
10.5 What tools are needed for accurate live data readings?
Tools needed for accurate live data readings include OEM diagnostic tools, aftermarket diagnostic tools, and diagnostic software.
10.6 What should I do after replacing a sensor?
After replacing a sensor, calibrate the sensor, inspect wiring and connectors, and verify sensor data to ensure it is accurate and consistent.
10.7 How does temperature affect sensor accuracy?
Extreme temperatures can affect the sensor’s accuracy, leading to incorrect readings. Ensure sensors are designed to withstand the operating temperatures of the vehicle.
10.8 Can voltage fluctuations affect sensor readings?
Yes, voltage fluctuations can affect the sensor’s output, leading to inaccurate readings. Ensure a stable voltage supply to the sensors.
10.9 What is the role of ECU adaptations in sensor accuracy?
ECU adaptations allow the ECU to learn and compensate for changes in sensor readings, component wear, and environmental conditions, ensuring optimal engine operation.
10.10 Where can I get reliable diagnostic tools and information for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
You can get reliable diagnostic tools and information for Mercedes-Benz vehicles at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
In conclusion, while aftermarket sensors may offer a cost-effective alternative to OEM sensors, it’s essential to be aware of their potential impact on the accuracy of Mercedes live data. By understanding the factors that affect sensor accuracy, following best practices for sensor replacement, and using reliable diagnostic tools, you can ensure your Mercedes-Benz performs optimally.
Ready to ensure your Mercedes-Benz performs at its best? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice on diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and professional repair guidance. Reach us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or on WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Don’t compromise on accuracy; choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for all your Mercedes-Benz diagnostic needs!