Installing the wrong software variant can lead to a host of issues, from decreased performance and system instability to complete vehicle failure. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the critical importance of using the correct software for your Mercedes-Benz. We offer expert guidance and support to ensure you always have the right tools and information, preventing costly mistakes and maximizing your vehicle’s potential. Proper software enhances diagnostic capabilities, unlocks hidden features, and streamlines maintenance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Software Variants in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 1.1 The Complexity of Automotive Software
- 1.2 Why Software Variants Exist
- 1.3 Identifying the Correct Software Variant
- 2. The Risks of Installing the Wrong Software
- 2.1 System Instability and Malfunctions
- 2.2 Reduced Performance
- 2.3 Feature Loss
- 2.4 Potential for Hardware Damage
- 2.5 Voiding Warranty
- 3. Real-World Examples of Software Variant Issues
- 3.1 The Case of Unintended Acceleration
- 3.2 Volkswagen’s Emissions Scandal
- 3.3 Tesla’s Autopilot Issues
- 4. How to Avoid Software Variant Problems
- 4.1 Use a Reliable Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tool
- 4.2 Verify Software Compatibility
- 4.3 Obtain Software from Trusted Sources
- 4.4 Follow Installation Instructions Carefully
- 4.5 Back Up Your Existing Software
- 4.6 Understanding the Role of Flashing in Mercedes-Benz Software Updates
- 4.7 Importance of Correct Flashing
- 4.8 Potential Risks of Incorrect Flashing
- 5. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 5.1 Diagnostic Tools
- 5.2 Software and Firmware
- 5.3 Expert Support
- 5.4 Training and Resources
- 6. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.1 Reading DTCs
- 6.2 Interpreting DTCs
- 6.3 Clearing DTCs
- 7. The Benefits of Using Genuine Mercedes-Benz Software
- 7.1 Optimal Performance and Compatibility
- 7.2 Enhanced Security
- 7.3 Access to Updates and Support
- 7.4 Warranty Protection
- 8. The Importance of Regular Software Updates
- 8.1 Performance Enhancements
- 8.2 Bug Fixes
- 8.3 Security Patches
- 8.4 New Features
- 9. Common Software-Related Issues in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 9.1 Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems
- 9.2 Transmission Control Module (TCM) Problems
- 9.3 Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Problems
- 9.4 Infotainment System Problems
- 10. Troubleshooting Software-Related Problems
- 10.1 Identify the Symptoms
- 10.2 Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 10.3 Consult Technical Resources
- 10.4 Perform Software Updates or Reprogramming
- 10.5 Seek Professional Assistance
- 11. Advanced Techniques for Software Management
- 11.1 Coding and Programming
- 11.2 SCN Coding
- 11.3 Variant Coding
- 12. The Future of Automotive Software
- 12.1 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 12.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 12.3 Cybersecurity
- 13. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 13.1 Warranty Voiding
- 13.2 Emissions Regulations
- 13.3 Safety Standards
- 13.4 Intellectual Property
- 14. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool for Your Needs
- 14.1 Entry-Level Code Readers
- 14.2 Mid-Range Diagnostic Scanners
- 14.3 Professional-Grade Diagnostic Systems
- 15. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Software: Best Practices
- 15.1 Regularly Check for Updates
- 15.2 Use a Battery Maintainer During Updates
- 15.3 Document All Changes
- 15.4 Seek Professional Assistance When Needed
1. Understanding Software Variants in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles rely heavily on sophisticated software to control various systems, from the engine and transmission to the infotainment and safety features. These software systems aren’t monolithic; they’re often divided into different variants, each tailored to specific vehicle models, production years, and even regional specifications.
1.1 The Complexity of Automotive Software
The software within a Mercedes-Benz is not a single, unified program. Instead, it’s a network of interconnected modules, each responsible for controlling a specific function or system. According to a 2021 McKinsey report, premium vehicles can contain over 100 million lines of code. These modules communicate with each other via complex communication protocols, such as CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, FlexRay, and Ethernet.
 Automotive software complexity
Automotive software complexity
Alt Text: Illustration of interconnected software modules in a car, showing the complexity of automotive software.
1.2 Why Software Variants Exist
Several factors necessitate the use of different software variants:
- Model-Specific Configurations: Different Mercedes-Benz models have unique hardware configurations, requiring software tailored to those specific components.
- Production Year Updates: As Mercedes-Benz refines its vehicles, software updates are introduced to improve performance, fix bugs, or add new features.
- Regional Regulations: Emission standards, safety requirements, and other regulations vary across different regions, requiring software adaptations for specific markets.
- Optional Equipment: The presence or absence of optional equipment, such as adaptive cruise control or a premium sound system, can influence the required software variant.
1.3 Identifying the Correct Software Variant
Determining the correct software variant for your Mercedes-Benz is crucial. This information is typically linked to your vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) and can be accessed through:
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tools: Professional diagnostic tools, like those offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, can accurately identify the installed software and the appropriate updates.
- Mercedes-Benz Online Services: The official Mercedes-Benz online portal allows authorized technicians to access software information based on the VIN.
- Vehicle Documentation: While not always exhaustive, the vehicle’s owner’s manual or service records may contain some software-related information.
2. The Risks of Installing the Wrong Software
Installing an incorrect software variant can have severe implications for your Mercedes-Benz. The consequences can range from minor inconveniences to major system failures.
2.1 System Instability and Malfunctions
One of the most common consequences is system instability. The software may not properly communicate with the vehicle’s hardware, leading to erratic behavior, warning lights, and malfunctions. According to a study by the German Automobile Club (ADAC), software glitches are a leading cause of vehicle breakdowns.
2.2 Reduced Performance
The wrong software can negatively impact performance. For example, installing a software variant designed for a different engine type could result in reduced power, poor fuel economy, and transmission issues.
2.3 Feature Loss
Certain features may cease to function correctly or become entirely unavailable if the wrong software is installed. This could include safety systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) or driver-assistance features like lane-keeping assist.
2.4 Potential for Hardware Damage
In some cases, installing an incompatible software variant can even lead to hardware damage. For instance, incorrect software could overstress certain components, causing them to fail prematurely. A report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) highlighted instances where incorrect software updates led to engine control unit (ECU) failures.
 Hardware damage due to software issues
Hardware damage due to software issues
Alt Text: Damaged ECU, highlighting the potential for hardware damage due to incorrect software.
2.5 Voiding Warranty
Tampering with your Mercedes-Benz’s software, especially by installing unauthorized or incorrect variants, can void your vehicle’s warranty. Mercedes-Benz, like most manufacturers, reserves the right to deny warranty claims if the vehicle has been modified in a way that deviates from the factory specifications.
3. Real-World Examples of Software Variant Issues
Several high-profile cases illustrate the potential consequences of software errors in vehicles.
3.1 The Case of Unintended Acceleration
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, Toyota faced widespread scrutiny due to reports of unintended acceleration. While the exact cause was debated, software glitches were identified as a contributing factor in some cases. A NASA study commissioned by the NHTSA found that software errors could, under certain conditions, lead to unintended acceleration.
3.2 Volkswagen’s Emissions Scandal
Volkswagen’s “Dieselgate” scandal involved the use of defeat devices – software designed to cheat emissions tests. This software detected when the vehicle was undergoing testing and altered the engine’s performance to reduce emissions. In real-world driving conditions, the vehicles emitted significantly higher levels of pollutants.
3.3 Tesla’s Autopilot Issues
Tesla’s Autopilot system, while innovative, has also been associated with several accidents. In some cases, software errors or misinterpretations of sensor data have been cited as contributing factors. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) has investigated multiple crashes involving Tesla vehicles using Autopilot.
4. How to Avoid Software Variant Problems
Preventing software variant issues requires a combination of caution, expertise, and the right tools.
4.1 Use a Reliable Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tool
Investing in a high-quality Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tool is essential. These tools allow you to accurately identify your vehicle’s software and ensure compatibility before making any changes. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of diagnostic tools designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
4.2 Verify Software Compatibility
Before installing any software update or modification, always verify its compatibility with your specific vehicle model, production year, and region. Refer to official Mercedes-Benz documentation or consult with a qualified technician.
4.3 Obtain Software from Trusted Sources
Only obtain software from trusted sources, such as authorized Mercedes-Benz dealers or reputable aftermarket suppliers. Avoid downloading software from unofficial websites or file-sharing networks, as these sources may contain malware or corrupted files.
4.4 Follow Installation Instructions Carefully
Carefully follow the installation instructions provided with the software. Pay close attention to any warnings or precautions. If you are unsure about any step, seek professional assistance.
4.5 Back Up Your Existing Software
Before making any changes to your vehicle’s software, create a backup of the existing software. This will allow you to revert to the previous version if something goes wrong.
4.6 Understanding the Role of Flashing in Mercedes-Benz Software Updates
Flashing, in the context of Mercedes-Benz software, refers to the process of writing new software or firmware onto the electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle. This is a critical operation that requires precision and the correct tools.
4.7 Importance of Correct Flashing
- ECU Replacement or Upgrade: When replacing an ECU, the new unit must be flashed with the appropriate software variant to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- Software Updates: To enhance performance, fix bugs, or add new features, Mercedes-Benz releases software updates that require flashing the ECUs.
- Calibration and Configuration: Flashing is also used to calibrate and configure various vehicle systems, such as engine management, transmission control, and ABS.
4.8 Potential Risks of Incorrect Flashing
- ECU Damage: Using the wrong software or an interrupted flashing process can permanently damage the ECU, rendering it useless.
- System Malfunctions: Incorrectly flashed software can cause various systems to malfunction, leading to warning lights, performance issues, or even complete system failure.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unverified or malicious software can introduce security vulnerabilities, making the vehicle susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access.
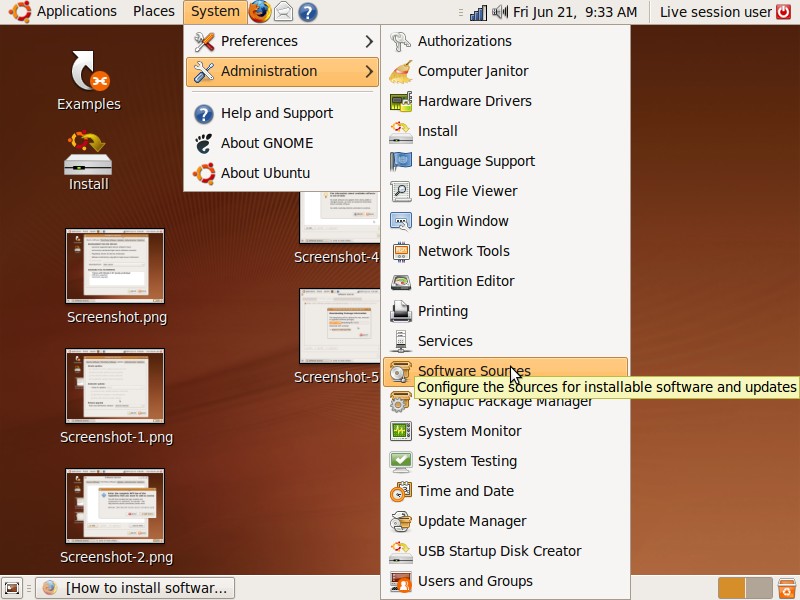
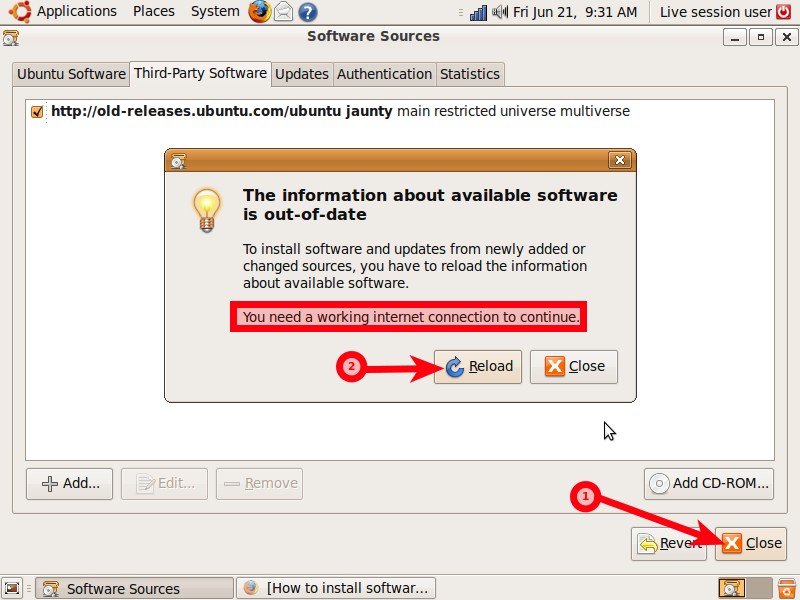
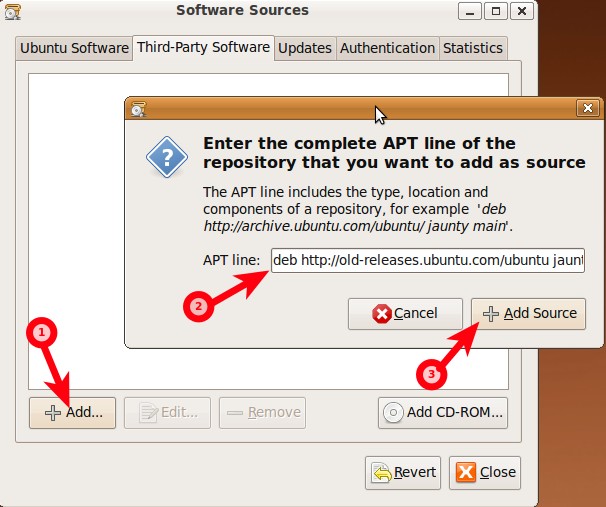 Third-Party Software tab
Third-Party Software tab
Alt Text: Screenshot of third-party software tab, showing the importance of trusted sources.
5. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians with the tools, information, and support they need to safely and effectively manage their vehicle’s software.
5.1 Diagnostic Tools
We offer a comprehensive range of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools, from entry-level code readers to advanced professional-grade systems. Our tools are designed to accurately identify your vehicle’s software, diagnose problems, and perform software updates.
5.2 Software and Firmware
We provide access to a vast library of Mercedes-Benz software and firmware, sourced from trusted suppliers. Our software is guaranteed to be compatible with your vehicle and free from malware.
5.3 Expert Support
Our team of experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance. We can help you troubleshoot software issues, select the right software variant, and perform software updates.
5.4 Training and Resources
We offer a variety of training programs and resources to help you learn about Mercedes-Benz software and diagnostics. Our training programs cover topics such as software identification, flashing, coding, and troubleshooting.
6. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in a vehicle’s computer system when a problem is detected. Understanding these codes is crucial for diagnosing and resolving software-related issues.
6.1 Reading DTCs
Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools can read DTCs from various vehicle systems, providing valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
6.2 Interpreting DTCs
DTCs are typically alphanumeric codes, such as “P0101” or “C1200.” Each code corresponds to a specific fault or malfunction. Resources like the MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN database can help you interpret these codes and understand their meaning.
6.3 Clearing DTCs
After repairing the problem, it’s essential to clear the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer system. This will turn off the warning lights and ensure that the system is functioning correctly.
7. The Benefits of Using Genuine Mercedes-Benz Software
Using genuine Mercedes-Benz software offers numerous advantages over aftermarket or pirated versions.
7.1 Optimal Performance and Compatibility
Genuine software is specifically designed and tested for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. It integrates seamlessly with the vehicle’s systems, maximizing efficiency and reliability.
7.2 Enhanced Security
Genuine software is rigorously tested for security vulnerabilities, protecting your vehicle from hacking and unauthorized access. Mercedes-Benz invests heavily in cybersecurity to safeguard its vehicles and customers.
7.3 Access to Updates and Support
When you use genuine software, you gain access to the latest updates and technical support from Mercedes-Benz. This ensures that your vehicle is always running the most current and secure software.
7.4 Warranty Protection
Using genuine software helps protect your vehicle’s warranty. Mercedes-Benz may void the warranty if unauthorized or pirated software is installed.
8. The Importance of Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates are essential for maintaining the performance, security, and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
8.1 Performance Enhancements
Software updates often include performance enhancements that can improve fuel economy, acceleration, and overall driving experience.
8.2 Bug Fixes
Software updates address bugs and glitches that can cause system malfunctions or erratic behavior.
8.3 Security Patches
Software updates include security patches that protect your vehicle from hacking and unauthorized access.
8.4 New Features
Software updates may introduce new features and functionalities, enhancing the overall ownership experience.
9. Common Software-Related Issues in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Several software-related issues are commonly encountered in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
9.1 Engine Control Unit (ECU) Problems
ECU problems can manifest as performance issues, warning lights, or even complete engine failure. Software updates or reprogramming may be necessary to resolve these issues.
9.2 Transmission Control Module (TCM) Problems
TCM problems can cause erratic shifting, transmission slippage, or complete transmission failure. Software updates or reprogramming may be required to address these issues.
9.3 Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Problems
ABS problems can compromise braking performance and safety. Software updates or reprogramming may be necessary to restore proper ABS functionality.
9.4 Infotainment System Problems
Infotainment system problems can range from minor glitches to complete system failure. Software updates or reprogramming may be required to resolve these issues.
 Reload available software
Reload available software
Alt Text: Display showing reload available software, emphasizing the need for regular updates.
10. Troubleshooting Software-Related Problems
Troubleshooting software-related problems requires a systematic approach.
10.1 Identify the Symptoms
Carefully document the symptoms you are experiencing. This will help you narrow down the potential causes of the problem.
10.2 Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use a Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tool to read DTCs from the vehicle’s computer system. This will provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
10.3 Consult Technical Resources
Consult technical resources, such as the MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN database, to interpret the DTCs and understand their meaning.
10.4 Perform Software Updates or Reprogramming
If necessary, perform software updates or reprogramming to resolve the problem. Follow the installation instructions carefully and ensure that the software is compatible with your vehicle.
10.5 Seek Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about any step, seek professional assistance from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
11. Advanced Techniques for Software Management
Beyond basic software updates, advanced techniques can further optimize your Mercedes-Benz’s performance and functionality.
11.1 Coding and Programming
Coding and programming allow you to customize various vehicle settings and features. This can include things like enabling or disabling certain functions, adjusting lighting parameters, or modifying the behavior of the transmission.
11.2 SCN Coding
SCN (Software Calibration Number) coding is a process used to match the software in an ECU to the specific vehicle configuration. This is often required when replacing an ECU or performing certain software updates.
11.3 Variant Coding
Variant coding allows you to configure the software in an ECU to match the vehicle’s specific options and equipment. This is essential for ensuring that all systems function correctly.
12. The Future of Automotive Software
Automotive software is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and features being introduced at an accelerating pace.
12.1 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-Air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to deliver software updates to vehicles remotely, without requiring a visit to the dealership. This makes it easier and more convenient to keep your vehicle’s software up-to-date.
12.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being increasingly used in automotive software to enhance features like driver assistance, navigation, and voice control.
12.3 Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as vehicles become more connected. Manufacturers are investing heavily in cybersecurity to protect vehicles from hacking and unauthorized access.
13. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Modifying your vehicle’s software can have legal and ethical implications.
13.1 Warranty Voiding
As previously mentioned, modifying your vehicle’s software can void the warranty.
13.2 Emissions Regulations
Tampering with emissions control software is illegal in many jurisdictions.
13.3 Safety Standards
Modifying safety-related software can compromise the safety of the vehicle and its occupants.
13.4 Intellectual Property
Unauthorized copying or distribution of software is a violation of intellectual property laws.
14. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate diagnostic tool for your Mercedes-Benz is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
14.1 Entry-Level Code Readers
These tools are suitable for basic tasks like reading and clearing DTCs.
14.2 Mid-Range Diagnostic Scanners
These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming and component testing.
14.3 Professional-Grade Diagnostic Systems
These systems provide the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including coding, programming, and SCN coding.
15. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Software: Best Practices
Adhering to best practices ensures your Mercedes-Benz software remains optimized and secure.
15.1 Regularly Check for Updates
Periodically check for software updates and install them promptly.
15.2 Use a Battery Maintainer During Updates
Use a battery maintainer during software updates to prevent power interruptions.
15.3 Document All Changes
Document all software changes you make to your vehicle.
15.4 Seek Professional Assistance When Needed
Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician when needed.
By understanding the complexities of Mercedes-Benz software and following these guidelines, you can avoid the pitfalls of installing the wrong software variant and ensure that your vehicle continues to perform at its best.
FAQ Section
Q: What happens if I install the wrong software variant in my Mercedes-Benz?
Installing the wrong software variant can cause system instability, reduced performance, feature loss, and potential hardware damage. In some cases, it can also void your vehicle’s warranty.
Q: How do I find the correct software variant for my Mercedes-Benz?
You can find the correct software variant by using a Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tool, accessing Mercedes-Benz online services, or consulting your vehicle’s documentation.
Q: Where can I obtain Mercedes-Benz software?
You should only obtain Mercedes-Benz software from trusted sources, such as authorized Mercedes-Benz dealers or reputable aftermarket suppliers like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Q: How often should I update my Mercedes-Benz software?
You should regularly check for software updates and install them promptly. Mercedes-Benz typically releases software updates to improve performance, fix bugs, and enhance security.
Q: What is SCN coding?
SCN (Software Calibration Number) coding is a process used to match the software in an ECU to the specific vehicle configuration. This is often required when replacing an ECU or performing certain software updates.
Q: What is variant coding?
Variant coding allows you to configure the software in an ECU to match the vehicle’s specific options and equipment. This is essential for ensuring that all systems function correctly.
Q: What is Over-the-Air (OTA) update?
Over-the-Air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to deliver software updates to vehicles remotely, without requiring a visit to the dealership.
Q: Is it legal to modify my Mercedes-Benz software?
Modifying your vehicle’s software can have legal and ethical implications. Tampering with emissions control software is illegal in many jurisdictions, and modifying safety-related software can compromise the safety of the vehicle and its occupants.
Q: What should I do if I’m not sure how to update my Mercedes-Benz software?
If you are unsure about any step, seek professional assistance from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
Q: Where can I find reliable Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools and software?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive range of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools and software, sourced from trusted suppliers. We also provide expert support and training to help you manage your vehicle’s software safely and effectively.
Avoid the risks of incorrect software and unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance with diagnostics, software updates, and feature unlocking. Our team is ready to provide the right tools and guidance to ensure your Mercedes-Benz performs at its best.
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
