Navigating the world of automotive diagnostics can be complex, especially when dealing with older vehicles. Is your 1994 Ford Ranger Obd2 compatible? No, the 1994 Ford Ranger is equipped with OBD1, not OBD2, but you can still access diagnostic information using the Check Engine Light (CEL) to read codes, making it essential to understand how to retrieve and interpret these codes for effective vehicle maintenance. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to diagnose your 1994 Ford Ranger, interpret the diagnostic codes, and maintain your vehicle effectively, ensuring you have the knowledge to keep your Ford Ranger running smoothly. You’ll discover the ins and outs of the OBD1 system in your Ranger, empowering you to perform basic diagnostics and potentially save on repair costs, all while leveraging resources like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for advanced insights.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD1 and OBD2: What’s the Difference?
- 1.1 Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
- 1.2 Why the 1994 Ford Ranger Uses OBD1
- 2. Diagnosing Your 94 Ford Ranger: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1 Locating the OBD1 Connector
- 2.2 Preparing for the Diagnostic Test
- 2.3 Performing the Jumper Test
- 2.4 Reading the Diagnostic Codes
- 2.5 Understanding the Codes
- 2.6 Clearing the Codes
- 2.7 Why Clearing Codes is Important
- 3. Interpreting 3-Digit OBD1 Codes for Your Ford Ranger
- 3.1 Accessing a Code List
- 3.2 Common OBD1 Codes and Their Meanings
- 3.3 Troubleshooting Based on Codes
- 3.4 Example: Code 116 – Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit
- 3.5 When to Seek Professional Help
- 4. Essential Maintenance Tips for Your 1994 Ford Ranger
- 4.1 Regular Oil Changes
- 4.2 Checking and Replacing Fluids
- 4.3 Inspecting and Maintaining Brakes
- 4.4 Tire Maintenance
- 4.5 Battery Maintenance
- 4.6 Checking Belts and Hoses
- 4.7 Air Filter Replacement
- 4.8 Spark Plug Replacement
- 5. Resources for Ford Ranger Owners
- 5.1 Online Forums and Communities
- 5.2 Repair Manuals
- 5.3 Diagnostic Tools
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the 94 Ford Ranger
- 6.1 Using a Multimeter for Sensor Testing
- 6.2 Vacuum Leak Testing
- 6.3 Fuel Pressure Testing
- 6.4 Compression Testing
- 7. Enhancing Your Ford Ranger’s Performance
- 7.1 Upgrading Air Intake and Exhaust Systems
- 7.2 Chip Tuning and Performance Programmers
- 7.3 Suspension Upgrades
- 7.4 Tire Upgrades
- 8. Common Issues and Solutions for the 1994 Ford Ranger
- 8.1 Engine Misfires
- 8.2 Transmission Problems
- 8.3 Brake Problems
- 8.4 Electrical Issues
- 9. The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
- 9.1 Identifying Potential Problems Early
- 9.2 Maintaining Vehicle Value
- 9.3 Ensuring Safety
- 9.4 Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 10. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Advanced Diagnostics
- 10.1 Accessing Diagnostic Information
- 10.2 Understanding Repair Principles
- 10.3 Contacting Experts for Advice
- FAQ: Diagnosing and Maintaining Your 94 Ford Ranger
- 1. What does OBD1 mean for my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 2. How do I read the diagnostic codes on my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 3. Where can I find a list of OBD1 codes for my Ford Ranger?
- 4. What does code 111 mean on my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 5. How do I clear the diagnostic codes from my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 6. How often should I change the oil in my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 7. What are the common transmission problems in a 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 8. Can I upgrade the performance of my 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 9. What are some common electrical issues in the 1994 Ford Ranger?
- 10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with my Ford Ranger’s diagnostics?
1. Understanding OBD1 and OBD2: What’s the Difference?
What are the fundamental differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems? OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) and OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics 2) are automotive diagnostic systems, with OBD2 being the more advanced and standardized version. OBD1, used in vehicles before 1996, is manufacturer-specific, meaning each carmaker had its own diagnostic connectors, codes, and communication protocols, while OBD2, mandated in the United States in 1996, offers a universal diagnostic connector (SAE J1962), a standardized set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and enhanced monitoring capabilities, covering a broader range of vehicle systems, thus improving diagnostic accuracy and ease of use.
1.1 Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
What are the key differences that set OBD1 and OBD2 apart? Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized across all manufacturers |
| Connector | Varies by manufacturer | Universal SAE J1962 connector |
| Diagnostic Codes | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) |
| Systems Monitored | Limited | Comprehensive, including emissions, engine, and transmission |
| Data Parameters | Limited | Extensive, with numerous live data parameters |
| Year of Adoption | Before 1996 | 1996 and later (in the United States) |
| Ease of Use | More complex, requires specific knowledge | Easier to use with generic scanners |
| Emissions Focus | Less emphasis on emissions | Strong emphasis on emissions monitoring |
| Diagnostic Access | Often requires specific tools and procedures | Accessible with standard OBD2 scanners |
 OBD1 Connector
OBD1 Connector
1.2 Why the 1994 Ford Ranger Uses OBD1
Why does a 1994 Ford Ranger come equipped with OBD1 instead of OBD2? The 1994 Ford Ranger was manufactured before the OBD2 standard became mandatory in the United States in 1996. As such, it uses the older OBD1 system, which was common for vehicles produced in the early to mid-1990s. This means that the diagnostic procedures and equipment required for a 1994 Ranger are specific to the OBD1 system, necessitating different tools and knowledge compared to newer, OBD2-compliant vehicles.
2. Diagnosing Your 94 Ford Ranger: A Step-by-Step Guide
How can you effectively diagnose issues with your 1994 Ford Ranger using its OBD1 system? Diagnosing your 1994 Ford Ranger involves using the Check Engine Light (CEL) to read diagnostic codes, as the vehicle is equipped with an OBD1 system. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do it:
2.1 Locating the OBD1 Connector
Where can you find the OBD1 connector in your 1994 Ford Ranger? The OBD1 connector in your 1994 Ford Ranger is typically located in the engine bay. Look for a connector that may have a cap marked “EEC” (Electronic Engine Control) clipped to the engine fuse box, often found on the driver’s side of the engine compartment. It usually consists of a trapezoidal connector with several pins, along with a separate single grey connector on the same harness.
2.2 Preparing for the Diagnostic Test
What steps should you take to prepare your Ford Ranger for a diagnostic test? Before starting the diagnostic test, ensure the following:
- Turn off the ignition: Make sure the key is in the “off” position.
- Locate the connectors: Identify the OBD1 connector and the separate single grey connector on the same harness.
- Prepare a jumper wire: Have a short jumper wire or an unfolded paper clip ready to connect the necessary pins.
2.3 Performing the Jumper Test
How do you perform the jumper test to initiate the diagnostic mode? To perform the jumper test:
- Connect the jumper wire: Use the jumper wire or paper clip to connect the single grey connector (the “Self Test Input”) to the “Signal Return” slot on the larger OBD1 connector. This connection puts the EEC into test mode when the key is turned on.
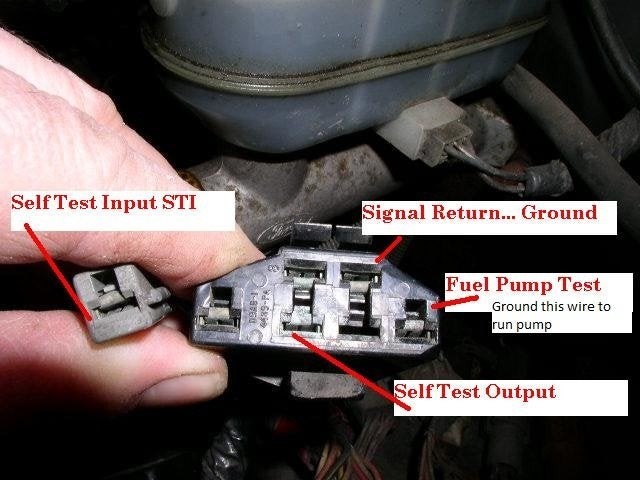 OBD1 Connector Slots
OBD1 Connector Slots
2.4 Reading the Diagnostic Codes
How do you read the diagnostic codes displayed by the Check Engine Light? After completing the jumper connection, follow these steps to read the diagnostic codes:
- Turn the key to the “on” position: Do not start the engine.
- Observe the Check Engine Light (CEL): The CEL will flash once to indicate that the computer has booted up. After the initial flash, it will begin to display the diagnostic codes.
- Interpret the flashes: The codes are three-digit numbers. For example, if the CEL flashes once, pauses, flashes once again, pauses, and then flashes six times, followed by a long pause, the code is 116. Each digit of the code is represented by a series of flashes separated by short pauses.
- Record the codes: Write down each code as it is displayed. The system will cycle through all stored codes and then repeat them. When you see the same code repeated, you know you have recorded all the codes in memory.
2.5 Understanding the Codes
What does code 111 indicate in the OBD1 system? Code 111 indicates that there are no diagnostic trouble codes stored in the system’s memory. This means that the computer has not detected any faults or issues.
2.6 Clearing the Codes
How can you clear the diagnostic codes from your Ford Ranger’s memory? To clear the diagnostic codes:
- Ensure the key is in the “on” position: The engine should not be running.
- Remove the jumper wire: While the key is still on, remove the jumper wire from the OBD1 connector. This action clears all the stored codes in the computer’s memory.
- Verify the codes are cleared: Turn off the key, then turn it back on to recheck for codes. If the codes have been successfully cleared, only code 111 (no codes) should appear.
- Alternative method: If you turn off the key and then remove the jumper wire, the codes will be saved in memory.
2.7 Why Clearing Codes is Important
Why is it important to clear diagnostic codes after addressing an issue? Clearing the codes is important for several reasons:
- Confirming the repair: After fixing a problem, clearing the codes allows you to verify that the issue has been resolved and that the Check Engine Light does not reappear.
- Avoiding misdiagnosis: Old codes can remain in the system’s memory and lead to misdiagnosis if not cleared, as they may indicate problems that no longer exist.
- Monitoring for new issues: Clearing the codes allows you to monitor for new problems that may arise, as any new codes will indicate current issues needing attention.
3. Interpreting 3-Digit OBD1 Codes for Your Ford Ranger
How do you interpret the 3-digit OBD1 codes to understand the problems with your Ford Ranger? Interpreting 3-digit OBD1 codes is essential for diagnosing issues in your 1994 Ford Ranger. These codes can help you identify specific problems within the vehicle’s systems. Here’s a guide to understanding common codes:
3.1 Accessing a Code List
Where can you find a reliable list of 3-digit OBD1 codes for Ford vehicles? You can find a comprehensive list of 3-digit OBD1 codes for Ford vehicles at websites such as The Ranger Station: https://www.therangerstation.com/tech_library/3digitcodes.shtml.
3.2 Common OBD1 Codes and Their Meanings
What are some common OBD1 codes and what do they typically indicate? Here’s a table of common OBD1 codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| 111 | System Pass / No Malfunction | No issues detected |
| 116 | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit | Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issue, coolant level low |
| 121 | Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Circuit | Faulty TPS, misadjusted TPS, wiring issue |
| 129 | Insufficient Mass Air Flow (MAF) | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leak, restricted air intake |
| 157 | MAF Sensor Circuit Low Voltage | Faulty MAF sensor, wiring issue, poor connection |
| 172 | Oxygen Sensor (O2S) Circuit Lean (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Vacuum leak, low fuel pressure, faulty O2 sensor, exhaust leak |
| 173 | O2S Circuit Rich (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | High fuel pressure, faulty O2 sensor, leaking fuel injector |
| 212 | Ignition System Fault | Faulty ignition module, coil pack, distributor issue, wiring problem |
| 327 | EGR Valve Position Sensor Circuit Low | Faulty EGR valve position sensor, wiring issue, vacuum leak |
| 512 | Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Test Failure | Computer memory issue, poor connection, low battery voltage |
3.3 Troubleshooting Based on Codes
How do you proceed with troubleshooting once you have identified the diagnostic codes? Once you have retrieved the diagnostic codes, follow these steps for troubleshooting:
- Research the code: Use a reliable source, such as the provided link to The Ranger Station, to understand the meaning of the code and potential causes.
- Inspect the related components: Check the sensors, wiring, and connectors associated with the code. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test the components: Use a multimeter to test the sensors and wiring for proper voltage, resistance, and continuity.
- Address the identified issues: Repair or replace any faulty components, fix wiring problems, or correct any other identified issues.
- Clear the codes: After making the necessary repairs, clear the diagnostic codes from the system’s memory.
- Test drive the vehicle: Drive the vehicle to see if the Check Engine Light reappears. If the light stays off, the issue has been resolved. If it reappears, recheck the codes and continue troubleshooting.
3.4 Example: Code 116 – Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit
How would you troubleshoot a Code 116 related to the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor? If you retrieve code 116, indicating a problem with the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor circuit, follow these steps:
- Inspect the ECT sensor: Locate the ECT sensor, usually found on the engine block or cylinder head near the thermostat housing. Check for any visible damage or corrosion.
- Check the wiring and connectors: Inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the ECT sensor. Look for loose connections, damaged wires, or corrosion.
- Test the ECT sensor: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the ECT sensor. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
- Check the coolant level: Ensure the coolant level in the radiator and overflow tank is adequate. Low coolant can cause inaccurate temperature readings.
- Replace the ECT sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Clear the code: After replacing the sensor, clear the diagnostic code from the system’s memory.
- Test drive the vehicle: Drive the vehicle to see if the Check Engine Light reappears.
3.5 When to Seek Professional Help
When should you consider seeking professional help for diagnosing your Ford Ranger? While you can perform basic diagnostics using the OBD1 system, there are situations where seeking professional help is advisable:
- Complex issues: If you are unable to identify the cause of the problem after retrieving and researching the diagnostic codes.
- Multiple codes: If multiple codes are present, indicating several potential issues, it may be challenging to diagnose and repair the problems without professional assistance.
- Lack of experience: If you are not comfortable working on your vehicle or lack the necessary tools and equipment.
- Persistent issues: If you have attempted to repair the problem but the Check Engine Light continues to reappear.
4. Essential Maintenance Tips for Your 1994 Ford Ranger
What are the essential maintenance tasks to keep your 1994 Ford Ranger running smoothly? Maintaining your 1994 Ford Ranger is crucial for its longevity and reliability. Here are essential maintenance tips to keep your vehicle in top condition:
4.1 Regular Oil Changes
How often should you change the oil in your 1994 Ford Ranger? Regular oil changes are vital for maintaining the health of your engine. It is generally recommended to change the oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or every 3 to 6 months, depending on your driving conditions and the type of oil used. Refer to your owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
4.2 Checking and Replacing Fluids
What fluids should you regularly check and when should you replace them? Regularly check and replace the following fluids:
- Engine coolant: Check the coolant level regularly and flush the system every 2 to 3 years to prevent corrosion and maintain optimal cooling performance.
- Brake fluid: Check the brake fluid level and condition. Replace it every 2 to 3 years to ensure proper braking performance and prevent moisture contamination.
- Power steering fluid: Check the power steering fluid level and condition. Replace it as needed to maintain smooth steering operation.
- Transmission fluid: Check the transmission fluid level and condition. Replace it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure smooth shifting and prevent transmission damage.
- Windshield washer fluid: Keep the windshield washer fluid reservoir full for clear visibility.
4.3 Inspecting and Maintaining Brakes
How often should you inspect your brakes and what maintenance is required? Inspect your brakes regularly, at least every 6 months or 6,000 miles. Check the brake pads, rotors, calipers, and brake lines for wear, damage, or leaks. Replace brake pads and rotors as needed to ensure safe and effective braking performance.
4.4 Tire Maintenance
What tire maintenance tasks are essential for your Ford Ranger? Proper tire maintenance is essential for safety and fuel efficiency. Key tasks include:
- Checking tire pressure: Check the tire pressure monthly and inflate the tires to the recommended pressure specified in the owner’s manual or on the tire placard.
- Rotating tires: Rotate the tires every 6,000 to 8,000 miles to promote even wear and extend tire life.
- Inspecting tire tread: Regularly inspect the tire tread for wear and damage. Replace tires when the tread depth reaches the minimum legal limit.
- Balancing tires: Have the tires balanced when you notice vibrations or uneven wear.
4.5 Battery Maintenance
How can you maintain the battery in your 1994 Ford Ranger? Proper battery maintenance ensures reliable starting performance. Key tasks include:
- Checking battery terminals: Clean the battery terminals regularly to remove corrosion and ensure a good connection.
- Testing battery voltage: Periodically test the battery voltage to ensure it is within the proper range.
- Securing the battery: Make sure the battery is securely mounted to prevent vibration damage.
- Replacing the battery: Replace the battery every 3 to 5 years, or as needed, to maintain reliable starting power.
4.6 Checking Belts and Hoses
How often should you check the belts and hoses in your Ford Ranger? Regularly inspect the belts and hoses for cracks, wear, or leaks. Replace them as needed to prevent breakdowns and maintain proper engine operation. Key areas to check include:
- Serpentine belt: Check the serpentine belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Replace it every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, or as needed.
- Hoses: Check the radiator hoses, heater hoses, and vacuum hoses for leaks, cracks, or swelling. Replace them every 4 to 5 years, or as needed.
4.7 Air Filter Replacement
How often should you replace the air filter in your 1994 Ford Ranger? Replace the air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more frequently if you drive in dusty conditions. A clean air filter ensures proper airflow to the engine, improving performance and fuel efficiency.
4.8 Spark Plug Replacement
How often should you replace the spark plugs in your Ford Ranger? Replace the spark plugs every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, depending on the type of spark plugs used. New spark plugs ensure proper ignition and optimal engine performance.
5. Resources for Ford Ranger Owners
What resources are available to help Ford Ranger owners maintain and repair their vehicles? Several resources are available to assist Ford Ranger owners with maintenance and repairs, including online forums, repair manuals, and diagnostic tools.
5.1 Online Forums and Communities
What are some popular online forums where Ford Ranger owners can find information and support? Online forums and communities can provide valuable information, tips, and support for Ford Ranger owners. Some popular forums include:
- The Ranger Station: This website offers a wealth of information, including technical articles, how-to guides, and a forum for Ranger enthusiasts.
- Ford Ranger Forum: A dedicated forum for Ford Ranger owners to discuss various topics, share experiences, and seek advice.
- Ranger-Forums.com: Another popular forum with a large community of Ranger owners and enthusiasts.
5.2 Repair Manuals
Where can you find reliable repair manuals for your 1994 Ford Ranger? Repair manuals provide detailed instructions, diagrams, and specifications for performing maintenance and repairs on your vehicle. Some reliable sources for repair manuals include:
- Haynes Repair Manual: Haynes manuals offer step-by-step instructions and illustrations for various repair tasks.
- Chilton Repair Manual: Chilton manuals provide comprehensive coverage of vehicle maintenance and repair procedures.
- Factory Service Manual: The official factory service manual provides the most detailed and accurate information for your specific vehicle.
5.3 Diagnostic Tools
What diagnostic tools can you use to troubleshoot your Ford Ranger? While the 1994 Ford Ranger uses the OBD1 system, there are tools available to help with diagnostics:
- Code Readers: Basic code readers can display the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Multimeters: Multimeters can be used to test sensors, wiring, and other electrical components.
- Vacuum Gauges: Vacuum gauges can help diagnose vacuum leaks, which can cause various engine problems.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the 94 Ford Ranger
What advanced diagnostic techniques can you use for your 1994 Ford Ranger to pinpoint elusive issues? For more complex issues, advanced diagnostic techniques can help pinpoint the root cause of problems in your 1994 Ford Ranger:
6.1 Using a Multimeter for Sensor Testing
How can a multimeter help diagnose sensor issues in your Ford Ranger? A multimeter is an essential tool for testing sensors and electrical components. Here’s how to use it:
- Voltage Testing: Check for proper voltage supply to the sensor. Refer to the repair manual for the correct voltage specifications.
- Resistance Testing: Measure the resistance of the sensor to determine if it is within the specified range.
- Continuity Testing: Check for continuity in the wiring to ensure there are no breaks or shorts.
6.2 Vacuum Leak Testing
How can you identify and locate vacuum leaks in your Ford Ranger’s engine? Vacuum leaks can cause various engine problems, such as rough idling, poor performance, and increased fuel consumption. Methods for testing vacuum leaks include:
- Visual Inspection: Check vacuum hoses for cracks, leaks, or loose connections.
- Smoke Testing: Use a smoke machine to introduce smoke into the intake system and identify leaks.
- Carburetor Cleaner Method: Spray carburetor cleaner around vacuum lines and intake manifold gaskets. If the engine RPM changes, there is likely a vacuum leak in that area.
6.3 Fuel Pressure Testing
How do you test the fuel pressure in your Ford Ranger to diagnose fuel system issues? Testing fuel pressure can help diagnose issues related to the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel pressure regulator. Here’s how to do it:
- Connect the Fuel Pressure Gauge: Attach a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail test port.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and observe the fuel pressure reading.
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications. Low fuel pressure can indicate a faulty fuel pump or clogged fuel filter, while high fuel pressure can indicate a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
6.4 Compression Testing
How do you perform a compression test to assess the health of your Ford Ranger’s engine cylinders? A compression test can help assess the condition of the engine’s cylinders, valves, and piston rings. Here’s how to perform a compression test:
- Warm Up the Engine: Run the engine until it reaches operating temperature.
- Remove Spark Plugs: Remove all spark plugs from the engine.
- Insert Compression Tester: Insert a compression tester into each spark plug hole.
- Crank the Engine: Crank the engine for several seconds and record the compression reading.
- Compare Readings: Compare the compression readings for each cylinder. Low compression in one or more cylinders can indicate worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket.
7. Enhancing Your Ford Ranger’s Performance
What steps can you take to enhance the performance of your 1994 Ford Ranger? While the 1994 Ford Ranger is not a high-performance vehicle, there are several ways to enhance its performance and improve its driving experience:
7.1 Upgrading Air Intake and Exhaust Systems
How can upgrading the air intake and exhaust systems improve your Ford Ranger’s performance? Upgrading the air intake and exhaust systems can improve engine airflow, resulting in increased horsepower and torque. Consider the following:
- Cold Air Intake: A cold air intake can increase airflow to the engine by drawing in cooler air from outside the engine compartment.
- Performance Exhaust System: A performance exhaust system can reduce backpressure and improve exhaust flow, resulting in increased horsepower and torque.
7.2 Chip Tuning and Performance Programmers
Can chip tuning or performance programmers enhance your Ford Ranger’s engine performance? Chip tuning and performance programmers can optimize engine parameters, such as fuel injection and ignition timing, to improve performance. However, be cautious when using these devices, as they can potentially damage the engine if not used correctly.
7.3 Suspension Upgrades
How can upgrading the suspension improve your Ford Ranger’s handling and ride quality? Upgrading the suspension can improve handling, ride quality, and off-road capability. Options include:
- Lift Kits: Lift kits can increase ground clearance and allow for larger tires.
- Performance Shocks and Struts: Upgrading to performance shocks and struts can improve handling and ride quality.
- Sway Bars: Adding or upgrading sway bars can reduce body roll and improve handling.
7.4 Tire Upgrades
How can upgrading your tires improve your Ford Ranger’s traction and handling? Upgrading the tires can improve traction, handling, and off-road capability. Consider the following:
- All-Terrain Tires: All-terrain tires provide a good balance of on-road and off-road performance.
- Mud Tires: Mud tires provide maximum traction in muddy or off-road conditions.
- Performance Tires: Performance tires can improve handling and grip on paved roads.
8. Common Issues and Solutions for the 1994 Ford Ranger
What are some common problems encountered with the 1994 Ford Ranger and how can they be resolved? The 1994 Ford Ranger, like any older vehicle, can experience common issues. Here are some problems and their solutions:
8.1 Engine Misfires
What causes engine misfires in a 1994 Ford Ranger and how can you fix them? Engine misfires can be caused by:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Replace worn or damaged spark plugs.
- Damaged Spark Plug Wires: Replace damaged spark plug wires.
- Faulty Ignition Coil: Replace the faulty ignition coil.
- Vacuum Leaks: Locate and repair vacuum leaks.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Clean or replace faulty fuel injectors.
8.2 Transmission Problems
What are common transmission issues in the 1994 Ford Ranger and how can they be addressed? Common transmission problems include:
- Slipping Gears: This can be caused by low transmission fluid, worn clutches, or a faulty torque converter. A transmission fluid change or rebuild may be necessary.
- Rough Shifting: Rough shifting can be caused by worn synchronizers or a faulty shift solenoid.
- Transmission Leaks: Transmission leaks can be caused by damaged seals or gaskets. Replace the damaged seals or gaskets.
8.3 Brake Problems
What brake problems are common in the 1994 Ford Ranger and how can they be resolved? Common brake problems include:
- Worn Brake Pads: Replace worn brake pads.
- Warped Rotors: Replace warped rotors.
- Leaking Brake Calipers: Rebuild or replace leaking brake calipers.
- Brake Line Leaks: Repair or replace leaking brake lines.
8.4 Electrical Issues
What electrical problems are frequently encountered in the 1994 Ford Ranger and how can they be fixed? Common electrical issues include:
- Faulty Sensors: Replace faulty sensors.
- Wiring Problems: Repair or replace damaged wiring.
- Battery Problems: Replace a weak or dead battery.
- Alternator Problems: Replace a faulty alternator.
9. The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Why are regular check-ups important for maintaining your 1994 Ford Ranger’s reliability and longevity? Regular check-ups are crucial for maintaining your 1994 Ford Ranger. These check-ups help:
9.1 Identifying Potential Problems Early
How can regular check-ups help identify potential problems before they become major issues? Regular check-ups allow you to identify potential problems early, before they become major issues. This can save you money and prevent breakdowns.
9.2 Maintaining Vehicle Value
How does regular maintenance contribute to maintaining the value of your Ford Ranger? Regular maintenance helps maintain the value of your vehicle by keeping it in good condition.
9.3 Ensuring Safety
How do regular inspections and maintenance ensure the safety of your Ford Ranger? Regular inspections and maintenance ensure your safety by identifying and addressing potential safety issues, such as worn brakes, damaged tires, or faulty lighting.
9.4 Improving Fuel Efficiency
How does regular maintenance contribute to improving the fuel efficiency of your Ford Ranger? Regular maintenance can improve fuel efficiency by ensuring that the engine is running properly and that components such as the air filter and spark plugs are in good condition.
10. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Advanced Diagnostics
How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN assist with advanced diagnostics and solutions for your Ford Ranger? While MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN primarily focuses on Mercedes-Benz vehicles, the site offers valuable information on automotive diagnostics and repair principles that can be applied to other vehicles, including the 1994 Ford Ranger.
10.1 Accessing Diagnostic Information
What types of diagnostic information can you find on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN that are relevant to your Ford Ranger? You can find general diagnostic information, troubleshooting tips, and repair procedures that can be adapted to your Ford Ranger.
10.2 Understanding Repair Principles
How can understanding general repair principles from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with your Ford Ranger’s maintenance? Understanding general repair principles can help you better understand the inner workings of your Ford Ranger and perform maintenance and repairs more effectively.
10.3 Contacting Experts for Advice
How can you leverage the expertise available through MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for specific Ford Ranger issues? You can contact the experts at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for advice on specific Ford Ranger issues, even if the site primarily focuses on Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Their expertise in automotive diagnostics and repair can be valuable in troubleshooting complex problems.
By following this comprehensive guide, you can effectively diagnose and maintain your 1994 Ford Ranger, ensuring its reliability and longevity. Remember to utilize available resources, such as online forums, repair manuals, and websites like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, to enhance your knowledge and skills.
Is your 1994 Ford Ranger giving you trouble? Don’t let diagnostic challenges keep you off the road. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice, comprehensive diagnostic solutions, and guidance on maintaining your classic Ford Ranger. Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or connect via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and support.
FAQ: Diagnosing and Maintaining Your 94 Ford Ranger
1. What does OBD1 mean for my 1994 Ford Ranger?
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) is the diagnostic system used in your 1994 Ford Ranger. Unlike the standardized OBD2, OBD1 is manufacturer-specific, meaning you’ll need to use specific procedures and code lists to diagnose issues.
2. How do I read the diagnostic codes on my 1994 Ford Ranger?
To read the codes, locate the OBD1 connector in the engine bay, use a jumper wire to connect the “Self Test Input” to the “Signal Return” slot, turn the key to the “on” position (without starting the engine), and observe the Check Engine Light (CEL) flashes. Count the flashes to determine the three-digit code.
3. Where can I find a list of OBD1 codes for my Ford Ranger?
You can find a comprehensive list of OBD1 codes for Ford vehicles at websites like The Ranger Station: https://www.therangerstation.com/tech_library/3digitcodes.shtml.
4. What does code 111 mean on my 1994 Ford Ranger?
Code 111 indicates that there are no diagnostic trouble codes stored in the system’s memory, meaning the computer has not detected any faults or issues.
5. How do I clear the diagnostic codes from my 1994 Ford Ranger?
To clear the codes, ensure the key is in the “on” position (engine not running), remove the jumper wire from the OBD1 connector while the key is still on, then turn off the key. This clears all stored codes in the computer’s memory.
6. How often should I change the oil in my 1994 Ford Ranger?
It’s generally recommended to change the oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or every 3 to 6 months, depending on your driving conditions and the type of oil used. Refer to your owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
7. What are the common transmission problems in a 1994 Ford Ranger?
Common transmission problems include slipping gears, rough shifting, and transmission leaks. Slipping gears can be caused by low transmission fluid, worn clutches, or a faulty torque converter.
8. Can I upgrade the performance of my 1994 Ford Ranger?
Yes, you can enhance performance by upgrading the air intake and exhaust systems, using chip tuning or performance programmers (with caution), upgrading the suspension, and upgrading the tires.
9. What are some common electrical issues in the 1994 Ford Ranger?
Common electrical issues include faulty sensors, wiring problems, battery problems, and alternator problems. These can often be resolved by replacing the faulty components or repairing damaged wiring.
10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with my Ford Ranger’s diagnostics?
While primarily focused on Mercedes-Benz vehicles, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers valuable information on automotive diagnostic and repair principles that can be applied to other vehicles, including the 1994 Ford Ranger. You can also contact their experts for advice on specific issues.