The Difference Between Obd2 And Uds is that OBD2 is a standardized protocol primarily for emissions-related diagnostics, while UDS is a more comprehensive protocol used for a wider range of diagnostic and control functions in modern vehicles. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights and tools to navigate these complex systems, ensuring you get the most out of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics. Understanding these protocols is crucial for anyone involved in automotive diagnostics and repair, offering enhanced diagnostics for vehicle issues, parameter identification, and modifications to Electronic Control Unit behavior.
Contents
- Table of Contents
- 1. What Is The UDS Protocol?
- Why is UDS Important for Mercedes-Benz Owners and Technicians?
- 2. UDS vs CAN Bus: Standards & OSI Model
- Overview of UDS Standards & Concepts
- 3. UDS – No Standard Connector?
- 4. UDS Message Structure [ISO 14229-1/3]
- Protocol Control Information (PCI)
- UDS Service ID (SID)
- UDS Sub Function Byte
- UDS ‘Request Data Parameters’ – incl. Data Identifier (DID)
- 5. Positive vs. Negative UDS Responses [ISO 14229-1]
- 6. CAN ISO-TP – Transport Protocol [ISO 15765-2]
- ISO-TP: Single-Frame Communication
- ISO-TP: Multi-Frame Communication
- 7. UDS vs. OBD2 vs. WWH-OBD vs. OBDonUDS
- What is WWH-OBD (ISO 27145)?
- What is OBDonUDS (SAE J1979-2)?
- 8. How To Request/Record UDS Data
- Can a CAN bus data logger be used to request UDS data?
- How would multi-frame UDS communication work with a data logger?
- What data can be recorded via UDS data logging?
- Is UDS a standardized protocol?
- Who benefits from UDS data logging?
- Is it better to use UDS or raw CAN data for logging sensor values?
- Will I be able to request data from a specific car via UDS?
- 9. Example 1: Record Single Frame UDS Data (Speed Via WWH-OBD)
- 10. Example 2: Record Multi-Frame UDS Data (EV SoC%)
- 11. How To Decode Multi-Frame UDS Data?
- 12. Example 3: Record The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- 3.1: How to record the VIN via OBD2 (SAE J1979)
- 3.2: How to record the VIN via UDS (ISO 14229-2)
- 3.3: How to record the VIN via WWH-OBD (ISO 27145-3)
- 13. Example 4: Record Diagnostic Trouble Codes (WWH-OBD)
- 14. UDS Data Logging – Applications
- UDS Telematics For Prototype Electric Vehicles
- Training A Predictive Maintenance Model
- FAQ
- What Are The Key Differences Between UDS And OBD2?
- How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With UDS Diagnostics?
- Can I Use A Standard OBD2 Scanner For UDS Diagnostics?
- What Is The Role Of CAN Bus In UDS Communication?
- How Does WWH-OBD Relate To UDS?
- What Is ISO-TP, And Why Is It Important For UDS?
- How Do I Request And Record UDS Data?
- What Are Data Identifiers (DIDs) In UDS?
- How Can I Decode Multi-Frame UDS Data?
- What Are Some Common Applications Of UDS Data Logging?
Table of Contents
- What is the UDS protocol?
- UDS vs CAN bus: Standards & OSI model
- UDS – no standard connector?
- UDS message structure [ISO 14229-1/3]
- Positive vs. negative UDS responses [ISO 14229-1]
- CAN ISO-TP – Transport Protocol [ISO 15765-2]
- UDS vs. OBD2 vs. WWH-OBD vs. OBDonUDS
- How to request/record UDS data
- Example 1: Record Single Frame UDS data (Speed via WWH-OBD)
- Example 2: Record multi-frame UDS data (EV SoC%)
- How to decode multi-frame UDS data?
- Example 3: Record the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- 3.1: How to record the VIN via OBD2 (SAE J1979)
- 3.2: How to record the VIN via UDS (ISO 14229-2)
- 3.3: How to record the VIN via WWH-OBD (ISO 27145-3)
- Example 4: Record Diagnostic Trouble Codes (WWH-OBD)
- UDS data logging – applications
- UDS telematics for prototype electric vehicles
- Training a predictive maintenance model
- FAQ
1. What Is The UDS Protocol?
Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS), as defined by ISO 14229, is a versatile communication protocol that facilitates diagnostics, firmware updates, and routine testing across various Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in modern vehicles. UDS stands out for its standardization across manufacturers and communication standards such as CAN, KWP 2000, Ethernet, and LIN. It’s a cornerstone in automotive diagnostics, supported by all tier 1 Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). This protocol uses a client-server model, where a tester tool (client) communicates with a vehicle ECU (server). You can interface with your car using a CAN bus interface connected to the OBD2 connector, sending specific UDS requests to the vehicle. If the targeted ECU supports UDS, it will respond, allowing you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), extract parameter data like temperature and VIN, initiate diagnostic sessions, and modify ECU behavior. This makes UDS an invaluable tool for enhanced diagnostics and control, often referred to as vehicle manufacturer enhanced diagnostics.
Why is UDS Important for Mercedes-Benz Owners and Technicians?
For Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians, UDS offers a deeper level of access and control over vehicle systems compared to standard OBD2 protocols. This is particularly important for:
- Accessing Advanced Features: UDS allows for the unlocking of hidden features and customization options that are not available through OBD2.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: UDS provides access to a wider range of diagnostic data, enabling more accurate and detailed troubleshooting.
- Firmware Updates: UDS facilitates the updating of ECU firmware, ensuring that the vehicle’s systems are running the latest software versions.
2. UDS vs CAN Bus: Standards & OSI Model
To fully grasp UDS, it’s essential to differentiate it from CAN bus and understand its place in the OSI model. CAN, detailed in our CAN bus tutorial, provides the foundational communication layer, specifically the data-link and physical layers as per ISO 11898. Conversely, UDS (ISO 14229) operates as a higher-layer protocol, utilizing the session and application layers in the OSI model. This distinction highlights that UDS builds upon CAN, providing the diagnostic services on top of the communication network.
Overview of UDS Standards & Concepts
UDS encompasses numerous standards and concepts, which can initially seem complex. Here’s a high-level overview focusing on CAN as the communication basis:
- Application Layer: Described by ISO 14229-1, defining client-server communication flows, UDS services, and response codes. ISO standards also cover UDS application layers for various lower-layer protocols like UDSonCAN (ISO 14229-3).
- Presentation Layer: Typically vehicle manufacturer-specific.
- Session Layer: Defined in ISO 14229-2, outlining service request/confirmation/indication primitives.
- Transport + Network Layer: For CAN, ISO 15765-2 (ISO-TP) manages the transport of diagnostic data.
- Data Link Layer: In CAN, this is described by ISO 11898-1.
- Physical Layer: Also in CAN, detailed by ISO 11898-2.
3. UDS – No Standard Connector?
Unlike other higher-layer CAN protocols like OBD2, J1939, and ISOBUS, UDS does not specify a standard connector. However, in practice, the OBD2 connector (SAE J1962) is commonly used in most vehicles. For example, electric vehicles from Nissan, Hyundai, and VW may offer limited or no OBD2 communication but respond to UDS requests via the OBD2 connector.
4. UDS Message Structure [ISO 14229-1/3]
UDS is a request-based protocol. The UDS request frame includes several key fields:
Protocol Control Information (PCI)
Required for UDS requests on CAN bus, related to ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2). The PCI field provides information about the type and length of the message.
UDS Service ID (SID)
Each UDS service has a unique identifier. The UDS request message includes the SID in the data payload to specify the desired service. Identifiers are split between request SIDs (e.g., 0x22) and response SIDs (e.g., 0x62). The response SIDs generally add 0x40 to the request SIDs.
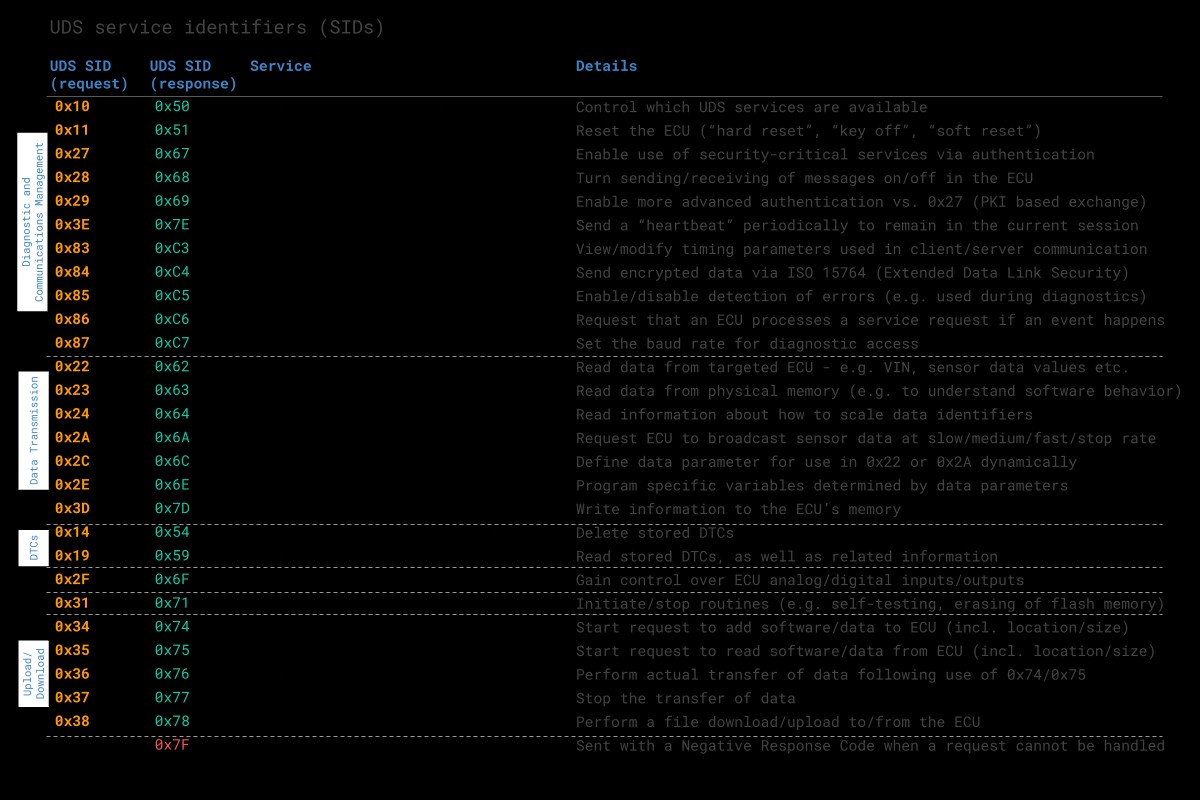 UDS Sevices Table Overview
UDS Sevices Table Overview
UDS Sub Function Byte
Used in some UDS request frames. It allows for further configuration of the request.
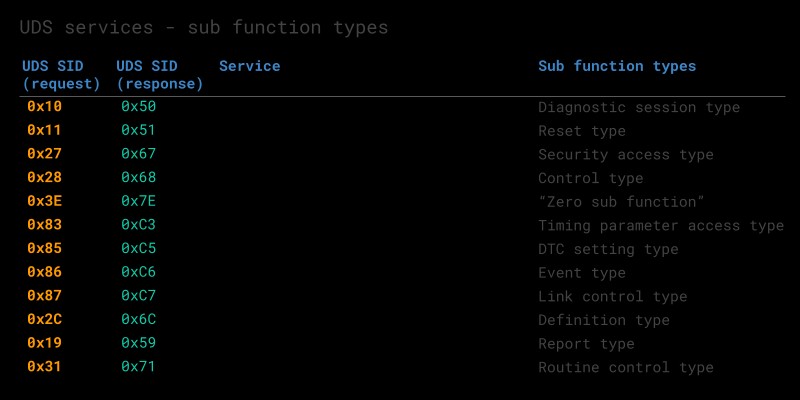 UDS Sub Function Byte Table Overview
UDS Sub Function Byte Table Overview
UDS ‘Request Data Parameters’ – incl. Data Identifier (DID)
Various types of request data parameters are used to provide further configuration of a request beyond the SID and optional sub function byte. For example, service 0x22 (Read Data by Identifier) uses a Data Identifier (DID), which is a 2-byte value between 0 and 65535 (0xFFFF).
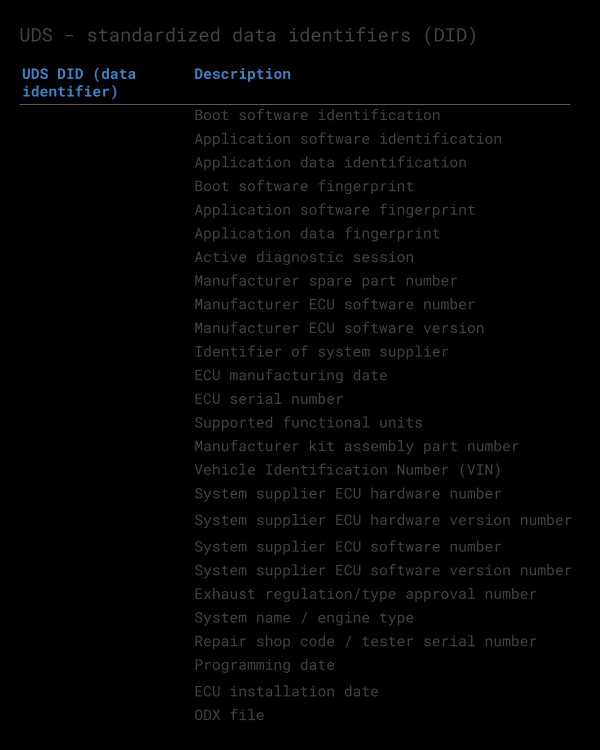 UDS Standard Data Identifiers DID 0x22
UDS Standard Data Identifiers DID 0x22
5. Positive vs. Negative UDS Responses [ISO 14229-1]
When an ECU responds positively to a UDS request, the response frame is structured with similar elements as the request frame. However, in some cases, an ECU may provide a negative response to a UDS request, such as if the service is not supported. The negative response frame includes:
- PCI field
- Negative Response Code SID (0x7F)
- SID of the rejected request
- Negative Response Code (NRC)
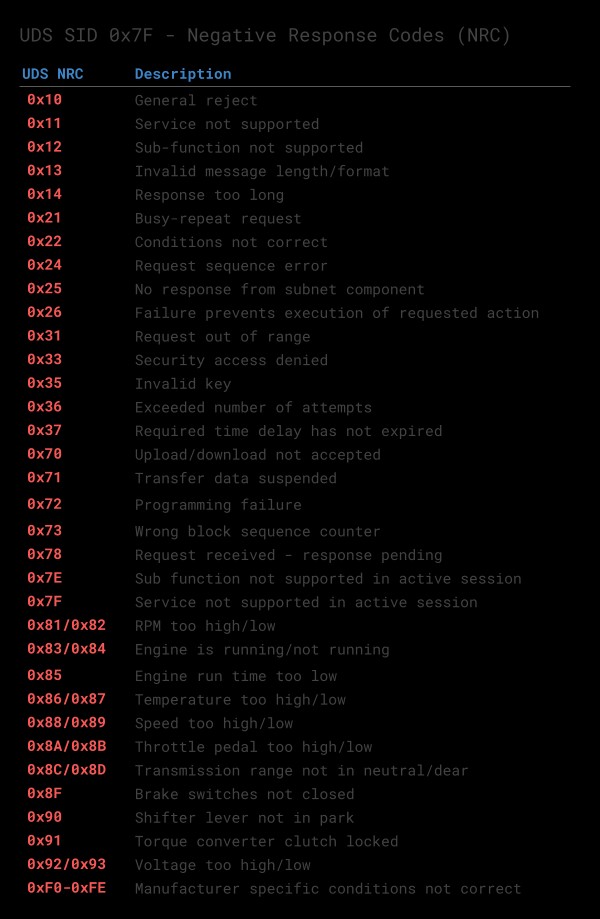 UDS NRC Response Code Table Negative Responses
UDS NRC Response Code Table Negative Responses
6. CAN ISO-TP – Transport Protocol [ISO 15765-2]
ISO 15765-2 specifies a transport protocol and network layer services for use in CAN-based vehicle networks. The standard outlines how to communicate CAN data payloads up to 4095 bytes through segmentation, flow control, and reassembly. ISO-TP defines specific CAN frames for enabling this communication:
ISO-TP: Single-Frame Communication
In the simplest case, a tester tool sends a Single Frame to request data from an ECU. If the response can be contained in a 7-byte payload, the ECU provides a Single Frame response.
ISO-TP: Multi-Frame Communication
When the payload exceeds 7 bytes, it needs to be split across multiple CAN frames. The tester sends a Single Frame request to an ECU. The ECU sends a First Frame (FF) that contains information on the total packet length and the initial chunk of data. The tester sends a Flow Control (FC) frame, which tells the ECU how the rest of the data transfer should be transmitted. The ECU sends Consecutive Frames (CF) that contain the remaining data payload.
7. UDS vs. OBD2 vs. WWH-OBD vs. OBDonUDS
A common question is how UDS relates to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2), World-Wide Harmonized OBD (WWH-OBD), and OBDonUDS. OBD is implemented differently across countries and vehicles. The OSI model comprising CAN-based vehicle diagnostic protocols:
- ISO OBD (or EOBD): OBD protocol specification legislated for use in EU cars.
- SAE OBD: OBD protocol specification legislated for use in the US.
- HD OBD (SAE J1939): Typically refers to heavy-duty OBD and is commonly implemented through the J1939 protocol.
- UDS (ISO 14229): Implemented by vehicle manufacturers for richer diagnostics data/functionality beyond the limits of the emissions-focused OBD protocols.
- WWH-OBD and OBDonUDS: Provide an updated version of OBD2 for emissions-related diagnostics, based on UDS.
What is WWH-OBD (ISO 27145)?
WWH-OBD is a global standard for vehicle diagnostics, developed by the UN under the Global Technical Regulations (GTR) mandate. It aims to provide a single, future-proof alternative to existing OBD protocols (ISO OBD, SAE OBD, HD OBD). WWH-OBD is based on UDS to suit the enhanced diagnostics functionality already deployed by most automotive OEMs.
What is OBDonUDS (SAE J1979-2)?
OBDonUDS serves as an update to the SAE J1979 standard. The aim is to initiate a transition phase starting in 2023, where ECUs are allowed to support either OBD2 or OBDonUDS. From 2027, OBDonUDS will be a mandatory requirement for all vehicles produced in the US.
8. How To Request/Record UDS Data
Now that you understand the basics of UDS and ISO-TP, let’s look at how you can work with UDS data in practice. We’ll focus on how UDS can be used to log various data parameters.
Can a CAN bus data logger be used to request UDS data?
Yes, a CAN bus data logger can be configured to request UDS data. You can configure the device to transmit custom CAN frames as periodic or single-shot frames, controlling the CAN ID, data payload, period time, and delay.
How would multi-frame UDS communication work with a data logger?
For multi-frame communication, you can configure the data logger with a request frame and add the Flow Control frame as a separate frame to be transmitted a set number of milliseconds after the request frame.
What data can be recorded via UDS data logging?
A common use case for recording UDS data via standalone data loggers is to acquire diagnostic trouble code values for diagnosing issues. UDS also allows you to request the current value of various sensors related to each ECU.
Is UDS a standardized protocol?
While UDS provides a standardized structure for diagnostic communication, the actual content of the communication remains proprietary and is often only known to the manufacturer of a specific vehicle/ECU.
Who benefits from UDS data logging?
UDS data logging is particularly relevant to automotive engineers working at OEMs. It can also benefit after-market users like vehicle fleet managers and even private individuals who can identify the reverse-engineered information required to request and decode UDS parameters.
Is it better to use UDS or raw CAN data for logging sensor values?
If you have direct access to the CAN bus, it may seem easier to simply log raw CAN traffic and process it. However, due to increasing use of gateways that block access to raw CAN bus data via the OBD2 connector, UDS is frequently used for extracting sensor values.
Will I be able to request data from a specific car via UDS?
Since most ECUs today support UDS communication, the answer is yes, most likely. However, if you are in the aftermarket and wish to record proprietary UDS information from a car/truck, it may be difficult.
9. Example 1: Record Single Frame UDS Data (Speed Via WWH-OBD)
To showcase UDS in practice, we’ll start with a basic example. As explained, WWH-OBD is based on UDS and is mandated in all EU trucks after 2014. As a result, you can typically request speed, RPM, fuel level, etc., similarly to how you would do so via OBD2. However, in WWH-OBD (ISO 27145-2), the OBD2 PIDs are replaced by the WWH-OBD DIDs (Data Identifiers).
Specifically, WWH-OBD DIDs match OBD2 PIDs, except that 0xF4 is added in front. For example, the OBD2 PID for Speed is 0x0D, which becomes 0xF40D in the WWH-OBD context.
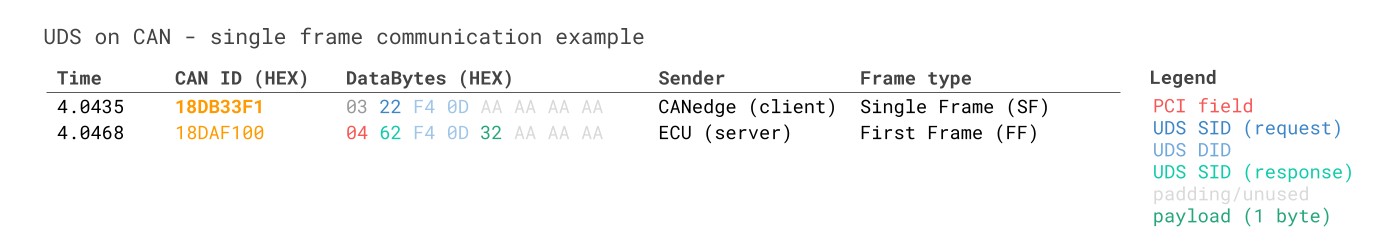 WWH-OBD Request Response Speed Example
WWH-OBD Request Response Speed Example
10. Example 2: Record Multi-Frame UDS Data (EV SoC%)
In this section, we’ll illustrate how multi-frame UDS communication works in the context of CAN ISO-TP. We’ll use UDS SID 0x22 to request the current value of State of Charge (SoC%) from a Kia EV6 electric vehicle.
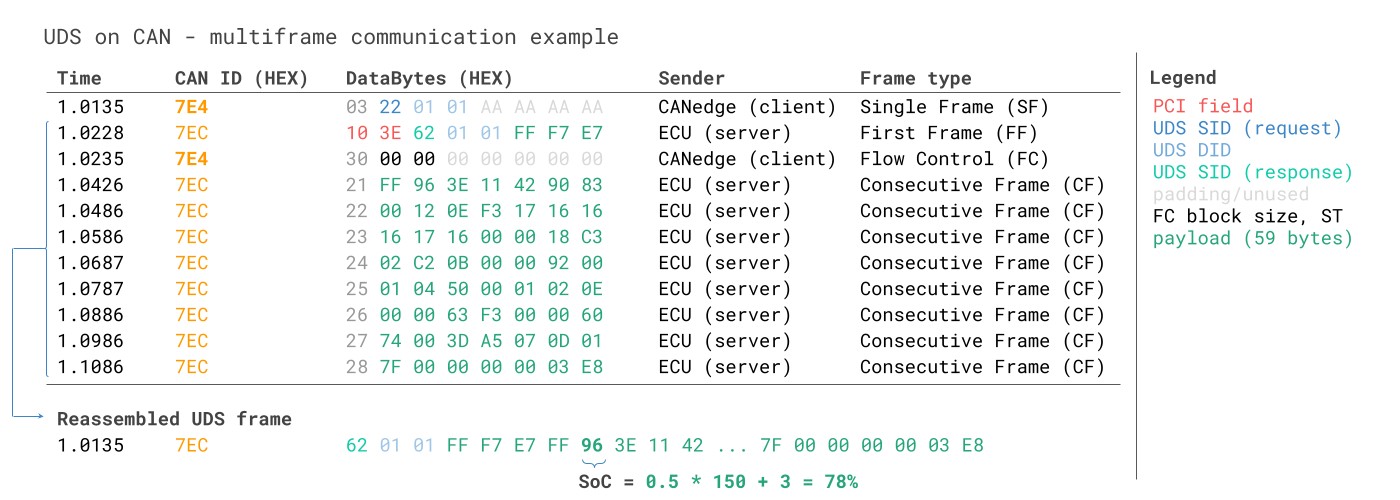 UDS ISO-TP Multi Frame Request Response Electric Vehicle SoC
UDS ISO-TP Multi Frame Request Response Electric Vehicle SoC
11. How To Decode Multi-Frame UDS Data?
To extract physical values like State of Charge, you need to know how to interpret the response CAN frames. The decoding information is typically proprietary and only known to the OEM. However, the information can be found for many EVs via online resources. We also collect this information in our free EV data pack for several brands.
 Electric Vehicle Data Pack
Electric Vehicle Data Pack
12. Example 3: Record The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a unique identifier code used for road vehicles. A VIN consists of 17 ASCII characters and can be extracted on-request from a vehicle.
3.1: How to record the VIN via OBD2 (SAE J1979)
To extract the Vehicle Identification Number from a passenger car using OBD2 requests, you use Service 0x09 and the PID 0x02:
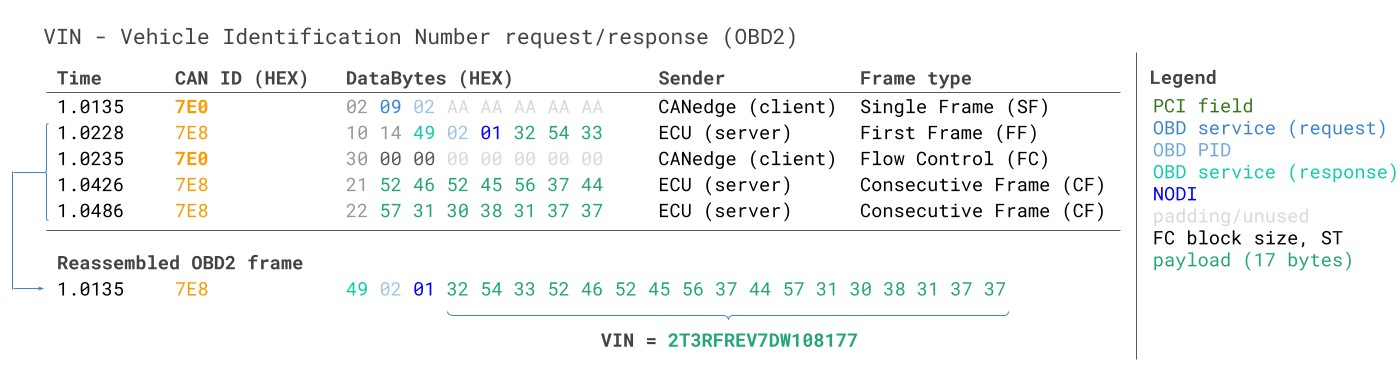 VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
3.2: How to record the VIN via UDS (ISO 14229-2)
To read the Vehicle Identification Number via UDS, you can use the UDS SID 0x22 and the DID 0xF190:
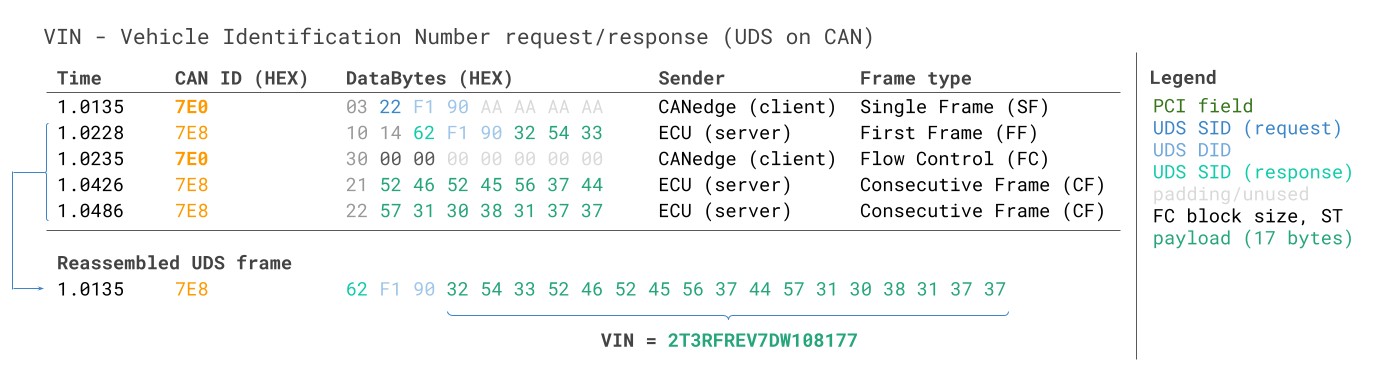 VIN Vehicle Identification Number UDS Unified Diagnostic Services
VIN Vehicle Identification Number UDS Unified Diagnostic Services
3.3: How to record the VIN via WWH-OBD (ISO 27145-3)
If you need to request the Vehicle Identification Number from an EU truck after 2014, you can use the WWH-OBD protocol. The structure is identical to the UDS example, except that WWH-OBD specifies the use of the DID 0xF802 for the VIN.
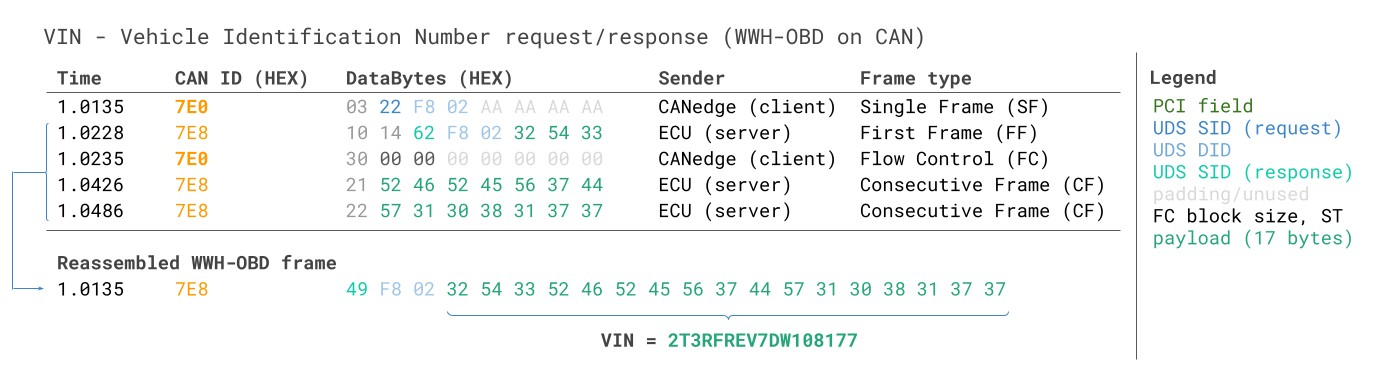 VIN Vehicle Identification Number WWH-OBD World Wide Harmonized
VIN Vehicle Identification Number WWH-OBD World Wide Harmonized
13. Example 4: Record Diagnostic Trouble Codes (WWH-OBD)
Below shows a request/response trace for reading 6 x Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) via WWH-OBD:
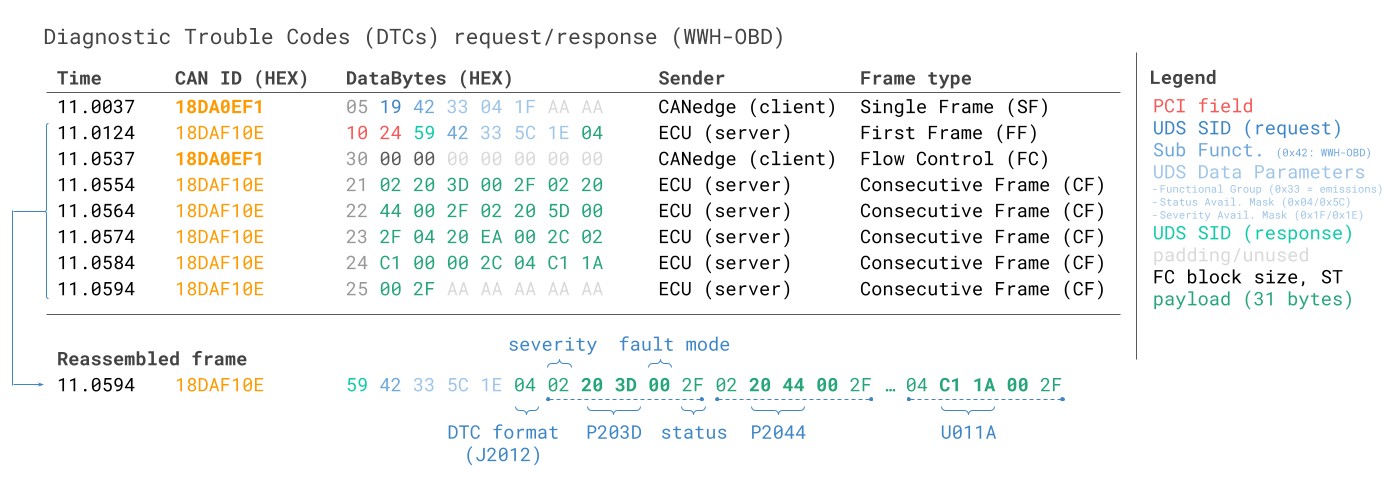 WWH-OBD Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC ISO TP
WWH-OBD Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC ISO TP
 OBD2 Trouble Code Lookup Tool
OBD2 Trouble Code Lookup Tool
14. UDS Data Logging – Applications
In this section, we’ll outline example use cases for recording UDS data.
UDS Telematics For Prototype Electric Vehicles
As an OEM, you may need to get data on various sensor parameters from prototype EVs while they are operating in the field.
Training A Predictive Maintenance Model
If you’re looking to implement predictive maintenance across fleets of heavy-duty vehicles, the first step is typically to “train your model.”
FAQ
What Are The Key Differences Between UDS And OBD2?
UDS is a broader protocol for vehicle diagnostics and control, while OBD2 is mainly focused on emissions-related diagnostics. UDS offers enhanced capabilities for accessing advanced features and comprehensive diagnostics, making it essential for modern automotive systems.
How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With UDS Diagnostics?
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert support to help you effectively use UDS for your Mercedes-Benz. Our resources enable you to unlock hidden features, troubleshoot complex issues, and maintain your vehicle with confidence.
Can I Use A Standard OBD2 Scanner For UDS Diagnostics?
While a standard OBD2 scanner can access some basic information, it is not sufficient for UDS diagnostics. UDS requires specialized tools and software to communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs and access the full range of diagnostic data.
What Is The Role Of CAN Bus In UDS Communication?
CAN bus serves as the communication network over which UDS operates. It provides the physical layer for transmitting diagnostic requests and responses between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s ECUs.
How Does WWH-OBD Relate To UDS?
WWH-OBD is a global standard for vehicle diagnostics based on UDS. It aims to harmonize diagnostic protocols and leverage the enhanced capabilities of UDS for emissions-related diagnostics.
What Is ISO-TP, And Why Is It Important For UDS?
ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2) is a transport protocol used with UDS to handle large data payloads. It enables the segmentation, flow control, and reassembly of diagnostic messages, allowing for the transmission of data exceeding the CAN frame size limit.
How Do I Request And Record UDS Data?
Requesting and recording UDS data involves sending specific diagnostic requests to the vehicle’s ECUs and logging the responses. This process requires specialized tools, knowledge of UDS protocols, and understanding of the vehicle’s diagnostic parameters.
What Are Data Identifiers (DIDs) In UDS?
Data Identifiers (DIDs) are used in UDS to specify the diagnostic parameters to be read or written. They are unique codes that identify specific data elements within the vehicle’s ECUs, such as sensor readings, system settings, and diagnostic trouble codes.
How Can I Decode Multi-Frame UDS Data?
Decoding multi-frame UDS data requires reassembling the segmented messages and interpreting the data according to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. This process often involves using specialized software and databases to translate the raw data into meaningful diagnostic information.
What Are Some Common Applications Of UDS Data Logging?
Common applications of UDS data logging include vehicle diagnostics, performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and research and development. It enables engineers and technicians to gather detailed insights into the vehicle’s operation and identify potential issues before they lead to failures.
By understanding the differences between OBD2 and UDS, you can effectively utilize the advanced diagnostic capabilities of UDS to maintain and optimize your vehicle’s performance.
For expert guidance on using UDS for your Mercedes-Benz, contact us today. Our team at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is ready to assist you with the right tools, information, and support. Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Contact us on WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for immediate assistance and expert advice!