Coding is necessary after retrofitting new hardware components in your Mercedes-Benz to ensure seamless integration and optimal functionality, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers the expertise and tools to guide you through the process. The coding process involves reprogramming the vehicle’s software to recognize and communicate with the new hardware, enabling features and preventing errors, and we’re here to help. Explore coding requirements, ECU programming and diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of Vehicle Coding
- 1.1. What is Vehicle Coding?
- 1.2. Why is Coding Required After Retrofitting?
- 1.3. Common Misconceptions About Vehicle Coding
- 2. The Role of the ECU in Hardware Retrofitting
- 2.1. What is an ECU and How Does it Work?
- 2.2. How Does the ECU Interact With New Hardware Components?
- 2.3. The Importance of ECU Calibration After Hardware Installation
- 3. Potential Issues Without Proper Coding
- 3.1. Error Messages and Warning Lights
- 3.2. Malfunctioning Hardware Components
- 3.3. Reduced Vehicle Performance
- 3.4. Safety Concerns
- 4. Examples of Hardware Retrofits That Require Coding
- 4.1. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
- 4.2. Parking Sensors
- 4.3. Headlight Upgrades
- 4.4. Navigation Systems
- 4.5. Entertainment Systems
- 5. How to Determine if Coding is Necessary
- 5.1. Consult the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
- 5.2. Check With the Hardware Manufacturer
- 5.3. Consult With a Qualified Technician
- 5.4. Look for Error Messages or Warning Lights
- 5.5. Research Online Forums and Communities
- 6. Tools and Software Used for Vehicle Coding
- 6.1. Diagnostic Scanners
- 6.2. Coding Software
- 6.3. Online Coding Platforms
- 6.4. Common Coding Software Options
- 7. Step-by-Step Guide to Vehicle Coding (General Overview)
- 7.1. Preparation
- 7.2. Connecting to the Vehicle’s ECU
- 7.3. Identifying the Correct Control Module
- 7.4. Entering the Correct Coding Parameters
- 7.5. Verifying the Coding
- 8. Common Coding Procedures for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 8.1. SCN Coding
- 8.2. Variant Coding
- 8.3. Retrofit Coding
- 8.4. Using XENTRY for Coding
- 8.5. Example: Activating Ambient Lighting
- 9. Potential Risks of Incorrect Coding
- 9.1. Damaged ECU
- 9.2. System Instability
- 9.3. Voided Warranty
- 9.4. Safety Hazards
- 10. When to Seek Professional Help
- 10.1. Complex Coding Procedures
- 10.2. Uncertainty About Coding Parameters
- 10.3. Lack of Experience
- 10.4. Warning Signs Indicating Coding Problems
- 10.5. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist
- 11. Tips for Safe and Successful Vehicle Coding
- 11.1. Research Thoroughly
- 11.2. Use Reliable Tools
- 11.3. Follow Instructions Carefully
- 11.4. Back Up Your Vehicle’s Data
- 11.5. Test After Coding
- 12. The Future of Vehicle Coding
- 12.1. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 12.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Coding
- 12.3. Cybersecurity Concerns
- 12.4. Ethical Considerations
- 13. Real-World Examples of Coding Success
- 13.1. Enhancing Performance With ECU Tuning
- 13.2. Enabling Hidden Features
- 13.3. Retrofitting Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 14. Troubleshooting Common Coding Issues
- 14.1. Check Connections
- 14.2. Verify Coding Parameters
- 14.3. Clear Error Codes
- 14.4. Restart the Vehicle
- 14.5. Seek Expert Advice
- 15. Case Studies: Successful Coding Projects
- 15.1. Retrofitting a Rearview Camera to an Older Mercedes-Benz
- 15.2. Activating AMG Performance Displays on a C-Class
- 15.3. Enabling Lane-Keeping Assist on an E-Class
- 16. Resources for Learning More About Vehicle Coding
- 16.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 16.2. Technical Documentation
- 16.3. Training Courses
- 16.4. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Resources
- 17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 17.1. What is the best diagnostic tool for Mercedes?
- 17.2. How do I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes?
- 17.3. How often should I service my Mercedes?
- 17.4. Can I code my Mercedes myself?
- 17.5. What are the risks of coding my car?
- 17.6. What is SCN coding?
- 17.7. How much does it cost to code a Mercedes?
- 17.8. What is variant coding?
- 17.9. What is the OBD-II port?
- 17.10. What is an ECU?
- 18. Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Vehicle Coding
1. Understanding the Basics of Vehicle Coding
Vehicle coding, also known as programming or software calibration, is the process of modifying a vehicle’s software to enable new features or adjust existing ones. Coding is crucial after retrofitting new hardware components because the vehicle’s computer system, known as the Engine Control Unit (ECU), needs to be updated to recognize and communicate with the new hardware. This process ensures that the new component functions correctly and integrates seamlessly with the vehicle’s existing systems.
1.1. What is Vehicle Coding?
Vehicle coding involves making changes to the software that controls various functions of a car. This can include enabling or disabling certain features, adjusting performance parameters, or configuring the vehicle to recognize new hardware components. The coding process typically involves using specialized software and diagnostic tools to access the vehicle’s ECU and make the necessary modifications.
1.2. Why is Coding Required After Retrofitting?
When new hardware components are installed in a vehicle, the ECU needs to be updated to recognize and communicate with these components. Without proper coding, the new hardware may not function correctly, or the vehicle may display error messages. Coding ensures that the new hardware is properly integrated into the vehicle’s systems, allowing it to function as intended.
1.3. Common Misconceptions About Vehicle Coding
One common misconception is that vehicle coding is only necessary for high-end modifications or performance enhancements. In reality, coding is often required even for basic retrofits, such as installing a new radio or adding parking sensors. Another misconception is that coding is a simple process that anyone can do. However, coding can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Attempting to code a vehicle without the proper training and tools can lead to serious problems, including damage to the ECU.
2. The Role of the ECU in Hardware Retrofitting
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the central computer system in a vehicle, responsible for controlling various functions such as engine performance, transmission, and safety systems. When new hardware components are retrofitted, the ECU needs to be updated to recognize and communicate with these components.
2.1. What is an ECU and How Does it Work?
The ECU is a sophisticated computer that monitors and controls various systems in a vehicle. It receives input from sensors throughout the vehicle and uses this information to make decisions about how to control various functions. For example, the ECU monitors the engine’s temperature, speed, and load to determine the optimal amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders.
2.2. How Does the ECU Interact With New Hardware Components?
When a new hardware component is installed, it needs to communicate with the ECU to function properly. This communication typically occurs through a data bus, such as the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. The ECU needs to be programmed to recognize the new component and understand the data it sends and receives.
2.3. The Importance of ECU Calibration After Hardware Installation
ECU calibration is the process of adjusting the ECU’s settings to optimize performance and ensure compatibility with new hardware components. Without proper calibration, the new hardware may not function correctly, or the vehicle may experience performance issues. Calibration involves fine-tuning various parameters, such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and boost pressure, to achieve the desired results.
3. Potential Issues Without Proper Coding
Failure to properly code a vehicle after retrofitting new hardware components can lead to a variety of issues, ranging from minor inconveniences to serious safety concerns. Some of the most common problems include:
3.1. Error Messages and Warning Lights
One of the most common issues is the appearance of error messages and warning lights on the dashboard. These messages indicate that the vehicle’s computer system has detected a problem with the new hardware. While some error messages may be benign, others can indicate a serious issue that needs to be addressed immediately.
3.2. Malfunctioning Hardware Components
Without proper coding, the new hardware components may not function correctly. For example, a new radio may not be able to receive certain channels, or parking sensors may not be able to detect obstacles. In some cases, the hardware may not function at all.
3.3. Reduced Vehicle Performance
Improper coding can also lead to reduced vehicle performance. For example, the engine may not run as efficiently, resulting in lower fuel economy. The transmission may not shift smoothly, leading to jerky acceleration. In some cases, the vehicle may even stall or fail to start.
3.4. Safety Concerns
In some cases, improper coding can create safety concerns. For example, if the ABS system is not properly coded after installing new brake components, it may not function correctly in an emergency situation. This could lead to a loss of control and a potential accident.
4. Examples of Hardware Retrofits That Require Coding
Many different types of hardware retrofits require coding to ensure proper functionality. Some of the most common examples include:
4.1. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
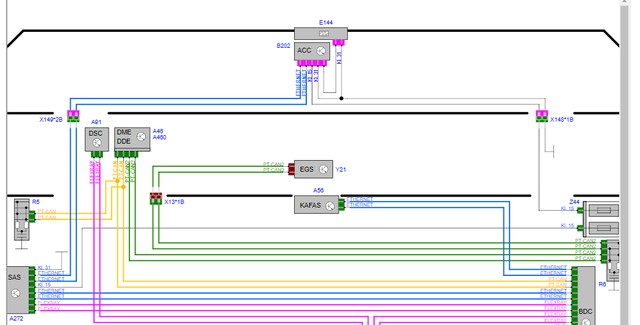
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is a system that automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. Retrofitting ACC typically requires coding to enable the system and calibrate it to the vehicle’s specific parameters. As the original poster mentioned, retrofitting ACC requires connecting wires to the SAS (Steering Angle Sensor) module and the front power distribution box, which necessitates coding for the system to function correctly.
4.2. Parking Sensors
Parking sensors are designed to help drivers avoid obstacles when parking. Retrofitting parking sensors typically requires coding to enable the system and calibrate it to the vehicle’s specific dimensions.
4.3. Headlight Upgrades
Upgrading to LED or Xenon headlights can improve visibility and enhance the vehicle’s appearance. However, these upgrades often require coding to ensure that the new headlights function correctly and do not cause any issues with the vehicle’s electrical system.
4.4. Navigation Systems
Installing a new navigation system can provide drivers with turn-by-turn directions and real-time traffic information. However, the new navigation system typically needs to be coded to integrate with the vehicle’s existing systems, such as the audio system and the instrument cluster.
4.5. Entertainment Systems
Upgrading the vehicle’s entertainment system can enhance the driving experience. However, the new entertainment system typically needs to be coded to integrate with the vehicle’s existing systems, such as the speakers and the steering wheel controls.
5. How to Determine if Coding is Necessary
Determining whether coding is necessary after retrofitting new hardware components can be challenging. However, there are several ways to determine if coding is required:
5.1. Consult the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
The vehicle’s owner’s manual may provide information about which retrofits require coding. The manual may also provide instructions on how to perform the coding process.
5.2. Check With the Hardware Manufacturer
The hardware manufacturer may provide information about whether coding is required for their product. The manufacturer may also provide instructions on how to perform the coding process.
5.3. Consult With a Qualified Technician
A qualified technician can assess the retrofit and determine whether coding is necessary. The technician can also perform the coding process if needed. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN has qualified technicians who can help you.
5.4. Look for Error Messages or Warning Lights
If error messages or warning lights appear on the dashboard after the retrofit, this is a strong indication that coding is required.
5.5. Research Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities dedicated to vehicle modification can be a valuable resource for determining whether coding is required for a particular retrofit. Other users may have experience with the same retrofit and can provide helpful advice and information.
6. Tools and Software Used for Vehicle Coding
Vehicle coding requires specialized tools and software to access the vehicle’s ECU and make the necessary modifications. Some of the most common tools and software include:
6.1. Diagnostic Scanners
Diagnostic scanners are handheld devices that can read and clear error codes from the vehicle’s ECU. Some diagnostic scanners can also perform basic coding functions.
6.2. Coding Software
Coding software is specialized software that allows users to access and modify the vehicle’s ECU. This software typically requires a laptop computer and a special interface cable to connect to the vehicle.
6.3. Online Coding Platforms
Online coding platforms provide access to a variety of coding tools and resources. These platforms typically require a subscription and may offer additional features, such as remote coding support.
6.4. Common Coding Software Options
Several coding software options are available for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most popular options include:
- XENTRY/DAS: XENTRY/DAS is the official diagnostic and coding software used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships. It provides comprehensive access to the vehicle’s ECU and allows for advanced coding and programming functions.
- Vediamo: Vediamo is a powerful coding software that is popular among enthusiasts and tuners. It offers advanced coding capabilities and allows for customization of various vehicle parameters.
- DTS Monaco: DTS Monaco is another popular coding software that is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive features. It supports a wide range of Mercedes-Benz vehicles and allows for both basic and advanced coding functions.
Choosing the right coding software depends on your specific needs and technical expertise. XENTRY/DAS is the most comprehensive option, but it can be expensive and requires extensive training to use effectively. Vediamo and DTS Monaco are more affordable and user-friendly, but they may not offer the same level of functionality as XENTRY/DAS.
7. Step-by-Step Guide to Vehicle Coding (General Overview)
The vehicle coding process can vary depending on the specific vehicle and the type of retrofit being performed. However, the following is a general overview of the steps involved:
7.1. Preparation
Before starting the coding process, it is important to gather all the necessary tools and information. This includes:
- A diagnostic scanner or coding software
- An interface cable to connect to the vehicle
- The vehicle’s VIN number
- The coding parameters for the new hardware component
- A stable power supply for the vehicle
7.2. Connecting to the Vehicle’s ECU
The next step is to connect the diagnostic scanner or coding software to the vehicle’s ECU. This typically involves connecting an interface cable to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, which is usually located under the dashboard.
7.3. Identifying the Correct Control Module
Once connected to the vehicle’s ECU, the next step is to identify the correct control module that needs to be coded. This may require consulting the vehicle’s service manual or technical documentation.
7.4. Entering the Correct Coding Parameters
After identifying the correct control module, the next step is to enter the correct coding parameters for the new hardware component. These parameters may be provided by the hardware manufacturer or can be found in online forums and communities.
7.5. Verifying the Coding
After entering the coding parameters, it is important to verify that the coding has been successfully applied. This can be done by checking for error messages or warning lights on the dashboard or by testing the functionality of the new hardware component.
8. Common Coding Procedures for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles often require specific coding procedures due to their complex electronic systems. Here are some common coding procedures for Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
8.1. SCN Coding
SCN (Software Calibration Number) coding is a process used by Mercedes-Benz to ensure that the vehicle’s software is properly calibrated and compatible with the hardware components. SCN coding requires a connection to the Mercedes-Benz online server and is typically performed by authorized dealerships or service centers.
8.2. Variant Coding
Variant coding is used to customize the vehicle’s features and functions according to the customer’s preferences. This can include enabling or disabling certain features, adjusting the sensitivity of sensors, or changing the language of the instrument cluster.
8.3. Retrofit Coding
Retrofit coding is used to enable new features or functions after installing aftermarket components. This can include adding features such as a rearview camera, blind-spot monitoring, or lane-keeping assist.
8.4. Using XENTRY for Coding
XENTRY is the official diagnostic and coding software used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships. It provides comprehensive access to the vehicle’s ECU and allows for advanced coding and programming functions. To use XENTRY for coding, you will need a valid XENTRY license and a compatible diagnostic interface.
8.5. Example: Activating Ambient Lighting
Activating ambient lighting in a Mercedes-Benz often requires coding to enable the feature in the vehicle’s ECU. This typically involves using XENTRY or another compatible coding software to access the relevant control module and enter the correct coding parameters.
9. Potential Risks of Incorrect Coding
Incorrect coding can have serious consequences, ranging from minor inconveniences to major safety issues. Some of the potential risks include:
9.1. Damaged ECU
Incorrect coding can damage the ECU, rendering the vehicle inoperable. This is a rare but serious risk that can be avoided by following the correct coding procedures and using reliable coding tools.
9.2. System Instability
Incorrect coding can cause system instability, leading to unpredictable behavior and malfunctions. This can include issues such as erratic engine performance, transmission problems, and electrical system failures.
9.3. Voided Warranty
Incorrect coding can void the vehicle’s warranty, leaving you responsible for any repairs or damages. It is important to check with your vehicle manufacturer or dealer before performing any coding to ensure that it will not void your warranty.
9.4. Safety Hazards
Incorrect coding can create safety hazards, such as disabling safety features or causing malfunctions that could lead to an accident. It is important to exercise caution when coding your vehicle and to ensure that all safety systems are functioning correctly after the coding process.
10. When to Seek Professional Help
While some coding procedures can be performed by experienced DIYers, others require professional expertise. It is important to know when to seek professional help to avoid potential risks and ensure that the coding is performed correctly.
10.1. Complex Coding Procedures
Complex coding procedures, such as SCN coding or variant coding, require specialized knowledge and equipment and should be performed by a qualified technician.
10.2. Uncertainty About Coding Parameters
If you are unsure about the correct coding parameters for a particular retrofit, it is best to consult with a professional. Incorrect coding parameters can lead to serious problems.
10.3. Lack of Experience
If you have no experience with vehicle coding, it is best to seek professional help. Coding can be complex and requires a thorough understanding of vehicle systems.
10.4. Warning Signs Indicating Coding Problems
Warning signs that indicate coding problems include error messages, warning lights, system malfunctions, and erratic vehicle behavior. If you experience any of these symptoms after coding your vehicle, it is important to seek professional help immediately.
10.5. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of services to assist with vehicle coding, including:
- Diagnostic scanning
- Coding and programming
- ECU calibration
- Remote coding support
- Technical assistance
Our team of qualified technicians has the expertise and equipment to perform coding procedures safely and effectively. We can also provide guidance and support to DIYers who are comfortable performing coding procedures themselves.
11. Tips for Safe and Successful Vehicle Coding
Vehicle coding can be a rewarding experience, but it is important to take precautions to ensure safety and success. Here are some tips for safe and successful vehicle coding:
11.1. Research Thoroughly
Before starting any coding procedure, research thoroughly to understand the process and the potential risks. Consult with online forums, technical documentation, and qualified technicians to gather as much information as possible.
11.2. Use Reliable Tools
Use reliable coding tools and software to avoid potential problems. Choose reputable brands and ensure that the tools are compatible with your vehicle.
11.3. Follow Instructions Carefully
Follow the instructions carefully when performing coding procedures. Pay close attention to the coding parameters and ensure that they are entered correctly.
11.4. Back Up Your Vehicle’s Data
Back up your vehicle’s data before performing any coding procedures. This will allow you to restore the vehicle to its original state if something goes wrong.
11.5. Test After Coding
Test the vehicle after coding to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly. Check for error messages, warning lights, and any other signs of problems.
12. The Future of Vehicle Coding
Vehicle coding is an evolving field, and new technologies and techniques are constantly emerging. Some of the trends shaping the future of vehicle coding include:
12.1. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. OTA updates allow manufacturers to remotely update the vehicle’s software, adding new features, fixing bugs, and improving performance.
12.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Coding
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate and improve the coding process. AI-powered coding tools can analyze vehicle data, identify coding errors, and suggest optimal coding parameters.
12.3. Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity is a growing concern in the automotive industry. As vehicles become more connected, they become more vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks. Vehicle manufacturers are investing in cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle systems from unauthorized access and modification.
12.4. Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important in vehicle coding. As vehicles become more autonomous, it is important to ensure that the coding algorithms are fair, unbiased, and transparent.
13. Real-World Examples of Coding Success
Vehicle coding has enabled countless enthusiasts and professionals to enhance the functionality and performance of their vehicles. Here are a few real-world examples of coding success:
13.1. Enhancing Performance With ECU Tuning
ECU tuning involves modifying the engine’s software to improve performance. This can include increasing horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency. Many enthusiasts have successfully enhanced the performance of their vehicles through ECU tuning.
13.2. Enabling Hidden Features
Many vehicles have hidden features that can be enabled through coding. This can include features such as ambient lighting, sport displays, and advanced driver-assistance systems.
13.3. Retrofitting Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) can improve safety and convenience. Many enthusiasts have successfully retrofitted ADAS features such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and blind-spot monitoring.
14. Troubleshooting Common Coding Issues
Even with careful planning and execution, coding issues can still arise. Here are some tips for troubleshooting common coding issues:
14.1. Check Connections
Check all connections to ensure that they are secure and properly connected. Loose or damaged connections can cause coding errors.
14.2. Verify Coding Parameters
Verify that the coding parameters are correct and compatible with your vehicle. Incorrect coding parameters can lead to system malfunctions.
14.3. Clear Error Codes
Clear any error codes that may be present in the vehicle’s ECU. Error codes can interfere with the coding process.
14.4. Restart the Vehicle
Restart the vehicle after coding to allow the changes to take effect.
14.5. Seek Expert Advice
If you are unable to resolve the coding issue, seek expert advice from a qualified technician.
15. Case Studies: Successful Coding Projects
Examining successful coding projects can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Here are a few case studies of successful coding projects:
15.1. Retrofitting a Rearview Camera to an Older Mercedes-Benz
Retrofitting a rearview camera to an older Mercedes-Benz can improve safety and convenience. This project involves installing a rearview camera, connecting it to the vehicle’s display screen, and coding the system to enable the camera.
15.2. Activating AMG Performance Displays on a C-Class
Activating AMG performance displays on a C-Class can enhance the driving experience. This project involves coding the instrument cluster to display performance data such as horsepower, torque, and G-forces.
15.3. Enabling Lane-Keeping Assist on an E-Class
Enabling lane-keeping assist on an E-Class can improve safety and convenience. This project involves installing the necessary hardware, connecting it to the vehicle’s ECU, and coding the system to enable lane-keeping assist.
16. Resources for Learning More About Vehicle Coding
Numerous resources are available for those interested in learning more about vehicle coding. Here are a few helpful resources:
16.1. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities dedicated to vehicle modification can be a valuable resource for learning about vehicle coding. These forums offer a wealth of information, advice, and support from experienced enthusiasts.
16.2. Technical Documentation
Technical documentation, such as service manuals and wiring diagrams, can provide detailed information about vehicle systems and coding procedures.
16.3. Training Courses
Training courses on vehicle coding are available from various providers. These courses can provide hands-on experience and expert guidance.
16.4. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Resources
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of resources for learning about vehicle coding, including:
- Articles and tutorials
- Coding software and tools
- Remote coding support
- Technical assistance
Our team of qualified technicians is available to answer your questions and provide guidance on vehicle coding.
17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
17.1. What is the best diagnostic tool for Mercedes?
The best diagnostic tool for Mercedes depends on your needs and budget. Options range from handheld scanners to comprehensive software suites like XENTRY/DAS.
17.2. How do I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes?
Hidden features can be unlocked through coding, which involves modifying the vehicle’s software using specialized tools and software.
17.3. How often should I service my Mercedes?
Mercedes-Benz recommends servicing your vehicle every 10,000 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first.
17.4. Can I code my Mercedes myself?
Yes, you can code your Mercedes yourself, but it requires specialized knowledge, tools, and software. It is important to research thoroughly and follow instructions carefully to avoid potential problems.
17.5. What are the risks of coding my car?
The risks of coding your car include damaging the ECU, causing system instability, voiding the warranty, and creating safety hazards.
17.6. What is SCN coding?
SCN (Software Calibration Number) coding is a process used by Mercedes-Benz to ensure that the vehicle’s software is properly calibrated and compatible with the hardware components.
17.7. How much does it cost to code a Mercedes?
The cost to code a Mercedes varies depending on the complexity of the coding procedure and the expertise of the technician.
17.8. What is variant coding?
Variant coding is used to customize the vehicle’s features and functions according to the customer’s preferences.
17.9. What is the OBD-II port?
The OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized port used to access the vehicle’s ECU. It is typically located under the dashboard.
17.10. What is an ECU?
The ECU (Engine Control Unit) is the central computer system in a vehicle, responsible for controlling various functions such as engine performance, transmission, and safety systems.
18. Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Vehicle Coding
Coding is an essential aspect of modern vehicle modification, enabling enthusiasts and professionals to enhance the functionality, performance, and customization of their vehicles. While coding can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and equipment, the rewards can be significant. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can safely and successfully unlock the power of vehicle coding and take your driving experience to the next level.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance with diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and comprehensive repair and maintenance guidance. Our team is here to provide the support and expertise you need. Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or connect via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
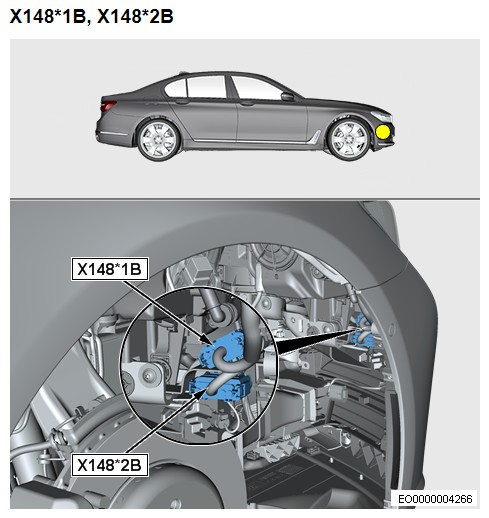
 Mercedes-Benz ACC Radar Connector
Mercedes-Benz ACC Radar Connector
 Mercedes-Benz Wiring Diagram
Mercedes-Benz Wiring Diagram