Typical values for common Mercedes ABS/ESP live data parameters can vary depending on the specific model, year, and engine type, but understanding these values is crucial for accurate diagnosis, which MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert guidance on decoding ABS/ESP systems, interpreting live data parameters, and ensuring optimal vehicle performance, using diagnostic tools and advanced LSI keywords. For reliable insights into Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, ABS sensor readings, and ESP module analysis, continue reading.
Contents
- 1. Understanding ABS/ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 1.1. Importance of ABS and ESP
- 1.2. Role of Live Data Parameters
- 2. Key ABS/ESP Live Data Parameters
- 2.1. Wheel Speed Sensors
- 2.1.1. Typical Values and Ranges
- 2.1.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 2.2. Brake Pressure Sensors
- 2.2.1. Typical Values and Ranges
- 2.2.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 2.3. Steering Angle Sensor
- 2.3.1. Typical Values and Ranges
- 2.3.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 2.4. Yaw Rate Sensor
- 2.4.1. Typical Values and Ranges
- 2.4.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 2.5. Lateral Acceleration Sensor
- 2.5.1. Typical Values and Ranges
- 2.5.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 3. Diagnostic Tools for Reading Live Data
- 3.1. OBD-II Scanners
- 3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Systems
- 3.3. Mercedes-Benz Specific Tools
- 4. Common ABS/ESP Problems and Their Live Data Signatures
- 4.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 4.2. Brake Pressure Sensor Failure
- 4.3. Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction
- 4.4. Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
- 4.5. Lateral Acceleration Sensor Problems
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading ABS/ESP Live Data with OBDLink
- 5.1. Downloading Enhanced Diagnostics
- 5.2. Selecting Your Vehicle Manufacturer
- 5.3. Choosing Your Vehicle Model Year
- 5.4. Selecting Diagnostics
- 5.5. Downloading Diagnostics
- 5.6. Selecting Vehicle Network
- 5.7. Viewing Diagnostics
- 5.8. Trouble Codes
- 5.9. Freeze Frame
- 5.10. PID Values
- 5.11. Report
- 6. Practical Examples of Diagnosing ABS/ESP Issues
- 6.1. Diagnosing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 6.2. Diagnosing a Brake Pressure Sensor Issue
- 6.3. Diagnosing a Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction
- 7. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8. Maintaining ABS/ESP Systems
- 8.1. Regular Inspections
- 8.2. Brake Fluid Maintenance
- 8.3. Sensor Cleaning
- 9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- 9.1. Case Study 1: ABS Activation During Normal Driving
- 9.2. Case Study 2: ESP Failure After Suspension Work
- 9.3. Case Study 3: Brake Pedal Vibration
- 10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 10.1. Actuator Testing
- 10.2. Component Testing
- 10.3. Signal Analysis
- 11. Potential Risks of Incorrect Diagnoses
- 11.1. Unnecessary Repairs
- 11.2. Increased Costs
- 11.3. Safety Hazards
- 12. FAQ: Common Questions About ABS/ESP Live Data
- 12.1. What is ABS?
- 12.2. What is ESP?
- 12.3. How do wheel speed sensors work?
- 12.4. What is a steering angle sensor?
- 12.5. What is yaw rate?
- 12.6. What is lateral acceleration?
- 12.7. How can I read ABS/ESP live data?
- 12.8. What are typical wheel speed sensor values?
- 12.9. What are typical brake pressure sensor values?
- 12.10. Where can I find more information about ABS/ESP systems?
- 13. Staying Updated with the Latest Information
- 13.1. Training Programs
- 13.2. Online Resources
- 13.3. Vendor Updates
- 14. The Future of ABS/ESP Diagnostics
- 14.1. Advanced Sensors
- 14.2. Sophisticated Control Algorithms
- 14.3. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
- 15. Conclusion: Mastering ABS/ESP Live Data for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
1. Understanding ABS/ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP) are critical safety features in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. ABS prevents wheel lock-up during braking, while ESP helps maintain directional control by detecting and reducing skids.
1.1. Importance of ABS and ESP
ABS and ESP enhance safety by improving braking performance and stability. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), vehicles equipped with ESP have a significantly lower risk of rollovers and skidding accidents. Regular maintenance and diagnostics of these systems are essential to ensure their effectiveness.
1.2. Role of Live Data Parameters
Live data parameters from the ABS/ESP system provide real-time information about sensor readings, actuator states, and control module calculations. Monitoring these parameters helps technicians diagnose issues and verify system functionality, which is a key service offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
2. Key ABS/ESP Live Data Parameters
Several live data parameters are crucial for diagnosing ABS/ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These include wheel speed sensor readings, brake pressure, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration.
2.1. Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are vital for ABS and ESP, as they measure the rotational speed of each wheel. Discrepancies in these readings can indicate sensor failure, wiring issues, or problems with the ABS/ESP module.
2.1.1. Typical Values and Ranges
Normal wheel speed sensor values should be consistent across all wheels during straight-line driving. Variations of more than 5% can indicate a problem. When braking, wheel speed should decrease proportionally.
2.1.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
A wheel speed sensor that reads zero while the vehicle is moving indicates a faulty sensor or a break in the wiring. Erratic or inconsistent readings can point to a damaged sensor or debris interfering with the sensor.
2.2. Brake Pressure Sensors
Brake pressure sensors measure the hydraulic pressure in the brake lines. These sensors help the ABS/ESP module determine if the driver is applying the brakes and how much braking force is being applied.
2.2.1. Typical Values and Ranges
With the brake pedal released, brake pressure should be close to zero. During moderate braking, pressure should increase to several hundred PSI (pounds per square inch). Maximum braking can result in pressures exceeding 1000 PSI.
2.2.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
Low or no brake pressure when the pedal is applied indicates a problem with the master cylinder, brake lines, or pressure sensor. Excessively high pressure can suggest a faulty ABS/ESP module or a blockage in the brake lines.
2.3. Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel. This information is used by the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction and to apply corrective braking forces if needed.
2.3.1. Typical Values and Ranges
The steering angle sensor should read zero when the steering wheel is centered. As the wheel is turned, the angle should increase proportionally in either the positive or negative direction.
2.3.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
An incorrect or erratic steering angle reading can cause the ESP system to activate unnecessarily or fail to activate when needed. This can be caused by a misaligned sensor, wiring issues, or a faulty ESP module.
2.4. Yaw Rate Sensor
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. This information is used by the ESP system to detect and correct skidding or loss of control.
2.4.1. Typical Values and Ranges
During straight-line driving, the yaw rate should be close to zero. When cornering, the yaw rate should increase proportionally to the vehicle’s speed and the sharpness of the turn.
2.4.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
A yaw rate sensor that consistently reads zero or provides erratic readings can indicate a faulty sensor or wiring issue. Incorrect yaw rate data can prevent the ESP system from functioning properly.
2.5. Lateral Acceleration Sensor
The lateral acceleration sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration. This information is used by the ESP system to detect and correct skidding or loss of control.
2.5.1. Typical Values and Ranges
During straight-line driving, lateral acceleration should be close to zero. When cornering, lateral acceleration should increase proportionally to the vehicle’s speed and the sharpness of the turn.
2.5.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
A lateral acceleration sensor that consistently reads zero or provides erratic readings can indicate a faulty sensor or wiring issue. Incorrect lateral acceleration data can prevent the ESP system from functioning properly.
3. Diagnostic Tools for Reading Live Data
Several diagnostic tools can be used to read live data from the ABS/ESP system in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools range from basic OBD-II scanners to advanced diagnostic systems.
3.1. OBD-II Scanners
Basic OBD-II scanners can read generic ABS data, such as trouble codes and some basic sensor readings. However, they may not provide access to all the live data parameters needed for thorough diagnostics.
3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Systems
Advanced diagnostic systems, such as the Autel MaxiSYS or Launch X431, offer more comprehensive coverage of ABS/ESP systems. These tools can access a wide range of live data parameters, perform actuator tests, and provide detailed diagnostic information.
3.3. Mercedes-Benz Specific Tools
Mercedes-Benz specific tools, such as the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system, provide the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. These tools are designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles and offer access to all available live data parameters and diagnostic functions. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN specializes in providing guidance and support for these advanced diagnostic systems.
4. Common ABS/ESP Problems and Their Live Data Signatures
Certain ABS/ESP problems have characteristic live data signatures that can help technicians quickly identify the issue.
4.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
A faulty wheel speed sensor will typically produce a zero reading or erratic readings while the other sensors are functioning normally. This can trigger ABS and ESP warning lights.
4.2. Brake Pressure Sensor Failure
A brake pressure sensor failure can result in low or no pressure readings when the brake pedal is applied. This can prevent the ABS system from functioning properly and may trigger a warning light.
4.3. Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction
A steering angle sensor malfunction can cause incorrect or erratic readings, leading the ESP system to activate unnecessarily or fail to activate when needed. This can result in unstable handling and may trigger a warning light.
4.4. Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
Yaw rate sensor issues can cause the ESP system to misinterpret the vehicle’s rotation, leading to incorrect corrective actions. This can result in unstable handling and may trigger a warning light.
4.5. Lateral Acceleration Sensor Problems
Lateral acceleration sensor problems can cause the ESP system to misinterpret the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, leading to incorrect corrective actions. This can result in unstable handling and may trigger a warning light.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading ABS/ESP Live Data with OBDLink
Using the OBDLink app and adapter, you can access enhanced diagnostics for many vehicle types, including Mercedes-Benz. This allows you to read and clear codes for ABS, SRS, and TPMS.
5.1. Downloading Enhanced Diagnostics
- Start your vehicle and connect your phone/tablet to your OBDLink adapter.
- Ensure your device isn’t streaming to other Bluetooth/BLE devices.
- When you connect for the first time, tap Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons in the dialog box. If you don’t see this option, your vehicle may not be supported for enhanced diagnostics. Standard OBD-II diagnostics will still be available.
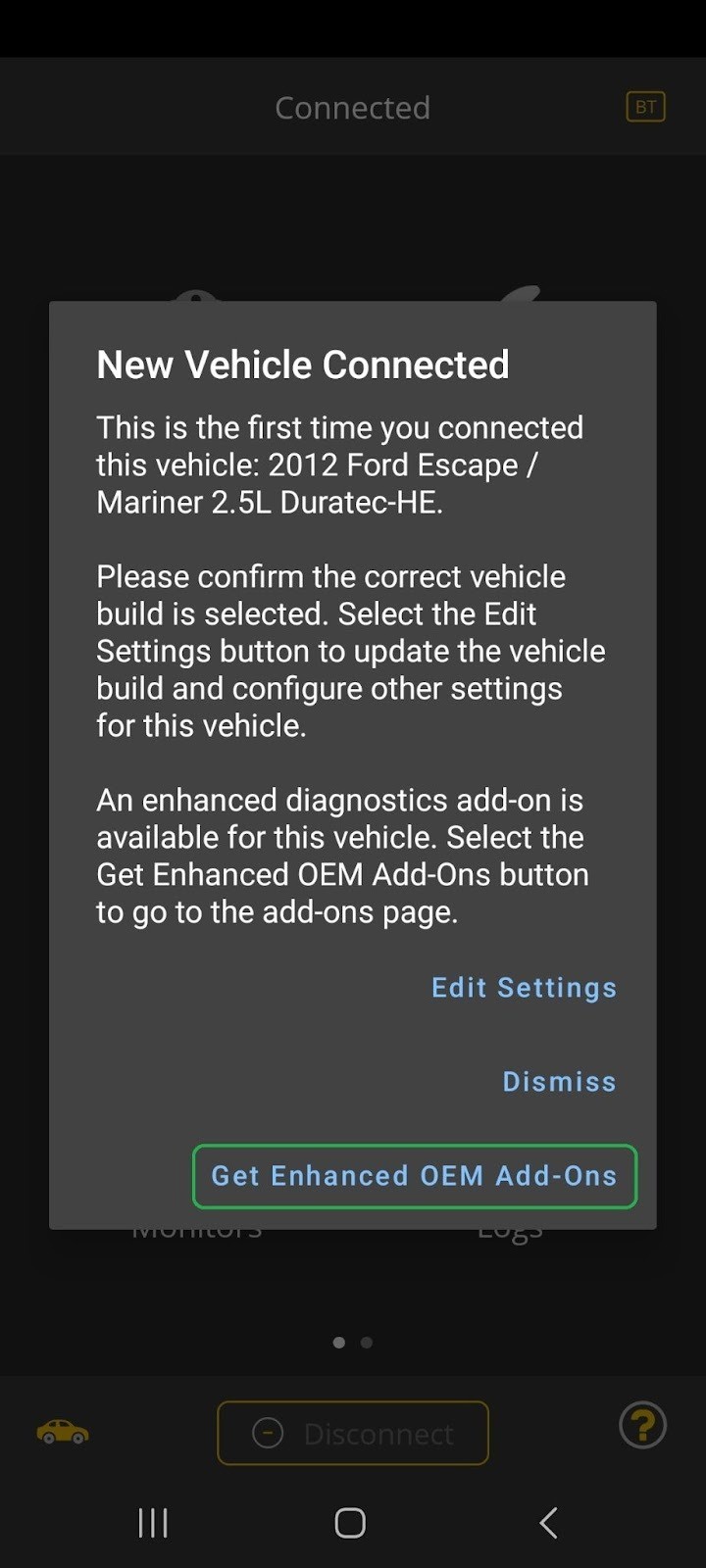 iOS screen showing a New Vehicle Connected message. The Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option is highlighted.
iOS screen showing a New Vehicle Connected message. The Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option is highlighted.
5.2. Selecting Your Vehicle Manufacturer
- If this isn’t your first time connecting, go to Settings > Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons.
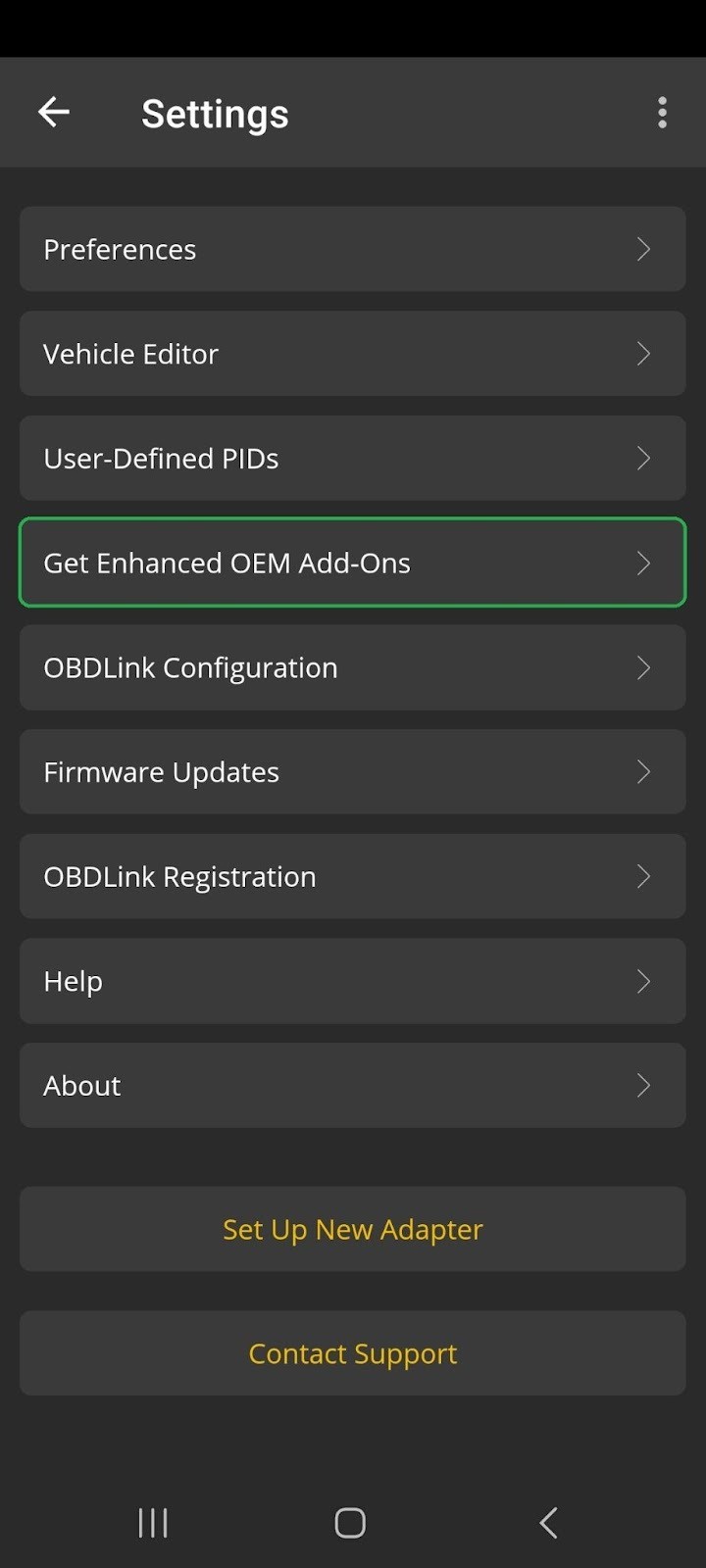 Android screenshot of the Settings menu. The Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option is highlighted.
Android screenshot of the Settings menu. The Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons option is highlighted.
- Browse the list and tap your vehicle manufacturer. Note that some add-ons are exclusive to the OBDLink MX+ adapter, including those for GM; Honda, Acura; and Hyundai, Kia.
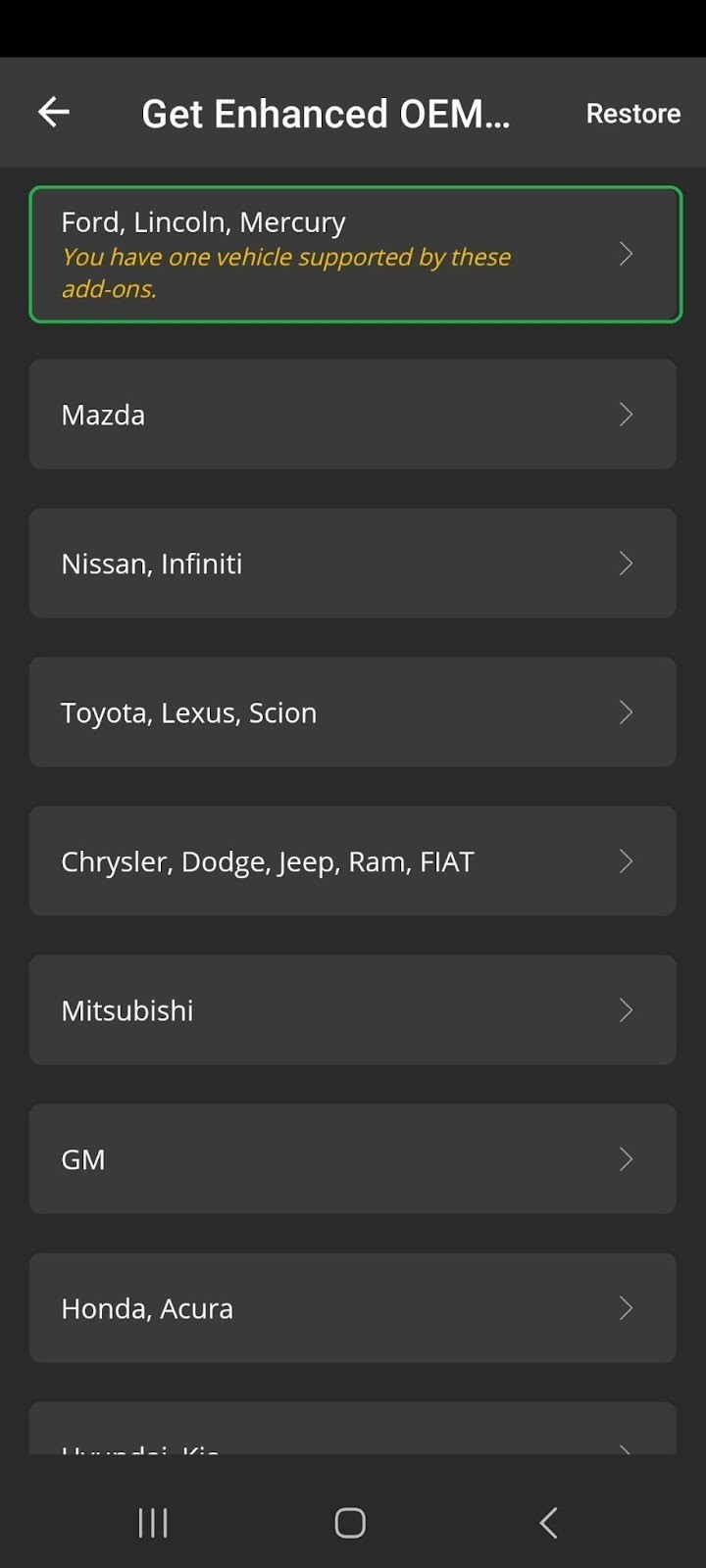 Android screen showing Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons options. The Ford, Lincoln, Mercury option is highlighted.
Android screen showing Get Enhanced OEM Add-Ons options. The Ford, Lincoln, Mercury option is highlighted.
5.3. Choosing Your Vehicle Model Year
- Browse the list and tap your vehicle’s model year.
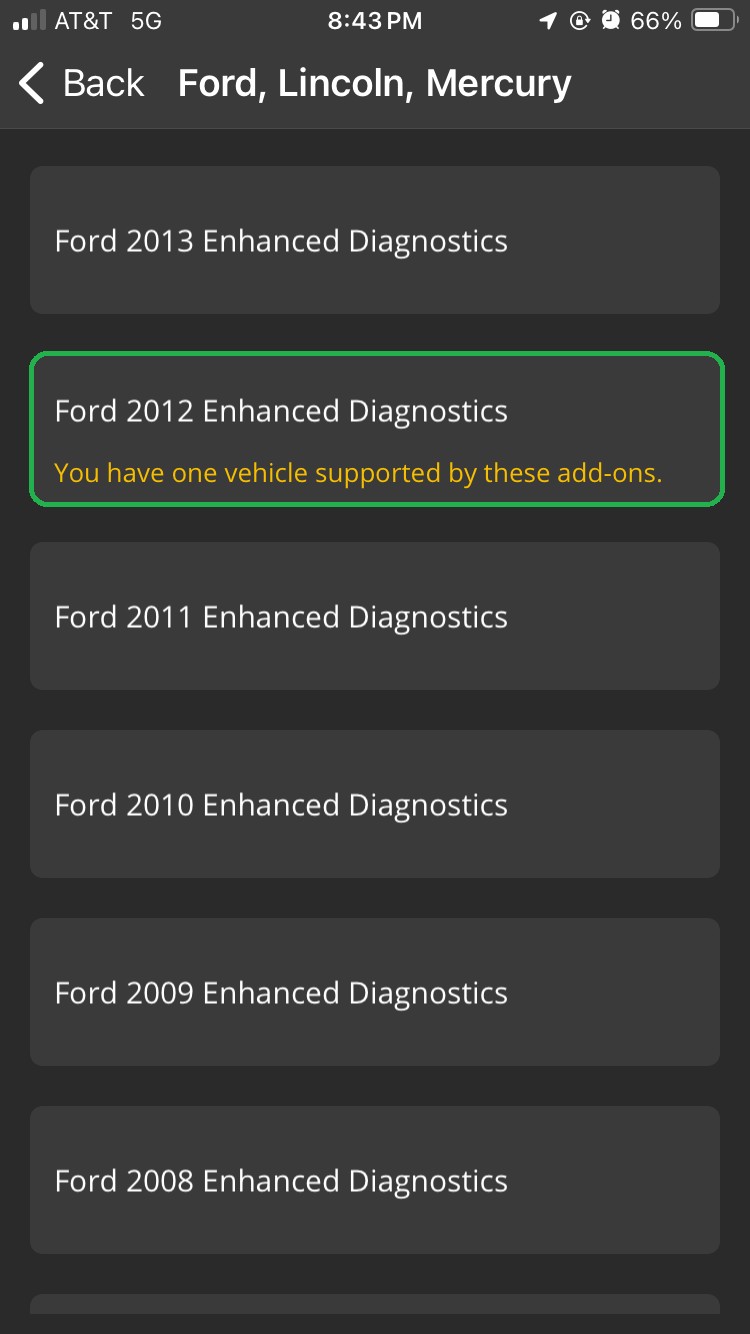 iOS screen listing Ford, Lincoln, Mercury enhanced diagnostics by model year. The Ford 2012 button is highlighted.
iOS screen listing Ford, Lincoln, Mercury enhanced diagnostics by model year. The Ford 2012 button is highlighted.
5.4. Selecting Diagnostics
- Tap Choose to select the diagnostics for your vehicle.
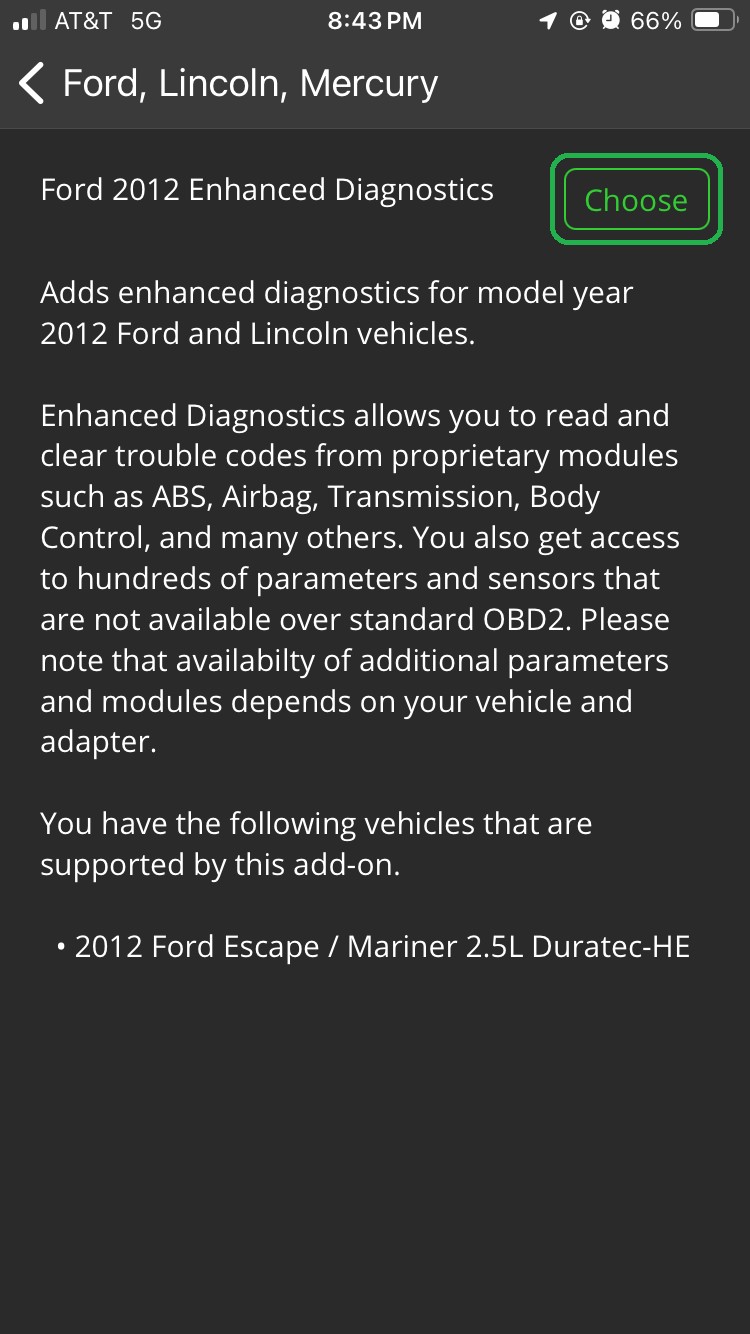 iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Choose button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Choose button is highlighted.
5.5. Downloading Diagnostics
- If prompted, tap GET FREE ADD-ON to use all your OBDLink adapter features.
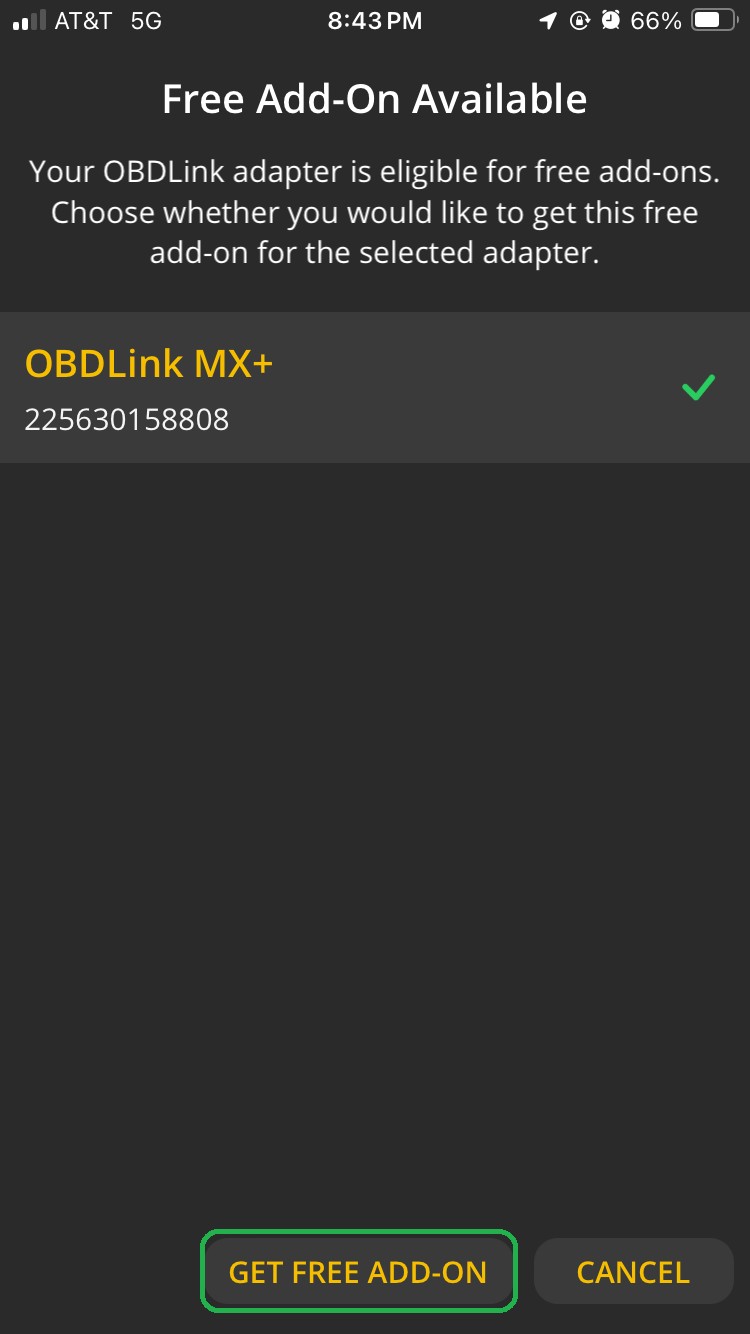 iOS screen showing Free Add-On Available message. Diagnostics information. The Get Free Add-on button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Free Add-On Available message. Diagnostics information. The Get Free Add-on button is highlighted.
- Tap Get to download diagnostics for your vehicle. This may take 1-2 minutes.
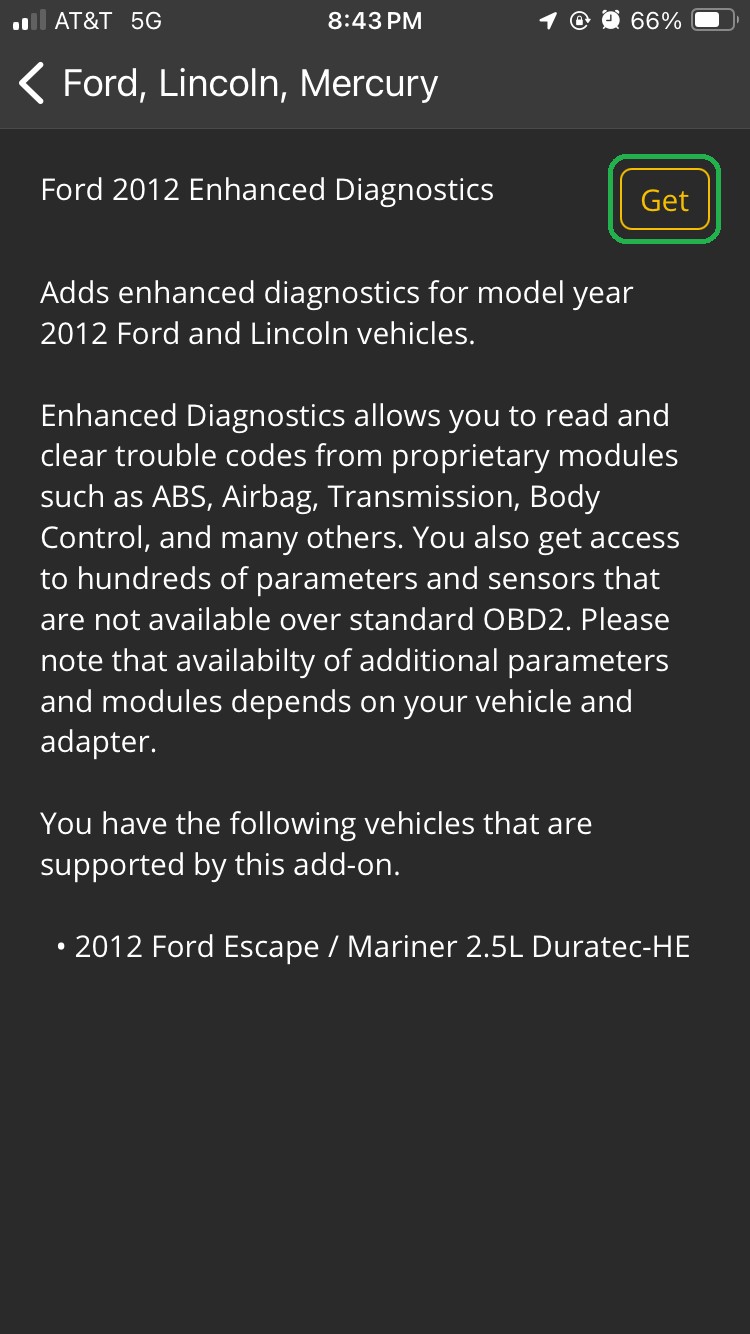 iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Get button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Get button is highlighted.
- If your adapter is connected, tap Disconnect to allow the app to continue downloading enhanced diagnostics.
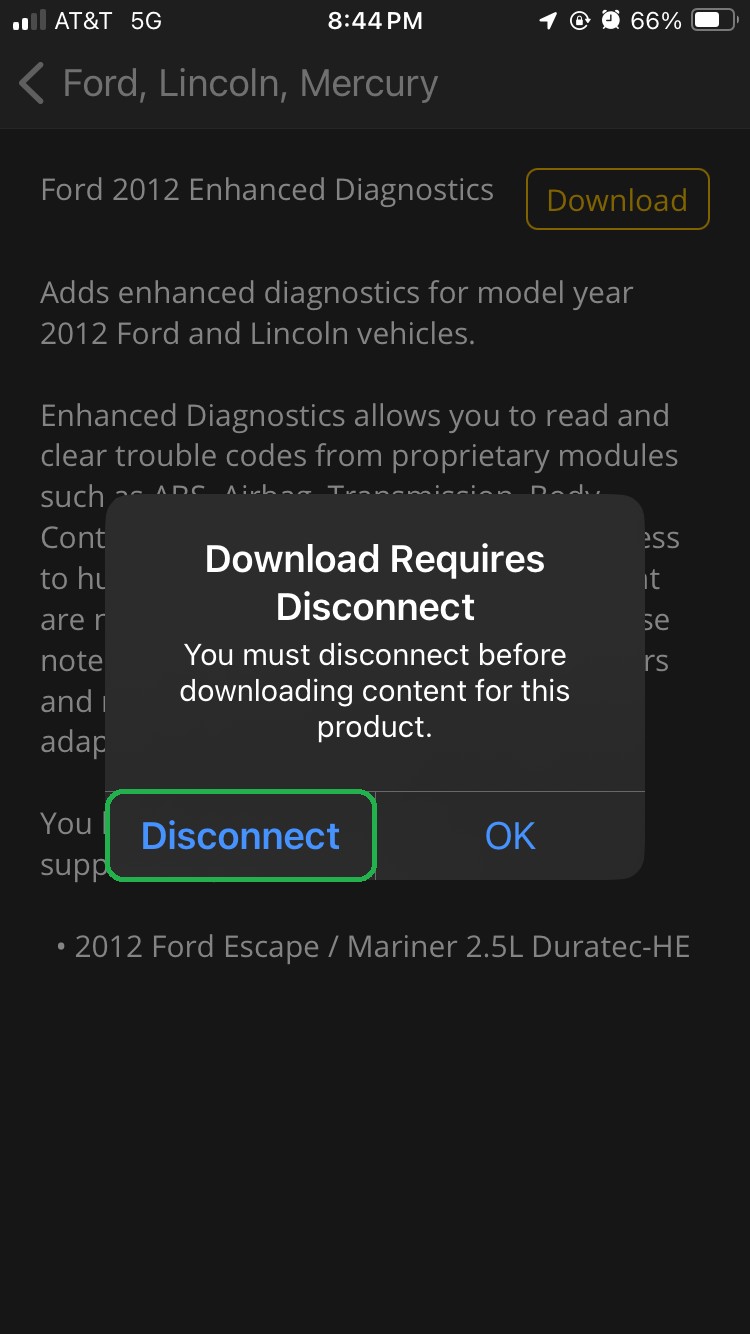 iOS screen showing Download Requires Disconnect message. The Disconnect button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Download Requires Disconnect message. The Disconnect button is highlighted.
- Once the download is complete, the diagnostics are installed. Tap the back arrow twice to return to the home screen.
 iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Installed button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Ford 2012 Enhanced Diagnostics information. The Installed button is highlighted.
5.6. Selecting Vehicle Network
This step is not required for GM, Honda, Acura, Hyundai, and Kia vehicles.
- Confirm your device is connected to the OBDLink adapter.
 iOS home screen. The Connected button is highlighted.
iOS home screen. The Connected button is highlighted.
- Select the diagnostic network that has the modules you need. It’s recommended to select Generic OBD2 for everyday use.
 iOS screen showing Enhanced Network selection options. Generic OBD2 is checked. The Connect button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing Enhanced Network selection options. Generic OBD2 is checked. The Connect button is highlighted.
- The app will scan for supported enhanced Parameter IDs (PIDs). Tap Yes to allow the scan.
 iOS screen showing a Warning message about scanning for PIDs. The Yes button is highlighted.
iOS screen showing a Warning message about scanning for PIDs. The Yes button is highlighted.
5.7. Viewing Diagnostics
- Confirm your device is connected to the OBDLink adapter and tap Diagnostics on the main screen.
 iOS home screen. The Connected button and the Diagnostics selection are highlighted.
iOS home screen. The Connected button and the Diagnostics selection are highlighted.
- Tap Yes on the warning message to continue.
 iOS Warning message about not running the engine during diagnostic testing. The Yes button is highlighted.
iOS Warning message about not running the engine during diagnostic testing. The Yes button is highlighted.
5.8. Trouble Codes
The Trouble Codes tab displays any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). If no DTCs are present, you will see a screen indicating all tests passed.
 iOS screen showing the Trouble Codes tab. There is a green checkmark indicating all tests passed.
iOS screen showing the Trouble Codes tab. There is a green checkmark indicating all tests passed.
If there are DTCs, you will see a screen with the option to Clear Codes.
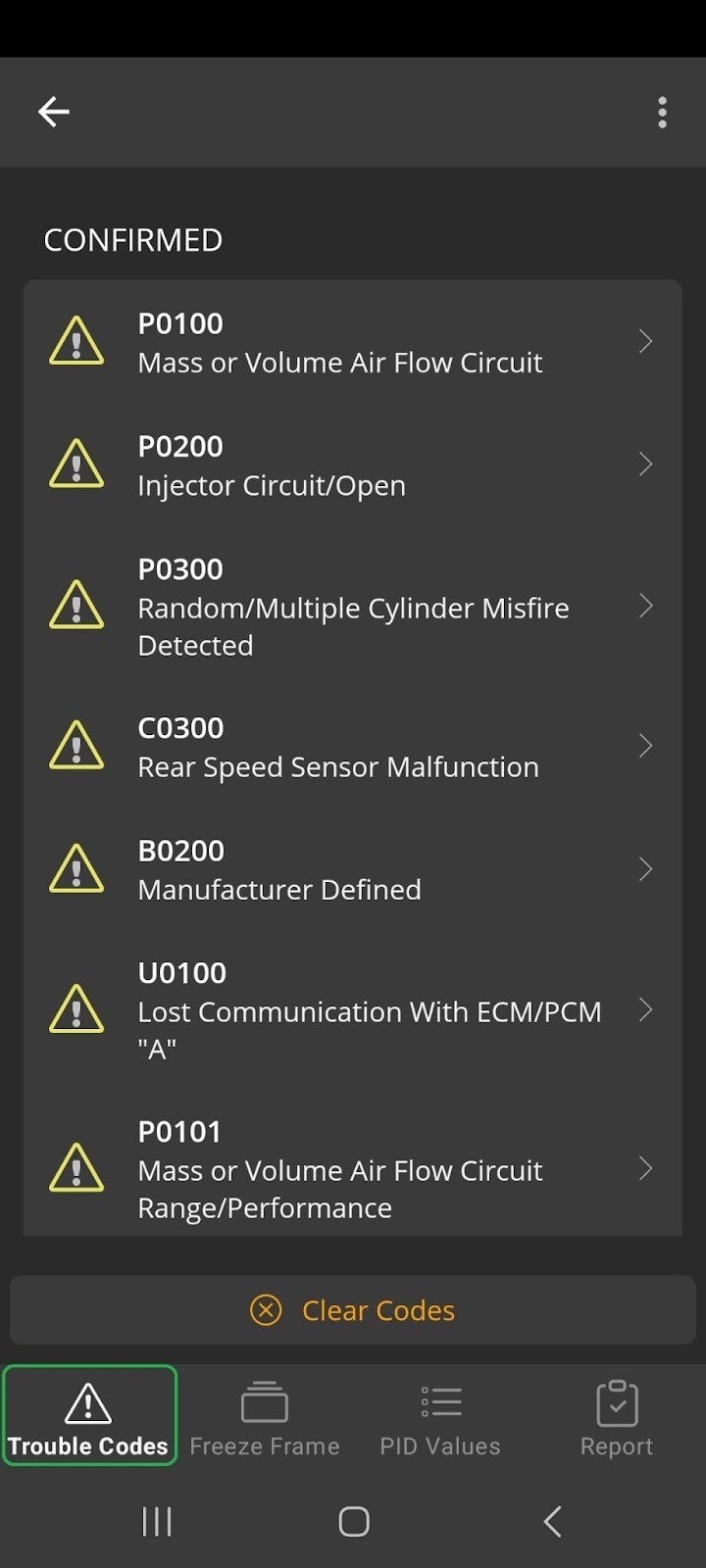 Android screen showing Trouble Codes tab when trouble codes are detected.
Android screen showing Trouble Codes tab when trouble codes are detected.
5.9. Freeze Frame
The Freeze Frame tab displays PID values captured when a DTC was generated. This data can help you understand what was happening at the time of the fault.
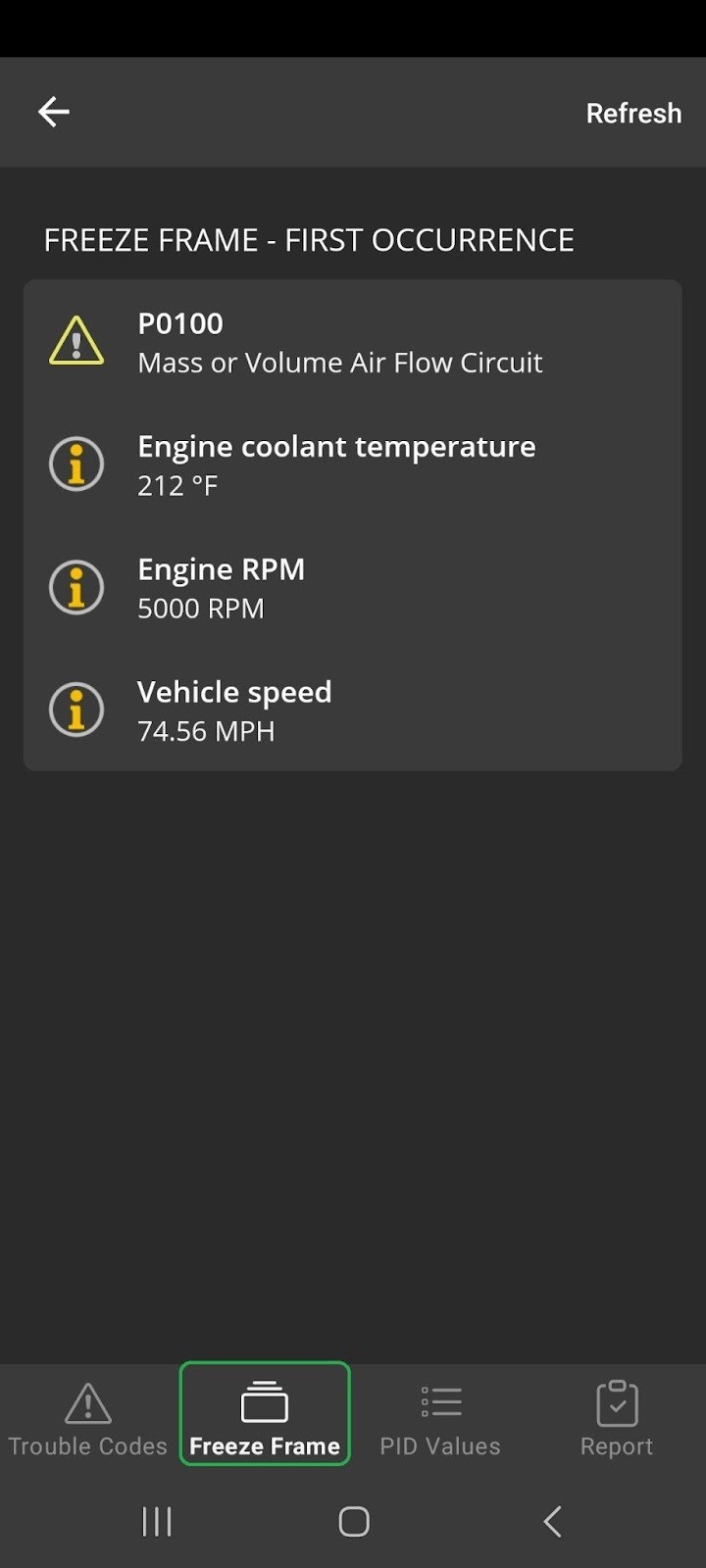 Android screen showing Freeze Frame tab.
Android screen showing Freeze Frame tab.
5.10. PID Values
The PID Values tab displays real-time data for various parameters, such as vehicle speed and engine RPM.
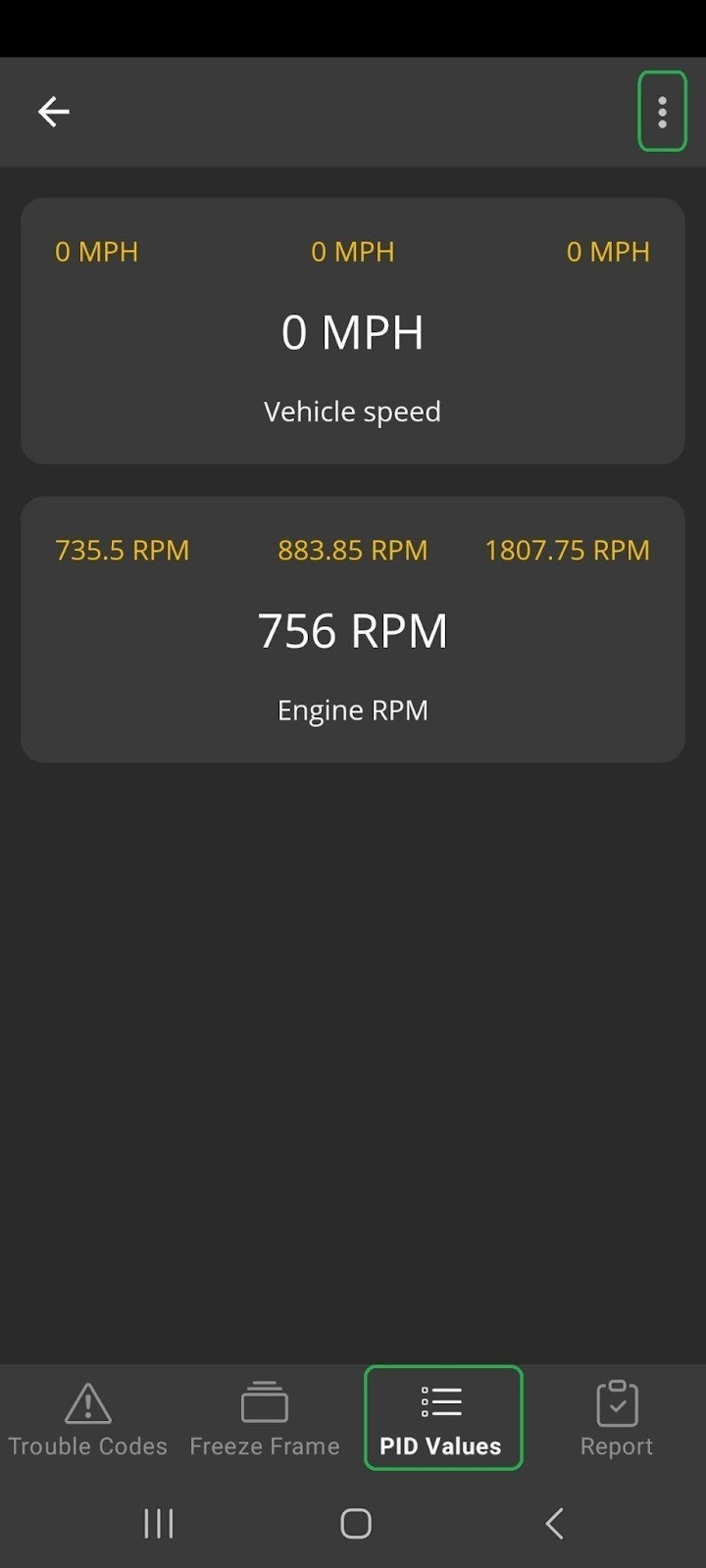 Android screen showing the PID Values tab. The menu (3 dots) button is highlighted.
Android screen showing the PID Values tab. The menu (3 dots) button is highlighted.
5.11. Report
The Report tab generates a comprehensive diagnostics report. You can refresh, store, load, and share the report.
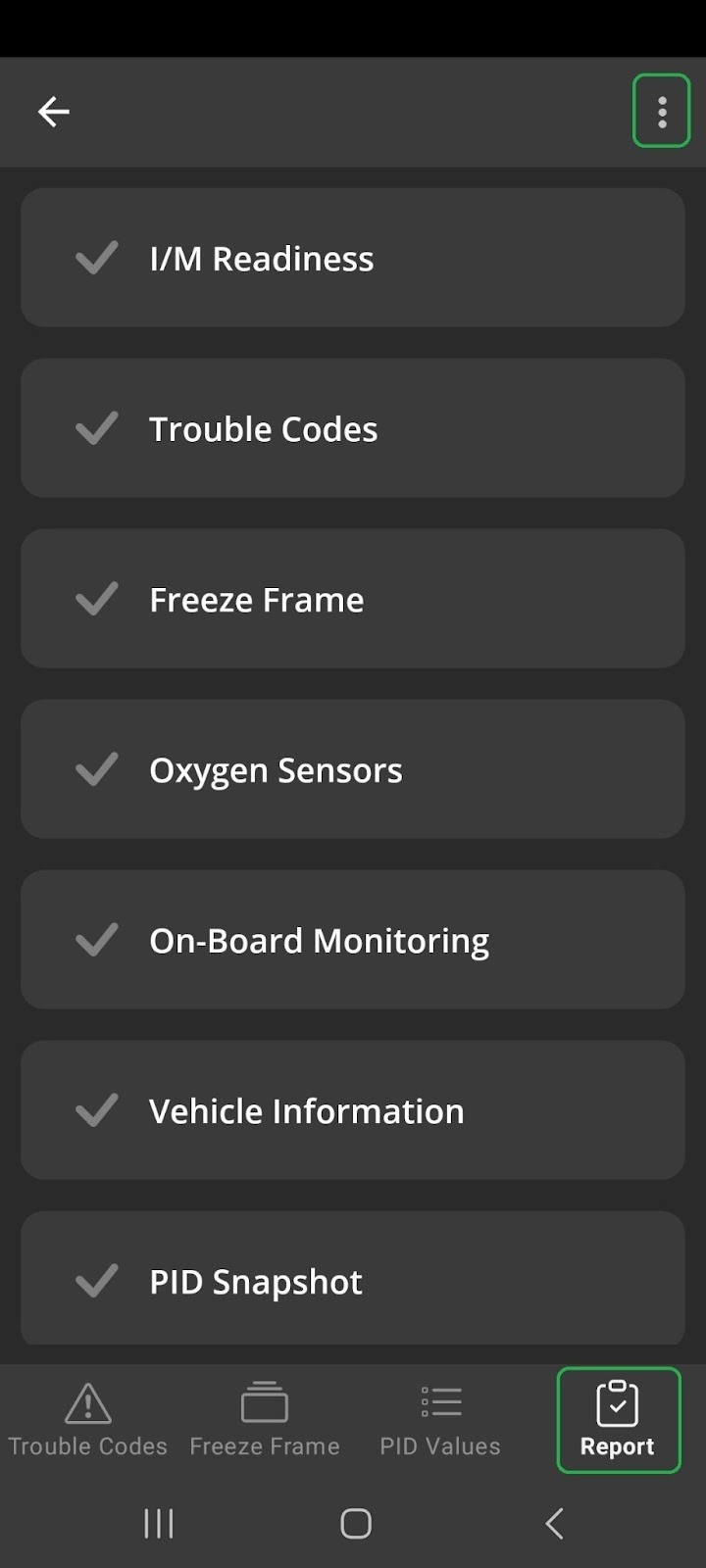 Android screen showing the Reports tab. The Disc icon and Menu button (3 vertical dots) are highlighted.
Android screen showing the Reports tab. The Disc icon and Menu button (3 vertical dots) are highlighted.
6. Practical Examples of Diagnosing ABS/ESP Issues
Consider a few practical examples of diagnosing ABS/ESP issues using live data parameters to illustrate how to effectively use this information.
6.1. Diagnosing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
A Mercedes-Benz C-Class has an ABS warning light illuminated. Using an advanced diagnostic tool, the technician observes that the front left wheel speed sensor reads zero while the vehicle is moving. All other wheel speed sensors are functioning normally. This indicates a faulty front left wheel speed sensor, which is then replaced.
6.2. Diagnosing a Brake Pressure Sensor Issue
A Mercedes-Benz E-Class has an ABS/ESP warning light illuminated. The technician uses a diagnostic tool to monitor brake pressure and finds that the pressure remains low even when the brake pedal is fully depressed. This suggests a problem with the brake pressure sensor or the master cylinder. Further inspection reveals a faulty brake pressure sensor, which is replaced.
6.3. Diagnosing a Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction
A Mercedes-Benz S-Class exhibits unstable handling and has an ESP warning light illuminated. The technician uses a diagnostic tool to monitor the steering angle sensor and finds that the readings are erratic and do not correspond to the actual steering wheel position. This indicates a faulty steering angle sensor, which is replaced and recalibrated.
7. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers extensive resources and expertise for diagnosing and repairing Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Their services include:
- Detailed diagnostic guides: Step-by-step instructions for identifying and resolving ABS/ESP issues.
- Expert support: Access to experienced technicians who can provide guidance and assistance.
- Tool recommendations: Advice on selecting the best diagnostic tools for your needs.
- Training programs: Comprehensive training programs to enhance your diagnostic skills.
By utilizing the resources available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, technicians and vehicle owners can effectively diagnose and repair ABS/ESP issues, ensuring the safety and reliability of their Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
8. Maintaining ABS/ESP Systems
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of ABS/ESP systems. This includes checking brake fluid levels, inspecting brake lines and hoses, and verifying the condition of wheel speed sensors.
8.1. Regular Inspections
Regular inspections can help identify potential problems before they lead to system failures. Check for signs of wear or damage to brake components, such as worn brake pads or leaking brake lines.
8.2. Brake Fluid Maintenance
Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, which can reduce its effectiveness and damage ABS/ESP components. It is important to flush and replace brake fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
8.3. Sensor Cleaning
Wheel speed sensors can accumulate debris, which can interfere with their readings. Cleaning the sensors regularly can help ensure accurate data and prevent ABS/ESP issues.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving ABS/ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
9.1. Case Study 1: ABS Activation During Normal Driving
A Mercedes-Benz owner reports that the ABS system activates intermittently during normal driving, even when the brakes are not being applied forcefully. Live data analysis reveals that one of the wheel speed sensors is providing erratic readings. Replacing the faulty wheel speed sensor resolves the issue.
9.2. Case Study 2: ESP Failure After Suspension Work
A Mercedes-Benz technician notes that the ESP system is not functioning properly after performing suspension work on a vehicle. Live data analysis reveals that the steering angle sensor is not properly calibrated. Recalibrating the steering angle sensor restores the ESP system to normal operation.
9.3. Case Study 3: Brake Pedal Vibration
A Mercedes-Benz driver experiences excessive vibration in the brake pedal during ABS activation. Live data analysis reveals that the ABS pump is malfunctioning. Replacing the ABS pump resolves the issue.
10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Beyond basic live data analysis, advanced diagnostic techniques can provide additional insights into ABS/ESP system performance.
10.1. Actuator Testing
Actuator testing involves using a diagnostic tool to activate individual ABS/ESP components, such as the ABS pump and solenoids. This can help identify malfunctioning components and verify system functionality.
10.2. Component Testing
Component testing involves using a multimeter or oscilloscope to test individual ABS/ESP components. This can help identify faulty sensors, wiring issues, and other problems.
10.3. Signal Analysis
Signal analysis involves using an oscilloscope to examine the signals from ABS/ESP sensors. This can help identify subtle issues, such as signal noise or intermittent dropouts, that may not be apparent from live data readings.
11. Potential Risks of Incorrect Diagnoses
Misdiagnosing ABS/ESP issues can lead to unnecessary repairs, increased costs, and potential safety hazards.
11.1. Unnecessary Repairs
Incorrect diagnoses can result in the replacement of functioning components, wasting time and money.
11.2. Increased Costs
Misdiagnoses can lead to a cycle of trial-and-error repairs, resulting in increased labor and parts costs.
11.3. Safety Hazards
Misdiagnosing ABS/ESP issues can leave the vehicle with impaired braking and stability, increasing the risk of accidents.
12. FAQ: Common Questions About ABS/ESP Live Data
Here are some frequently asked questions about ABS/ESP live data parameters in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
12.1. What is ABS?
ABS stands for Anti-lock Braking System. It prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
12.2. What is ESP?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It helps maintain directional control by detecting and reducing skids.
12.3. How do wheel speed sensors work?
Wheel speed sensors measure the rotational speed of each wheel using magnetic or Hall effect principles.
12.4. What is a steering angle sensor?
A steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel, providing data to the ESP system.
12.5. What is yaw rate?
Yaw rate is the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, measured by the yaw rate sensor.
12.6. What is lateral acceleration?
Lateral acceleration is the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, measured by the lateral acceleration sensor.
12.7. How can I read ABS/ESP live data?
You can read ABS/ESP live data using an OBD-II scanner or an advanced diagnostic tool.
12.8. What are typical wheel speed sensor values?
Typical wheel speed sensor values should be consistent across all wheels during straight-line driving.
12.9. What are typical brake pressure sensor values?
Typical brake pressure sensor values should be close to zero with the brake pedal released and increase proportionally when the pedal is applied.
12.10. Where can I find more information about ABS/ESP systems?
You can find more information about ABS/ESP systems at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, which offers expert guidance and resources.
13. Staying Updated with the Latest Information
The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, so it is important to stay updated with the latest information and techniques.
13.1. Training Programs
Consider attending training programs offered by reputable organizations to enhance your diagnostic skills.
13.2. Online Resources
Utilize online resources, such as forums and technical websites, to stay informed about the latest diagnostic techniques and best practices.
13.3. Vendor Updates
Stay informed about updates and new features for your diagnostic tools by subscribing to vendor newsletters and attending product demonstrations.
14. The Future of ABS/ESP Diagnostics
The future of ABS/ESP diagnostics will likely involve more advanced sensors, more sophisticated control algorithms, and more comprehensive diagnostic tools.
14.1. Advanced Sensors
Future ABS/ESP systems may incorporate more advanced sensors, such as radar and lidar, to provide even more accurate data about the vehicle’s surroundings.
14.2. Sophisticated Control Algorithms
Future ABS/ESP systems may use more sophisticated control algorithms to provide even more precise and effective braking and stability control.
14.3. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
Future diagnostic tools may offer even more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, such as the ability to simulate driving conditions and predict potential problems.
15. Conclusion: Mastering ABS/ESP Live Data for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mastering ABS/ESP live data parameters is essential for accurately diagnosing and repairing these critical safety systems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. By understanding the typical values and ranges of key parameters, recognizing common problem signatures, and utilizing advanced diagnostic techniques, technicians and vehicle owners can ensure the safety and reliability of their vehicles.
For expert guidance, comprehensive diagnostic tools, and detailed resources, turn to MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a Mercedes-Benz enthusiast, their expertise will help you navigate the complexities of ABS/ESP systems and keep your vehicle performing at its best.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us today for expert guidance on selecting the right diagnostic tools, understanding ABS/ESP live data, and ensuring optimal vehicle performance. Reach out to MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.