What Are Typical Live Data Values For Mercedes Steering Wheel Control Button Parameters? Understanding these values is crucial for diagnosing issues with your Mercedes-Benz. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive insights and diagnostic tools to help you interpret live data effectively. By knowing what’s normal, you can quickly pinpoint problems, ensuring a smoother and safer driving experience. Accessing this information can help ensure optimal system performance and driver safety.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Steering Wheel Control Button Parameters in Mercedes-Benz
- 1.1 What Parameters Are Monitored?
- 1.2 Why Monitor These Parameters?
- 2. Typical Live Data Values for Steering Wheel Control Buttons
- 2.1 Button State Values
- 2.2 Resistance Values
- 2.3 Voltage Levels
- 2.4 Communication Signals (CAN Bus)
- 3. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 3.1 Non-Responsive Buttons
- 3.2 Intermittent Functionality
- 3.3 Multiple Buttons Failing Simultaneously
- 4. Using Diagnostic Tools for Analysis
- 4.1 OBD-II Scanners
- 4.2 Multimeters
- 4.3 Advanced Diagnostic Software
- 4.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Diagnostic Tool
- 5. Case Studies
- 5.1 Case Study 1: Non-Responsive Audio Controls
- 5.2 Case Study 2: Intermittent Cruise Control
- 5.3 Case Study 3: Multiple Button Failures
- 6. Preventive Maintenance
- 6.1 Regular Inspections
- 6.2 Cleaning
- 6.3 Wiring Checks
- 6.4 Software Updates
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 7.1 CAN Bus Analysis
- 7.2 Oscilloscope Testing
- 7.3 Component-Level Testing
- 8. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Assistance
- 8.1 Diagnostic Tools
- 8.2 Detailed Guides
- 8.3 Expert Support
- 8.4 Community Forum
- 9. Practical Tips for Accurate Readings
- 9.1 Use High-Quality Equipment
- 9.2 Ensure Proper Connections
- 9.3 Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
- 9.4 Double-Check Readings
- 10. The Future of Steering Wheel Controls
- 10.1 Touch-Sensitive Controls
- 10.2 Voice Recognition
- 10.3 Haptic Feedback
- 10.4 Integration with ADAS
- 11. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 11.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Solutions
- 11.2 Expert Knowledge and Support
- 11.3 Community Support
- 12. FAQ Section
- 13. Call to Action
1. Understanding Steering Wheel Control Button Parameters in Mercedes-Benz
Steering wheel control buttons in Mercedes-Benz vehicles allow drivers to conveniently manage various functions without taking their hands off the wheel. These functions typically include audio control, phone operation, cruise control, and access to vehicle settings. Understanding the parameters associated with these buttons is crucial for diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal functionality.
1.1 What Parameters Are Monitored?
Several parameters are monitored to ensure the proper functioning of the steering wheel control buttons. These include:
- Button State: Indicates whether a button is pressed or released.
- Resistance Values: Each button press may correspond to a specific resistance value, which the vehicle’s control unit interprets.
- Voltage Levels: Changes in voltage levels signal button activation.
- Communication Signals: Data transmitted via the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus to the central control unit.
1.2 Why Monitor These Parameters?
Monitoring these parameters helps in diagnosing issues such as:
- Non-Responsive Buttons: When buttons fail to perform their intended functions.
- Intermittent Functionality: When buttons work sporadically.
- Faulty Wiring: Issues in the wiring harness connecting the buttons to the control unit.
- Control Unit Malfunctions: Problems within the central control unit that processes button inputs.
2. Typical Live Data Values for Steering Wheel Control Buttons
Typical live data values for Mercedes steering wheel control buttons can vary based on the specific model and year. However, certain ranges and patterns are generally observed.
2.1 Button State Values
- Inactive/Released: Typically shows a value of 0 or a low voltage level (e.g., 0V to 0.5V).
- Active/Pressed: Shows a value of 1 or a higher voltage level (e.g., 3V to 5V).
2.2 Resistance Values
Each button may have a unique resistance value when pressed. These values are usually within a specific range, such as:
- Button 1: 500 ohms
- Button 2: 1000 ohms
- Button 3: 1500 ohms
- Button 4: 2000 ohms
These values are interpreted by the control unit to determine which button has been pressed. According to a study by Bosch, resistance-based systems are common in automotive control interfaces due to their reliability and ease of implementation.
2.3 Voltage Levels
Voltage levels also vary depending on the button being pressed. Common ranges include:
- Inactive: 0V to 0.5V
- Active Button 1: 1V
- Active Button 2: 2V
- Active Button 3: 3V
- Active Button 4: 4V
These voltage levels are read by the vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit) to execute the corresponding functions.
2.4 Communication Signals (CAN Bus)
Data transmitted via the CAN bus is critical for the overall system. Typical values include:
- Message ID: A unique identifier for the steering wheel control message.
- Data Bytes: Represent the button state, resistance, or voltage values in a digital format.
Analyzing these signals requires specialized tools and knowledge of the CAN bus protocol used by Mercedes-Benz.
3. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Several common issues can arise with Mercedes steering wheel control buttons. Understanding these issues and how to troubleshoot them can save time and money.
3.1 Non-Responsive Buttons
When buttons fail to respond, consider the following steps:
- Check Fuses: Ensure that the fuse associated with the steering wheel controls is intact.
- Scan for DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the steering wheel controls. The MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN diagnostic tool can be invaluable here.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any signs of damage or corrosion in the wiring harness connecting the buttons to the control unit.
- Test Button Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance values of each button when pressed. Compare these values to the expected ranges.
- Check Control Unit: If the above steps don’t reveal the issue, the control unit itself may be faulty.
3.2 Intermittent Functionality
Intermittent issues can be more challenging to diagnose. Common causes include:
- Loose Connections: Check for loose or corroded connections in the wiring harness.
- Faulty Buttons: The buttons themselves may be failing. Testing their resistance and voltage output can help identify faulty ones.
- Software Glitches: In some cases, a software update may be required to resolve intermittent issues.
3.3 Multiple Buttons Failing Simultaneously
If multiple buttons fail simultaneously, the issue is likely related to:
- Common Ground: A problem with the common ground connection for the buttons.
- Control Unit: A failure within the central control unit.
- CAN Bus Issues: Problems with the CAN bus communication.
4. Using Diagnostic Tools for Analysis
Diagnostic tools are essential for accurately analyzing steering wheel control button parameters.
4.1 OBD-II Scanners
An OBD-II scanner can read DTCs related to the steering wheel controls. This can provide valuable insights into the nature of the problem.
4.2 Multimeters
A multimeter is used to measure resistance and voltage values. This helps in verifying the functionality of individual buttons and the integrity of the wiring.
4.3 Advanced Diagnostic Software
Advanced diagnostic software, such as that offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, can provide detailed live data and diagnostic capabilities specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles. This includes:
- Real-time Monitoring: Viewing live data values for button states, resistance, and voltage.
- CAN Bus Analysis: Decoding CAN bus messages to identify communication issues.
- Component Testing: Performing specific tests on the steering wheel control buttons and related components.
4.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Diagnostic Tool
- Connect the Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the OBD-II port of your Mercedes-Benz.
- Power On: Turn on the ignition but do not start the engine.
- Select Vehicle: Choose your vehicle’s make, model, and year in the diagnostic tool’s menu.
- Access Live Data: Navigate to the live data section and select the parameters related to the steering wheel controls.
- Monitor Values: Observe the values as you press each button. Look for any discrepancies or out-of-range values.
- Record Data: Record the data for further analysis and comparison.
5. Case Studies
Examining real-world case studies can provide practical insights into diagnosing and resolving steering wheel control button issues.
5.1 Case Study 1: Non-Responsive Audio Controls
- Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz C-Class
- Issue: Audio control buttons on the steering wheel were non-responsive.
- Diagnosis:
- Scanned for DTCs using an OBD-II scanner – no relevant codes found.
- Checked the fuse for the audio system – fuse was intact.
- Used a multimeter to test the resistance values of the audio control buttons – values were out of range.
- Resolution: Replaced the faulty audio control button assembly.
5.2 Case Study 2: Intermittent Cruise Control
- Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz E-Class
- Issue: Cruise control buttons would work intermittently.
- Diagnosis:
- Scanned for DTCs – code related to CAN bus communication.
- Inspected the wiring harness – found a loose connection.
- Used advanced diagnostic software to monitor CAN bus messages – confirmed intermittent communication issues.
- Resolution: Cleaned and tightened the loose connection in the wiring harness.
5.3 Case Study 3: Multiple Button Failures
- Vehicle: 2020 Mercedes-Benz S-Class
- Issue: Several steering wheel buttons failed simultaneously.
- Diagnosis:
- Scanned for DTCs – multiple codes related to control unit communication.
- Checked the common ground connection – found it to be corroded.
- Tested the control unit – determined it was faulty.
- Resolution: Replaced the corroded ground connection and the faulty control unit.
6. Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance can help avoid common issues with steering wheel control buttons.
6.1 Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect the steering wheel control buttons and wiring for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
6.2 Cleaning
Keep the buttons clean and free of dirt and debris. Use a soft cloth and mild cleaning solution to gently wipe the buttons.
6.3 Wiring Checks
Periodically check the wiring harness for loose connections or damage. Ensure that all connections are secure and properly insulated.
6.4 Software Updates
Keep the vehicle’s software up to date. Software updates can resolve known issues and improve the overall performance of the steering wheel controls.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For complex issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be required.
7.1 CAN Bus Analysis
Analyzing CAN bus messages can provide detailed insights into communication issues. This requires specialized tools and knowledge of the CAN bus protocol used by Mercedes-Benz.
7.2 Oscilloscope Testing
An oscilloscope can be used to measure voltage signals and identify any anomalies in the electrical signals.
7.3 Component-Level Testing
Component-level testing involves testing individual components, such as resistors and capacitors, to identify faulty parts.
8. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Assistance
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of resources and tools to help diagnose and resolve steering wheel control button issues.
8.1 Diagnostic Tools
Access to advanced diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
8.2 Detailed Guides
Step-by-step guides and tutorials on diagnosing and troubleshooting steering wheel control button issues.
8.3 Expert Support
Access to expert support from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians.
8.4 Community Forum
A community forum where users can share their experiences, ask questions, and get advice from other Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians.
9. Practical Tips for Accurate Readings
To ensure accurate live data readings, consider the following tips:
9.1 Use High-Quality Equipment
Using high-quality diagnostic tools and multimeters ensures accurate and reliable readings.
9.2 Ensure Proper Connections
Make sure that all connections are secure and properly grounded.
9.3 Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for testing and diagnosing steering wheel control button issues.
9.4 Double-Check Readings
Double-check all readings to ensure accuracy. If possible, compare the readings to known good values.
10. The Future of Steering Wheel Controls
The future of steering wheel controls is likely to involve more advanced features and technologies.
10.1 Touch-Sensitive Controls
Touch-sensitive controls are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. These controls offer a sleek and modern look but can also be more challenging to diagnose and repair.
10.2 Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology is also being integrated into steering wheel controls. This allows drivers to control various functions using voice commands.
10.3 Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback provides tactile feedback to the driver, confirming that a button has been pressed.
10.4 Integration with ADAS
Steering wheel controls are increasingly being integrated with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). This allows drivers to control ADAS features, such as adaptive cruise control and lane departure warning, using the steering wheel controls.
11. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
Choosing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN ensures access to expert knowledge, specialized tools, and comprehensive support for diagnosing and resolving steering wheel control button issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. With detailed guides, advanced diagnostic software, and a supportive community, users can confidently tackle complex problems and maintain the optimal performance of their vehicles.
11.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Solutions
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive diagnostic solutions tailored specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. This includes advanced diagnostic tools, detailed guides, and expert support.
11.2 Expert Knowledge and Support
Access to expert knowledge and support from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians ensures that users can get the help they need to resolve complex issues.
11.3 Community Support
A supportive community forum allows users to share their experiences, ask questions, and get advice from other Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians.
12. FAQ Section
Q1: What are the typical live data values for Mercedes steering wheel control button parameters?
A1: Typical values vary, but button state is usually 0V when inactive and 3-5V when active. Resistance values differ for each button, typically ranging from 500 to 2000 ohms. CAN bus signals have specific message IDs and data bytes representing button status.
Q2: How can I diagnose non-responsive steering wheel buttons?
A2: First, check the fuses. Next, scan for DTCs using an OBD-II scanner. Inspect the wiring for damage and test the button resistance with a multimeter. If issues persist, the control unit may be faulty.
Q3: What diagnostic tools do I need to analyze steering wheel control button parameters?
A3: You’ll need an OBD-II scanner for DTCs, a multimeter for resistance and voltage checks, and advanced diagnostic software for live data and CAN bus analysis.
Q4: How often should I perform preventive maintenance on my steering wheel controls?
A4: Regular inspections should be done every 6 months, including cleaning and wiring checks. Software updates should be performed as they become available.
Q5: What does intermittent functionality of steering wheel buttons indicate?
A5: It often points to loose connections, faulty buttons, or software glitches. Check wiring connections, test button resistance, and consider a software update.
Q6: Can multiple button failures indicate a serious problem?
A6: Yes, it often suggests a problem with the common ground, a faulty control unit, or issues with the CAN bus communication.
Q7: What role does CAN bus analysis play in diagnosing steering wheel control issues?
A7: CAN bus analysis helps in identifying communication problems between the steering wheel controls and the vehicle’s control unit, providing insights into data transmission issues.
Q8: How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN assist in diagnosing steering wheel control problems?
A8: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers advanced diagnostic tools, detailed guides, expert support, and a community forum to help diagnose and resolve issues effectively.
Q9: What are some advanced diagnostic techniques for complex steering wheel control issues?
A9: Advanced techniques include CAN bus analysis, oscilloscope testing to measure voltage signals, and component-level testing to identify faulty parts.
Q10: What future technologies are being integrated into steering wheel controls?
A10: Future technologies include touch-sensitive controls, voice recognition, haptic feedback, and integration with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS).
13. Call to Action
Are you experiencing issues with your Mercedes-Benz steering wheel control buttons? Don’t let these problems compromise your driving experience. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance.
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let us help you diagnose and resolve your steering wheel control button issues with our advanced diagnostic tools, detailed guides, and expert support. Contact us now for a consultation and ensure your Mercedes-Benz performs at its best.
 Mercedes-Benz Enhanced Diagnostics
Mercedes-Benz Enhanced Diagnostics
 Mercedes-Benz Settings Menu
Mercedes-Benz Settings Menu
 Mercedes-Benz Enhanced OEM Add-Ons
Mercedes-Benz Enhanced OEM Add-Ons
 Mercedes-Benz Model Year Selection
Mercedes-Benz Model Year Selection
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Selection
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Selection
 Mercedes-Benz Free Add-On
Mercedes-Benz Free Add-On
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Download
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Download
 Mercedes-Benz Disconnect Message
Mercedes-Benz Disconnect Message
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Installed
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Installed
 Mercedes-Benz Adapter Connection
Mercedes-Benz Adapter Connection
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Network Selection
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Network Selection
 Mercedes-Benz PID Scanning Warning
Mercedes-Benz PID Scanning Warning
 Mercedes-Benz PID Scanning
Mercedes-Benz PID Scanning
 Mercedes-Benz Vehicle Editor
Mercedes-Benz Vehicle Editor
 Mercedes-Benz Enhanced Network Selection
Mercedes-Benz Enhanced Network Selection
 Mercedes-Benz Generic OBD2 Option
Mercedes-Benz Generic OBD2 Option
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Selection Main Screen
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Selection Main Screen
 Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Testing Warning
Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Testing Warning
 Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Pass
Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Pass
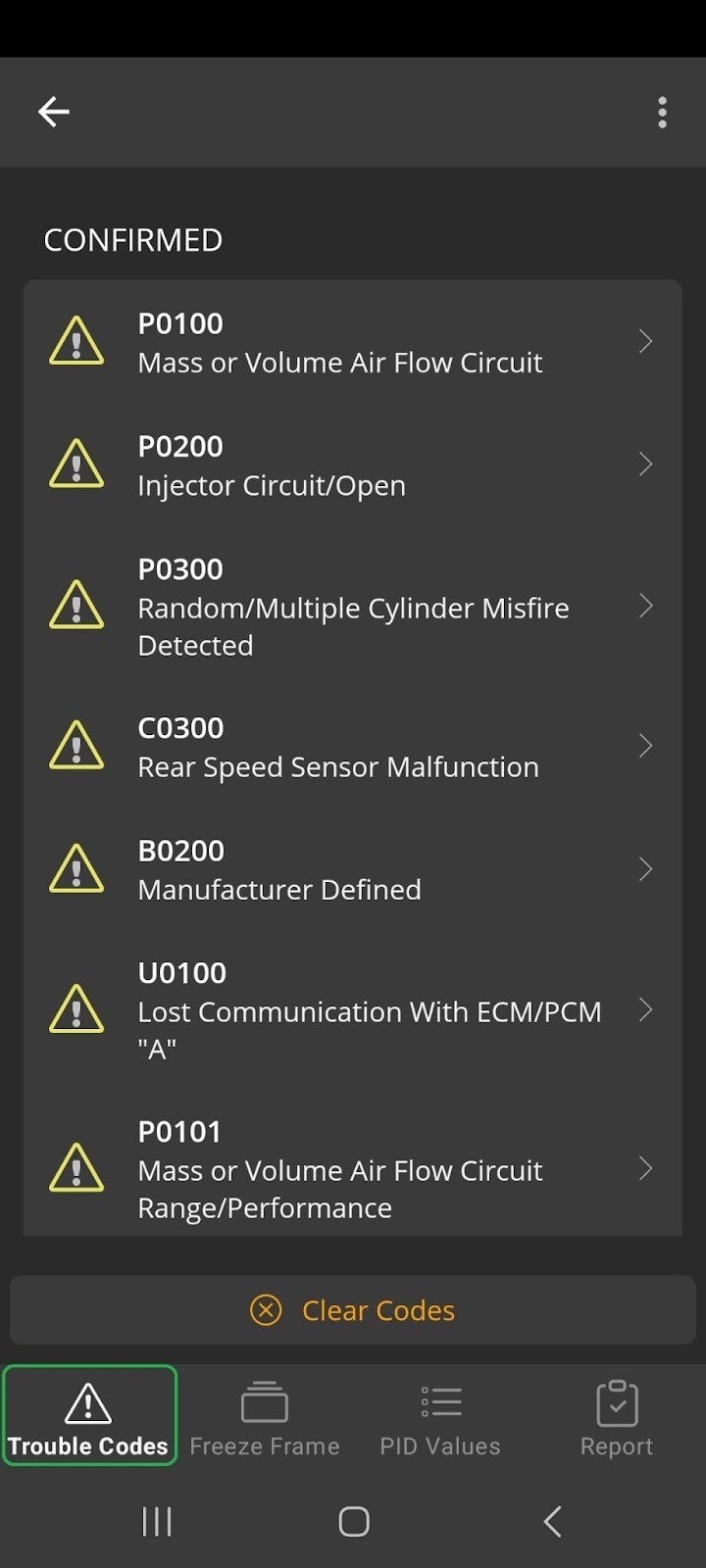 Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Detected
Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Detected
 Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Menu
Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Menu
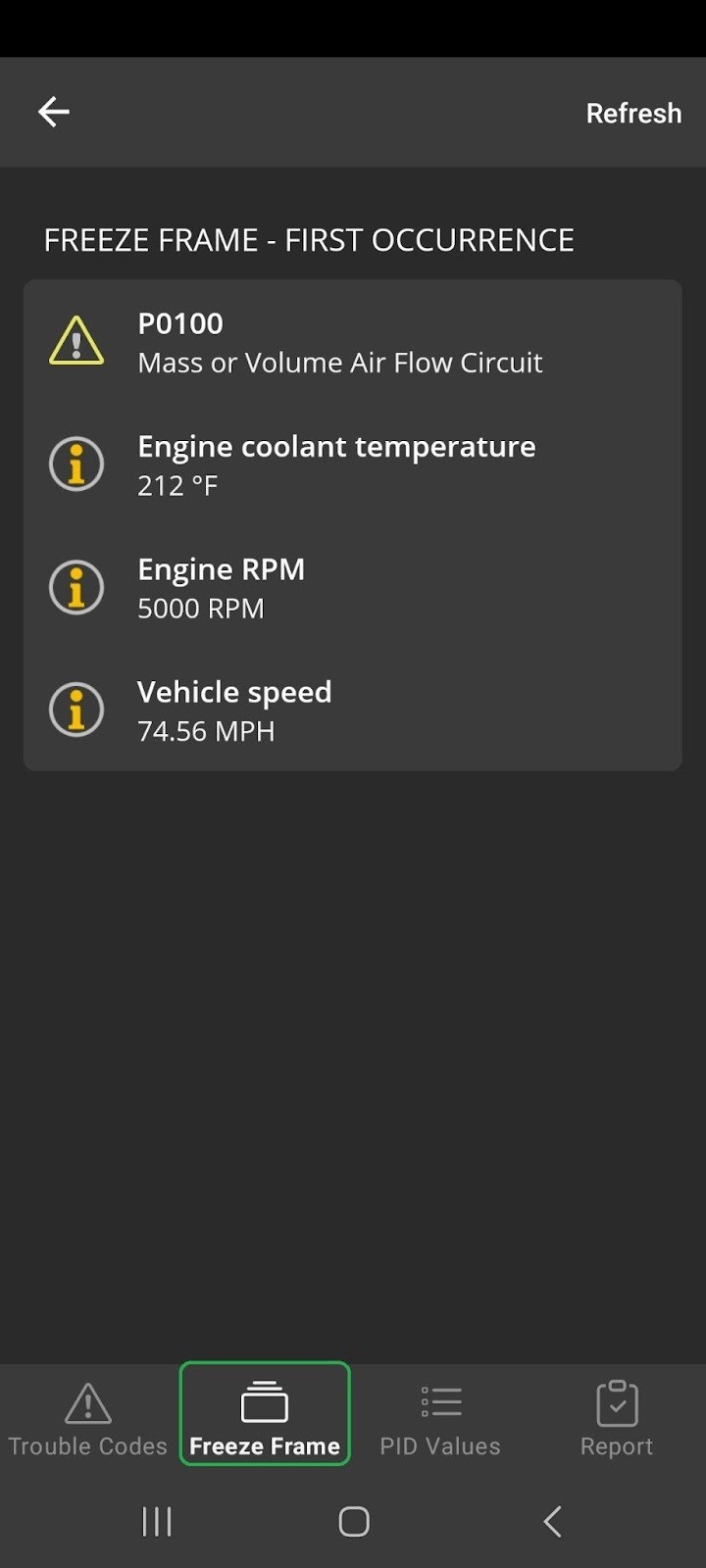 Mercedes-Benz Freeze Frame Data
Mercedes-Benz Freeze Frame Data
 Mercedes-Benz PID Values Menu
Mercedes-Benz PID Values Menu
 Mercedes-Benz PID Values Options
Mercedes-Benz PID Values Options
 Mercedes-Benz Reports Menu
Mercedes-Benz Reports Menu
 Mercedes-Benz Report Options
Mercedes-Benz Report Options
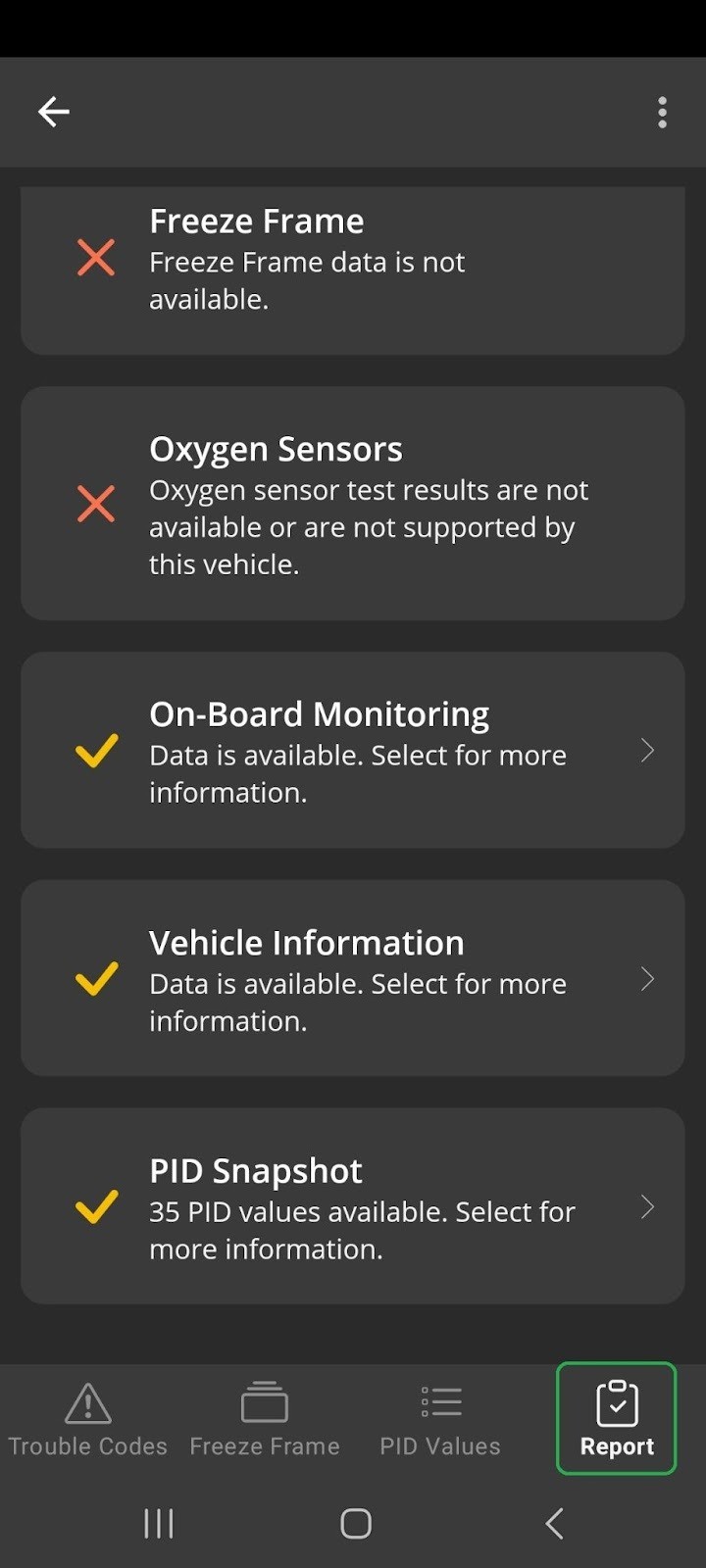 Mercedes-Benz Report Loading
Mercedes-Benz Report Loading
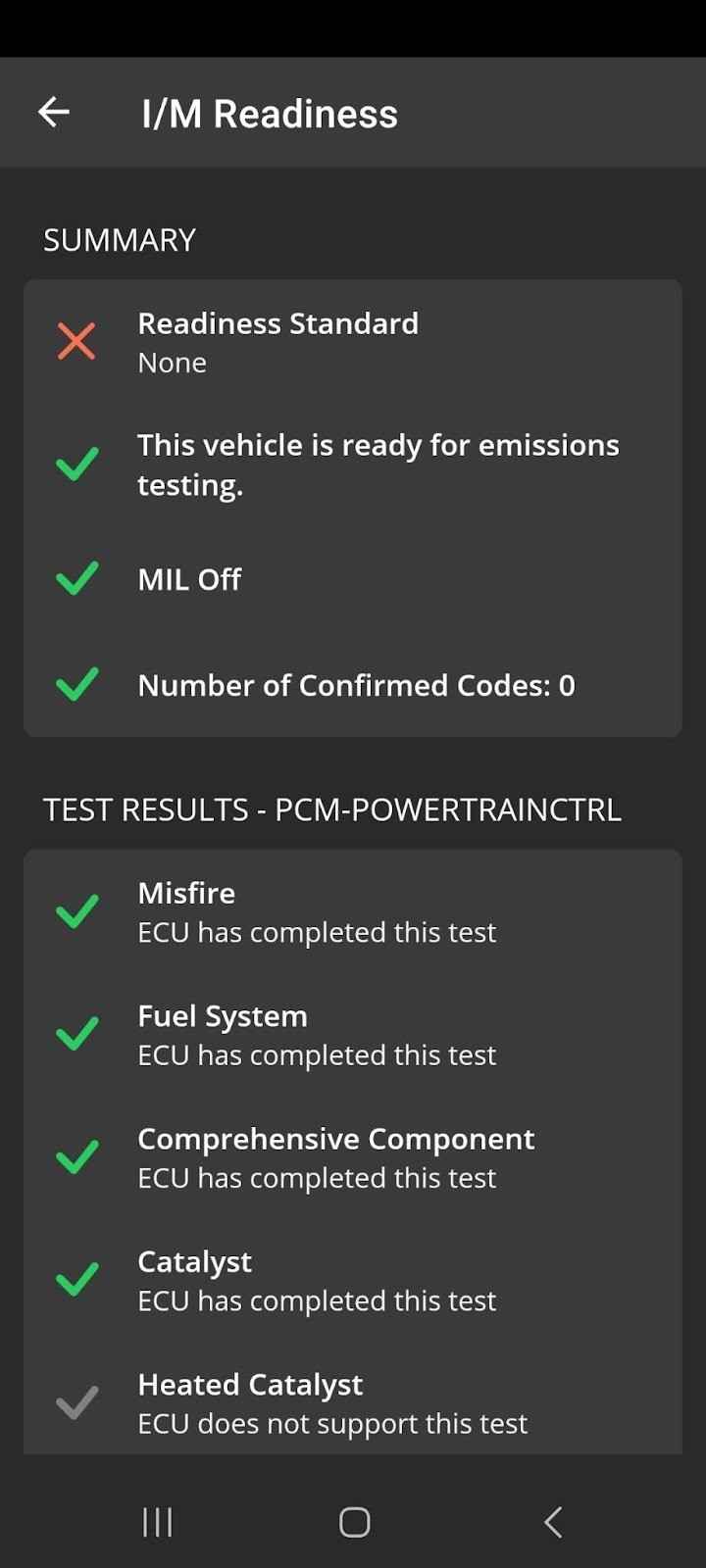 Mercedes-Benz I M Readiness Report
Mercedes-Benz I M Readiness Report
 Mercedes-Benz Monitor Menu Options
Mercedes-Benz Monitor Menu Options
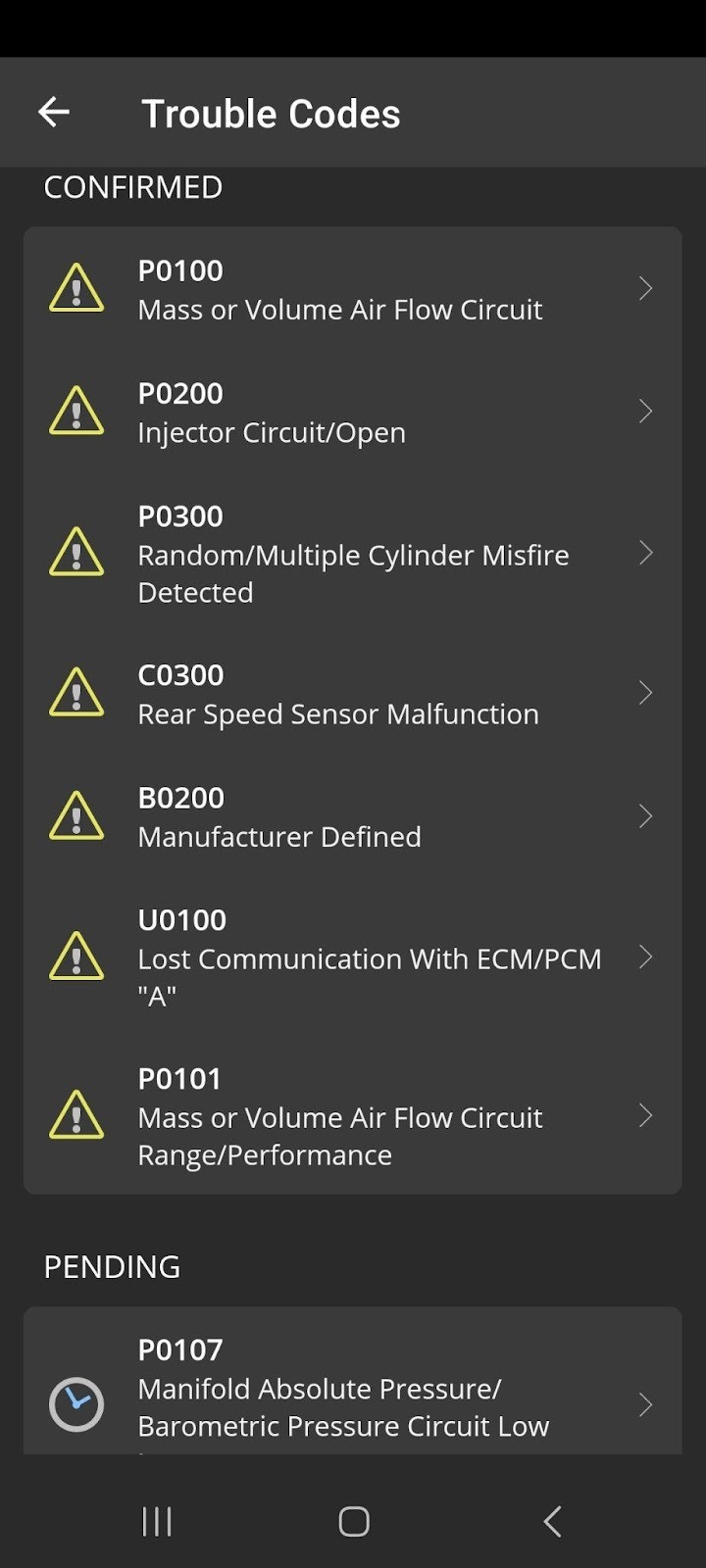 Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Report
Mercedes-Benz Trouble Codes Report
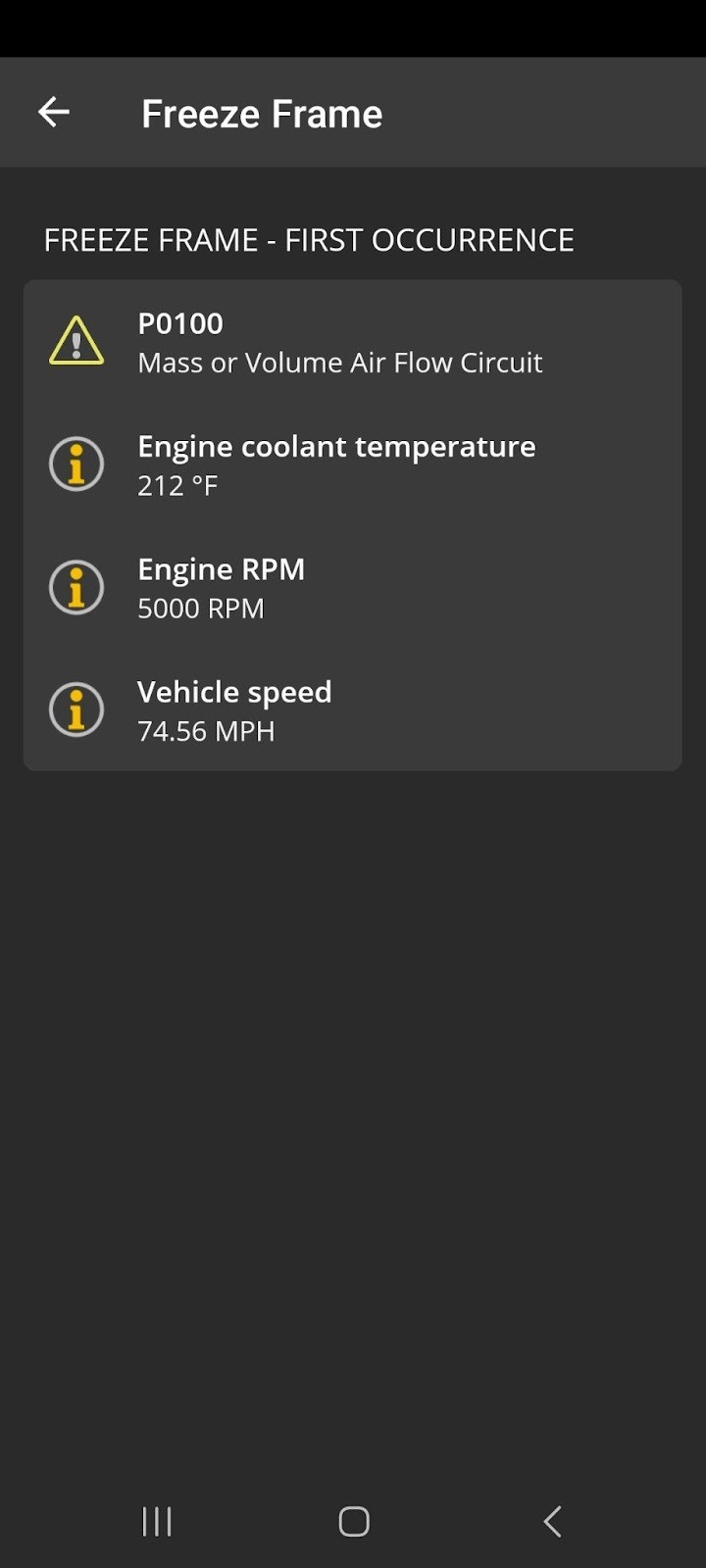 Mercedes-Benz Freeze Frame Report
Mercedes-Benz Freeze Frame Report
 Mercedes-Benz On-Board Monitoring
Mercedes-Benz On-Board Monitoring
 Mercedes-Benz Vehicle Information
Mercedes-Benz Vehicle Information