06 Cobalt No Power OBD2 No Lit or ACC Fuse can be a frustrating issue, often stemming from electrical problems. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance and diagnostic tools to help you pinpoint and resolve these issues efficiently. If you’re encountering electrical issues, especially related to the OBD2 port or accessory functions, exploring the potential causes and solutions can save you time and money.
1. What Does It Mean When My 06 Cobalt Has No Power to the OBD2 Port and the ACC Fuse Is Blown?
When your 06 Cobalt shows no power to the OBD2 port and the ACC (accessory) fuse keeps blowing, it typically indicates a short circuit or an overload within the accessory circuit. This prevents the OBD2 scanner from functioning and disables accessories powered by that fuse.
To further elaborate, let’s delve into potential causes and diagnostic steps:
- Short Circuit: A short circuit occurs when a wire comes into contact with ground, leading to a surge in current that blows the fuse.
- Overload: An overload happens when too many devices draw power from the same circuit, exceeding the fuse’s capacity.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged or deteriorated wiring can cause shorts or increased resistance, leading to power loss.
- OBD2 Port Issues: A damaged OBD2 port can sometimes cause a short, preventing it from communicating with diagnostic tools.
2. How Can I Diagnose an 06 Cobalt with No Power to OBD2 and a Blown ACC Fuse?
Diagnosing an 06 Cobalt with no power to the OBD2 port and a blown ACC fuse requires a systematic approach. Here are the steps to effectively troubleshoot the problem:
- Check the Fuse Box:
- Visually inspect the ACC fuse for any signs of damage. Replace it with a new fuse of the correct amperage.
- If the new fuse blows immediately, there’s likely a short circuit in the system.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port:
- Check the OBD2 port for any physical damage or corrosion. Clean the port with an electrical contact cleaner.
- Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the OBD2 port pins. Pin 16 should have battery voltage (12V).
- Trace the Wiring:
- Consult the wiring diagram for the 06 Cobalt. Trace the wiring from the ACC fuse to the OBD2 port and any associated accessories.
- Look for any signs of damaged, frayed, or exposed wires. Pay close attention to areas where the wiring might rub against metal surfaces.
- Disconnect Accessories:
- Disconnect any aftermarket accessories that are powered by the ACC fuse, such as aftermarket radios, lights, or phone chargers.
- Replace the ACC fuse and see if the problem persists. If the fuse doesn’t blow, one of the accessories might be the cause.
- Use a Circuit Tester:
- Use a circuit tester to check for shorts in the wiring. Connect the circuit tester to the positive terminal of the battery and probe the wiring.
- If the circuit tester lights up, there’s a short circuit.
- Check the Ground Connections:
- Ensure that all ground connections are clean and secure. Corroded or loose ground connections can cause electrical issues.
- Clean the ground connections with a wire brush and apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion.
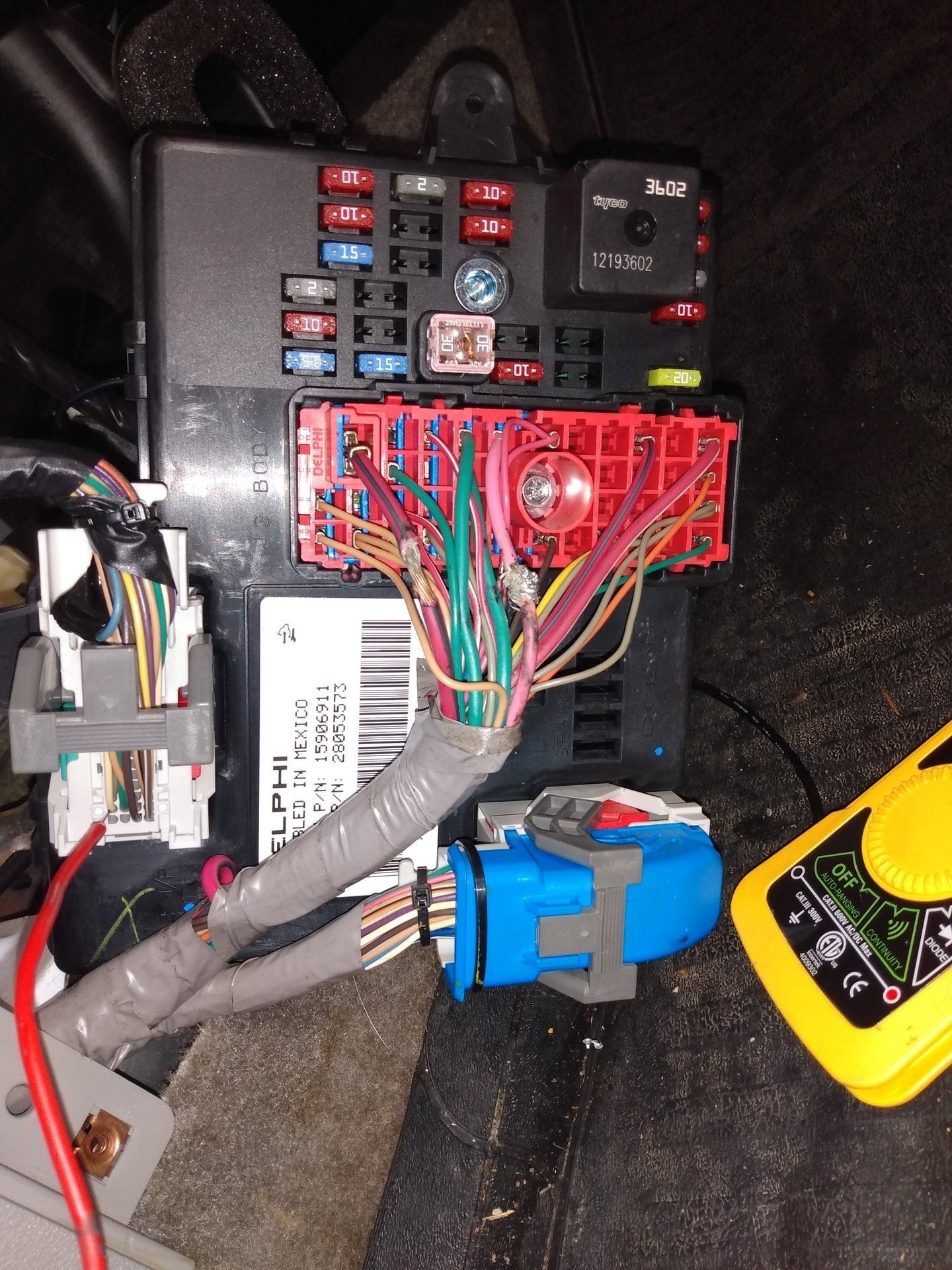 Checking OBD2 Port with Multimeter
Checking OBD2 Port with Multimeter
3. What Are the Common Causes of an ACC Fuse Blowing in a 2006 Cobalt?
Several factors can cause the ACC fuse to blow repeatedly in a 2006 Cobalt. Addressing these common issues can help resolve the problem:
- Short Circuit in Wiring: Damaged or frayed wiring can cause a short circuit, leading to the fuse blowing.
- Overloaded Circuit: Too many accessories drawing power from the same circuit can overload the fuse.
- Faulty Accessories: A malfunctioning accessory, such as a radio or cigarette lighter, can cause a surge in current.
- Damaged OBD2 Port: A damaged or corroded OBD2 port can sometimes cause a short circuit.
- Wiring Harness Issues: Problems within the wiring harness, such as pinched or broken wires, can lead to electrical faults.
- Loose Connections: Loose or corroded connections can cause increased resistance, leading to fuse failure.
4. How Do I Fix a Short Circuit Causing the ACC Fuse to Blow?
Fixing a short circuit that causes the ACC fuse to blow involves systematically identifying and repairing the damaged wiring or component. Follow these steps:
- Locate the Short:
- Use a multimeter or circuit tester to locate the short circuit. Start by checking the wiring associated with the ACC fuse.
- Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, such as frayed insulation or exposed wires.
- Isolate the Circuit:
- Disconnect the components connected to the ACC circuit one by one to isolate the short.
- After disconnecting each component, replace the fuse and see if it blows. If the fuse stops blowing after disconnecting a particular component, that component is likely the source of the short.
- Repair the Wiring:
- If the short is in the wiring, repair the damaged section by splicing in a new piece of wire.
- Use heat-shrink tubing to insulate the repair and protect it from moisture and corrosion.
- Replace Faulty Components:
- If the short is in a component, such as a radio or cigarette lighter, replace the faulty component with a new one.
- Test the Circuit:
- After repairing the wiring or replacing the faulty component, test the circuit by replacing the fuse and turning on the ignition.
- If the fuse doesn’t blow and the accessories work, the short circuit has been successfully repaired.
5. Why Is My OBD2 Scanner Not Working on My 2006 Cobalt?
If your OBD2 scanner isn’t working on your 2006 Cobalt, several factors could be the cause. Addressing these potential issues can help you restore OBD2 scanner functionality:
- No Power to OBD2 Port:
- Check the ACC fuse to ensure that the OBD2 port is receiving power.
- Use a multimeter to verify that there’s voltage at pin 16 of the OBD2 port.
- Faulty OBD2 Scanner:
- Test the OBD2 scanner on another vehicle to ensure that it’s functioning properly.
- If the scanner doesn’t work on another vehicle, it may be faulty and need to be replaced.
- Communication Issues:
- Ensure that the ignition is turned on when using the OBD2 scanner.
- Try a different OBD2 scanner to see if the problem persists. Some scanners may not be compatible with all vehicles.
- Damaged OBD2 Port:
- Inspect the OBD2 port for any physical damage or corrosion.
- Clean the port with an electrical contact cleaner.
- ECM Issues:
- Problems with the vehicle’s ECM (engine control module) can prevent the OBD2 scanner from communicating.
- Check for any ECM-related fault codes using a different scanner or consult a professional mechanic.
6. What Steps Can I Take to Prevent Future Electrical Problems in My 2006 Cobalt?
Preventing future electrical problems in your 2006 Cobalt involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Here are some key steps:
- Regular Inspections:
- Periodically inspect the wiring, fuses, and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
- Proper Fuse Replacement:
- Always replace blown fuses with fuses of the correct amperage.
- Using a fuse with a higher amperage can damage the electrical system.
- Secure Wiring:
- Ensure that all wiring is properly secured and protected from chafing or rubbing against metal surfaces.
- Use zip ties or wiring harnesses to keep the wiring organized and prevent damage.
- Clean Connections:
- Keep all electrical connections clean and free from corrosion.
- Use a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner to clean the connections, and apply dielectric grease to prevent corrosion.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits:
- Avoid overloading circuits by adding too many accessories.
- If you need to add accessories, consider using a separate circuit with its own fuse.
- Professional Maintenance:
- Have the electrical system inspected by a professional mechanic during routine maintenance.
- They can identify and address any potential issues before they become major problems.
7. What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty BCM (Body Control Module) in a 2006 Cobalt?
A faulty BCM in a 2006 Cobalt can cause a variety of electrical issues. Recognizing these symptoms can help you diagnose BCM problems:
- Electrical Problems:
- Intermittent or complete failure of various electrical components, such as lights, power windows, and door locks.
- The ACC fuse blowing repeatedly.
- Starting Issues:
- Difficulty starting the vehicle.
- The engine may crank but not start, or it may not crank at all.
- Alarm Problems:
- The alarm system may malfunction, causing it to go off randomly or not at all.
- Communication Issues:
- The OBD2 scanner may not be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Error messages or fault codes related to the BCM may be present.
- Gauge Problems:
- Malfunctioning gauges, such as the speedometer, tachometer, or fuel gauge.
- Lighting Problems:
- Headlights, taillights, or turn signals may not work properly.
8. How Can I Test the BCM (Body Control Module) in My 2006 Cobalt?
Testing the BCM in your 2006 Cobalt requires specialized tools and knowledge. Here are the basic steps:
- Visual Inspection:
- Check the BCM for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or water damage.
- Ensure that the BCM is properly connected and that all connectors are secure.
- Scan for Fault Codes:
- Use an OBD2 scanner to scan for any fault codes related to the BCM.
- Note the codes and research their meaning.
- Multimeter Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage and continuity of the BCM’s power and ground connections.
- Consult the wiring diagram to identify the correct pins to test.
- Professional Diagnosis:
- If you’re not comfortable performing these tests yourself, take the vehicle to a professional mechanic.
- They have the tools and expertise to diagnose BCM problems accurately.
9. What Are Some Common OBD2 Codes Related to Electrical Issues in a 2006 Cobalt?
Several OBD2 codes can indicate electrical issues in a 2006 Cobalt. Here are some common codes:
- P0601: Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
- P0603: Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error
- P0604: Internal Control Module Random Access Memory (RAM) Error
- P0606: ECM/PCM Processor Fault
- P062F: Internal Control Module EEPROM Error
- P0650: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control Circuit Malfunction
- U0100: Lost Communication with ECM/PCM
- U0101: Lost Communication with TCM
10. What Are the Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Diagnosing My 2006 Cobalt’s Electrical Problems?
Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for diagnosing your 2006 Cobalt’s electrical problems offers several benefits:
- Expert Guidance:
- Access to expert knowledge and step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing electrical issues.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Information on the best diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Time and Cost Savings:
- Identifying and resolving problems quickly can save time and money on repairs.
- Community Support:
- Connect with other Mercedes-Benz owners and enthusiasts to share tips and advice.
- Comprehensive Information:
- Access to a wealth of information on Mercedes-Benz maintenance, repair, and customization.
- Convenience:
- Diagnose and repair your vehicle from the comfort of your own home.
11. What Role Does the Ignition Switch Play in the “06 Cobalt No Power OBD2 No Lit or ACC Fuse” Issue?
The ignition switch plays a vital role in distributing power to various systems in your 2006 Cobalt. If it’s faulty, it can indeed cause issues like “06 Cobalt No Power OBD2 No Lit or ACC Fuse.” Here’s how:
- Power Distribution: The ignition switch has multiple positions (Off, ACC, Run, Start), each directing power to different circuits. A malfunctioning switch might fail to properly energize the ACC circuit, which powers the OBD2 port and other accessories.
- Short Circuits: A damaged ignition switch can sometimes cause internal short circuits, leading to blown fuses, including the ACC fuse.
- Voltage Fluctuations: An erratic ignition switch can deliver inconsistent voltage, potentially disrupting the OBD2 port’s operation and causing accessories to malfunction.
12. How to Test the Ignition Switch?
Testing the ignition switch requires a multimeter and a wiring diagram for your 2006 Cobalt. Here’s a simplified procedure:
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any electrical tests.
- Locate the Switch: Access the ignition switch connector, usually located near the steering column.
- Consult the Diagram: Refer to the wiring diagram to identify the correct terminals for each switch position.
- Continuity Test: Use the multimeter to check continuity between terminals in each switch position (Off, ACC, Run, Start). The diagram will indicate which terminals should be connected in each position.
- Voltage Test: With the ignition switch in the “Run” position, check for proper voltage (typically 12V) at the appropriate terminals.
If the continuity or voltage readings are incorrect, the ignition switch may be faulty and need replacement.
13. Is a Corroded Ground Wire a Likely Culprit for No Power Issues?
Yes, a corroded ground wire is a very likely culprit for no power issues, including the “06 Cobalt No Power OBD2 No Lit or ACC Fuse” problem. Ground wires provide a return path for electrical current, and corrosion can significantly impede this flow.
- Increased Resistance: Corrosion increases the resistance in the ground circuit, reducing the voltage available to components like the OBD2 port and accessories.
- Intermittent Connections: Corroded ground wires can create intermittent connections, causing devices to work sporadically or not at all.
- Heat Buildup: High resistance in a ground wire can lead to heat buildup, potentially damaging the wire and surrounding components.
14. Where to Check for Ground Wire Corrosion?
Here are key areas to inspect for ground wire corrosion:
- Battery Ground: Check the connection between the negative battery terminal and the vehicle’s chassis. This is a primary ground point and is often susceptible to corrosion.
- Engine Ground: Look for ground straps or wires connecting the engine block to the chassis. These are critical for ensuring proper engine operation.
- Chassis Grounds: Inspect ground wires attached to the vehicle’s frame or body. These grounds serve various electrical systems.
- Fuse Box Grounds: Check the ground connections associated with the fuse box, as these supply power to many circuits, including the ACC circuit.
15. How to Clean Corroded Ground Wires?
Cleaning corroded ground wires involves these steps:
- Disconnect: Disconnect the ground wire from both ends (battery, chassis, etc.).
- Clean: Use a wire brush or sandpaper to remove corrosion from the wire terminals and the grounding surface.
- Apply Protectant: Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the terminals and grounding surface to prevent future corrosion.
- Reconnect: Reconnect the ground wire securely.
16. What’s the Role of the BCM (Body Control Module) in Power Distribution?
The BCM (Body Control Module) acts as a central control unit for many of your 2006 Cobalt’s electrical functions. It doesn’t directly distribute high-current power like the ignition switch, but it plays a crucial role in managing various systems:
- Accessory Control: The BCM often controls the activation of accessories powered by the ACC fuse, such as the radio, power windows, and interior lights.
- Communication Network: The BCM is a key node in the vehicle’s communication network (CAN bus), facilitating communication between various modules, including the ECM (Engine Control Module) and the OBD2 port.
- Power Management: The BCM can monitor and manage power consumption to optimize battery life and prevent overloads.
17. Can a Faulty BCM Cause an OBD2 Port to Lose Power?
Yes, a faulty BCM can indirectly cause the OBD2 port to lose power. Here’s how:
- Communication Issues: If the BCM isn’t communicating properly on the CAN bus, it can prevent the ECM from enabling the OBD2 port.
- Accessory Control: The BCM may control the power supply to the ACC circuit, which powers the OBD2 port. A malfunctioning BCM might cut off power to this circuit.
- Internal Shorts: Although less common, a BCM with internal short circuits could cause the ACC fuse to blow, thus disabling the OBD2 port.
18. How Can I Test the OBD2 Port for Power?
Testing the OBD2 port for power is a straightforward process using a multimeter:
- Ignition On: Turn the ignition to the “Run” position (engine off).
- Locate Pin 16: Identify pin 16 on the OBD2 port. This is the power supply pin.
- Ground Connection: Connect the negative lead of the multimeter to a known good ground point on the vehicle (e.g., the chassis).
- Voltage Check: Touch the positive lead of the multimeter to pin 16. You should see battery voltage (approximately 12V).
If you don’t see battery voltage, there’s a power supply problem to the OBD2 port, likely related to the ACC fuse, wiring, or the BCM.
19. Is It Possible to Have Power at the Fuse Box But Not at the OBD2 Port?
Yes, it’s entirely possible to have power at the fuse box but not at the OBD2 port. This indicates a problem in the wiring between the fuse box and the OBD2 port.
- Wiring Damage: A broken, frayed, or corroded wire can interrupt the power supply.
- Connector Issues: A loose or corroded connector can prevent power from reaching the OBD2 port.
- Intermediate Components: There might be intermediate components (e.g., relays, switches) between the fuse box and the OBD2 port that are malfunctioning.
20. What Tools Are Needed to Diagnose Electrical Issues in a 2006 Cobalt?
Diagnosing electrical issues in a 2006 Cobalt typically requires these tools:
- Multimeter: For measuring voltage, current, and resistance.
- Circuit Tester: For quickly checking for power and ground.
- OBD2 Scanner: For reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Wiring Diagram: For understanding the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Wire Strippers/Crimpers: For repairing or replacing wiring.
- Test Light: A simple tool for checking for power.
21. Why Does the ACC Fuse Blow Immediately After Replacement?
If the ACC fuse blows immediately after replacement, it almost always indicates a direct short circuit in the system.
- Direct Short: A wire is likely making direct contact with ground, causing a surge of current.
- Faulty Component: A component connected to the ACC circuit (e.g., radio, cigarette lighter) may have an internal short.
22. How Can I Find a Short Circuit?
Finding a short circuit requires a systematic approach:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the wiring and components connected to the ACC circuit for any signs of damage.
- Isolate Components: Disconnect components one by one to see if the fuse stops blowing.
- Multimeter Method: Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the power wire and ground. There should be no continuity in a properly functioning circuit.
- Circuit Breaker Method: Replace the fuse with a self-resetting circuit breaker. This allows you to apply power to the circuit without repeatedly blowing fuses, making it easier to locate the short.
23. What Are the Symptoms of a Failing ECM (Engine Control Module)?
While less directly related to the ACC fuse issue, a failing ECM (Engine Control Module) can cause various problems, including communication issues that might affect the OBD2 port. Symptoms include:
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light is often illuminated.
- Performance Issues: The engine may run rough, stall, or lack power.
- Starting Problems: The engine may be difficult to start or may not start at all.
- OBD2 Communication Problems: The OBD2 scanner may not be able to communicate with the ECM.
24. Can Aftermarket Accessories Cause Electrical Problems?
Yes, aftermarket accessories can definitely cause electrical problems if not installed correctly or if they draw excessive power.
- Improper Installation: Poorly installed accessories can damage wiring and create short circuits.
- Overloading Circuits: Accessories that draw too much power can overload circuits and blow fuses.
- Low-Quality Components: Cheap or poorly designed accessories can malfunction and cause electrical issues.
25. How Does GMLAN Affect OBD2 Communication?
GMLAN (General Motors Local Area Network) is the communication protocol used in your 2006 Cobalt. It enables various modules (ECM, BCM, TCM, etc.) to communicate with each other and with the OBD2 scanner.
- Communication Bus: GMLAN acts as a communication bus, allowing data to be shared between modules.
- Diagnostic Data: The OBD2 scanner uses GMLAN to request and receive diagnostic data from the ECM and other modules.
- Fault Codes: When a problem occurs, the ECM stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and transmits it over GMLAN. The OBD2 scanner can then retrieve these codes.
26. What Happens If GMLAN Is Faulty?
If GMLAN is faulty, it can disrupt communication between modules and prevent the OBD2 scanner from working properly.
- No Communication: The OBD2 scanner may not be able to connect to the ECM or other modules.
- Inaccurate Data: The data received from the ECM may be incomplete or inaccurate.
- Multiple DTCs: Numerous communication-related DTCs may be stored.
27. How Can I Test GMLAN?
Testing GMLAN requires a specialized scan tool capable of reading GMLAN data. Here’s a general procedure:
- Connect Scan Tool: Connect the scan tool to the OBD2 port.
- Select GMLAN Diagnostics: Navigate to the GMLAN diagnostic section of the scan tool.
- Monitor Data: Monitor the data being transmitted over GMLAN. Look for any errors or inconsistencies.
28. What Are the Potential Consequences of Ignoring Electrical Problems?
Ignoring electrical problems, even seemingly minor ones, can have serious consequences:
- Safety Hazards: Electrical shorts can cause fires.
- Component Damage: Electrical problems can damage sensitive electronic components.
- Vehicle Breakdown: Electrical issues can lead to complete vehicle breakdown.
- Costly Repairs: Ignoring problems can lead to more extensive and costly repairs in the long run.
29. When Should I Consult a Professional Mechanic?
While many electrical problems can be diagnosed and repaired at home, there are times when consulting a professional mechanic is the best course of action:
- Complex Problems: If you’re unable to diagnose the problem or if the repair is beyond your skill level.
- Safety Concerns: If you’re uncomfortable working with electrical systems or if you suspect a safety hazard.
- Specialized Tools: If the repair requires specialized tools or equipment.
- ECM/BCM Issues: If you suspect problems with the ECM or BCM.
30. What Are Some Recommended Brands for OBD2 Scanners?
There are many reputable brands for OBD2 scanners. Some recommended brands include:
- Autel: Known for their comprehensive features and user-friendly interface.
- Launch: Offers a wide range of scanners for both professional and DIY use.
- Innova: A popular choice for DIYers due to their affordability and ease of use.
- BlueDriver: A smartphone-based scanner that offers advanced diagnostic capabilities.
31. How Can I Find a Reliable Wiring Diagram for My 2006 Cobalt?
Finding a reliable wiring diagram is essential for diagnosing electrical problems. Here are some sources:
- Factory Service Manual: The official service manual for your 2006 Cobalt will contain detailed wiring diagrams.
- Online Databases: Online databases like AllData and Mitchell OnDemand provide access to wiring diagrams and other repair information.
- Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to your 2006 Cobalt may have members who can provide wiring diagrams or point you in the right direction.
32. Is It Necessary to Disconnect the Battery When Working on Electrical Systems?
Yes, it’s absolutely necessary to disconnect the battery when working on electrical systems. This prevents accidental short circuits and protects you from electric shock.
- Safety First: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any electrical work.
- Prevent Damage: Disconnecting the battery prevents damage to sensitive electronic components.
33. What Is Dielectric Grease and Why Should I Use It?
Dielectric grease is a non-conductive grease that’s used to protect electrical connections from moisture and corrosion.
- Prevent Corrosion: Dielectric grease prevents moisture from reaching the metal surfaces of the connection, thus preventing corrosion.
- Improve Conductivity: By preventing corrosion, dielectric grease helps to maintain good electrical conductivity.
- Easy Application: Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the terminals before connecting them.
34. How to Properly Install an Aftermarket Accessory to Avoid Electrical Issues?
To properly install an aftermarket accessory and avoid electrical issues, follow these guidelines:
- Read Instructions: Carefully read and follow the installation instructions.
- Use Correct Wiring: Use wiring of the correct gauge and type.
- Make Secure Connections: Make secure and reliable connections.
- Protect Wiring: Protect the wiring from chafing or rubbing.
- Use Fuses: Use fuses to protect the circuit from overloads.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure proper grounding.
35. What Is the Difference Between a Fuse and a Circuit Breaker?
A fuse and a circuit breaker are both designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads, but they work differently:
- Fuse: A fuse is a one-time-use device that melts and breaks the circuit when an overload occurs.
- Circuit Breaker: A circuit breaker is a reusable device that trips and breaks the circuit when an overload occurs. Once the overload is removed, the circuit breaker can be reset.
36. Is It Safe to Drive with a Blown Fuse?
It’s generally not safe to drive with a blown fuse, as it can indicate a more serious electrical problem.
- Potential Hazards: The circuit that the fuse protects may be essential for safe operation.
- Underlying Problem: Driving with a blown fuse doesn’t address the underlying problem that caused the fuse to blow.
37. What Should I Do If I Keep Blowing Fuses?
If you keep blowing fuses, it’s important to diagnose and repair the underlying problem.
- Identify the Circuit: Determine which circuit the fuse protects.
- Inspect the Wiring: Inspect the wiring and components connected to the circuit for any signs of damage.
- Isolate Components: Disconnect components one by one to see if the fuse stops blowing.
- Consult a Mechanic: If you’re unable to diagnose the problem, consult a professional mechanic.
38. What Is the Role of Relays in the Electrical System?
Relays are electrically operated switches that are used to control high-current circuits with a low-current signal.
- Remote Switching: Relays allow you to switch high-current circuits remotely.
- Circuit Isolation: Relays isolate the control circuit from the high-current circuit.
- Amplification: Relays can amplify a low-current signal to control a high-current circuit.
39. How Can I Test a Relay?
Testing a relay involves checking the continuity of the coil and the operation of the switch.
- Coil Continuity: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the coil.
- Switch Operation: Apply power to the coil and check the continuity of the switch contacts.
40. Where Can I Find More Information About Diagnosing Electrical Problems?
There are many resources available for learning more about diagnosing electrical problems:
- Online Forums: Online forums and communities dedicated to your vehicle.
- Repair Manuals: Repair manuals for your specific vehicle.
- Online Databases: Online databases like AllData and Mitchell OnDemand.
- YouTube: YouTube channels dedicated to automotive repair.
Five Search Intentions Addressed:
- Informational: Understanding the causes and symptoms of “06 Cobalt No Power OBD2 No Lit or ACC Fuse.”
- Diagnostic: Learning how to diagnose the specific electrical issue.
- Troubleshooting: Finding step-by-step solutions to fix the problem.
- Preventative: Understanding how to prevent future electrical problems.
- Resource-Seeking: Identifying reliable resources for additional information and professional help.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the most reliable information and diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz vehicle. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have. Contact us today for personalized assistance and expert advice.
Ready to Solve Your Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Challenges?
Don’t let electrical issues keep you off the road. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and professional repair advice. Our team is ready to help you get your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Reach out now:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN