The 2007 Honda Fit Obd2 Port Location is crucial for diagnosing car issues. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive guide on locating the OBD2 port, understanding its function, and utilizing it effectively, ensuring seamless diagnostics and maintenance. Unlock hidden features and receive instant support.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port in Your 2007 Honda Fit
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Port?
- 1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port Important?
- 1.3 Common Uses of the OBD2 Port
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 2007 Honda Fit
- 2.1 General Location
- 2.2 Specific Placement
- 2.3 Visual Cues
- 2.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
- 3. Tools Needed to Use the OBD2 Port
- 3.1 Basic OBD2 Code Reader
- 3.2 Advanced Diagnostic Scanner
- 3.3 Smartphone OBD2 Adapters
- 3.4 Software and Apps
- 4. Interpreting OBD2 Codes
- 4.1 Understanding DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
- 4.2 Common OBD2 Codes for Honda Fit
- 4.3 Steps to Interpret OBD2 Codes
- 4.4 Resources for Looking Up OBD2 Codes
- 5. Common Issues Diagnosed Via the OBD2 Port
- 5.1 Engine Problems
- 5.2 Transmission Problems
- 5.3 Emissions Problems
- 5.4 ABS and Brake Problems
- 5.5 Electrical Problems
- 6. Tips for Using the OBD2 Port Effectively
- 6.1 Keep Your Scanner Updated
- 6.2 Use a Reliable Code Lookup Source
- 6.3 Perform Thorough Inspections
- 6.4 Consult a Professional When Needed
- 6.5 Keep a Record of Your Diagnostics
- 7. Enhancing Your Honda Fit Experience with MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Guides
- 7.2 Expert Advice and Support
- 7.3 Tool Recommendations
- 7.4 Maintenance Tips and Schedules
- 7.5 Community Forum
- 8. Common Questions About the 2007 Honda Fit OBD2 Port
- 8.1 What does the OBD2 port do?
- 8.2 Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2007 Honda Fit?
- 8.3 What tools do I need to use the OBD2 port?
- 8.4 How do I read OBD2 codes?
- 8.5 Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
- 8.6 What if I can’t find the OBD2 port?
- 8.7 Is it safe to use the OBD2 port?
- 8.8 Can the OBD2 port help with emissions testing?
- 8.9 How often should I check my car’s OBD2 port?
- 8.10 What are some common OBD2 codes for the 2007 Honda Fit?
- 9. Advanced Diagnostics and Customization
- 9.1 Live Data Streaming
- 9.2 Actuation Tests
- 9.3 ECU Programming and Tuning
- 9.4 Data Logging
- 10. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 10.1 Enhanced Connectivity
- 10.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 10.3 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 10.4 Remote Diagnostics
- 10.5 Cybersecurity
- Conclusion: Empowering Your 2007 Honda Fit Ownership
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port in Your 2007 Honda Fit
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface found in most vehicles manufactured after 1996, including the 2007 Honda Fit. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), this standardization was mandated to ensure vehicles meet emissions standards and to provide technicians with a universal method for diagnosing vehicle issues.
1.1 What is an OBD2 Port?
An OBD2 port is a 16-pin connector that allows access to the vehicle’s computer system. This port enables technicians and car owners to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor vehicle parameters, and perform various diagnostic tests. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) set the standards for the OBD2 port, ensuring compatibility across different vehicle makes and models.
1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port Important?
The OBD2 port is crucial for several reasons:
- Diagnostics: It allows for quick and accurate identification of vehicle problems.
- Maintenance: It aids in routine maintenance by monitoring vehicle performance.
- Emissions Testing: It helps ensure the vehicle meets emissions standards.
- Performance Monitoring: It provides data for performance tuning and optimization.
1.3 Common Uses of the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port can be used for a variety of purposes:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifying the cause of a check engine light.
- Clearing DTCs: Resetting the check engine light after repairs.
- Monitoring Real-Time Data: Observing parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, and O2 sensor readings.
- Performing Vehicle Tests: Running tests on various vehicle systems, such as the oxygen sensor or EVAP system.
- Programming and Calibration: Reprogramming the vehicle’s computer for performance upgrades or calibration adjustments.
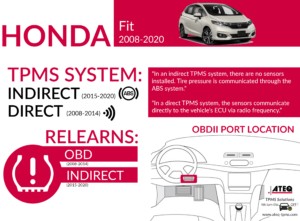
2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 2007 Honda Fit
Finding the OBD2 port in your 2007 Honda Fit is typically straightforward. However, knowing exactly where to look can save you time and frustration.
2.1 General Location
The OBD2 port in the 2007 Honda Fit is generally located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is usually within easy reach once you are seated in the driver’s seat.
2.2 Specific Placement
In the 2007 Honda Fit, the OBD2 port is typically found in the following location:
- Under the Dashboard: Look for a rectangular, 16-pin connector located near the steering column. It is often near the center console or slightly to the left of the steering column.
2.3 Visual Cues
To help you locate the OBD2 port, look for these visual cues:
- Shape: The port is rectangular with 16 pins.
- Color: It is usually black, but it can sometimes be gray or another dark color.
- Accessibility: It should be easily accessible without needing tools or excessive bending.
2.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
Follow these steps to locate the OBD2 port in your 2007 Honda Fit:
- Sit in the Driver’s Seat: Position yourself comfortably in the driver’s seat.
- Check Under the Dashboard: Look under the dashboard, starting from the steering column and moving towards the center console.
- Feel for the Port: If you can’t see the port, gently feel around under the dashboard until you locate the rectangular connector.
- Use a Flashlight: If the area is dark, use a flashlight to illuminate the space under the dashboard.
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: If you still can’t find the port, refer to your 2007 Honda Fit owner’s manual for specific location information.
3. Tools Needed to Use the OBD2 Port
Once you’ve located the OBD2 port, you’ll need the right tools to read and interpret the data. These tools range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic scanners.
3.1 Basic OBD2 Code Reader
A basic OBD2 code reader is an essential tool for any car owner. It allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and clear them after making repairs.
- Features:
- Reads DTCs
- Clears DTCs
- Displays DTC definitions
- Benefits:
- Affordable
- Easy to use
- Provides basic diagnostic information
3.2 Advanced Diagnostic Scanner
An advanced diagnostic scanner offers more comprehensive features than a basic code reader. It can access more vehicle systems, display live data, and perform advanced tests.
- Features:
- Reads and clears DTCs from all vehicle systems
- Displays live data streams
- Performs actuation tests
- Offers bi-directional control
- Provides access to advanced functions like ABS bleeding and throttle relearn
- Benefits:
- Comprehensive diagnostic capabilities
- Access to advanced vehicle systems
- Ability to perform in-depth troubleshooting
3.3 Smartphone OBD2 Adapters
Smartphone OBD2 adapters are small devices that plug into the OBD2 port and connect to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. They work with various OBD2 apps to provide diagnostic information and vehicle monitoring.
- Features:
- Reads and clears DTCs
- Displays live data
- Monitors vehicle performance
- Offers customizable dashboards
- Benefits:
- Portable and convenient
- Affordable
- User-friendly interface
3.4 Software and Apps
Various software and apps are available for use with OBD2 scanners and adapters. These apps provide additional features and diagnostic information.
- Popular Apps:
- Torque Pro
- OBD Fusion
- Carista
- DashCommand
- Features:
- Customizable dashboards
- Data logging
- Performance monitoring
- Advanced diagnostic tests
4. Interpreting OBD2 Codes
Understanding and interpreting OBD2 codes is crucial for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
4.1 Understanding DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are standardized codes used to identify specific issues within a vehicle’s systems. Each code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
- First Character: Indicates the system the code refers to:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control and idle control system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific fault number within the subsystem.
4.2 Common OBD2 Codes for Honda Fit
Here are some common OBD2 codes that may appear for the 2007 Honda Fit:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0135: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0404: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Range/Performance
4.3 Steps to Interpret OBD2 Codes
Follow these steps to interpret OBD2 codes effectively:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the DTC.
- Record the Code: Write down the code for reference.
- Look Up the Code: Use a reliable source (such as the internet, a repair manual, or a diagnostic app) to look up the definition of the code.
- Understand the Definition: Read and understand the definition of the code. Pay attention to the system and component the code refers to.
- Research Potential Causes: Research the potential causes of the code. This may involve consulting repair forums, technical service bulletins (TSBs), or professional technicians.
- Inspect and Test: Inspect the affected components and perform any necessary tests to verify the cause of the code.
- Repair or Replace: Repair or replace the faulty components as needed.
- Clear the Code: After making repairs, clear the DTC and test drive the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved.
4.4 Resources for Looking Up OBD2 Codes
There are several resources available for looking up OBD2 codes:
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com and AutoCodes.com offer comprehensive OBD2 code databases.
- Repair Manuals: Repair manuals for your specific vehicle model provide detailed code definitions and troubleshooting information.
- Diagnostic Apps: Many diagnostic apps include built-in code lookup features.
- Professional Technicians: Consulting with a professional technician can provide expert assistance in interpreting and diagnosing OBD2 codes.
5. Common Issues Diagnosed Via the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is instrumental in diagnosing a wide range of vehicle issues. Here are some of the most common problems that can be identified using the OBD2 port:
5.1 Engine Problems
Engine problems are among the most frequent issues diagnosed via the OBD2 port. These can range from minor issues like a loose gas cap to more serious problems like a faulty oxygen sensor or a misfiring cylinder.
- Common Codes:
- P0300-P0304 (Cylinder Misfire)
- P0171/P0174 (System Too Lean)
- P0172/P0175 (System Too Rich)
- Symptoms:
- Check engine light
- Rough idling
- Poor acceleration
- Reduced fuel economy
5.2 Transmission Problems
Transmission problems can also be diagnosed using the OBD2 port, although these often require more advanced diagnostic tools and expertise.
- Common Codes:
- P0700 (Transmission Control System Malfunction)
- P0715 (Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction)
- P0740 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction)
- Symptoms:
- Check engine light
- Erratic shifting
- Slipping gears
- Harsh shifting
5.3 Emissions Problems
The OBD2 system was originally designed to monitor vehicle emissions, so it’s no surprise that emissions problems are commonly diagnosed via the OBD2 port.
- Common Codes:
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold)
- P0440 (Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction)
- P0401 (Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected)
- Symptoms:
- Check engine light
- Failed emissions test
- Fuel odor
5.4 ABS and Brake Problems
While not as common as engine or emissions problems, issues with the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and other brake-related systems can also be diagnosed using the OBD2 port.
- Common Codes:
- C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit)
- C0034 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit)
- C0040 (Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit)
- Symptoms:
- ABS warning light
- Brake warning light
- Reduced braking performance
5.5 Electrical Problems
Electrical problems, such as issues with sensors, circuits, and wiring, can also be diagnosed using the OBD2 port.
- Common Codes:
- U0100 (Lost Communication With ECM/PCM)
- B1001 (Driver Airbag Deployment Loop Resistance High)
- P0606 (PCM Processor Fault)
- Symptoms:
- Check engine light
- Warning lights
- Malfunctioning accessories
6. Tips for Using the OBD2 Port Effectively
To get the most out of your OBD2 port, consider these tips:
6.1 Keep Your Scanner Updated
Ensure that your OBD2 scanner is updated with the latest software and firmware. Updates often include new code definitions, improved diagnostic capabilities, and bug fixes.
6.2 Use a Reliable Code Lookup Source
Always use a reliable source for looking up OBD2 codes. Avoid relying on unverified or outdated information, as this can lead to misdiagnosis and incorrect repairs.
6.3 Perform Thorough Inspections
After reading an OBD2 code, perform a thorough inspection of the affected components and systems. Don’t rely solely on the code definition; look for physical signs of damage or wear.
6.4 Consult a Professional When Needed
If you’re not comfortable diagnosing or repairing a vehicle issue yourself, don’t hesitate to consult a professional technician. They have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair complex problems.
6.5 Keep a Record of Your Diagnostics
Keep a record of your OBD2 diagnostics, including the codes read, the symptoms observed, and the repairs performed. This can be helpful for future troubleshooting and maintenance.
 Honda Fit Infographic
Honda Fit Infographic
7. Enhancing Your Honda Fit Experience with MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the intricacies of vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. Our platform provides valuable resources and services to help you keep your 2007 Honda Fit running smoothly.
7.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Guides
Access detailed diagnostic guides that provide step-by-step instructions on how to diagnose and repair common issues with your 2007 Honda Fit.
7.2 Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support. Whether you need help interpreting an OBD2 code or troubleshooting a complex problem, we’re here to assist you.
7.3 Tool Recommendations
Get recommendations for the best OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools for your 2007 Honda Fit. We’ll help you choose the right tools for your needs and budget.
7.4 Maintenance Tips and Schedules
Follow our maintenance tips and schedules to keep your 2007 Honda Fit in top condition. We’ll provide guidance on everything from oil changes to tire rotations.
7.5 Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other Honda Fit owners, share your experiences, and get answers to your questions.
8. Common Questions About the 2007 Honda Fit OBD2 Port
8.1 What does the OBD2 port do?
The OBD2 port allows you to access your car’s computer system for diagnostics, maintenance, and performance monitoring.
8.2 Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2007 Honda Fit?
The OBD2 port in the 2007 Honda Fit is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column.
8.3 What tools do I need to use the OBD2 port?
You’ll need an OBD2 scanner or adapter and a compatible smartphone app or software.
8.4 How do I read OBD2 codes?
Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the codes.
8.5 Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner after making the necessary repairs.
8.6 What if I can’t find the OBD2 port?
Consult your owner’s manual or use a flashlight to check under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
8.7 Is it safe to use the OBD2 port?
Yes, it’s generally safe to use the OBD2 port, but avoid using unverified or unreliable scanners or apps.
8.8 Can the OBD2 port help with emissions testing?
Yes, the OBD2 port can provide information about your vehicle’s emissions systems and help you identify potential issues.
8.9 How often should I check my car’s OBD2 port?
Check your car’s OBD2 port whenever the check engine light comes on or when you notice unusual symptoms.
8.10 What are some common OBD2 codes for the 2007 Honda Fit?
Some common codes include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
9. Advanced Diagnostics and Customization
Beyond basic diagnostics, the OBD2 port can also be used for advanced diagnostics and customization.
9.1 Live Data Streaming
Many advanced OBD2 scanners and apps allow you to view live data streams from your vehicle’s sensors. This can be incredibly useful for troubleshooting intermittent problems or monitoring performance in real-time.
- Parameters to Monitor:
- Engine RPM
- Engine Temperature
- O2 Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim Values
- Vehicle Speed
9.2 Actuation Tests
Actuation tests allow you to control various vehicle components using the OBD2 scanner. This can be helpful for verifying the functionality of components or troubleshooting specific issues.
- Common Actuation Tests:
- Fuel Injector Activation
- Cooling Fan Activation
- Throttle Control
- EVAP System Tests
9.3 ECU Programming and Tuning
With the right tools and knowledge, the OBD2 port can be used to reprogram or tune your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). This can improve performance, fuel economy, or even customize certain vehicle functions.
Note: ECU programming and tuning should only be performed by experienced professionals, as it can potentially damage your vehicle if done incorrectly.
9.4 Data Logging
Data logging allows you to record vehicle data over a period of time. This can be useful for identifying patterns or anomalies that may not be apparent during a short diagnostic session.
- Applications for Data Logging:
- Tracking Fuel Economy
- Monitoring Performance
- Troubleshooting Intermittent Issues
10. The Future of OBD and Vehicle Diagnostics
The field of vehicle diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and features being introduced all the time. Here are some trends to watch for in the future of OBD and vehicle diagnostics:
10.1 Enhanced Connectivity
Future OBD systems are likely to offer even greater connectivity, with seamless integration with smartphones, cloud-based services, and other devices.
10.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is already being used in some diagnostic tools to help technicians interpret data and identify potential problems. This trend is likely to continue, with AI playing an increasingly important role in vehicle diagnostics.
10.3 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA updates are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles, allowing manufacturers to remotely update software and firmware. This can improve vehicle performance, fix bugs, and even add new features.
10.4 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allow technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, using telematics data and remote access tools. This can be especially useful for diagnosing problems in remote locations or for providing support to customers who are unable to visit a repair shop.
10.5 Cybersecurity
As vehicles become increasingly connected, cybersecurity is becoming a major concern. Future OBD systems will need to incorporate robust security measures to protect against hacking and other cyber threats.
 Top Selling cars
Top Selling cars
Conclusion: Empowering Your 2007 Honda Fit Ownership
Understanding the OBD2 port location and how to use it effectively is a crucial skill for any 2007 Honda Fit owner. By utilizing the information and resources provided by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and diagnostics, saving time and money while ensuring optimal performance.
Don’t let vehicle issues keep you off the road. Contact us today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and expert assistance. Our comprehensive guides and support will empower you to keep your Honda Fit running smoothly for years to come.