Facing a persistent “P1000” code on your 2010 Ford F350? It can be frustrating, especially when trying to get your vehicle ready for an emissions test or simply ensuring optimal performance. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand these challenges and offer in-depth knowledge and solutions to help you diagnose and resolve OBD2 issues efficiently. We provide the expertise to navigate these complexities, ensuring your Ford runs smoothly and complies with all necessary regulations.
Unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz. Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 2010 Ford F350 OBD2 P1000 Code
- 1.1. What Does the P1000 Code Mean?
- 1.2. Common Causes of the P1000 Code
- 1.3. Symptoms Associated with the P1000 Code
- 2. Diagnosing the P1000 Code on Your 2010 Ford F350
- 2.1. Tools Needed for Diagnosis
- 2.2. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- 2.3. Common Diagnostic Mistakes to Avoid
- 3. Performing a Ford F350 Drive Cycle to Clear the P1000 Code
- 3.1. What is a Ford Drive Cycle?
- 3.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Drive Cycle on a 2010 Ford F350
- 3.3. Tips for Successfully Completing a Drive Cycle
- 4. Addressing Common Issues Preventing OBD-II Readiness
- 4.1. Oxygen (O2) Sensor Problems
- 4.2. Catalytic Converter Inefficiency
- 4.3. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Leaks
- 4.4. Misfire Issues
- 5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 5.1. Using Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System)
- 5.2. Performing Pinpoint Tests
- 5.3. Analyzing Freeze Frame Data
- 6. Preventing Future P1000 Code Issues
- 6.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- 6.2. Best Practices for Battery Maintenance
- 6.3. Safe OBD-II Scanning Practices
- 7. When to Seek Professional Help from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 7.2. Recurring P1000 Code
- 7.3. Lack of Diagnostic Experience
- 8. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
- 8.1. Expert Knowledge of Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 8.2. State-of-the-Art Diagnostic Equipment
- 8.3. Personalized Service and Support
- 8.4. Cost-Effective Solutions
- 9. Real-World Examples of P1000 Code Resolution
- 9.1. Case Study 1: Battery Issues
- 9.2. Case Study 2: EVAP System Leak
- 9.3. Case Study 3: O2 Sensor Failure
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the 2010 Ford F350 OBD2 P1000 Code
- 10.1. What does the P1000 code mean on a Ford F350?
- 10.2. Can I drive my Ford F350 with a P1000 code?
- 10.3. How do I clear the P1000 code on my Ford F350?
- 10.4. How long does it take to complete a Ford drive cycle?
- 10.5. What if the P1000 code returns after completing a drive cycle?
- 10.6. Can a faulty O2 sensor cause the P1000 code?
- 10.7. How can I check the readiness status of my Ford F350’s OBD system?
- 10.8. Is it safe to clear trouble codes without fixing the underlying issue?
- 10.9. What is the Ford IDS system, and how can it help with diagnosing the P1000 code?
- 10.10. Where can I find a reliable mechanic to diagnose and repair my Ford F350?
- Take Action Now
1. Understanding the 2010 Ford F350 OBD2 P1000 Code
The P1000 code in a 2010 Ford F350 indicates that the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system has not completed its self-tests. This means the vehicle’s computer hasn’t finished evaluating all the systems after a reset or battery disconnection. Understanding this code is the first step toward resolving it.
1.1. What Does the P1000 Code Mean?
The P1000 code, specific to Ford vehicles, signifies that the OBD-II system hasn’t completed all required tests and calibrations since the last memory reset. According to Ford Motor Company’s official documentation, this code appears when the vehicle’s diagnostic system hasn’t finished running all necessary self-tests to ensure all components are functioning correctly.
 Ford F350 engine diagnostic
Ford F350 engine diagnostic
1.2. Common Causes of the P1000 Code
Several factors can trigger a P1000 code. Addressing these potential issues can help clear the code and ensure your vehicle is ready for inspection. Common causes include:
- Recent Battery Disconnection or Replacement: Disconnecting the battery resets the OBD system, requiring it to relearn and retest all systems.
- Clearing Trouble Codes: Using a scan tool to clear DTCs also resets the OBD system, necessitating a complete system re-evaluation.
- Recent PCM (Powertrain Control Module) Reset or Reprogramming: Any changes to the PCM’s software can cause the system to restart its diagnostic routines.
- Faulty Sensors or Components: Although less common, a malfunctioning sensor can prevent the OBD system from completing its tests.
- OBD-II System Incompletion: The vehicle simply hasn’t been driven enough under the right conditions for all tests to run.
1.3. Symptoms Associated with the P1000 Code
While the P1000 code itself doesn’t directly impact vehicle performance, its presence can lead to other issues.
 Ford F350 dashboard warning lightsHere are some common symptoms:
Ford F350 dashboard warning lightsHere are some common symptoms:
- Inability to Pass Emissions Testing: Most states require all OBD systems to be ready for testing, and a P1000 code indicates that the system is not ready.
- Check Engine Light: Although the P1000 code itself may not activate the check engine light, other related issues might.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: If the OBD system isn’t ready, some engine parameters may not be optimally adjusted, leading to decreased fuel economy.
- Suboptimal Performance: While not always noticeable, the engine’s performance may not be at its peak if the OBD system hasn’t completed its diagnostic checks.
2. Diagnosing the P1000 Code on Your 2010 Ford F350
Diagnosing a P1000 code requires a systematic approach to ensure all potential issues are addressed. Using the right tools and following a step-by-step process can help identify and resolve the problem efficiently.
2.1. Tools Needed for Diagnosis
Having the right tools on hand is essential for diagnosing and resolving the P1000 code.
 OBD2 scanner diagnostic toolHere’s a list of recommended tools:
OBD2 scanner diagnostic toolHere’s a list of recommended tools:
- OBD-II Scanner: This tool reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Advanced scanners can also provide live data and perform specific diagnostic tests.
- Multimeter: Used to check voltage, continuity, and resistance in electrical circuits.
- Ford Workshop Manual: Provides detailed information on the vehicle’s systems and diagnostic procedures.
- Basic Hand Tools: Wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and pliers for accessing and inspecting components.
2.2. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Follow these steps to diagnose the P1000 code on your 2010 Ford F350:
- Check for Other Trouble Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any other stored or pending codes. Address these codes first, as they may be preventing the OBD system from completing its tests.
- Verify Battery Condition: Ensure the battery is fully charged and in good condition. A weak battery can cause various electrical issues, including OBD system resets.
- Inspect Sensor Connections: Check all sensor connections related to the engine and emissions systems. Look for loose, corroded, or damaged connections.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Inspect the engine bay for any obvious signs of damage, such as broken hoses, frayed wires, or leaking fluids.
- Review Recent Repairs: Consider any recent repairs or maintenance performed on the vehicle. A recent PCM reset or battery disconnection can trigger the P1000 code.
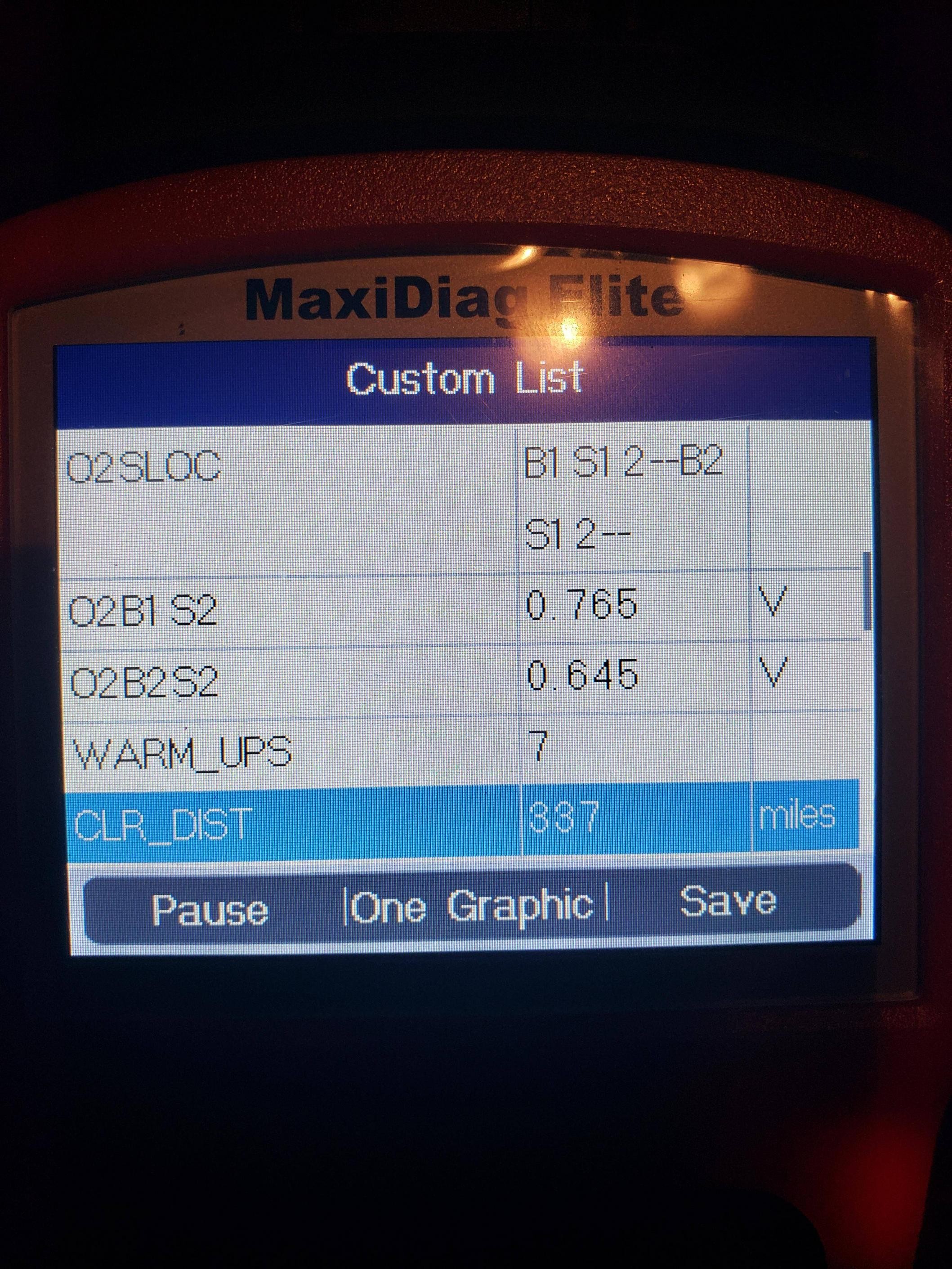
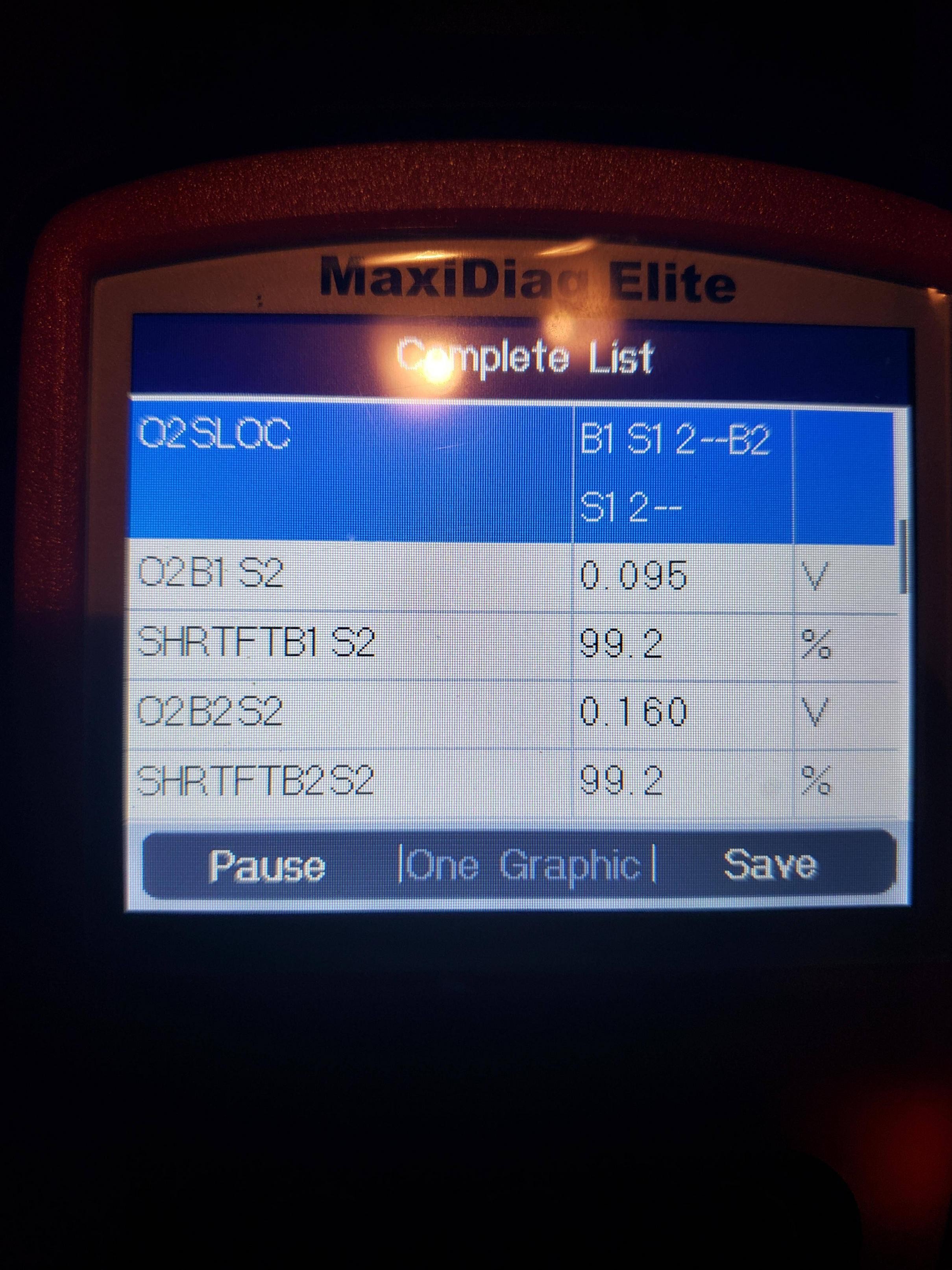
- Monitor Readiness Status: Use the OBD-II scanner to monitor the readiness status of the various OBD monitors. This will show which tests have not been completed.
2.3. Common Diagnostic Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common diagnostic mistakes can save time and prevent unnecessary repairs. Here are a few pitfalls to watch out for:
- Ignoring Other Trouble Codes: Always address any other DTCs before focusing on the P1000 code.
- Assuming Faulty Sensors: Don’t immediately replace sensors without thoroughly testing them.
- Skipping the Drive Cycle: The drive cycle is crucial for completing the OBD system tests. Ensure you follow the correct procedure.
- Neglecting Basic Maintenance: Ensure the vehicle is properly maintained, with fresh fluids and filters.
3. Performing a Ford F350 Drive Cycle to Clear the P1000 Code
A Ford drive cycle is a specific series of driving conditions designed to allow the vehicle’s OBD-II system to run all of its diagnostic tests. Completing a drive cycle is often necessary to clear the P1000 code.
3.1. What is a Ford Drive Cycle?
A Ford drive cycle involves a series of accelerations, decelerations, and steady-speed driving periods that simulate various driving conditions. This process allows the vehicle’s computer to test all critical systems, including the fuel system, oxygen sensors, and catalytic converters.
3.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Drive Cycle on a 2010 Ford F350
Follow these steps to perform a drive cycle on your 2010 Ford F350:
- Prepare the Vehicle:
- Ensure the fuel tank is between 1/4 and 3/4 full.
- Verify there are no major mechanical issues.
- Clear any existing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and allow it to idle for two minutes.
- Accelerate:
- Accelerate smoothly to 45 mph (72 km/h) and maintain this speed for eight minutes.
- Decelerate:
- Without using the brake, release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph (32 km/h).
- Accelerate Again:
- Accelerate gently back to 45 mph (72 km/h) and maintain this speed for another eight minutes.
- Decelerate Again:
- Repeat the coast-down deceleration to 20 mph (32 km/h).
- Idle:
- Come to a complete stop and allow the engine to idle for five minutes.
- Check Readiness Status:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check the readiness status of the OBD monitors. If all monitors are complete, the P1000 code should be cleared.
3.3. Tips for Successfully Completing a Drive Cycle
Successfully completing a drive cycle can be challenging. Here are some tips to increase your chances of success:
- Follow the Instructions Carefully: Adhere to the specified speeds and durations to ensure the tests run correctly.
- Choose the Right Location: Select a road with minimal traffic and few stops to avoid interrupting the cycle.
- Monitor Readiness Status: Use an OBD-II scanner to monitor the progress of the drive cycle in real-time.
- Be Patient: It may take several attempts to complete the drive cycle successfully.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Drive smoothly and avoid sudden accelerations or decelerations.
4. Addressing Common Issues Preventing OBD-II Readiness
Several factors can prevent the OBD-II system from achieving readiness, even after performing a drive cycle. Addressing these issues is crucial for clearing the P1000 code.
4.1. Oxygen (O2) Sensor Problems
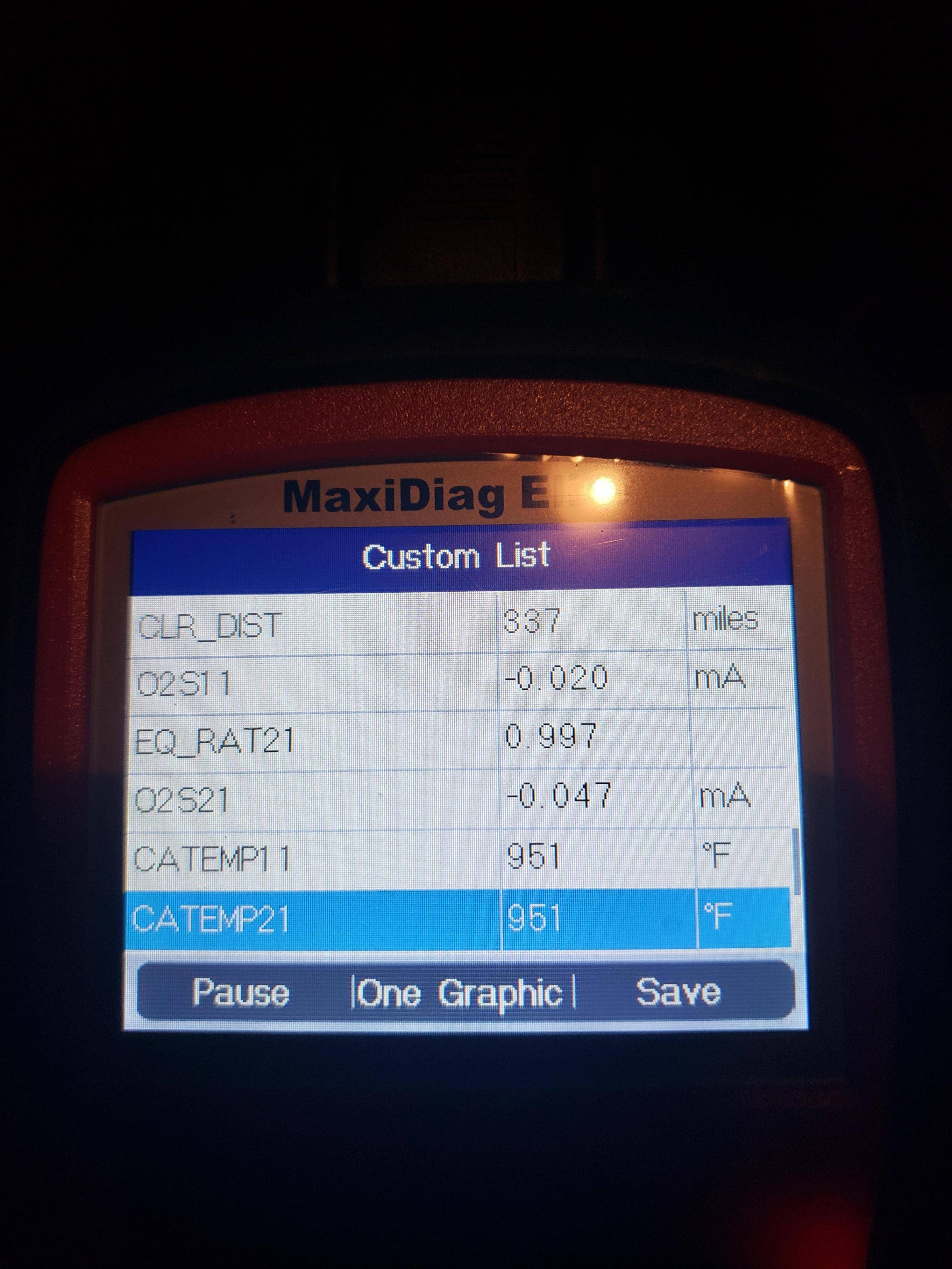
Oxygen sensors play a critical role in monitoring exhaust gases and adjusting the air-fuel mixture. Malfunctioning O2 sensors can prevent the OBD system from completing its tests.
- Symptoms of O2 Sensor Problems:
- Check engine light
- Poor fuel economy
- Rough idling
- Failed emissions test
- How to Diagnose O2 Sensors:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for O2 sensor-related codes.
- Inspect the sensors for physical damage.
- Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s voltage and resistance.
- How to Resolve O2 Sensor Issues:
- Replace faulty O2 sensors with OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts.
- Ensure the sensor connections are clean and secure.
- Check for exhaust leaks that can affect O2 sensor readings.
4.2. Catalytic Converter Inefficiency
The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less toxic substances. An inefficient catalytic converter can prevent the OBD system from achieving readiness.
- Symptoms of Catalytic Converter Problems:
- Check engine light (often with codes P0420 or P0430)
- Reduced engine power
- Rattling noise from the exhaust
- Failed emissions test
- How to Diagnose Catalytic Converter Issues:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for catalytic converter-related codes.
- Monitor the inlet and outlet temperatures of the converter using an infrared thermometer.
- Perform an exhaust backpressure test.
- How to Resolve Catalytic Converter Problems:
- Replace the catalytic converter if it is damaged or inefficient.
- Address any underlying issues that may be causing the converter to fail, such as engine misfires or oil leaks.
4.3. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Leaks
The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Leaks in the EVAP system can prevent the OBD system from completing its tests.
- Symptoms of EVAP System Leaks:
- Check engine light (often with codes P0440, P0442, or P0455)
- Fuel odor
- Poor fuel economy
- How to Diagnose EVAP System Leaks:
- Perform an EVAP system leak test using a smoke machine.
- Inspect the fuel cap for damage.
- Check the EVAP system hoses and components for cracks or leaks.
- How to Resolve EVAP System Leaks:
- Replace the fuel cap if it is damaged.
- Repair or replace any leaking EVAP system hoses or components.
- Ensure the EVAP system is properly sealed.
4.4. Misfire Issues
Engine misfires occur when one or more cylinders fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. Misfires can prevent the OBD system from achieving readiness and can also damage the catalytic converter.
- Symptoms of Misfire Issues:
- Check engine light (often with codes P0300-P030x)
- Rough idling
- Reduced engine power
- Poor fuel economy
- How to Diagnose Misfire Issues:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for misfire-related codes.
- Inspect the spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors.
- Perform a compression test to check for cylinder issues.
- How to Resolve Misfire Problems:
- Replace faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
- Repair any vacuum leaks that may be causing misfires.
- Address any mechanical issues that may be affecting cylinder compression.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
When basic diagnostic steps don’t resolve the P1000 code, advanced techniques may be necessary. These methods require specialized tools and expertise.
5.1. Using Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System)
The Ford IDS is a comprehensive diagnostic tool used by Ford dealerships and professional mechanics. It provides advanced diagnostic capabilities, including:
- Module Programming: Allows reprogramming of the PCM and other vehicle modules.
- Parameter Reset: Resets learned parameters to factory settings.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Performs in-depth diagnostic tests of various vehicle systems.
- Data Logging: Records live data for analysis.
5.2. Performing Pinpoint Tests
Pinpoint tests are detailed diagnostic procedures outlined in the Ford workshop manual. These tests guide technicians through a series of steps to isolate specific issues.
- How to Perform Pinpoint Tests:
- Refer to the Ford workshop manual for the specific pinpoint test related to the P1000 code.
- Follow the step-by-step instructions carefully.
- Use a multimeter and other specialized tools as required.
- Record the results of each test.
- Based on the test results, identify the faulty component or circuit.
5.3. Analyzing Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the operating conditions of the vehicle at the moment a trouble code is set. Analyzing this data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the P1000 code.
- How to Analyze Freeze Frame Data:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the freeze frame data associated with the P1000 code.
- Review the data, paying attention to parameters such as engine speed, load, temperature, and O2 sensor readings.
- Look for any anomalies or out-of-range values that may indicate a problem.
- Use this information to guide further diagnostic steps.
6. Preventing Future P1000 Code Issues
Preventing future P1000 code issues involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Here are some best practices to keep your 2010 Ford F350 running smoothly.
6.1. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing a wide range of issues, including those that can trigger the P1000 code.
- Oil Changes: Change the engine oil and filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly check and top off all fluids, including coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Filter Replacements: Replace the air filter, fuel filter, and cabin air filter as needed.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace the spark plugs according to the recommended interval.
- Tune-Ups: Perform regular tune-ups to ensure the engine is running efficiently.
6.2. Best Practices for Battery Maintenance
Maintaining a healthy battery is essential for preventing OBD system resets and P1000 codes.
- Keep the Battery Clean: Clean the battery terminals regularly to prevent corrosion.
- Check the Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Avoid leaving the vehicle unused for extended periods, as this can lead to battery discharge.
- Use a Battery Maintainer: If the vehicle will be stored for a long time, use a battery maintainer to keep the battery charged.
6.3. Safe OBD-II Scanning Practices
Using an OBD-II scanner correctly can help prevent accidental resets and data loss.
- Use a Quality Scanner: Invest in a high-quality OBD-II scanner from a reputable brand.
- Follow the Instructions: Read and follow the scanner’s instructions carefully.
- Avoid Clearing Codes Unnecessarily: Only clear trouble codes after addressing the underlying issue.
- Back Up Data: Before making any changes to the PCM, back up the existing data.
7. When to Seek Professional Help from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
While many P1000 code issues can be resolved with careful diagnosis and maintenance, some situations require professional assistance.
7.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
If you’ve performed basic diagnostic steps and are still unable to clear the P1000 code, it may be time to seek professional help. Complex diagnostic issues often require specialized tools and expertise.
7.2. Recurring P1000 Code
If the P1000 code keeps returning after being cleared, there may be an underlying issue that needs to be addressed by a professional. Recurring codes can indicate a more serious problem with the vehicle’s systems.
7.3. Lack of Diagnostic Experience
If you’re not comfortable performing diagnostic tests or working on your vehicle, it’s best to seek professional help. Attempting to diagnose and repair complex issues without the proper knowledge and experience can lead to further damage.
8. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
Choosing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for your diagnostic needs offers several advantages.
8.1. Expert Knowledge of Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Our team of experienced technicians has in-depth knowledge of Mercedes-Benz vehicles and their diagnostic systems. We stay up-to-date on the latest technologies and diagnostic techniques to provide the best possible service.
8.2. State-of-the-Art Diagnostic Equipment
We use state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, including the Ford IDS, to accurately diagnose and resolve complex issues. Our tools allow us to perform advanced tests and programming to ensure your vehicle is running at its best.
8.3. Personalized Service and Support
We provide personalized service and support to each of our customers. We take the time to understand your specific needs and concerns, and we work with you to develop a customized diagnostic and repair plan.
8.4. Cost-Effective Solutions
We offer cost-effective solutions to your diagnostic needs. We provide transparent pricing and strive to minimize unnecessary repairs. Our goal is to get your vehicle back on the road quickly and affordably.
9. Real-World Examples of P1000 Code Resolution
Understanding how the P1000 code has been resolved in real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights.
9.1. Case Study 1: Battery Issues
- Problem: A 2010 Ford F350 repeatedly displayed the P1000 code after the owner replaced the battery.
- Solution: A technician at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN discovered that the new battery had a slightly lower voltage than the original, causing the OBD system to reset intermittently. Replacing the battery with one that met the manufacturer’s specifications resolved the issue.
9.2. Case Study 2: EVAP System Leak
- Problem: A 2010 Ford F350 exhibited the P1000 code along with a noticeable fuel odor.
- Solution: A smoke test revealed a small leak in the EVAP system hose. Replacing the damaged hose and clearing the code resolved the issue.
9.3. Case Study 3: O2 Sensor Failure
- Problem: A 2010 Ford F350 displayed the P1000 code along with poor fuel economy.
- Solution: Diagnostic testing revealed a faulty O2 sensor. Replacing the sensor and performing a drive cycle cleared the code and improved fuel economy.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the 2010 Ford F350 OBD2 P1000 Code
Here are some frequently asked questions about the 2010 Ford F350 Obd2 P1000 code.
10.1. What does the P1000 code mean on a Ford F350?
The P1000 code on a Ford F350 indicates that the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system has not completed its self-tests since the last reset or battery disconnection.
10.2. Can I drive my Ford F350 with a P1000 code?
Yes, you can drive your Ford F350 with a P1000 code, but you won’t be able to pass an emissions test until the code is resolved and the OBD system is ready.
10.3. How do I clear the P1000 code on my Ford F350?
To clear the P1000 code, you need to perform a Ford drive cycle to allow the OBD system to complete its tests. Ensure there are no other underlying issues preventing readiness.
10.4. How long does it take to complete a Ford drive cycle?
A Ford drive cycle can take anywhere from 20 to 30 minutes, depending on traffic conditions and how well you follow the specified driving patterns.
10.5. What if the P1000 code returns after completing a drive cycle?
If the P1000 code returns after completing a drive cycle, there may be an underlying issue preventing the OBD system from achieving readiness. You should perform further diagnostic tests or seek professional help.
10.6. Can a faulty O2 sensor cause the P1000 code?
Yes, a faulty O2 sensor can prevent the OBD system from completing its tests and trigger the P1000 code.
10.7. How can I check the readiness status of my Ford F350’s OBD system?
You can check the readiness status of your Ford F350’s OBD system using an OBD-II scanner. The scanner will show which monitors have completed their tests and which are still pending.
10.8. Is it safe to clear trouble codes without fixing the underlying issue?
No, it is not safe to clear trouble codes without fixing the underlying issue. Clearing codes without addressing the problem will only temporarily hide the symptom and may lead to further damage.
10.9. What is the Ford IDS system, and how can it help with diagnosing the P1000 code?
The Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System) is a comprehensive diagnostic tool used by Ford dealerships and professional mechanics. It provides advanced diagnostic capabilities, including module programming, parameter reset, advanced diagnostics, and data logging, which can help identify and resolve complex issues related to the P1000 code.
10.10. Where can I find a reliable mechanic to diagnose and repair my Ford F350?
You can find a reliable mechanic to diagnose and repair your Ford F350 at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. Our experienced technicians have the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose and resolve complex issues.
Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Take Action Now
Don’t let the P1000 code keep you from enjoying your 2010 Ford F350. Whether you’re dealing with a stubborn OBD system, recurring trouble codes, or complex diagnostic issues, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help.
Contact us today for expert diagnostic services, personalized support, and cost-effective solutions. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our address is 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Let us help you get your Ford F350 back on the road and running smoothly.
Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.