The 2013 Mazda Obd2 Protocol is primarily CAN (ISO15765-4), as mandated for all US vehicles from 2008 onward; however, understanding the specific protocol can help you choose the right diagnostic tools for your vehicle. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive guidance on decoding your Mazda’s OBD2 system. With our expertise, you can accurately diagnose issues and maintain your vehicle’s optimal performance, ensuring a smooth and informed maintenance experience. Explore diagnostic tool options and Mazda-specific protocols.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Protocols
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. Why is OBD2 Important?
- 1.3. Key OBD2 Protocols
- 2. Identifying the OBD2 Protocol for Your 2013 Mazda
- 2.1. The Dominance of CAN Protocol
- 2.2. Why CAN Became the Standard
- 2.3. Practical Steps to Verify CAN Protocol on Your 2013 Mazda
- 2.4. Understanding the DLC Pinout
- 2.5. What if You’re Unsure?
- 3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scan Tool for Your 2013 Mazda
- 3.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 3.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
- 3.3. Professional-Grade Scan Tools
- 3.4. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scan Tool
- 3.5. Recommended OBD2 Scan Tools for 2013 Mazda
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings for 2013 Mazda
- 4.1. P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 4.2. P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
- 4.3. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 4.4. P0101 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
- 4.5. P0507 – Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
- 4.6. Resources for Decoding OBD2 Codes
- 5. Benefits of Understanding Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 Protocol
- 5.1. Accurate Diagnostics
- 5.2. Cost Savings
- 5.3. Preventative Maintenance
- 5.4. Informed Decision-Making
- 5.5. Empowerment
- 6. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues on Your 2013 Mazda
- 6.1. Addressing False Codes
- 6.2. Dealing with Intermittent Issues
- 6.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
- 6.4. When to Seek Professional Help
- 7. Maintaining Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 System
- 7.1. Regular Check-Ups
- 7.2. Keeping Your Scan Tool Updated
- 7.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
- 7.4. Monitoring Vehicle Performance
- 7.5. Consulting Professionals
- 8. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2013 Mazda
- 8.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 8.2. Performing Component Testing
- 8.3. Using Bi-Directional Control
- 8.4. Programming and Coding
- 8.5. Understanding Advanced Parameters
- 9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 9.1. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 9.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 9.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
- 9.4. Integration with Mobile Apps
- 9.5. Enhanced Security Measures
- 10. OBD2 and Vehicle Modifications
- 10.1. Impact of Modifications on OBD2
- 10.2. Tuning and OBD2
- 10.3. Aftermarket Parts and OBD2
- 10.4. Ensuring Compliance
- 10.5. Consulting Professionals
- 11. Resources for Learning More About OBD2
- 11.1. Online Courses
- 11.2. Workshops and Seminars
- 11.3. Books and Manuals
- 11.4. Online Forums and Communities
- 11.5. Professional Certifications
- 12. Conclusion: Mastering Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 System
- 13. FAQ: Common Questions About 2013 Mazda OBD2 Protocol
- 13.1. What does OBD2 stand for?
- 13.2. Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2013 Mazda?
- 13.3. What OBD2 protocol does a 2013 Mazda use?
- 13.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my 2013 Mazda?
- 13.5. How do I check for OBD2 codes on my 2013 Mazda?
- 13.6. What do I do if I get a P0171 code on my 2013 Mazda?
- 13.7. How often should I check my 2013 Mazda for OBD2 codes?
- 13.8. Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
- 13.9. What are the benefits of understanding my 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 system?
- 13.10. Where can I get help with OBD2 diagnostics for my 2013 Mazda?
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Protocols
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related issues. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks sold in the United States after 1996 are required to be OBD2 compliant to ensure effective monitoring of vehicle emissions. This system provides access to a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance. The OBD2 system uses a standardized 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) to communicate with diagnostic tools, making it easier to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitor various vehicle parameters.
1.2. Why is OBD2 Important?
OBD2 is crucial for several reasons:
- Emissions Control: It helps ensure vehicles meet emissions standards by monitoring the performance of the engine and emissions control systems.
- Diagnostics: It allows mechanics and vehicle owners to diagnose problems quickly and accurately.
- Standardization: The standardized interface and protocols mean that any compliant scan tool can be used on any OBD2-compliant vehicle, regardless of manufacturer.
- Preventative Maintenance: By monitoring vehicle parameters, OBD2 can help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
1.3. Key OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 systems use several communication protocols to transmit data. Here’s a brief overview:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used mainly by General Motors.
- ISO9141-2: Used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Also used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): Mandated for all US vehicles from 2008 onward and widely used in modern vehicles.
2. Identifying the OBD2 Protocol for Your 2013 Mazda
2.1. The Dominance of CAN Protocol
Since 2008, the CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol has been the standard for all vehicles sold in the United States, including the 2013 Mazda. CAN is a robust and efficient communication protocol that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other. This includes the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), and other systems.
2.2. Why CAN Became the Standard
CAN was chosen as the standard protocol due to its superior performance and reliability compared to older protocols. According to SAE International, CAN offers several advantages:
- High-Speed Communication: CAN allows for faster data transfer rates, which is essential for modern vehicles with complex electronic systems.
- Error Detection: CAN includes built-in error detection mechanisms, ensuring data integrity.
- Flexibility: CAN is a flexible protocol that can be adapted to various vehicle architectures.
2.3. Practical Steps to Verify CAN Protocol on Your 2013 Mazda
While CAN is the standard, it’s always a good idea to verify the protocol used in your specific 2013 Mazda. Here’s how you can do it:
- Check the OBD2 Port (DLC): Locate the 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Inspect the Pins: Examine the pins in the DLC. CAN protocol requires specific pins to be populated.
- Use a Scan Tool: Connect an OBD2 scan tool to the DLC and check for communication. If the scan tool successfully communicates with the vehicle, it likely uses the CAN protocol.
2.4. Understanding the DLC Pinout
The DLC pinout can provide clues about the protocol used by your 2013 Mazda. Here’s a breakdown of the key pins:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K-Line
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 16: Battery Positive
If pins 6 and 14 are present, your 2013 Mazda likely uses the CAN protocol.
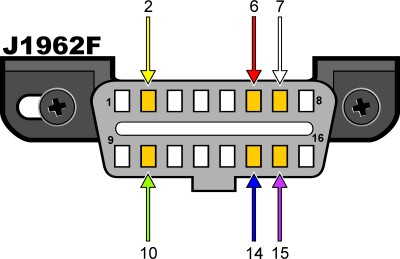 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
2.5. What if You’re Unsure?
If you’re unsure about the OBD2 protocol used in your 2013 Mazda, consult your vehicle’s repair manual or contact a professional mechanic. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, our experts can help you identify the correct protocol and recommend suitable diagnostic tools. Reach out to us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scan Tool for Your 2013 Mazda
3.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic OBD2 scanners are designed to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). They are a cost-effective option for basic diagnostics and can help you identify common issues.
Pros:
- Affordable
- Easy to use
- Reads and clears DTCs
Cons:
- Limited functionality
- May not support advanced features
3.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer a wider range of features, including live data streaming, component testing, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
Pros:
- Comprehensive diagnostics
- Live data streaming
- Component testing
Cons:
- More expensive
- Can be complex to use
3.3. Professional-Grade Scan Tools
Professional-grade scan tools are designed for use in automotive repair shops. They offer the most comprehensive features, including advanced diagnostics, programming, and access to vehicle-specific data.
Pros:
- Extensive functionality
- Access to vehicle-specific data
- Programming capabilities
Cons:
- Very expensive
- Requires specialized training
3.4. Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scan Tool
When choosing an OBD2 scan tool for your 2013 Mazda, consider the following features:
- CAN Protocol Support: Ensure the scan tool supports the CAN (ISO15765-4) protocol.
- DTC Reading and Clearing: The ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Live Data Streaming: The ability to view real-time data from the vehicle’s sensors.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Access to Mazda-specific diagnostic codes.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface that is easy to navigate.
- Software Updates: Regular software updates to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicle models.
3.5. Recommended OBD2 Scan Tools for 2013 Mazda
Here are some recommended OBD2 scan tools that are compatible with the 2013 Mazda:
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A versatile scan tool with comprehensive features.
- Launch CRP129E: An affordable scan tool with live data streaming.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A Bluetooth scan tool that works with your smartphone.
- INNOVA 3100RS: A reliable scan tool for basic diagnostics.
4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings for 2013 Mazda
4.1. P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
Meaning: This code indicates that the engine’s air-fuel mixture is too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel.
Possible Causes:
- Vacuum leak
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty or clogged fuel injectors
- Low fuel pressure
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- Check the oxygen sensor for proper operation.
- Clean or replace fuel injectors.
- Check fuel pressure.
4.2. P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
Meaning: This code indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires, meaning one or more cylinders are not firing properly.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Vacuum leak
- Low fuel pressure
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect and replace spark plugs.
- Check ignition coils for proper operation.
- Inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- Check fuel pressure.
4.3. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Meaning: This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Exhaust leak
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the catalytic converter for damage.
- Check the oxygen sensor for proper operation.
- Inspect the exhaust system for leaks.
4.4. P0101 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
Meaning: This code indicates that there is an issue with the mass air flow (MAF) sensor, which measures the amount of air entering the engine.
Possible Causes:
- Dirty or faulty MAF sensor
- Vacuum leak
- Intake air leaks
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Clean the MAF sensor.
- Inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- Check for intake air leaks.
4.5. P0507 – Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
Meaning: This code indicates that the engine’s idle speed is higher than expected.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty idle air control (IAC) valve
- Vacuum leak
- Throttle body issues
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the IAC valve for proper operation.
- Inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- Check the throttle body for issues.
4.6. Resources for Decoding OBD2 Codes
Decoding OBD2 codes can be complex, but several resources can help:
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com and AutoCodes.com offer comprehensive databases of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
- Repair Manuals: Your vehicle’s repair manual provides detailed information about OBD2 codes and troubleshooting steps.
- Professional Mechanics: Consulting a professional mechanic can provide accurate diagnostics and repairs.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance on decoding OBD2 codes and troubleshooting vehicle issues. Contact us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States or call +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
5. Benefits of Understanding Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 Protocol
5.1. Accurate Diagnostics
Knowing the correct OBD2 protocol ensures that you use the right diagnostic tools and interpret the data accurately. This leads to more precise diagnostics and effective repairs.
5.2. Cost Savings
By accurately diagnosing issues yourself, you can avoid unnecessary trips to the mechanic and save money on repairs.
5.3. Preventative Maintenance
Understanding the OBD2 system allows you to monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems before they become major issues.
5.4. Informed Decision-Making
With a clear understanding of your vehicle’s condition, you can make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
5.5. Empowerment
Taking control of your vehicle’s diagnostics empowers you to be a more proactive and informed vehicle owner.
6. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues on Your 2013 Mazda
6.1. Addressing False Codes
Sometimes, OBD2 systems can generate false codes due to sensor malfunctions or other issues. Here’s how to address them:
- Verify the Code: Use a reliable scan tool to verify the code.
- Check the Sensor: Inspect the sensor associated with the code for damage or contamination.
- Clear the Code: Clear the code and see if it returns.
- Consult a Professional: If the code persists, consult a professional mechanic.
6.2. Dealing with Intermittent Issues
Intermittent issues can be challenging to diagnose. Here are some tips for dealing with them:
- Monitor Live Data: Use a scan tool to monitor live data from the vehicle’s sensors.
- Check Wiring: Inspect wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Record Conditions: Record the conditions under which the issue occurs (e.g., temperature, driving conditions).
- Consult a Professional: If the issue persists, consult a professional mechanic.
6.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the vehicle’s operating conditions at the time a DTC was set. This information can be valuable for troubleshooting:
- Access Freeze Frame Data: Use a scan tool to access freeze frame data.
- Analyze the Data: Analyze the data to identify the conditions that triggered the DTC.
- Use the Data for Troubleshooting: Use the data to guide your troubleshooting efforts.
6.4. When to Seek Professional Help
While basic OBD2 diagnostics can be performed by vehicle owners, some issues require professional help. Consider seeking professional assistance if:
- You are unable to diagnose the issue.
- The issue is complex or requires specialized tools.
- You are uncomfortable performing the repairs yourself.
7. Maintaining Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 System
7.1. Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups of your OBD2 system can help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
7.2. Keeping Your Scan Tool Updated
Ensure that your OBD2 scan tool is updated with the latest software to ensure compatibility with your vehicle.
7.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
Address any OBD2 issues promptly to prevent further damage to your vehicle.
7.4. Monitoring Vehicle Performance
Regularly monitor your vehicle’s performance to identify any changes that may indicate a problem.
7.5. Consulting Professionals
Consult with professional mechanics for regular maintenance and diagnostics.
8. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2013 Mazda
8.1. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
Advanced OBD2 scan tools can access manufacturer-specific codes, which provide more detailed information about vehicle issues.
8.2. Performing Component Testing
Component testing allows you to test individual components of the vehicle’s systems, such as sensors and actuators.
8.3. Using Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s systems, such as activating the fuel pump or turning on the cooling fan.
8.4. Programming and Coding
Some advanced scan tools offer programming and coding capabilities, which allow you to reprogram the vehicle’s ECUs or customize vehicle settings.
8.5. Understanding Advanced Parameters
Advanced OBD2 diagnostics involve understanding various parameters such as fuel trims, ignition timing, and sensor readings.
9. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
9.1. Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters allow you to connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 system using your smartphone or tablet.
9.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics offer remote diagnostics and data logging capabilities.
9.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
AI is being used to analyze OBD2 data and provide more accurate diagnostics and troubleshooting recommendations.
9.4. Integration with Mobile Apps
OBD2 systems are increasingly being integrated with mobile apps, providing vehicle owners with real-time data and diagnostic information.
9.5. Enhanced Security Measures
Enhanced security measures are being implemented to protect OBD2 systems from cyber threats.
10. OBD2 and Vehicle Modifications
10.1. Impact of Modifications on OBD2
Vehicle modifications can impact the OBD2 system and trigger diagnostic trouble codes.
10.2. Tuning and OBD2
Tuning involves modifying the vehicle’s ECU to improve performance, which can affect the OBD2 system.
10.3. Aftermarket Parts and OBD2
Aftermarket parts can sometimes cause issues with the OBD2 system if they are not compatible with the vehicle.
10.4. Ensuring Compliance
When modifying your vehicle, ensure that the modifications comply with emissions regulations and do not negatively impact the OBD2 system.
10.5. Consulting Professionals
Consult with professional mechanics before making any modifications to your vehicle to ensure that they are done safely and correctly.
11. Resources for Learning More About OBD2
11.1. Online Courses
Online courses offer comprehensive training on OBD2 diagnostics and troubleshooting.
11.2. Workshops and Seminars
Workshops and seminars provide hands-on training on OBD2 diagnostics.
11.3. Books and Manuals
Books and manuals offer detailed information about OBD2 systems and protocols.
11.4. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities provide a platform for sharing information and asking questions about OBD2 diagnostics.
11.5. Professional Certifications
Professional certifications demonstrate your expertise in OBD2 diagnostics.
12. Conclusion: Mastering Your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 System
Understanding the OBD2 protocol of your 2013 Mazda, primarily CAN (ISO15765-4), is essential for accurate diagnostics, preventative maintenance, and informed vehicle ownership. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide the expertise and tools you need to master your vehicle’s OBD2 system. By choosing the right scan tool, understanding common codes, and staying informed about future trends, you can keep your 2013 Mazda running smoothly and efficiently.
For expert guidance on OBD2 diagnostics, tool recommendations, and troubleshooting assistance, contact us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, call +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. Let us help you take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics and maintenance!
13. FAQ: Common Questions About 2013 Mazda OBD2 Protocol
13.1. What does OBD2 stand for?
OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related issues.
13.2. Where is the OBD2 port located in a 2013 Mazda?
The OBD2 port (DLC) is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
13.3. What OBD2 protocol does a 2013 Mazda use?
The 2013 Mazda primarily uses the CAN (ISO15765-4) protocol, which is standard for all US vehicles since 2008.
13.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my 2013 Mazda?
Yes, you can use any OBD2 scanner that supports the CAN protocol, but advanced scanners may offer more features.
13.5. How do I check for OBD2 codes on my 2013 Mazda?
You can use an OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your vehicle’s computer.
13.6. What do I do if I get a P0171 code on my 2013 Mazda?
A P0171 code indicates that the engine’s air-fuel mixture is too lean. Possible causes include vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or dirty fuel injectors.
13.7. How often should I check my 2013 Mazda for OBD2 codes?
You should check for OBD2 codes whenever you notice unusual performance or warning lights on your dashboard.
13.8. Can I clear OBD2 codes myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using a scan tool, but it’s important to address the underlying issue to prevent the code from returning.
13.9. What are the benefits of understanding my 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 system?
Understanding your vehicle’s OBD2 system allows for accurate diagnostics, cost savings, preventative maintenance, and informed decision-making.
13.10. Where can I get help with OBD2 diagnostics for my 2013 Mazda?
You can get help with OBD2 diagnostics from professional mechanics, online resources, and experts at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert guidance and assistance with your 2013 Mazda’s OBD2 system. We are here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.