Understanding Bmw Obd2 Oil Pressure readings is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance and longevity, and at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide the expertise and resources to help you interpret this data effectively. By connecting an OBD2 scanner and accessing the oil pressure parameter, you can quickly identify potential issues. With the right tools and knowledge, you can proactively address engine problems before they escalate.
Contents
- 1. What is BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure and Why Does It Matter?
- 1.1 The Importance of Oil Pressure
- 1.2 OBD2 Systems: A Brief Overview
- 1.3 Why Monitor Oil Pressure Through OBD2?
- 2. Understanding BMW Oil Pressure Specifications
- 2.1 Factors Affecting Oil Pressure Specifications
- 2.2 Common BMW Oil Pressure Ranges
- 2.3 How to Find the Correct Specs for Your BMW
- 3. Tools Needed to Check BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
- 3.1 OBD2 Scanners: Types and Recommendations
- 3.2 Required Adapters and Cables
- 3.3 Software and Apps for Monitoring Oil Pressure
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
- 4.1 Preparing Your BMW for the Test
- 4.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.3 Accessing Live Data
- 4.4 Interpreting the Results
- 5. Common Issues Indicated by Abnormal Oil Pressure
- 5.1 Low Oil Pressure: Causes and Symptoms
- 5.2 High Oil Pressure: Causes and Symptoms
- 5.3 Other Potential Problems
- 6. Diagnosing and Troubleshooting BMW Oil Pressure Issues
- 6.1 Initial Inspection
- 6.2 Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnosis
- 6.3 Testing the Oil Pressure Sensor
- 6.4 Checking the Oil Pump
- 7. Repairing Common BMW Oil Pressure Problems
- 7.1 Replacing the Oil Pressure Sensor
- 7.2 Replacing the Oil Pump
- 7.3 Clearing Clogged Oil Passages
- 8. Maintaining Optimal BMW Oil Pressure
- 8.1 Regular Oil Changes
- 8.2 Using the Right Type of Oil
- 8.3 Inspecting and Replacing the Oil Filter
- 8.4 Monitoring Oil Levels
- 9. Advanced Techniques for BMW Oil Pressure Analysis
- 9.1 Data Logging and Analysis
- 9.2 Using Oscilloscopes for Sensor Testing
- 9.3 Pressure Testing with External Gauges
- 10. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Checking BMW Oil Pressure
- 10.1 Using the Wrong OBD2 Scanner
- 10.2 Incorrectly Interpreting Data
- 10.3 Neglecting Visual Inspections
- 10.4 Overlooking Other Symptoms
- 11. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in BMW Diagnostics
- 11.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
- 11.2 Expert Advice and Support
- 11.3 Training and Resources
- 11.4 Community Support
- 12. Case Studies: Real-World BMW Oil Pressure Issues
- 12.1 Case Study 1: Low Oil Pressure in a BMW 328i
- 12.2 Case Study 2: High Oil Pressure in a BMW 535i
- 12.3 Case Study 3: Intermittent Oil Pressure Issues in a BMW X5
- 13. Future Trends in BMW Diagnostics
- 13.1 Advances in OBD2 Technology
- 13.2 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 13.3 Remote Diagnostics
- 14. Conclusion: Mastering BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure Readings
- 15. FAQ: BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
- 15.1 What is normal oil pressure for a BMW?
- 15.2 How do I check my BMW’s oil pressure?
- 15.3 What does low oil pressure indicate in a BMW?
- 15.4 What does high oil pressure indicate in a BMW?
- 15.5 Can I drive my BMW with low oil pressure?
- 15.6 How often should I change the oil in my BMW?
- 15.7 What type of oil should I use in my BMW?
- 15.8 Where is the oil pressure sensor located on a BMW?
- 15.9 How do I replace the oil pressure sensor on a BMW?
- 15.10 What tools do I need to check BMW OBD2 oil pressure?
1. What is BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure and Why Does It Matter?
BMW OBD2 oil pressure refers to the data obtained from your BMW’s onboard diagnostics system regarding the oil pressure within the engine, and it matters because it provides crucial insights into the engine’s health and lubrication system. A healthy oil pressure ensures that all engine components are adequately lubricated, reducing friction and preventing wear. Monitoring the oil pressure via the OBD2 port allows you to detect potential problems early, preventing costly engine damage.
Oil pressure is the force that moves oil throughout your engine, lubricating critical components and preventing them from grinding against each other. Maintaining the correct oil pressure is crucial for engine longevity and performance.
1.1 The Importance of Oil Pressure
Maintaining proper oil pressure ensures vital engine parts receive adequate lubrication, minimizing friction and wear. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), inadequate oil pressure can lead to a 50% increase in engine wear.
1.2 OBD2 Systems: A Brief Overview
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in most vehicles since 1996 to monitor engine performance and diagnose issues. The OBD2 port allows you to access real-time data, including oil pressure readings, using a compatible scanner.
1.3 Why Monitor Oil Pressure Through OBD2?
Monitoring oil pressure through the OBD2 port offers several advantages:
- Early Detection: Identifies potential issues before they become major problems.
- Real-Time Data: Provides continuous monitoring of oil pressure during vehicle operation.
- Cost Savings: Prevents costly engine repairs by addressing problems early.
- Performance Monitoring: Helps optimize engine performance by ensuring proper lubrication.
2. Understanding BMW Oil Pressure Specifications
Understanding the specifications is critical in determining whether your BMW’s oil pressure is within the safe and optimal range. These specifications can vary depending on the engine type, model year, and driving conditions.
2.1 Factors Affecting Oil Pressure Specifications
Several factors can influence the correct oil pressure specifications for your BMW:
- Engine Type: Different engines have different oil pressure requirements.
- Model Year: Specifications can change between model years.
- Driving Conditions: Oil pressure can vary based on whether the engine is idling, cruising, or under heavy load.
2.2 Common BMW Oil Pressure Ranges
Typically, a BMW’s oil pressure should be within the following ranges:
- Idle: 10-20 PSI (pounds per square inch)
- Cruising (2,000-3,000 RPM): 30-50 PSI
- High Load: 50-75 PSI
These values are approximate and can vary. Always refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the exact specifications.
2.3 How to Find the Correct Specs for Your BMW
To find the exact oil pressure specifications for your BMW:
- Check the Service Manual: The official service manual provides the most accurate information.
- Consult a Mechanic: A qualified BMW mechanic can provide the correct specifications.
- Use Online Databases: Some online databases offer vehicle-specific information, but verify the data’s accuracy.
3. Tools Needed to Check BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
Checking the oil pressure in your BMW requires specific tools that allow you to access and interpret the data from the OBD2 system accurately.
3.1 OBD2 Scanners: Types and Recommendations
Several types of OBD2 scanners are available, each with its own features and capabilities:
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These scanners read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Advanced OBD2 Scanners: These scanners offer additional features like live data streaming, graphing, and enhanced diagnostics.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These scanners connect to your smartphone via Bluetooth and use a dedicated app to display data.
Recommendations include the following:
- For Basic Use: Autel MaxiCheck Pro
- For Advanced Use: Snap-on Solus Edge
- For Smartphone Use: BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool
3.2 Required Adapters and Cables
Ensure that you have the necessary adapters and cables to connect the OBD2 scanner to your BMW’s OBD2 port. Most scanners come with standard OBD2 connectors, but older models might require an adapter.
3.3 Software and Apps for Monitoring Oil Pressure
Several software applications and smartphone apps can be used to monitor oil pressure via the OBD2 port:
- Torque Pro (Android): A popular app with customizable dashboards and real-time data monitoring.
- OBD Fusion (iOS and Android): Offers comprehensive diagnostics and data logging.
- BimmerCode (iOS and Android): Specifically designed for BMW vehicles, allowing you to code and customize various features.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
To effectively check your BMW’s OBD2 oil pressure, follow these detailed steps to ensure accurate readings and proper interpretation.
4.1 Preparing Your BMW for the Test
Before starting the test:
- Park the Vehicle: Park your BMW on a level surface.
- Turn Off the Engine: Ensure the engine is turned off.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
4.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and wait for it to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
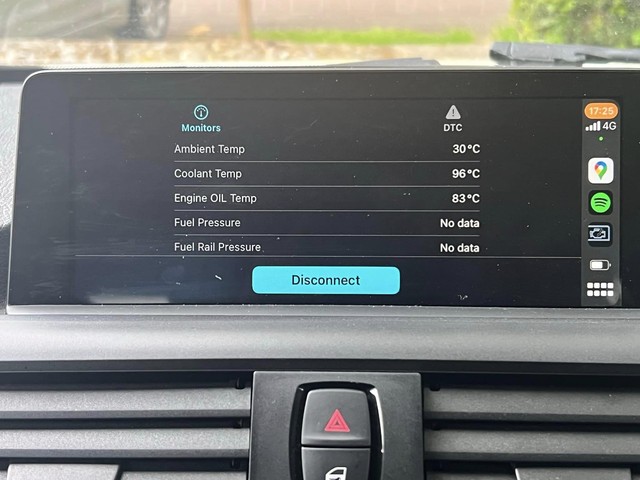 BMW OBD2 Scanner Connection
BMW OBD2 Scanner Connection
4.3 Accessing Live Data
- Navigate to Live Data: Use the scanner’s menu to navigate to the “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data” section.
- Select Oil Pressure: Look for the oil pressure parameter in the list of available data. It might be labeled as “Oil Pressure,” “Engine Oil Pressure,” or a similar term.
- Monitor the Reading: Start the engine and observe the oil pressure reading. Note the pressure at idle, during cruising (around 2,000-3,000 RPM), and under moderate acceleration.
4.4 Interpreting the Results
Compare the oil pressure readings with the specifications for your BMW model. If the readings are outside the specified range, there might be an issue with the oil pump, oil filter, pressure sensor, or other engine components.
5. Common Issues Indicated by Abnormal Oil Pressure
Abnormal oil pressure readings can indicate several potential issues within your BMW’s engine.
5.1 Low Oil Pressure: Causes and Symptoms
Low oil pressure can be caused by:
- Low Oil Level: Insufficient oil in the engine.
- Faulty Oil Pump: A worn or failing oil pump.
- Clogged Oil Filter: A blocked oil filter restricting oil flow.
- Oil Leaks: Leaks in the engine causing oil loss.
- Worn Engine Bearings: Excessive wear in engine bearings, reducing oil pressure.
Symptoms of low oil pressure include:
- Oil Pressure Warning Light: The oil pressure warning light illuminating on the dashboard.
- Engine Knocking: A knocking or ticking noise from the engine.
- Reduced Performance: Noticeable decrease in engine power and acceleration.
- Overheating: Engine overheating due to inadequate lubrication.
5.2 High Oil Pressure: Causes and Symptoms
High oil pressure can be caused by:
- Stuck Pressure Relief Valve: A malfunctioning pressure relief valve preventing proper oil flow regulation.
- Incorrect Oil Filter: Using an oil filter that is not compatible with your BMW.
- Clogged Oil Passages: Blocked oil passages restricting oil flow.
Symptoms of high oil pressure include:
- Oil Leaks: Increased pressure causing oil to leak from seals and gaskets.
- Filter Damage: Potential damage to the oil filter due to excessive pressure.
- Engine Strain: Additional strain on engine components.
5.3 Other Potential Problems
Other potential problems indicated by abnormal oil pressure readings include:
- Faulty Oil Pressure Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor providing inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring affecting the sensor signal.
- ECU Problems: Issues with the engine control unit (ECU) affecting data interpretation.
6. Diagnosing and Troubleshooting BMW Oil Pressure Issues
Effectively diagnosing and troubleshooting oil pressure problems requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying causes.
6.1 Initial Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection:
- Check Oil Level: Verify the oil level using the dipstick. Add oil if necessary.
- Inspect for Leaks: Look for any visible oil leaks around the engine, oil filter, and oil pan.
- Examine the Oil Filter: Check the oil filter for damage or blockages.
6.2 Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnosis
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use the OBD2 scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs related to the oil pressure system.
- Clear Codes and Retest: Clear the DTCs and retest to see if the codes reappear.
- Monitor Live Data: Monitor the oil pressure sensor readings in real-time to identify any inconsistencies.
6.3 Testing the Oil Pressure Sensor
- Locate the Sensor: Find the oil pressure sensor on the engine.
- Disconnect the Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Test with a Multimeter: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and voltage according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replace if Necessary: Replace the sensor if it does not meet the specified values.
6.4 Checking the Oil Pump
- Access the Oil Pump: Access the oil pump, typically located in the oil pan.
- Inspect for Damage: Check the oil pump for any visible damage or wear.
- Test the Pump’s Output: Use a pressure gauge to test the oil pump’s output pressure.
- Replace if Necessary: Replace the oil pump if it does not meet the specified pressure output.
7. Repairing Common BMW Oil Pressure Problems
Repairing common oil pressure problems involves addressing the root cause to restore proper engine lubrication.
7.1 Replacing the Oil Pressure Sensor
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Remove the old oil pressure sensor using a wrench or socket.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new oil pressure sensor, tightening it to the specified torque.
- Reconnect the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Test the System: Start the engine and use the OBD2 scanner to verify the oil pressure readings.
7.2 Replacing the Oil Pump
- Drain the Oil: Drain the engine oil into a container.
- Remove the Oil Pan: Remove the oil pan from the engine.
- Access the Oil Pump: Access the oil pump, typically located inside the oil pan.
- Remove the Old Pump: Remove the old oil pump.
- Install the New Pump: Install the new oil pump, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Reinstall the Oil Pan: Reinstall the oil pan, tightening the bolts to the specified torque.
- Refill the Oil: Refill the engine with the correct type and amount of oil.
- Test the System: Start the engine and use the OBD2 scanner to verify the oil pressure readings.
7.3 Clearing Clogged Oil Passages
- Identify the Blockage: Locate the clogged oil passages.
- Use Compressed Air: Use compressed air to blow out the blockage.
- Use a Cleaning Solvent: Use a cleaning solvent to dissolve any remaining debris.
- Reassemble the Components: Reassemble the components and ensure all connections are secure.
- Test the System: Start the engine and use the OBD2 scanner to verify the oil pressure readings.
8. Maintaining Optimal BMW Oil Pressure
Proper maintenance is essential to keep your BMW’s oil pressure within the optimal range, ensuring the engine’s longevity and performance.
8.1 Regular Oil Changes
Change the engine oil and filter at the intervals recommended by BMW. Regular oil changes prevent the buildup of sludge and contaminants that can reduce oil pressure. According to BMW’s service guidelines, oil changes should be performed every 10,000 miles or once a year, whichever comes first.
8.2 Using the Right Type of Oil
Use the correct type of oil specified for your BMW model. Using the wrong type of oil can affect oil pressure and engine performance. BMW typically recommends synthetic oils meeting the BMW LL-01 or LL-04 specifications.
8.3 Inspecting and Replacing the Oil Filter
Inspect the oil filter regularly and replace it at the recommended intervals. A clogged oil filter can restrict oil flow and reduce oil pressure. Use only high-quality oil filters that meet BMW’s specifications.
8.4 Monitoring Oil Levels
Check the oil level regularly and add oil as needed to maintain the correct level. Low oil levels can lead to low oil pressure and engine damage.
 BMW OBD2 Scanner Connection
BMW OBD2 Scanner Connection
9. Advanced Techniques for BMW Oil Pressure Analysis
For advanced users, several techniques can provide more detailed insights into your BMW’s oil pressure system.
9.1 Data Logging and Analysis
Use the OBD2 scanner to log oil pressure data over time. Analyze the data to identify any patterns or anomalies that could indicate potential problems. Software like OBD Fusion and Torque Pro allows you to log and export data for detailed analysis.
9.2 Using Oscilloscopes for Sensor Testing
An oscilloscope can be used to test the oil pressure sensor’s signal. This can provide more detailed information about the sensor’s performance than a multimeter.
9.3 Pressure Testing with External Gauges
Connect an external pressure gauge to the engine to verify the accuracy of the oil pressure sensor. This can help rule out sensor problems and identify mechanical issues.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Checking BMW Oil Pressure
Avoiding common mistakes can ensure accurate readings and prevent potential damage to your BMW’s engine.
10.1 Using the Wrong OBD2 Scanner
Using an incompatible or low-quality OBD2 scanner can result in inaccurate readings and unreliable data. Always use a scanner that is known to be compatible with BMW vehicles.
10.2 Incorrectly Interpreting Data
Misinterpreting the oil pressure readings can lead to incorrect diagnoses and unnecessary repairs. Always compare the readings with the specifications for your BMW model and consider all other factors that could affect oil pressure.
10.3 Neglecting Visual Inspections
Relying solely on OBD2 data without performing a visual inspection can lead to missed problems. Always perform a thorough visual inspection of the engine, oil filter, and oil pan to identify any visible issues.
10.4 Overlooking Other Symptoms
Ignoring other symptoms, such as engine knocking or overheating, can lead to delayed diagnoses and further engine damage. Consider all symptoms and data to make an accurate diagnosis.
11. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in BMW Diagnostics
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources and support for diagnosing and maintaining your BMW, ensuring you have the tools and knowledge to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
11.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a range of diagnostic tools compatible with BMW vehicles, allowing you to accurately read and interpret oil pressure data and other vital engine parameters.
11.2 Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians offers expert advice and support to help you diagnose and troubleshoot oil pressure problems and other engine issues. We provide detailed guidance and recommendations tailored to your specific BMW model.
11.3 Training and Resources
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers training programs and resources to help you learn how to use diagnostic tools effectively and perform basic maintenance tasks. Our resources include detailed guides, videos, and tutorials.
11.4 Community Support
Join our community of BMW enthusiasts to share your experiences, ask questions, and get support from other owners and experts. Our community forum is a valuable resource for troubleshooting problems and learning about BMW maintenance.
12. Case Studies: Real-World BMW Oil Pressure Issues
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving common BMW oil pressure problems.
12.1 Case Study 1: Low Oil Pressure in a BMW 328i
A BMW 328i owner experienced low oil pressure, indicated by the oil pressure warning light and engine knocking. Using an OBD2 scanner, the technician found no DTCs related to the oil pressure system. A visual inspection revealed a low oil level and several oil leaks. After adding oil and repairing the leaks, the oil pressure returned to normal.
12.2 Case Study 2: High Oil Pressure in a BMW 535i
A BMW 535i owner noticed oil leaking from the engine and suspected high oil pressure. Using an OBD2 scanner, the technician found no DTCs. A visual inspection revealed a damaged oil filter. Replacing the oil filter resolved the issue and stopped the oil leaks.
12.3 Case Study 3: Intermittent Oil Pressure Issues in a BMW X5
A BMW X5 owner experienced intermittent oil pressure issues. The oil pressure warning light would come on and off, and the engine would occasionally knock. Using an OBD2 scanner, the technician found a DTC related to the oil pressure sensor. Replacing the oil pressure sensor resolved the issue.
13. Future Trends in BMW Diagnostics
The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing and repairing vehicles.
13.1 Advances in OBD2 Technology
Future OBD2 systems will offer even more detailed data and advanced diagnostic capabilities. This will allow technicians to diagnose problems more quickly and accurately.
13.2 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being integrated into diagnostic tools to analyze data and provide more accurate diagnoses. These technologies can identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human technicians.
13.3 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allows technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely. This can be especially useful for owners who live in remote areas or who have difficulty bringing their vehicles to a shop.
14. Conclusion: Mastering BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure Readings
Mastering BMW OBD2 oil pressure readings is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance and longevity. By understanding the specifications, using the right tools, and following proper diagnostic procedures, you can identify and resolve oil pressure problems early, preventing costly engine damage.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to keep your BMW running smoothly. From comprehensive diagnostic tools to expert advice and training, we have everything you need to master BMW diagnostics.
Don’t wait until a small issue becomes a major problem. Take control of your BMW’s health today!
Ready to take control of your BMW’s oil pressure and overall engine health? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice, comprehensive diagnostic tools, and personalized support. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. You can also visit us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Let us help you keep your BMW running at its best.
15. FAQ: BMW OBD2 Oil Pressure
15.1 What is normal oil pressure for a BMW?
Normal oil pressure for a BMW typically ranges from 10-20 PSI at idle, 30-50 PSI during cruising (2,000-3,000 RPM), and 50-75 PSI under high load. Always refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the exact specifications.
15.2 How do I check my BMW’s oil pressure?
To check your BMW’s oil pressure, use an OBD2 scanner to access the live data stream and monitor the oil pressure parameter. Compare the readings with the specifications for your BMW model.
15.3 What does low oil pressure indicate in a BMW?
Low oil pressure in a BMW can indicate several issues, including low oil level, a faulty oil pump, a clogged oil filter, oil leaks, or worn engine bearings.
15.4 What does high oil pressure indicate in a BMW?
High oil pressure in a BMW can indicate a stuck pressure relief valve, an incorrect oil filter, or clogged oil passages.
15.5 Can I drive my BMW with low oil pressure?
Driving your BMW with low oil pressure can cause serious engine damage. It is recommended to stop driving immediately and address the issue.
15.6 How often should I change the oil in my BMW?
You should change the oil in your BMW every 10,000 miles or once a year, whichever comes first, according to BMW’s service guidelines.
15.7 What type of oil should I use in my BMW?
Use the correct type of oil specified for your BMW model. BMW typically recommends synthetic oils meeting the BMW LL-01 or LL-04 specifications.
15.8 Where is the oil pressure sensor located on a BMW?
The oil pressure sensor is typically located on the engine block, near the oil filter or oil pump. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location.
15.9 How do I replace the oil pressure sensor on a BMW?
To replace the oil pressure sensor on a BMW, disconnect the battery, remove the old sensor, install the new sensor, reconnect the connector, and reconnect the battery.
15.10 What tools do I need to check BMW OBD2 oil pressure?
To check BMW OBD2 oil pressure, you need an OBD2 scanner, the necessary adapters and cables, and software or apps for monitoring oil pressure.
