The equation for the OBD2 VIN number is a process that allows access to vehicle information, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you understand it. The process involves standardized communication protocols and data interpretation to retrieve the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) from a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. Key elements include diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data accessed via the OBD2 connector.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 VIN Number Equation
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. What is VIN?
- 1.3. Purpose of the OBD2 VIN Number Equation
- 2. Components Involved in the OBD2 VIN Number Retrieval
- 2.1. OBD2 Connector
- 2.2. Scan Tool or Diagnostic Device
- 2.3. Communication Protocols
- 2.4. Software and Applications
- 3. The Process of Retrieving the VIN via OBD2
- 3.1. Connecting the Scan Tool
- 3.2. Establishing Communication
- 3.3. Sending the Request Command
- 3.4. Receiving the Response
- 3.5. Interpreting the Data
- 4. Understanding OBD2 Modes and PIDs for VIN Retrieval
- 4.1. OBD2 Modes
- 4.2. Parameter IDs (PIDs)
- 4.3. Requesting the VIN
- 5. Practical Example: Retrieving the VIN Using a Scan Tool
- 5.1. Equipment Needed
- 5.2. Step-by-Step Guide
- 5.3. Interpreting the Results
- 6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 6.1. Communication Errors
- 6.2. Incorrect VIN Display
- 6.3. No Response from the Vehicle
- 7. Advanced Techniques for VIN Retrieval
- 7.1. Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 7.2. Accessing VIN Through Other Modules
- 7.3. Using OEM Software
- 8. Security Considerations
- 8.1. Protecting Vehicle Data
- 8.2. Preventing Unauthorized Access
- 8.3. Secure Communication Protocols
- 9. The Future of OBD and VIN Retrieval
- 9.1. Advancements in OBD Technology
- 9.2. Enhanced Security Features
- 9.3. Integration with Telematics Systems
- 10. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for OBD2 Diagnostics
- 10.1. Comprehensive Guides and Tutorials
- 10.2. Expert Support and Consultation
- 10.3. Customized Solutions for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 11. OBD2 Standards
- 12. The OBD2 Connector [SAE J1962]
- 13. OBD2 and CAN Bus [ISO 15765-4]
- 14. Transporting OBD2 Messages via ISO-TP [ISO 15765-2]
- 15. The OBD2 Diagnostic Message [SAE J1979, ISO 15031-5]
- 16. Multi-Frame Examples [ISO-TP]
- 16.1. OBD2 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- 16.2. OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- FAQ Section
- What is the OBD2 VIN number equation?
- Why is the VIN important?
- What equipment is needed to retrieve the VIN via OBD2?
- How do I connect the scan tool to the OBD2 port?
- What are the common issues during VIN retrieval?
- What are OBD2 modes and PIDs?
- How can I protect my vehicle data when using OBD2 diagnostics?
- What are the advancements in OBD technology?
- Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with OBD2 diagnostics?
- Where is the OBD2 port located in my vehicle?
1. Understanding the OBD2 VIN Number Equation
The OBD2 VIN number equation is not a mathematical formula but a process of retrieving the VIN from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system, with the MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN providing valuable insights. This equation involves standardized communication protocols and data interpretation. The VIN is a unique identifier for a vehicle, essential for accessing vehicle-specific information.
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2 is a standardized system in vehicles that provides access to diagnostic data, which is critical for identifying and resolving issues. It’s a built-in self-diagnostic system that allows extraction of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data via the OBD2 connector.
1.2. What is VIN?
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a unique code assigned to every vehicle, crucial for tracking vehicle history, registration, and diagnostics. It’s a 17-character code that includes information about the manufacturer, model, year, and place of assembly.
1.3. Purpose of the OBD2 VIN Number Equation
The primary purpose of the OBD2 VIN number equation is to allow technicians and vehicle owners to access the VIN stored in the vehicle’s computer system. This access helps in various diagnostic and informational purposes, such as:
- Verifying vehicle identity
- Retrieving vehicle specifications
- Accessing repair information
- Monitoring vehicle health
- Facilitating vehicle registration and history checks
2. Components Involved in the OBD2 VIN Number Retrieval
Several components are essential for the OBD2 VIN number retrieval, which helps to decode the VIN information more accurately.
2.1. OBD2 Connector
The OBD2 connector is a 16-pin port in the vehicle, usually located under the dashboard, serving as the interface for diagnostic tools. It’s a standardized port that allows communication between the vehicle’s computer and external diagnostic equipment.
2.2. Scan Tool or Diagnostic Device
A scan tool is used to send requests to the vehicle’s computer and interpret the responses, including the VIN. These tools range from basic handheld devices to advanced computer-based systems.
2.3. Communication Protocols
The communication protocols enable the scan tool to interact with the vehicle’s computer, including CAN (Controller Area Network), ISO 9141-2, and others. CAN bus is the most common protocol used in modern vehicles for OBD2 communication.
2.4. Software and Applications
Software and applications interpret the data received from the vehicle, which is necessary for translating raw data into readable information. They provide user interfaces for displaying the VIN and other diagnostic information.
3. The Process of Retrieving the VIN via OBD2
The process of retrieving the VIN via OBD2 involves distinct steps, which help to establish a connection and data exchange.
3.1. Connecting the Scan Tool
First, connect the scan tool to the OBD2 connector in the vehicle, ensuring a secure and stable connection. Proper connection is essential for establishing communication with the vehicle’s computer.
3.2. Establishing Communication
Turn on the ignition but do not start the engine. Then, power on the scan tool and allow it to establish communication with the vehicle’s computer, which is important for a successful data exchange. The scan tool uses specific protocols to initiate communication.
3.3. Sending the Request Command
Use the scan tool to send a specific request command to retrieve the VIN. This command typically follows the SAE J1979 standard for diagnostic test modes.
3.4. Receiving the Response
The vehicle’s computer responds by sending the VIN data back to the scan tool. This data is usually in hexadecimal format.
3.5. Interpreting the Data
The scan tool interprets the received data and displays the VIN in a readable format, which is crucial for confirming the vehicle’s identity and specifications.
4. Understanding OBD2 Modes and PIDs for VIN Retrieval
OBD2 modes and Parameter IDs (PIDs) are crucial for retrieving the VIN, with specific modes and PIDs designed for this purpose.
4.1. OBD2 Modes
OBD2 modes are diagnostic services that define the type of data being requested or accessed, enhancing the ability to retrieve VIN and other vehicle information.
- Mode 01: Request current powertrain diagnostic data
- Mode 03: Request stored diagnostic trouble codes
- Mode 09: Request vehicle information
4.2. Parameter IDs (PIDs)
Parameter IDs are codes used to request specific pieces of information within each mode, which is crucial for narrowing the request and receiving the correct data.
- PID 02 (Mode 09): Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
4.3. Requesting the VIN
To request the VIN, the scan tool sends a message with Mode 09 and PID 02. The vehicle responds with the VIN data, which the scan tool then interprets and displays.
5. Practical Example: Retrieving the VIN Using a Scan Tool
A practical example helps illustrate the process of retrieving the VIN using a scan tool, providing a step-by-step approach.
5.1. Equipment Needed
- OBD2 scan tool
- Vehicle with an OBD2 port
- Ignition key
5.2. Step-by-Step Guide
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the OBD2 port, ensuring a secure connection.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scan Tool: Turn on the scan tool and wait for it to establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer.
- Navigate to Vehicle Information: Use the scan tool’s menu to navigate to the “Vehicle Information” or “VIN Retrieval” section.
- Send the Request: Select the option to retrieve the VIN. The scan tool sends the Mode 09 PID 02 request.
- Receive and Display the VIN: The scan tool receives the VIN data from the vehicle and displays it on the screen.
5.3. Interpreting the Results
Verify that the VIN displayed by the scan tool matches the VIN on the vehicle’s dashboard or doorjamb. This ensures the accuracy of the retrieved information.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Common issues can arise during the VIN retrieval process, and troubleshooting steps can help resolve these problems effectively.
6.1. Communication Errors
- Issue: Scan tool fails to establish communication with the vehicle.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the scan tool is compatible with the vehicle.
- Check the OBD2 port for damage or debris.
- Verify the ignition is in the “ON” position.
- Try a different scan tool to rule out equipment malfunction.
6.2. Incorrect VIN Display
- Issue: Scan tool displays an incorrect or incomplete VIN.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the scan tool software is up to date.
- Try retrieving the VIN multiple times.
- Check for any error messages or codes on the scan tool.
6.3. No Response from the Vehicle
- Issue: The vehicle does not respond to the VIN request.
- Troubleshooting:
- Verify the vehicle supports OBD2 functionality.
- Check the vehicle’s computer for any faults or issues.
- Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific diagnostic steps.
7. Advanced Techniques for VIN Retrieval
Advanced techniques can be used for VIN retrieval, especially when standard methods fail, ensuring a more thorough process.
7.1. Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools offer more comprehensive features for VIN retrieval, including enhanced protocol support and deeper system access.
- Benefits:
- Support for a wider range of vehicles.
- Ability to access VIN from different modules in the vehicle.
- Advanced error detection and troubleshooting.
7.2. Accessing VIN Through Other Modules
In some cases, the VIN can be accessed through other modules in the vehicle, such as the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Transmission Control Unit (TCU).
- Procedure:
- Use the scan tool to access different modules in the vehicle.
- Look for VIN information in the module’s identification data.
- Compare the VIN from different modules to ensure consistency.
7.3. Using OEM Software
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) software provides specialized diagnostic capabilities, which may be necessary for certain vehicles.
- Advantages:
- Direct access to vehicle-specific diagnostic functions.
- Accurate and reliable VIN retrieval.
- Comprehensive diagnostic and troubleshooting support.
8. Security Considerations
Security considerations are important when retrieving the VIN via OBD2, which helps to protect vehicle data from unauthorized access.
8.1. Protecting Vehicle Data
Ensure that the scan tool and diagnostic software are secure to protect vehicle data from unauthorized access.
- Measures:
- Use reputable and secure scan tools.
- Keep diagnostic software updated with the latest security patches.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks when performing diagnostic procedures.
8.2. Preventing Unauthorized Access
Prevent unauthorized access to the vehicle’s OBD2 port to avoid potential security breaches.
- Best Practices:
- Store the vehicle in a secure location.
- Use an OBD2 port lock or cover to prevent physical access.
- Monitor the vehicle for any signs of unauthorized activity.
8.3. Secure Communication Protocols
Employ secure communication protocols to protect data transmitted between the scan tool and the vehicle.
- Recommendations:
- Use scan tools that support secure communication protocols.
- Encrypt sensitive data transmitted during diagnostic procedures.
- Regularly review and update security settings on the scan tool.
9. The Future of OBD and VIN Retrieval
The future of OBD and VIN retrieval involves technological advancements, which enhance the efficiency and security of accessing vehicle information.
9.1. Advancements in OBD Technology
Advancements in OBD technology are improving the accuracy and efficiency of VIN retrieval, and also broadening diagnostic capabilities.
- Trends:
- Wireless OBD2 adapters and mobile apps.
- Cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
- Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for predictive diagnostics.
9.2. Enhanced Security Features
Enhanced security features are being developed to protect vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access, aligning with the growing importance of cybersecurity.
- Innovations:
- Biometric authentication for scan tools.
- Secure data encryption and transmission protocols.
- Intrusion detection systems for OBD2 ports.
9.3. Integration with Telematics Systems
Integration with telematics systems is enabling remote VIN retrieval and diagnostic capabilities, which is beneficial for fleet management and vehicle monitoring.
- Benefits:
- Remote vehicle diagnostics.
- Real-time vehicle tracking and monitoring.
- Proactive maintenance alerts and scheduling.
10. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for OBD2 Diagnostics
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can be a valuable resource for mastering OBD2 diagnostics, as well as offering expert assistance and tailored solutions.
10.1. Comprehensive Guides and Tutorials
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides and tutorials on OBD2 diagnostics, which provide detailed steps for using diagnostic tools and retrieving vehicle information.
10.2. Expert Support and Consultation
Access expert support and consultation from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, which provides personalized assistance for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues, and which helps to ensure accurate VIN retrieval.
10.3. Customized Solutions for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides customized solutions for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including tailored diagnostic procedures and troubleshooting guides. This helps to ensure optimal performance and longevity of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
11. OBD2 Standards
On-board diagnostics, or OBD2, is a higher-layer protocol and comparable to other CAN-based higher-layer protocols like J1939, CANopen and NMEA 2000. The OBD2 standards specify the OBD2 connector, lower-layer protocols, and OBD2 parameter IDs (PID), and more.
The standards can be displayed in a 7-layer OSI model. Several layers are covered by both SAE and ISO standards. Generally, this reflects standards for OBD defined in USA (SAE) and EU (ISO). Several standards are almost technically equivalent, for example SAE J1979 vs. ISO 15031-5 and SAE J1962 vs. ISO 15031-3.
12. The OBD2 Connector [SAE J1962]
The 16-pin OBD2 connector lets you access data from your car easily and is specified in the standard SAE J1962 / ISO 15031-3. In the illustration is an example of a Type A OBD2 pin connector (also sometimes referred to as the Data Link Connector, DLC). A few things to note:
- The connector is near your steering wheel
- Pin 16 supplies battery power (often while the ignition is off)
- The OBD2 pinout depends on the communication protocol
- The most common lower-layer protocol is CAN bus, meaning that pins 6 (CAN-H) and 14 (CAN-L) will typically be connected
13. OBD2 and CAN Bus [ISO 15765-4]
Since 2008, CAN bus has been the mandatory lower-layer protocol for OBD2 in all cars sold in the US as per ISO 15765. ISO 15765-4 (aka Diagnostics over CAN or DoCAN) refers to a set of restrictions applied to the CAN standard (ISO 11898). Specifically, it standardizes the CAN interface for test equipment with focus on the physical, data link and network layer:
- The CAN bus bit-rate must be either 250K or 500K
- The CAN IDs can be 11-bit or 29-bit
- Specific CAN IDs are used for OBD requests/responses
- The diagnostic CAN frame data length must be 8 bytes
- The OBD2 adapter cable must be max 5 meters
14. Transporting OBD2 Messages via ISO-TP [ISO 15765-2]
All OBD2 data is communicated on the CAN bus through a transport protocol called ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2). This enables communication of payloads that exceed 8 bytes. This is necessary in OBD2 e.g. when extracting the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). ISO 15765-2 enables segmentation, flow control and reassembly.
15. The OBD2 Diagnostic Message [SAE J1979, ISO 15031-5]
To better understand OBD2 on CAN, consider a raw ‘Single Frame’ OBD2 CAN message. In simplified terms, an OBD2 message is comprised of an identifier, data length (PCI field) and data. The data is split in Mode, parameter ID (PID) and data bytes.
Before covering each part of the OBD2 message, consider this example request/response for the parameter ‘Vehicle Speed’. Here, an external tool sends a request message to the car with CAN ID 0x7DF and 2 payload bytes: Mode 0x01 and PID 0x0D. The car responds via CAN ID 0x7E8 and 3 payload bytes, including the value of Vehicle Speed in the 4th byte, 0x32 (50 in decimal form). By looking up the decoding rules for OBD2 PID 0x0D we determine that the physical value is 50 km/h.
16. Multi-Frame Examples [ISO-TP]
All OBD2 data is communicated using the ISO-TP (transport protocol) as per ISO 15765-2. Most of the examples so far reflect single-frame communication. Multi-frame OBD2 communication requires flow control frames.
16.1. OBD2 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is often relevant to telematics, diagnostics and more. To extract the Vehicle Identification Number from a vehicle using OBD2 requests, you use mode 0x09 and PID 0x02. The tester tool sends a Single Frame request with the PCI field (0x02), request service identifier (0x09) and PID (0x02).
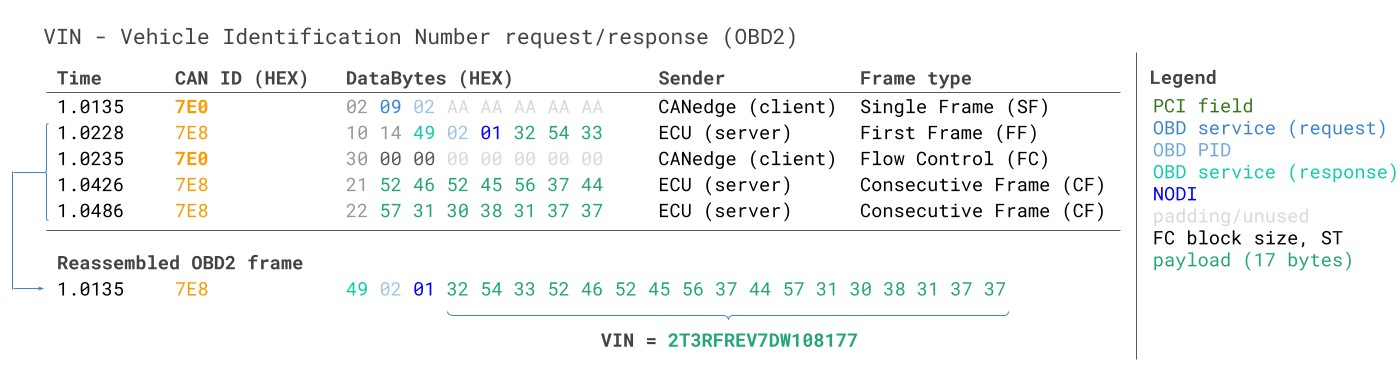 VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
16.2. OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
You can use OBD2 to request emissions-related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from using mode 0x03, i.e. ‘Show stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes’. No PID is included in the request. The targeted ECU(s) will then respond with the number of DTCs they have stored (including potentially 0 if they have none), with each DTC taking up 2 data bytes. As a result, multi-frame responses are necessary when more than 2 DTCs are stored.
FAQ Section
What is the OBD2 VIN number equation?
The OBD2 VIN number equation refers to the process of retrieving a vehicle’s VIN from its onboard diagnostic system using standardized communication protocols. It’s not a mathematical equation but rather a sequence of steps involving connecting a scan tool to the OBD2 port, sending a request command, and interpreting the response to display the VIN.
Why is the VIN important?
The VIN is important because it serves as a unique identifier for a vehicle, providing information about its manufacturer, model, year, and other specifications. It is used for vehicle registration, tracking vehicle history, accessing repair information, and verifying vehicle identity.
What equipment is needed to retrieve the VIN via OBD2?
To retrieve the VIN via OBD2, you need an OBD2 scan tool, a vehicle with an OBD2 port, and the ignition key. The scan tool is connected to the OBD2 port, and the ignition is turned on to establish communication with the vehicle’s computer.
How do I connect the scan tool to the OBD2 port?
To connect the scan tool, simply plug it into the 16-pin OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard. Ensure a secure and stable connection to establish communication with the vehicle’s computer.
What are the common issues during VIN retrieval?
Common issues during VIN retrieval include communication errors (scan tool failing to connect), incorrect VIN display, and no response from the vehicle. These issues can be resolved by ensuring compatibility, checking connections, updating software, and verifying vehicle support for OBD2 functionality.
What are OBD2 modes and PIDs?
OBD2 modes are diagnostic services that define the type of data being requested, such as current data or diagnostic trouble codes. Parameter IDs (PIDs) are codes used to request specific pieces of information within each mode, allowing you to target specific data like the VIN.
How can I protect my vehicle data when using OBD2 diagnostics?
To protect your vehicle data, use reputable and secure scan tools, keep diagnostic software updated with the latest security patches, avoid using public Wi-Fi networks during diagnostic procedures, and prevent unauthorized access to the OBD2 port.
What are the advancements in OBD technology?
Advancements in OBD technology include wireless OBD2 adapters, cloud-based diagnostic platforms, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive diagnostics. These advancements enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of vehicle diagnostics.
Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with OBD2 diagnostics?
Yes, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive guides and tutorials on OBD2 diagnostics, expert support and consultation, and customized solutions for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. This helps ensure accurate VIN retrieval and effective troubleshooting of vehicle issues.
Where is the OBD2 port located in my vehicle?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It may be near the steering column or in the center console area. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
Understanding the OBD2 VIN number equation is essential for accessing critical vehicle information, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides valuable resources and support for mastering this process. By following the steps outlined and leveraging the available tools, you can effectively retrieve and interpret the VIN, and ensure the security of your vehicle data.
Need assistance with OBD2 diagnostics or VIN retrieval? Contact us today for expert guidance and tailored solutions at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
