Is your Honda Accord 7 (2003-2007) triggering a check engine light? Understanding the Honda Accord 7 Obd2 system is crucial for accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the expertise you need. This guide simplifies the complexities of OBD2, offering solutions for identifying and resolving issues, ensuring your Accord runs smoothly and efficiently while exploring enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Unlock hidden potential with advanced OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools, and delve into automotive diagnostics and vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What is Honda Accord 7 OBD2 and Why Is It Important?
- 1.1 How Does OBD2 Work in a Honda Accord 7?
- 1.2 Benefits of Understanding Your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 System
- 2. Decoding the Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Connector and Protocol
- 2.1 Locating the OBD2 Connector in Your Honda Accord 7
- 2.2 Understanding the OBD2 Connector Pinout
- 2.3 Communication Protocols Used by Honda Accord 7 OBD2
- 3. Essential Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.1 Common Engine-Related DTCs for Honda Accord 7
- 3.2 Transmission-Related DTCs
- 3.3 ABS and SRS DTCs
- 3.4 Decoding Honda-Specific DTCs
- 4. Top OBD2 Scanners for Your Honda Accord 7
- 4.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners for Code Reading and Clearing
- 4.2 Mid-Range Scanners for Advanced Diagnostics
- 4.3 Professional-Grade Scanners for Comprehensive Analysis
- 4.4 Comparing Popular OBD2 Scanner Brands: Autel, Launch, Innova
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your Honda Accord 7
- 5.1 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to the Honda Accord 7
- 5.2 Reading and Interpreting DTCs
- 5.3 Clearing Codes and Understanding the Implications
- 6. Advanced Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
- 6.1 Live Data Streaming and Analysis
- 6.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 6.3 O2 Sensor Testing
- 6.4 EVAP System Testing
- 6.5 Bi-Directional Control (Actuator Testing)
- 7. Honda Accord 7 Specific OBD2 Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
- 7.1 Addressing Common Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Issues
- 7.2 Diagnosing Intermittent Problems
- 7.3 Using Honda Service Manuals and Technical Resources
- 7.4 Utilizing Online Forums and Communities for Honda Accord 7 Owners
- 8. Maintaining Your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 System for Optimal Performance
- 8.1 Regular Vehicle Maintenance and Its Impact on OBD2 Performance
- 8.2 Inspecting and Cleaning Sensors
- 8.3 Checking Wiring and Connectors for Damage
- 8.4 Performing Regular OBD2 Scans for Preventative Maintenance
- 9. When to Seek Professional Help with Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostics
- 9.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues Beyond DIY Capabilities
- 9.2 Safety-Critical Systems Like ABS and SRS
- 9.3 Engine and Transmission Internal Problems
- 9.4 Emissions-Related Issues Requiring Specialized Equipment
- 10. The Future of OBD2 and Honda Accord 7 Diagnostics
- 10.1 Advancements in OBD2 Technology and Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2 The Role of Telematics and Connected Car Technologies
- 10.3 Potential for Over-the-Air Updates and Remote Diagnostics
- FAQ: Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostics
- 1. What does OBD2 mean for my Honda Accord 7?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 port located on my Honda Accord 7?
- 3. How do I read the OBD2 codes on my Honda Accord 7?
- 4. What are some common OBD2 codes for the Honda Accord 7?
- 5. Can I clear the OBD2 codes on my Honda Accord 7 myself?
- 6. What is live data streaming, and how can it help diagnose my Honda Accord 7?
- 7. What’s the difference between a basic and an advanced OBD2 scanner?
- 8. When should I seek professional help for OBD2 diagnostics on my Honda Accord 7?
- 9. How can regular maintenance impact the OBD2 system’s performance in my Honda Accord 7?
- 10. Are there any Honda-specific OBD2 codes I should be aware of?
1. What is Honda Accord 7 OBD2 and Why Is It Important?
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system in your Honda Accord 7 is a sophisticated network that monitors various engine and vehicle parameters. It’s designed to detect malfunctions, reduce emissions, and provide valuable diagnostic information to technicians and car owners. Understanding your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 system can save you time and money by allowing you to identify potential problems early and make informed repair decisions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been mandated in all cars sold in the US since 1996 to standardize emissions monitoring and diagnostics.
1.1 How Does OBD2 Work in a Honda Accord 7?
The OBD2 system in your Honda Accord 7 utilizes sensors throughout the vehicle to monitor engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. When a sensor detects a problem, it sends a signal to the car’s computer (ECU), which then stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). This code can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner, providing valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
1.2 Benefits of Understanding Your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 System
Understanding your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 system offers several key benefits:
- Early Problem Detection: Identify potential issues before they lead to costly repairs.
- Informed Repair Decisions: Make informed decisions about repairs based on accurate diagnostic information.
- Cost Savings: Potentially save money by performing simple repairs yourself.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Address issues that can negatively impact fuel economy.
- Reduced Emissions: Ensure your vehicle meets emissions standards.
2. Decoding the Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Connector and Protocol
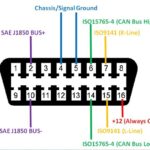
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin port located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of your Honda Accord 7. This port allows you to connect an OBD2 scanner to access diagnostic information stored in the vehicle’s computer. The Honda Accord 7 utilizes the SAE J1850 PWM or ISO 9141-2 communication protocol for OBD2 data transfer.
2.1 Locating the OBD2 Connector in Your Honda Accord 7
The OBD2 connector is typically located beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. You may need to look under the steering column or near the center console. Consult your owner’s manual for the precise location.
2.2 Understanding the OBD2 Connector Pinout
The OBD2 connector has a standardized pinout, with each pin serving a specific purpose. Some key pins include:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K-Line (communication)
- Pin 16: Battery Power (+12V)
2.3 Communication Protocols Used by Honda Accord 7 OBD2
The Honda Accord 7 typically uses the SAE J1850 PWM or ISO 9141-2 communication protocol. The specific protocol may vary depending on the model year and engine type. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or an online database to confirm the correct protocol for your vehicle.
3. Essential Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes stored by the vehicle’s computer when a fault is detected. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. Here are some common Honda Accord 7 OBD2 DTCs:
3.1 Common Engine-Related DTCs for Honda Accord 7
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issues, clogged fuel filter |
| P0172 | System Too Rich (Bank 1) | Faulty O2 sensor, fuel injector issues, high fuel pressure, faulty coolant temperature sensor |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0325 | Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) | Faulty knock sensor, wiring issues |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty O2 sensors |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Insufficient Flow Detected | Clogged EGR valve, vacuum leaks, faulty EGR solenoid |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty O2 sensor, wiring issues |
| P0441 | Evaporative Emission Control System Incorrect Purge Flow | Faulty purge valve, vacuum leaks, clogged EVAP lines |
| P0455 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak) | Loose gas cap, cracked EVAP lines, faulty purge valve, faulty vent valve |
3.2 Transmission-Related DTCs
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Internal transmission issues, faulty solenoids, wiring problems, low transmission fluid |
| P0715 | Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty input speed sensor, wiring issues |
| P0720 | Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty output speed sensor, wiring issues |
| P0730 | Incorrect Gear Ratio | Internal transmission damage, low transmission fluid, faulty solenoids |
| P0740 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty torque converter, faulty solenoid, wiring issues, low transmission fluid |
| P0753 | Shift Solenoid A Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues |
| P0758 | Shift Solenoid B Electrical | Faulty shift solenoid, wiring issues |
3.3 ABS and SRS DTCs
These codes typically require specialized diagnostic tools to read and interpret. Common issues can include:
- ABS: Wheel speed sensor faults, hydraulic pump issues, ECU problems.
- SRS: Airbag sensor faults, wiring issues, airbag module problems.
3.4 Decoding Honda-Specific DTCs
Honda uses some manufacturer-specific DTCs in addition to the standard OBD2 codes. These codes often provide more detailed information about the specific problem. Refer to a Honda service manual or a comprehensive OBD2 database for decoding these codes.
4. Top OBD2 Scanners for Your Honda Accord 7
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner is essential for effective diagnostics. Here are some top options for your Honda Accord 7, categorized by functionality and price:
4.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners for Code Reading and Clearing
These scanners are ideal for reading and clearing basic DTCs and performing simple diagnostics:
- Autel AutoLink AL319: A popular and affordable option for basic code reading and clearing.
- Foxwell NT301: A user-friendly scanner with a clear display and the ability to read and clear codes.
- Innova 3020rs: A reliable scanner that provides basic diagnostic information.
4.2 Mid-Range Scanners for Advanced Diagnostics
These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming, component testing, and some bi-directional control:
- Autel MaxiCheck MX808: A versatile scanner with advanced diagnostic capabilities and a user-friendly interface.
- LAUNCH CRP129E: A feature-rich scanner with live data streaming, special functions, and the ability to graph data.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A smartphone-based scanner that provides comprehensive diagnostic information and access to repair databases.
4.3 Professional-Grade Scanners for Comprehensive Analysis
These scanners are designed for professional technicians and offer the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced bi-directional control, programming, and coding:
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: A powerful scanner with advanced diagnostic functions and wireless connectivity.
- Snap-on Zeus: A high-end scanner with comprehensive coverage and advanced features.
- LAUNCH X431 V+: A professional-grade scanner with a wide range of diagnostic capabilities.
4.4 Comparing Popular OBD2 Scanner Brands: Autel, Launch, Innova
| Feature | Autel | Launch | Innova |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Range | Wide range, from affordable to high-end | Wide range, from affordable to high-end | Primarily focuses on affordable options |
| Functionality | Comprehensive diagnostics, advanced features, user-friendly interface | Comprehensive diagnostics, advanced features, wide vehicle coverage | Basic code reading and clearing, user-friendly interface |
| Vehicle Coverage | Extensive coverage of domestic, Asian, and European vehicles | Extensive coverage of domestic, Asian, and European vehicles | Good coverage of domestic and some Asian vehicles |
| Target Audience | DIYers, enthusiasts, and professional technicians | DIYers, enthusiasts, and professional technicians | DIYers and those seeking basic diagnostics |
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your Honda Accord 7
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to diagnose your Honda Accord 7:
- Locate the OBD2 Connector: Find the 16-pin OBD2 connector under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the connector.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner.
- Select Honda/Acura: Navigate to the vehicle selection menu and choose “Honda” or “Acura.”
- Read Codes: Select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option to retrieve stored DTCs.
- Record the Codes: Write down the DTCs and their descriptions.
- Research the Codes: Use a reliable online database or repair manual to research the meaning of each code.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If you have addressed the underlying issue, you can select the “Clear Codes” option to reset the system.
- Verify the Repair: After clearing the codes, start the engine and drive the vehicle to see if the codes reappear. If they do, further diagnosis and repair are necessary.
5.1 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to the Honda Accord 7
Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 connector. A loose connection can result in inaccurate readings or communication errors.
5.2 Reading and Interpreting DTCs
Carefully read and record all DTCs and their descriptions. Use a reliable source to interpret the codes accurately. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can provide assistance in decoding complex codes.
5.3 Clearing Codes and Understanding the Implications
Clearing codes can be helpful after a repair, but it’s important to understand the implications. Clearing codes will erase the stored diagnostic information, which can make it more difficult to diagnose intermittent problems. Only clear codes after you have addressed the underlying issue.
6. Advanced Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
Beyond basic code reading, the OBD2 system offers several advanced functions that can aid in diagnosis and repair:
6.1 Live Data Streaming and Analysis
Live data streaming allows you to monitor various engine parameters in real-time, such as:
- Engine RPM
- Coolant Temperature
- O2 Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim
- MAF Sensor Readings
Analyzing this data can help you identify problems that may not trigger a DTC.
6.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of engine parameters at the moment a DTC is stored. This information can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the fault.
6.3 O2 Sensor Testing
The OBD2 system allows you to test the performance of the O2 sensors, which are critical for fuel efficiency and emissions control.
6.4 EVAP System Testing
You can use an OBD2 scanner to perform EVAP system tests, which can help you identify leaks and other problems in the evaporative emissions control system.
6.5 Bi-Directional Control (Actuator Testing)
Some advanced OBD2 scanners offer bi-directional control, which allows you to activate and test various components, such as:
- Fuel Injectors
- EGR Valve
- IAC Valve
This capability can be invaluable for diagnosing component failures.
7. Honda Accord 7 Specific OBD2 Troubleshooting Tips and Tricks
Here are some troubleshooting tips specific to the Honda Accord 7:
7.1 Addressing Common Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Issues
- Misfires (P0300-P0304): Check spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, and valve adjustment.
- O2 Sensor Codes (P0130-P0141): Inspect O2 sensors for damage and proper function.
- Catalytic Converter Codes (P0420): Check for exhaust leaks and ensure O2 sensors are functioning correctly before replacing the catalytic converter.
- EGR Codes (P0401): Clean or replace the EGR valve and inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- EVAP Codes (P0440 series): Check the gas cap, purge valve, and vent valve for proper function.
7.2 Diagnosing Intermittent Problems
Intermittent problems can be challenging to diagnose. Use live data streaming and freeze frame data to try to capture the conditions that trigger the fault. Thoroughly inspect wiring and connectors for corrosion or damage.
7.3 Using Honda Service Manuals and Technical Resources
Honda service manuals and technical resources provide valuable information about specific diagnostic procedures and repair techniques for your Honda Accord 7.
7.4 Utilizing Online Forums and Communities for Honda Accord 7 Owners
Online forums and communities can be a valuable resource for sharing information and troubleshooting tips with other Honda Accord 7 owners.
8. Maintaining Your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 System for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your Honda Accord 7 OBD2 system functioning properly:
8.1 Regular Vehicle Maintenance and Its Impact on OBD2 Performance
- Oil Changes: Maintain regular oil changes to ensure proper engine lubrication and prevent sensor contamination.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommended interval to prevent misfires.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper airflow and prevent MAF sensor contamination.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter to ensure clean fuel delivery and prevent fuel injector clogging.
- O2 Sensor Replacement: Replace O2 sensors according to the manufacturer’s recommended interval to maintain optimal fuel efficiency and emissions control.
8.2 Inspecting and Cleaning Sensors
Regularly inspect and clean sensors such as the MAF sensor, IAT sensor, and throttle position sensor to ensure accurate readings.
8.3 Checking Wiring and Connectors for Damage
Inspect wiring and connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Repair or replace damaged wiring and connectors as needed.
8.4 Performing Regular OBD2 Scans for Preventative Maintenance
Perform regular OBD2 scans to check for stored DTCs and identify potential problems early.
9. When to Seek Professional Help with Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostics
While many OBD2 issues can be resolved with DIY diagnostics and repairs, there are times when seeking professional help is necessary:
9.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues Beyond DIY Capabilities
If you are unable to diagnose the problem using basic OBD2 tools and troubleshooting techniques, it’s best to seek professional help.
9.2 Safety-Critical Systems Like ABS and SRS
Diagnosis and repair of safety-critical systems like ABS and SRS should be performed by qualified technicians.
9.3 Engine and Transmission Internal Problems
Internal engine and transmission problems often require specialized tools and expertise.
9.4 Emissions-Related Issues Requiring Specialized Equipment
Some emissions-related issues may require specialized equipment for testing and repair.
10. The Future of OBD2 and Honda Accord 7 Diagnostics
The future of OBD2 diagnostics is evolving rapidly with advancements in technology:
10.1 Advancements in OBD2 Technology and Diagnostic Tools
- Wireless OBD2 Scanners: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enabled scanners offer greater flexibility and convenience.
- Smartphone-Based Diagnostics: Smartphone apps and OBD2 adapters provide accessible and affordable diagnostic solutions.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based platforms offer advanced data analysis, remote diagnostics, and access to repair databases.
10.2 The Role of Telematics and Connected Car Technologies
Telematics and connected car technologies are integrating OBD2 data to provide proactive maintenance alerts, remote diagnostics, and improved vehicle performance.
10.3 Potential for Over-the-Air Updates and Remote Diagnostics
Over-the-air updates and remote diagnostics offer the potential to improve vehicle performance, address software glitches, and provide remote assistance.
Understanding the Honda Accord 7 OBD2 system empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and repair needs. With the right tools and knowledge, you can diagnose problems early, make informed decisions, and keep your Accord running smoothly for years to come. For expert guidance and support, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today.
Are you facing persistent OBD2 issues with your Honda Accord 7 and need expert advice? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for professional diagnostics, guidance on advanced scanner features, and personalized troubleshooting tips. Reach us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you keep your Honda Accord 7 running at its best! Unlock the potential of your vehicle diagnostics, explore car maintenance solutions, and embrace automotive technology with our expert assistance.
FAQ: Honda Accord 7 OBD2 Diagnostics
1. What does OBD2 mean for my Honda Accord 7?
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system that monitors your Honda Accord 7’s engine and emissions. It helps identify potential issues by storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that can be read with a scanner.
2. Where is the OBD2 port located on my Honda Accord 7?
The OBD2 port is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, often near the steering column or center console.
3. How do I read the OBD2 codes on my Honda Accord 7?
You’ll need an OBD2 scanner. Plug it into the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored DTCs.
4. What are some common OBD2 codes for the Honda Accord 7?
Common codes include P0300 (Random Misfire), P0171 (System Too Lean), P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold), and P0401 (EGR Insufficient Flow).
5. Can I clear the OBD2 codes on my Honda Accord 7 myself?
Yes, using an OBD2 scanner, you can clear the codes. However, it’s essential to address the underlying issue first, as the codes may reappear if the problem persists.
6. What is live data streaming, and how can it help diagnose my Honda Accord 7?
Live data streaming allows you to monitor engine parameters in real-time, such as RPM, coolant temperature, and O2 sensor readings, helping you identify issues that may not trigger a specific DTC.
7. What’s the difference between a basic and an advanced OBD2 scanner?
Basic scanners read and clear codes. Advanced scanners offer features like live data streaming, component testing, and bi-directional control for more comprehensive diagnostics.
8. When should I seek professional help for OBD2 diagnostics on my Honda Accord 7?
Seek professional help if you’re unable to diagnose the problem, dealing with safety-critical systems like ABS or SRS, or suspect internal engine/transmission issues.
9. How can regular maintenance impact the OBD2 system’s performance in my Honda Accord 7?
Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, spark plug replacements, and air filter replacements, ensures optimal engine performance and prevents sensor contamination, leading to more accurate OBD2 readings.
10. Are there any Honda-specific OBD2 codes I should be aware of?
Yes, Honda uses some manufacturer-specific DTCs in addition to standard OBD2 codes. Refer to a Honda service manual or a comprehensive OBD2 database for decoding these codes.