Determining if your car is OBD2 compliant is crucial for diagnostics and maintenance; this means your vehicle adheres to the standardized On-Board Diagnostics system, version 2. This article from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN will explore the indicators, regulations, and practical tips to help you ascertain your vehicle’s compatibility, ensuring you can effectively use diagnostic tools and services. Knowing your car’s OBD2 compliance unlocks access to valuable data for vehicle health monitoring and potential issue resolution, which can improve vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Compliance
- 2. Regulatory Requirements for OBD2 Compliance
- 3. Quick Ways to Check for OBD2 Compliance
- 4. Decoding the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
- 5. Identifying the Standardized 16-Pin Connector
- 6. What If My Car Has a 16-Pin Connector But Isn’t OBD2 Compliant?
- 7. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Confirm Compliance
- 8. OBD2 Compliance by Country and Model Year
- 9. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
- 10. OBD2 vs. EOBD vs. JOBD: What’s the Difference?
- 11. Benefits of Using OBD2 Diagnostic Tools
- 12. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 13. How to Use OBD2 Data for Vehicle Maintenance
- 14. Opening Hidden Features on Mercedes Using OBD2
- 15. Choosing the Right OBD2 Tool for Your Needs
- 16. Maintaining OBD2 Compliance Over Time
- 17. Resources for Further Learning About OBD2
- 18. The Future of OBD: What’s Next?
- 19. Legal and Ethical Considerations for OBD2 Use
- 20. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Compliance
1. Understanding OBD2 Compliance
OBD2 compliance refers to a vehicle’s adherence to the On-Board Diagnostics, Second Generation (OBD2) standard. This standard was introduced in the United States in 1996 and later adopted by other countries, including Europe (EOBD) and Japan (JOBD). Its primary purpose is to monitor the performance of a vehicle’s engine and emissions control systems, providing valuable data for diagnosing issues and ensuring environmental regulations are met.
- What is OBD2? OBD2 is a standardized system that allows access to a vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) and other modules through a universal diagnostic connector. This connector, typically located under the dashboard, enables technicians and vehicle owners to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform various tests.
- Why is OBD2 compliance important? OBD2 compliance ensures that a vehicle can be easily diagnosed using standard diagnostic tools, regardless of its make or model. This standardization simplifies the diagnostic process, reduces repair costs, and helps maintain vehicle performance and longevity.
- Global adoption of OBD2: While the United States was the first country to mandate OBD2, other regions, including Europe and Asia, have adopted similar standards. For example, EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics) is the European equivalent of OBD2, while JOBD (Japanese On-Board Diagnostics) is used in Japan.
2. Regulatory Requirements for OBD2 Compliance
Understanding the regulatory requirements for OBD2 compliance is essential for determining if your vehicle meets the necessary standards. These regulations vary by region and model year, so it’s crucial to know the specific requirements for your vehicle’s country of sale.
- United States: In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandated that all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the country must be OBD2 compliant starting with the 1996 model year. This regulation ensures that all vehicles meet certain emissions standards and can be easily diagnosed using standard OBD2 tools.
- European Union: The European Union introduced EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics) regulations, which are similar to OBD2. For gasoline vehicles, EOBD compliance was required starting with the 2001 model year, while for diesel vehicles, it was required starting with the 2004 model year.
- Other countries: Many other countries have also adopted OBD2 or similar standards. Canada, for example, requires OBD2 compliance for vehicles manufactured for sale in the country starting with the 1998 model year. Australia requires OBD2 compliance for gasoline vehicles starting with the 2006 model year and diesel vehicles starting with the 2007 model year.
3. Quick Ways to Check for OBD2 Compliance
If you’re unsure whether your car is OBD2 compliant, there are several quick ways to check. These methods involve visually inspecting your vehicle, checking the owner’s manual, and consulting with automotive professionals.
- Check the vehicle’s manual: The easiest way to determine if your car is OBD2 compliant is to check the owner’s manual. The manual should state whether the vehicle meets OBD2 standards and provide information on the location of the diagnostic connector.
- Look for the OBD2 port: The OBD2 port is a standardized 16-pin connector typically located under the dashboard, within easy reach of the driver. If you can find this port in your vehicle, it’s a good indication that it is OBD2 compliant.
- Check the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) label: The VECI label, usually found under the hood, contains information about the vehicle’s emission control systems and whether it meets OBD2 standards. Look for a statement on the label that indicates OBD2 compliance.
 Vehicle Emission Control Information Label
Vehicle Emission Control Information Label
4. Decoding the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
The Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) label provides crucial details about your vehicle’s emission control systems and OBD2 compliance. Understanding how to read this label can help you quickly determine if your car meets the necessary standards.
- Location of the VECI label: The VECI label is typically located under the hood, often on the underside of the hood itself or on a nearby engine component.
- Key information on the label: The VECI label contains several key pieces of information, including:
- Vehicle model year: This indicates the year the vehicle was manufactured.
- Engine family: This identifies the specific engine used in the vehicle.
- Emission control systems: This lists the various emission control systems used in the vehicle, such as the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors.
- OBD2 compliance statement: This statement explicitly states whether the vehicle meets OBD2 standards. Look for phrases like “OBD2 Certified” or “Meets EPA OBD2 Requirements.”
- Interpreting the label: To determine if your vehicle is OBD2 compliant, look for the OBD2 compliance statement on the VECI label. If the label states that the vehicle meets OBD2 standards, it is likely OBD2 compliant.
5. Identifying the Standardized 16-Pin Connector
The standardized 16-pin connector, also known as the Data Link Connector (DLC), is a key component of the OBD2 system. Identifying this connector in your vehicle is a strong indicator of OBD2 compliance.
- Location of the connector: The DLC is typically located under the dashboard, within easy reach of the driver. Common locations include near the steering column, in the center console, or in the glove compartment.
- Appearance of the connector: The DLC is a D-shaped, 16-pin connector with two rows of eight pins each. It is designed to be a universal connector, allowing standard OBD2 tools to be easily connected.
- Verifying the pin configuration: While the DLC is a standardized connector, some manufacturers may use non-standard pin configurations in non-OBD2 compliant vehicles. To verify the pin configuration, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a service manual.
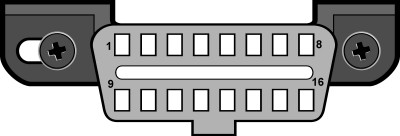 J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A
J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A
6. What If My Car Has a 16-Pin Connector But Isn’t OBD2 Compliant?
It’s possible for a car to have a 16-pin connector without being fully OBD2 compliant. This is because some manufacturers used the 16-pin connector before the OBD2 standard was fully implemented.
- Non-OBD2 compliant 16-pin connectors: Some European and Asian manufacturers equipped their vehicles with D-shaped 16-pin connectors long before they began installing OBD2 systems. These connectors may not fully conform to the SAE J1979 standard.
- How to identify a non-compliant connector: One way to identify a non-compliant connector is to compare it to the standard J1962 connector. Look for differences in the shape and configuration of the connector.
- What to do if your car has a non-compliant connector: If your car has a non-compliant connector, you may not be able to use standard OBD2 tools to diagnose it. In this case, you may need to use a specialized diagnostic tool or consult with a qualified technician.
7. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Confirm Compliance
One of the most reliable ways to confirm OBD2 compliance is to use an OBD2 scanner. These scanners plug into the DLC and communicate with the vehicle’s ECU to retrieve diagnostic information.
- How to use an OBD2 scanner: To use an OBD2 scanner, simply plug it into the DLC and turn on the ignition. The scanner will then attempt to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Interpreting the scanner’s results: If the scanner is able to successfully communicate with the ECU and retrieve diagnostic information, it’s a strong indication that the vehicle is OBD2 compliant. If the scanner is unable to communicate with the ECU, it may indicate that the vehicle is not OBD2 compliant or that there is a problem with the scanner or the vehicle’s ECU.
- Recommended OBD2 scanners: There are many different OBD2 scanners available on the market, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. Some popular OBD2 scanners include the BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool, the Autel MaxiCOM MK808, and the Bosch ADS 625X.
8. OBD2 Compliance by Country and Model Year
OBD2 compliance requirements vary by country and model year. Understanding these variations can help you determine if your vehicle meets the necessary standards based on its country of sale and model year.
| Country of Sale | Model Years | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 1996 | |
| European Union (Diesel) | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2007 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2004-06 |
| European Union(Petrol) | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2002 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2001 |
| Canada | 1998 | |
| Algeria | 2014 | |
| Argentina (Domestic) | 2008 | |
| Argentina (Imports) | 2009 | |
| Australia (Diesel) | 2007 | |
| Australia (Petrol) | 2006 | |
| Bahrain | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Brazil (Petrol) | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2007 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2005-06 |
| Brazil (Diesel) | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2015 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2013-14 |
| Chile (Diesel) | 2013 | |
| Chile (Petrol) | 2014 | |
| China (Beijing – Petrol) | 2008 | |
| China (Country – Diesel) | 2011 | |
| China (Country – Petrol) | 2010 | |
| Costa Rica | Limited Compliance from 2017 onward | |
| Hong Kong | 2006 | |
| India | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2017 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2013-16 |
| Iran | 2012 | |
| Israel | 2003 | |
| Japan | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2008 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2003-07 |
| Kuwait | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Mexico | 2007 | |
| Morocco | 2010 | |
| New Zealand (Diesel) | 2007 | |
| New Zealand (Petrol) | 2006 | |
| Nigeria | 2015 | |
| Oman | Full OBD-II compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Peru | 2003 | |
| Peru | 2017 | |
| Philippines | 2016 | |
| Qatar | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Russia | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2012 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2010-11 |
| Saudi Arabia | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Singapore | 2014 | |
| South Korea | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2010 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2005-09 |
| Taiwan | 2008 | |
| Thailand | 2013 | |
| Turkey | 2013 | |
| United Arab Emirates | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
| Vietnam | 2017 | |
| Yemen | Full OBD-II Compliance for 2018 and onward | Limited Compliance from 2017-18 |
- United States: All cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States must be OBD2 compliant starting with the 1996 model year.
- European Union: Gasoline vehicles must be EOBD compliant starting with the 2001 model year, while diesel vehicles must be EOBD compliant starting with the 2004 model year.
- Canada: All vehicles manufactured for sale in Canada must be OBD2 compliant starting with the 1998 model year.
- Australia: Gasoline vehicles must be OBD2 compliant starting with the 2006 model year, while diesel vehicles must be OBD2 compliant starting with the 2007 model year.
- Japan: Full OBD-II Compliance for 2008 and onward. Limited Compliance from 2003-07.
9. Understanding OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 protocols are the communication standards that define how diagnostic tools interact with a vehicle’s ECU. Understanding these protocols can help you choose the right diagnostic tool for your vehicle and troubleshoot communication issues.
- Common OBD2 protocols: There are five common OBD2 protocols:
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used primarily by General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used primarily by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by a variety of manufacturers.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): The most modern protocol, used by most vehicles manufactured after 2008.
- How to determine your vehicle’s protocol: You can determine your vehicle’s OBD2 protocol by consulting your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a service manual. You can also use an OBD2 scanner that automatically detects the protocol.
- Importance of protocol compatibility: It’s important to choose an OBD2 scanner that is compatible with your vehicle’s OBD2 protocol. If the scanner is not compatible, it will not be able to communicate with the ECU.
10. OBD2 vs. EOBD vs. JOBD: What’s the Difference?
While OBD2 is the standard used in the United States, other regions have their own versions of the standard, such as EOBD in Europe and JOBD in Japan. Understanding the differences between these standards can help you choose the right diagnostic tools and interpret diagnostic information correctly.
- OBD2 (United States): The original OBD2 standard, mandated in the United States starting with the 1996 model year.
- EOBD (Europe): The European version of OBD2, introduced in the early 2000s. EOBD is similar to OBD2 but has some differences in the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and the parameters that are monitored.
- JOBD (Japan): The Japanese version of OBD2, also introduced in the early 2000s. JOBD is similar to OBD2 and EOBD but has some unique features and requirements.
- Key differences: The main differences between OBD2, EOBD, and JOBD lie in the specific DTCs that are used, the parameters that are monitored, and the regulatory requirements that must be met.
- Interchangeability: In most cases, OBD2, EOBD, and JOBD tools are interchangeable, but it’s important to be aware of the differences between the standards to ensure accurate diagnosis and repair.
11. Benefits of Using OBD2 Diagnostic Tools
Using OBD2 diagnostic tools offers numerous benefits for both vehicle owners and technicians. These tools provide valuable insights into a vehicle’s health, allowing for proactive maintenance and efficient troubleshooting.
- Early detection of problems: OBD2 diagnostic tools can detect problems early, before they become major issues. This allows you to address issues proactively, saving you money on costly repairs down the road.
- Accurate diagnosis: OBD2 diagnostic tools provide accurate diagnostic information, helping you pinpoint the root cause of a problem quickly and efficiently. This reduces the time and effort required to diagnose and repair vehicles.
- Improved fuel efficiency: By monitoring engine performance and identifying issues that can affect fuel efficiency, OBD2 diagnostic tools can help you improve your vehicle’s fuel economy.
- Reduced emissions: OBD2 diagnostic tools can help you identify and address issues that can cause excessive emissions, helping you keep your vehicle environmentally friendly.
- Enhanced vehicle performance: By monitoring various engine parameters and identifying performance issues, OBD2 diagnostic tools can help you optimize your vehicle’s performance.
12. Common OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are standardized codes that indicate specific problems with a vehicle’s engine and emissions control systems. Understanding these codes can help you diagnose and repair your vehicle more effectively.
- P0 codes (Powertrain): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, and other powertrain components.
- B codes (Body): These codes relate to the body of the vehicle, such as the airbags, power windows, and door locks.
- C codes (Chassis): These codes relate to the chassis of the vehicle, such as the ABS, traction control, and suspension.
- U codes (Network): These codes relate to the vehicle’s communication network.
- Examples of common DTCs: Some common DTCs include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0171 (System Too Lean (Bank 1)), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)).
- How to interpret DTCs: To interpret DTCs, you can use an OBD2 scanner that displays the code’s description. You can also consult a service manual or online resources for more information.
13. How to Use OBD2 Data for Vehicle Maintenance
OBD2 data can be used for a variety of vehicle maintenance tasks, from monitoring engine performance to identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
- Monitoring engine performance: OBD2 data can be used to monitor various engine parameters, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim. This information can help you identify performance issues and optimize your vehicle’s performance.
- Identifying potential issues: By monitoring OBD2 data over time, you can identify potential issues before they trigger a DTC. For example, if you notice that your vehicle’s fuel trim is consistently high, it may indicate a vacuum leak or a problem with the fuel injectors.
- Performing routine maintenance: OBD2 data can be used to perform routine maintenance tasks, such as checking the health of the oxygen sensors and the catalytic converter.
- Tracking vehicle history: OBD2 data can be stored and tracked over time, providing a valuable record of your vehicle’s maintenance history.
14. Opening Hidden Features on Mercedes Using OBD2
While OBD2 is primarily used for diagnostics, it can also be used to unlock hidden features on some vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz models.
- What are hidden features? Hidden features are functions or settings that are present in the vehicle’s software but are not enabled by default. These features can include things like enhanced lighting options, improved audio settings, and customized driving modes.
- How to unlock hidden features: Unlocking hidden features typically involves using an OBD2 scanner or programming tool to modify the vehicle’s software. This process can be complex and may require specialized knowledge.
- Potential risks: Unlocking hidden features can void your vehicle’s warranty and may cause unintended consequences. It’s important to proceed with caution and consult with a qualified technician before attempting to unlock hidden features.
- Finding reliable resources: If you’re interested in unlocking hidden features on your Mercedes-Benz, it’s important to find reliable resources and follow instructions carefully. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can provide guidance and support for unlocking hidden features on Mercedes vehicles.
15. Choosing the Right OBD2 Tool for Your Needs
With so many different OBD2 tools available on the market, choosing the right one for your needs can be a challenge. Consider the following factors when selecting an OBD2 tool:
- Functionality: Determine what you want to use the OBD2 tool for. Do you need a basic code reader, or do you need an advanced diagnostic tool with features like data logging and bidirectional control?
- Compatibility: Make sure the OBD2 tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Ease of use: Choose an OBD2 tool that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: OBD2 tools range in price from a few dollars to several thousand dollars. Set a budget and choose a tool that offers the best value for your money.
- Customer reviews: Read customer reviews to get an idea of the tool’s performance and reliability.
16. Maintaining OBD2 Compliance Over Time
Maintaining OBD2 compliance over time is essential for ensuring your vehicle continues to meet emissions standards and can be easily diagnosed.
- Regular maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on your vehicle, including oil changes, tune-ups, and emissions system checks.
- Addressing DTCs promptly: If your vehicle triggers a DTC, address the issue promptly to prevent further damage and maintain OBD2 compliance.
- Avoiding modifications: Avoid making modifications to your vehicle’s engine or emissions control systems that could affect OBD2 compliance.
- Staying informed: Stay informed about changes to OBD2 regulations and requirements in your area.
17. Resources for Further Learning About OBD2
There are many resources available for further learning about OBD2, including online articles, forums, and training courses.
- Online articles: Websites like the EPA’s website and OBD Resource provide valuable information about OBD2 regulations and technology.
- Forums: Online forums like the OBDII.com forum are great places to ask questions and get advice from other OBD2 enthusiasts.
- Training courses: Many automotive training centers offer courses on OBD2 diagnostics and repair.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is a valuable resource for Mercedes-Benz owners who want to learn more about OBD2 diagnostics and maintenance.
18. The Future of OBD: What’s Next?
The future of OBD is likely to involve more advanced diagnostic capabilities, integration with cloud-based services, and enhanced cybersecurity features.
- OBD3: OBD3 is a proposed future version of OBD that would include real-time emissions monitoring and remote reporting of emissions violations.
- Cloud-based diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic services are becoming increasingly popular, allowing technicians to access diagnostic data and perform remote diagnostics.
- Cybersecurity: As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important concern. Future OBD systems will need to incorporate enhanced security features to protect against hacking and data breaches.
- Integration with ADAS: Future OBD systems may be integrated with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) to provide more comprehensive diagnostic information and improve vehicle safety.
19. Legal and Ethical Considerations for OBD2 Use
Using OBD2 diagnostic tools raises several legal and ethical considerations, particularly when it comes to accessing and sharing vehicle data.
- Privacy: Vehicle data can contain sensitive information about a driver’s location, driving habits, and personal information. It’s important to respect the privacy of vehicle owners and obtain their consent before accessing or sharing their data.
- Data security: Vehicle data should be stored and transmitted securely to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Warranty: Modifying a vehicle’s software or accessing certain diagnostic data may void the vehicle’s warranty. It’s important to be aware of the potential risks before using OBD2 diagnostic tools.
- Professional ethics: Automotive technicians have a responsibility to use OBD2 diagnostic tools ethically and responsibly, and to protect the privacy and security of their customers’ data.
20. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Compliance
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 compliance:
- Q: What does OBD2 compliant mean?
- A: OBD2 compliant means the vehicle adheres to the On-Board Diagnostics, Second Generation (OBD2) standard. This standard ensures that the vehicle can be easily diagnosed using standard diagnostic tools.
- Q: How can I check if my car is OBD2 compliant?
- A: You can check the vehicle’s manual, look for the OBD2 port, or check the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) label.
- Q: Where is the OBD2 port located?
- A: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, within easy reach of the driver.
- Q: What if my car has a 16-pin connector but isn’t OBD2 compliant?
- A: Some cars have a 16-pin connector but are not fully OBD2 compliant. In this case, you may need to use a specialized diagnostic tool or consult with a qualified technician.
- Q: What are the benefits of using OBD2 diagnostic tools?
- A: OBD2 diagnostic tools can detect problems early, provide accurate diagnostic information, improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance vehicle performance.
- Q: What are common OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
- A: Common DTCs include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0171 (System Too Lean (Bank 1)), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)).
- Q: Can I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes using OBD2?
- A: Yes, it is possible to unlock hidden features on some Mercedes-Benz models using OBD2 tools, but proceed with caution and consult with a qualified technician.
- Q: How do I choose the right OBD2 tool for my needs?
- A: Consider functionality, compatibility, ease of use, price, and customer reviews when selecting an OBD2 tool.
- Q: How can I maintain OBD2 compliance over time?
- A: Perform regular maintenance, address DTCs promptly, avoid modifications, and stay informed about changes to OBD2 regulations.
- Q: Where can I find reliable resources for learning more about OBD2?
- A: You can find reliable resources on websites like the EPA’s website, online forums, training courses, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Understanding if your car is OBD2 compliant is essential for effective diagnostics and maintenance. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily determine your vehicle’s compliance and take advantage of the many benefits that OBD2 technology offers.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on OBD2 diagnostics, unlocking hidden features, and comprehensive vehicle maintenance. Our team of experienced technicians is here to help you get the most out of your vehicle. Reach out now at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for personalized assistance.