Unplugging your OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port correctly is crucial for various maintenance and diagnostic tasks. This guide from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a step-by-step approach, ensuring you can safely disconnect and reconnect your OBD2 port. Understanding this process can save you time and prevent potential damage to your vehicle’s system, giving you access to critical data and features. Learn about diagnostic tools, car computer, and troubleshooting techniques.
Contents
- 1. What Is The OBD2 Port And Why Would You Need To Unplug It?
- 2. Where Is The OBD2 Port Located In A Mercedes-Benz?
- 3. Precautions To Take Before Unplugging The OBD2 Port
- 4. Step-By-Step Guide On How To Unplug The OBD2 Port
- 4.1. Gather Your Tools
- 4.2. Locate The OBD2 Port
- 4.3. Gently Remove The Shroud (If Applicable)
- 4.4. Disconnect The OBD2 Port
- 4.5. Reconnecting The OBD2 Port
- 4.6. Document Everything
- 5. Common Issues When Unplugging The OBD2 Port
- 6. How To Troubleshoot Common Issues
- 7. Alternative Methods To Unplug The OBD2 Port
- 8. Tools For Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Available At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 8.2. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 8.3. Mercedes-Benz Specific Scanners
- 8.4. Software And Updates
- 8.5. Accessories
- 9. Benefits Of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN For Your Diagnostic Needs
- 10. Common Mercedes-Benz Problems Diagnosed Using OBD2 Port
- 11. How To Interpret OBD2 Codes For Mercedes-Benz
- 12. OBD2 Port Security Tips
- 13. DIY Vs. Professional Diagnostics: When To Seek Help
- 14. Future Of OBD2 Technology
- 15. OBD3: The Next Generation Of Diagnostics
- 16. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Protocols
- 17. Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Structure
- 18. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Unplugging OBD2 Ports
- 18.1. What Happens If I Unplug The OBD2 Port While The Engine Is Running?
- 18.2. Can Unplugging The OBD2 Port Reset My Car’s Computer?
- 18.3. Will Unplugging The OBD2 Port Erase My Car’s Diagnostic Codes?
- 18.4. Can I Use An OBD2 Extension Cable?
- 18.5. Are All OBD2 Ports The Same?
- 18.6. Can A Faulty OBD2 Port Affect My Car’s Performance?
- 18.7. How Do I Know If My OBD2 Port Is Damaged?
- 18.8. Can I Replace The OBD2 Port Myself?
- 18.9. What Is The Difference Between OBD1 And OBD2?
- 18.10. Is It Safe To Leave An OBD2 Scanner Plugged In All The Time?
- 19. Contact Us
- 20. Call To Action
1. What Is The OBD2 Port And Why Would You Need To Unplug It?
The OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, serves as a gateway to your vehicle’s computer system. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 ports have been standard on all cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. since 1996. This standardized port allows technicians and vehicle owners to access a wealth of information related to engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems.
You might need to unplug it for several reasons:
- Diagnostic Testing: Using a scan tool to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Installing Performance Chips: Upgrading your vehicle’s performance by installing aftermarket chips.
- Security Measures: Disabling the port as a theft-prevention method.
- Resetting the ECU: Performing a hard reset of the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
- Maintenance Procedures: Some maintenance tasks require disconnecting the OBD2 port to prevent interference.
2. Where Is The OBD2 Port Located In A Mercedes-Benz?
Finding the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz is the first step to accessing your vehicle’s diagnostic information. Here’s how to locate it:
- Typical Location: In most Mercedes-Benz models, the OBD2 port is situated under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Specific Areas:
- Early Models: Check near the fuse box or under the steering wheel column.
- Later Models: Look for a rectangular, 16-pin connector near the pedals or in the driver’s side footwell.
- Consult Your Manual: If you’re having trouble finding it, refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
- Using a Mirror: If the area is hard to see, use a small mirror and flashlight to help locate the port.
- Physical Inspection: Feel around under the dash for the port, as it may be hidden from direct view.
Once you’ve located the OBD2 port, you’ll be ready to connect your diagnostic tool and start troubleshooting any issues your Mercedes-Benz may be experiencing.
3. Precautions To Take Before Unplugging The OBD2 Port
Before you start fiddling with the OBD2 port, remember safety first. Make sure you’re in the clear by taking these precautions:
- Turn Off the Ignition: Always turn off the engine and remove the key from the ignition to prevent electrical issues or accidental starting of the vehicle.
- Wear Safety Gear: Although it’s a low-voltage system, consider wearing gloves and eye protection for added safety.
- Read the Manual: Consult your Mercedes-Benz owner’s manual for specific instructions or warnings related to the OBD2 port.
- Static Electricity: Ground yourself to discharge any static electricity before touching any electronic components.
- Check for Aftermarket Devices: Ensure no aftermarket devices are connected to the OBD2 port that could interfere with the process.
- Battery Condition: A weak battery can sometimes cause issues during diagnostic procedures, so ensure your battery is in good condition.
- Documentation: Before disconnecting, document any existing settings or codes you might want to recall later.
4. Step-By-Step Guide On How To Unplug The OBD2 Port
Here’s a detailed guide on how to safely unplug the OBD2 port from your Mercedes-Benz.
4.1. Gather Your Tools
Having the right tools makes the job easier and prevents damage.
- Non-Marring Pry Bar: Use a plastic pry bar to gently remove the shroud without scratching the dashboard.
- Small Screwdriver Set: A set of small screwdrivers can help if clips are difficult to release.
- Flashlight: A flashlight will help you see the area under the dashboard clearly.
- Gloves: Wearing gloves will protect your hands and provide a better grip.
4.2. Locate The OBD2 Port
Refer to section 2 for guidance on locating the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz.
4.3. Gently Remove The Shroud (If Applicable)
Some Mercedes-Benz models have a shroud or cover around the OBD2 port.
- Identify the Clips: Look for clips holding the shroud in place.
- Use a Pry Bar: Gently use a non-marring pry bar to release the clips.
- Apply Even Pressure: Apply even pressure to avoid breaking the clips.
- Remove the Shroud: Once the clips are released, carefully remove the shroud.
4.4. Disconnect The OBD2 Port
Now it’s time to disconnect the OBD2 port itself.
- Check for Retaining Clips: Some ports have retaining clips on the sides.
- Release the Clips: If present, gently release the clips with your fingers or a small screwdriver.
- Pull the Port Out: Carefully pull the OBD2 port out of its housing.
- Avoid Force: If the port doesn’t come out easily, double-check for any missed clips or obstructions.
4.5. Reconnecting The OBD2 Port
Reconnecting the OBD2 port is just as important as disconnecting it.
- Align the Port: Align the OBD2 port with its housing.
- Push It Back In: Gently push the port back into place until it clicks or snaps in.
- Secure Retaining Clips: If there are retaining clips, ensure they are properly secured.
- Reattach the Shroud: If you removed a shroud, reattach it by aligning it and pressing until the clips click into place.
- Test the Connection: Use a diagnostic tool to ensure the connection is working correctly.
- Check for Loose Connections: Make sure the port is securely connected and doesn’t wiggle.
4.6. Document Everything
Keep a record of your actions to help with future troubleshooting.
- Take Photos: Take photos of the port and surrounding area before and after disconnecting.
- Write Down Steps: Write down each step you take to help you remember the process.
- Note Any Issues: Note any difficulties you encounter during the process.
- Save Information: Save all information in a safe place for future reference.
5. Common Issues When Unplugging The OBD2 Port
Even with careful precautions, issues can arise.
- Broken Clips: Applying too much force can break the retaining clips on the shroud or port.
- Bent Pins: Incorrectly inserting or removing devices can bend the pins inside the OBD2 port.
- Loose Connections: Over time, the connection can become loose, causing intermittent issues.
- Electrical Problems: Although rare, improper handling can lead to electrical shorts or other problems.
- Error Codes: Disconnecting the OBD2 port can sometimes trigger error codes that need to be cleared.
6. How To Troubleshoot Common Issues
If you run into any of these problems, here’s how to troubleshoot them:
- Broken Clips:
- Replacement: Order replacement clips from a Mercedes-Benz dealer or auto parts store.
- Temporary Fix: Use adhesive to temporarily secure the shroud or port.
- Bent Pins:
- Straighten Carefully: Use a small, fine-tipped tool to carefully straighten the bent pins.
- Professional Repair: If you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, take it to a professional.
- Loose Connections:
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
- Clean the Port: Use electronic contact cleaner to clean the port and connector.
- Electrical Problems:
- Check Fuses: Check the vehicle’s fuses to see if any have blown.
- Professional Help: Consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair electrical issues.
- Error Codes:
- Use a Scan Tool: Use a scan tool to read and clear the error codes.
- Research Codes: Research the error codes to understand the underlying issue.
7. Alternative Methods To Unplug The OBD2 Port
While the standard method works for most situations, alternative approaches may be necessary in certain cases.
- Using Specialized Tools:
- OBD2 Extension Cables: These cables provide more room to work and can help prevent damage to the port.
- Right-Angle Connectors: These connectors can be useful in tight spaces.
- Professional Assistance:
- Certified Technicians: If you’re not comfortable working on your car, seek help from a certified technician.
- Dealership Service: Mercedes-Benz dealerships have specialized tools and expertise for working on your vehicle.
- Wireless OBD2 Adapters:
- Bluetooth Adapters: These adapters allow you to access diagnostic information wirelessly via a smartphone or tablet.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Similar to Bluetooth adapters, Wi-Fi adapters offer wireless connectivity for diagnostics.
8. Tools For Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics Available At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of diagnostic tools tailored for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
8.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
These entry-level scanners are perfect for reading and clearing basic diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Code Reading | Reads standard OBD2 codes related to engine, transmission, and emissions. |
| Code Clearing | Clears DTCs and resets the check engine light. |
| Live Data | Displays real-time data such as RPM, coolant temperature, and vehicle speed. |
| I/M Readiness | Checks the status of emissions-related systems for state inspections. |
| Compatibility | Compatible with all Mercedes-Benz models that support OBD2. |
8.2. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
For more in-depth diagnostics, consider our advanced tools, which offer enhanced capabilities.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Code Reading | Reads manufacturer-specific codes in addition to standard OBD2 codes. |
| Bi-Directional Control | Allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s systems to test components and functions. |
| Special Functions | Supports special functions such as oil reset, brake reset, and battery registration. |
| ECU Programming | Enables reprogramming of the Engine Control Unit (ECU) for software updates and performance enhancements. |
| Data Logging | Records and analyzes live data over time to diagnose intermittent issues. |
| Multi-System Diagnostics | Scans all vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, SRS, and more. |
| Detailed Freeze Frame Data | Captures a snapshot of vehicle data when a DTC is triggered, providing valuable information for diagnostics. |
8.3. Mercedes-Benz Specific Scanners
These scanners are designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, offering the most comprehensive diagnostic coverage.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Full System Scan | Comprehensive scanning of all Mercedes-Benz systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, SRS, chassis, and body electronics. |
| Dealer-Level Diagnostics | Provides access to dealer-level diagnostic functions, including advanced coding, programming, and adaptations. |
| Guided Diagnostics | Offers step-by-step guidance for diagnosing complex issues, making the process easier for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. |
| SCN Coding | Supports SCN (Software Calibration Number) coding, which is required for certain programming and adaptation procedures on Mercedes-Benz vehicles. |
| Component Testing | Allows individual testing of components, such as sensors, actuators, and modules, to verify their functionality. |
| Real-Time Data Display | Displays real-time data in a user-friendly format, with graphs and charts for easy analysis. |
| Service Reset Functions | Includes service reset functions for oil changes, brake pad replacements, and other maintenance procedures. |
| Actuation and Adaptations | Supports actuation of components and adaptations, allowing you to calibrate and configure various systems. |
| Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Analysis | Provides detailed descriptions and troubleshooting tips for diagnostic trouble codes specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles. |
8.4. Software And Updates
Keeping your diagnostic tools up-to-date is essential for accurate and reliable diagnostics.
- Regular Updates: We provide regular software updates to ensure compatibility with the latest Mercedes-Benz models and diagnostic protocols.
- Online Support: Access our online support portal for troubleshooting tips, software downloads, and FAQs.
- Technical Support: Contact our technical support team for assistance with any issues you may encounter.
8.5. Accessories
Enhance your diagnostic capabilities with our range of accessories.
- OBD2 Extension Cables: These cables provide additional length and flexibility for connecting your diagnostic tool.
- Adapters: We offer adapters for connecting to older Mercedes-Benz models with different diagnostic connectors.
- Cases: Protect your diagnostic tools with our durable carrying cases.
9. Benefits Of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN For Your Diagnostic Needs
Choosing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for your diagnostic needs offers several key advantages.
- Expertise: We specialize in Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, providing tools and resources tailored to your vehicle.
- Quality: Our tools are sourced from trusted manufacturers and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability.
- Support: We offer comprehensive support, including online resources, technical assistance, and regular software updates.
- Value: We provide competitive pricing and a range of options to suit your budget and diagnostic needs.
- Convenience: Shop online from the comfort of your home or office, with fast shipping and easy returns.
10. Common Mercedes-Benz Problems Diagnosed Using OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port enables diagnosis of a wide array of Mercedes-Benz issues.
- Engine Problems:
- Misfires: Identify and diagnose engine misfires, which can cause rough running and reduced power.
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: Detect problems with oxygen sensors, which affect fuel efficiency and emissions.
- Catalytic Converter Failure: Diagnose issues with the catalytic converter, which can lead to emissions problems.
- Transmission Problems:
- Shift Issues: Identify problems with gear shifting, such as rough or delayed shifts.
- Transmission Slippage: Diagnose transmission slippage, which can cause reduced performance.
- Torque Converter Problems: Detect issues with the torque converter, which can affect power transfer.
- ABS and Brake Problems:
- ABS Sensor Failure: Diagnose issues with ABS sensors, which can affect braking performance.
- Brake Pad Wear: Detect excessive brake pad wear, which can compromise safety.
- Hydraulic Issues: Identify problems with the brake hydraulic system, such as leaks or malfunctions.
- SRS and Airbag Problems:
- Airbag Malfunctions: Diagnose issues with the airbag system, which can compromise safety.
- SRS Sensor Issues: Detect problems with SRS sensors, which monitor crash conditions.
- Seatbelt Problems: Identify issues with seatbelt pretensioners and other components.
- Electrical Problems:
- Sensor Failures: Diagnose failures of various sensors, such as temperature sensors and pressure sensors.
- Wiring Issues: Detect problems with wiring harnesses and connections.
- Module Malfunctions: Identify malfunctions of electronic control modules, such as the ECU or TCU.
11. How To Interpret OBD2 Codes For Mercedes-Benz
Understanding OBD2 codes is essential for effective diagnostics.
- Standard Codes:
- P Codes: Powertrain codes related to the engine and transmission.
- B Codes: Body codes related to comfort and convenience systems.
- C Codes: Chassis codes related to braking, suspension, and steering.
- U Codes: Network codes related to communication between control modules.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Mercedes-Benz uses manufacturer-specific codes for more detailed diagnostics.
- Accessing Codes: Use a Mercedes-Benz specific scan tool to access these codes.
- Using Online Resources:
- Code Databases: Online databases provide descriptions and troubleshooting tips for OBD2 codes.
- Forums: Mercedes-Benz forums can offer insights from other owners and technicians.
- Professional Assistance:
- Certified Technicians: Consult a certified technician for help interpreting complex codes.
- Dealership Service: Mercedes-Benz dealerships have specialized expertise for diagnosing and repairing your vehicle.
12. OBD2 Port Security Tips
Protecting your OBD2 port from unauthorized access is crucial to prevent theft and tampering.
- Physical Locks:
- OBD2 Port Locks: These devices physically block access to the OBD2 port, preventing unauthorized connections.
- Protective Cases: Use a protective case to cover the OBD2 port and deter tampering.
- Software Security:
- ECU Remapping: Remap the ECU to disable or encrypt the OBD2 port.
- Custom Firmware: Install custom firmware that requires a password for access.
- Monitoring and Alerts:
- OBD2 Trackers: Use an OBD2 tracker to monitor vehicle activity and receive alerts for unauthorized access.
- Security Systems: Integrate the OBD2 port into your vehicle’s security system for added protection.
- Regular Inspections:
- Check for Tampering: Regularly inspect the OBD2 port for signs of tampering.
- Monitor Connections: Monitor connections to the OBD2 port to detect unauthorized devices.
13. DIY Vs. Professional Diagnostics: When To Seek Help
Deciding whether to perform diagnostics yourself or seek professional help depends on the complexity of the issue and your comfort level.
- DIY Diagnostics:
- Simple Issues: DIY diagnostics are suitable for simple issues such as reading and clearing basic OBD2 codes.
- Basic Maintenance: DIY diagnostics can help with basic maintenance tasks such as oil reset and brake reset.
- Cost Savings: DIY diagnostics can save you money on labor costs.
- Professional Diagnostics:
- Complex Issues: Professional diagnostics are necessary for complex issues such as engine misfires and transmission problems.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Professional technicians have specialized tools and expertise for advanced diagnostics.
- Safety Concerns: Professional diagnostics are recommended for safety-related issues such as ABS and SRS problems.
- When To Seek Help:
- Unfamiliar Issues: Seek professional help if you are unfamiliar with the issue or uncomfortable performing the diagnostics.
- Persistent Problems: Seek professional help if the problem persists after attempting DIY diagnostics.
- Safety Concerns: Seek professional help if the issue poses a safety risk.
14. Future Of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities on the horizon.
- Enhanced Diagnostics:
- More Data: Future OBD systems will provide more detailed data for diagnostics.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics will allow technicians to diagnose issues remotely.
- Cybersecurity:
- Enhanced Security: Future OBD systems will incorporate enhanced security measures to prevent hacking and tampering.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption will protect sensitive vehicle information.
- Integration with Telematics:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Integration with telematics will enable real-time monitoring of vehicle performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance will anticipate potential issues before they occur.
- Standardization:
- Global Standards: Efforts are underway to standardize OBD systems globally.
- Improved Compatibility: Improved compatibility will make it easier to diagnose vehicles from different manufacturers.
15. OBD3: The Next Generation Of Diagnostics
The automotive industry is gearing up for OBD3, the next generation of on-board diagnostics. While OBD2 primarily focuses on emissions-related issues, OBD3 aims to provide a more comprehensive view of vehicle health, safety, and performance.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- Continuous Data Collection: OBD3 will continuously collect and transmit data about various vehicle systems, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance and potential issues.
- Proactive Alerts: The system will proactively alert drivers and service providers about problems, enabling timely repairs and preventing breakdowns.
- Enhanced Communication:
- Wireless Connectivity: OBD3 will utilize wireless communication technologies, such as cellular or satellite networks, to transmit data to remote servers.
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians will be able to perform remote diagnostics, accessing vehicle data and running tests without physically being present.
- Cybersecurity Measures:
- Secure Data Transmission: OBD3 will incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures to protect data from unauthorized access and tampering.
- Authentication Protocols: Robust authentication protocols will ensure that only authorized users can access and modify vehicle settings.
- Integration with ADAS:
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): OBD3 will integrate with ADAS, providing data about the performance and calibration of safety-critical systems.
- Predictive Safety: By analyzing data from ADAS, OBD3 can predict potential safety issues and alert drivers accordingly.
- Benefits of OBD3:
- Improved Vehicle Safety: Real-time monitoring and proactive alerts can help prevent accidents and improve overall vehicle safety.
- Reduced Downtime: Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance can minimize downtime and ensure that vehicles are always in optimal condition.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By monitoring fuel consumption and emissions, OBD3 can help drivers improve fuel efficiency and reduce their environmental impact.
16. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Protocols
Mercedes-Benz vehicles use specific diagnostic protocols that technicians need to be familiar with to accurately diagnose and repair issues. These protocols ensure that diagnostic tools can communicate effectively with the vehicle’s control modules.
- Controller Area Network (CAN) Bus:
- Communication Network: The CAN bus is a communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: It enables high-speed data transfer, which is essential for real-time diagnostics and control.
- Diagnostic Over CAN (DoCAN):
- Standardized Diagnostics: DoCAN is a standardized diagnostic protocol that allows diagnostic tools to communicate with ECUs over the CAN bus.
- Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS): It uses Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS) to provide a set of common diagnostic functions, such as reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), reading data streams, and performing control functions.
- Keyword Protocol 2000 (KWP2000):
- Older Models: KWP2000 is an older diagnostic protocol used in some Mercedes-Benz models.
- Serial Communication: It uses serial communication to transmit data between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s ECUs.
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic System (MBDS):
- Proprietary System: MBDS is a proprietary diagnostic system developed by Mercedes-Benz.
- Dealer-Level Diagnostics: It provides dealer-level diagnostic capabilities, including advanced coding, programming, and adaptations.
- Common Diagnostic Functions:
- Reading and Clearing DTCs: Reading and clearing DTCs is a fundamental diagnostic function that allows technicians to identify and resolve issues.
- Reading Data Streams: Reading data streams allows technicians to monitor real-time data from various sensors and systems.
- Actuation Tests: Actuation tests allow technicians to activate components and systems to verify their functionality.
- Adaptations and Coding: Adaptations and coding allow technicians to configure and calibrate various systems to ensure proper operation.
17. Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Structure
Mercedes-Benz diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) follow a specific structure that provides valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. Understanding this structure can help technicians diagnose issues more efficiently.
- Five-Character Code:
- Format: Mercedes-Benz DTCs consist of a five-character alphanumeric code.
- Example: P0101
- First Character:
- Category: The first character indicates the category of the code.
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (comfort, convenience)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- Category: The first character indicates the category of the code.
- Second Character:
- Standard or Manufacturer-Specific: The second character indicates whether the code is a standard OBD-II code or a manufacturer-specific code.
- 0: Standard OBD-II code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Standard or Manufacturer-Specific: The second character indicates whether the code is a standard OBD-II code or a manufacturer-specific code.
- Third Character:
- Subsystem: The third character indicates the subsystem related to the code.
- 0: Fuel and air metering
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- Subsystem: The third character indicates the subsystem related to the code.
- Fourth and Fifth Characters:
- Specific Fault: The fourth and fifth characters indicate the specific fault within the subsystem.
- Example: P0101 indicates a problem with the mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
- Additional Information:
- Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of vehicle conditions when the DTC was triggered.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Diagnostic tools often provide troubleshooting tips and repair procedures for specific DTCs.
18. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Unplugging OBD2 Ports
18.1. What Happens If I Unplug The OBD2 Port While The Engine Is Running?
Unplugging the OBD2 port while the engine is running can cause electrical issues or trigger error codes. It’s best to turn off the engine before disconnecting the port.
18.2. Can Unplugging The OBD2 Port Reset My Car’s Computer?
Yes, unplugging the OBD2 port can reset your car’s computer, but it’s not the most reliable method. A more effective way is to disconnect the battery for a few minutes.
18.3. Will Unplugging The OBD2 Port Erase My Car’s Diagnostic Codes?
Yes, unplugging the OBD2 port can erase diagnostic codes, but it’s better to use a scan tool to clear the codes properly.
18.4. Can I Use An OBD2 Extension Cable?
Yes, you can use an OBD2 extension cable to provide more room to work and prevent damage to the port.
18.5. Are All OBD2 Ports The Same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports are standardized with a 16-pin connector, but the location may vary by vehicle.
18.6. Can A Faulty OBD2 Port Affect My Car’s Performance?
Yes, a faulty OBD2 port can affect your car’s performance by preventing proper communication with diagnostic tools and other devices.
18.7. How Do I Know If My OBD2 Port Is Damaged?
Signs of a damaged OBD2 port include bent pins, loose connections, and difficulty connecting to diagnostic tools.
18.8. Can I Replace The OBD2 Port Myself?
Yes, you can replace the OBD2 port yourself, but it requires some technical knowledge and the right tools.
18.9. What Is The Difference Between OBD1 And OBD2?
OBD1 is an older, non-standardized diagnostic system, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in all cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. since 1996.
18.10. Is It Safe To Leave An OBD2 Scanner Plugged In All The Time?
Leaving an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time can drain the battery and potentially cause electrical issues. It’s best to unplug it when not in use.
19. Contact Us
Need more help with your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert assistance.
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
20. Call To Action
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice on choosing the right diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and performing essential maintenance. Our team is here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and efficiently. Reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for immediate assistance. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz!
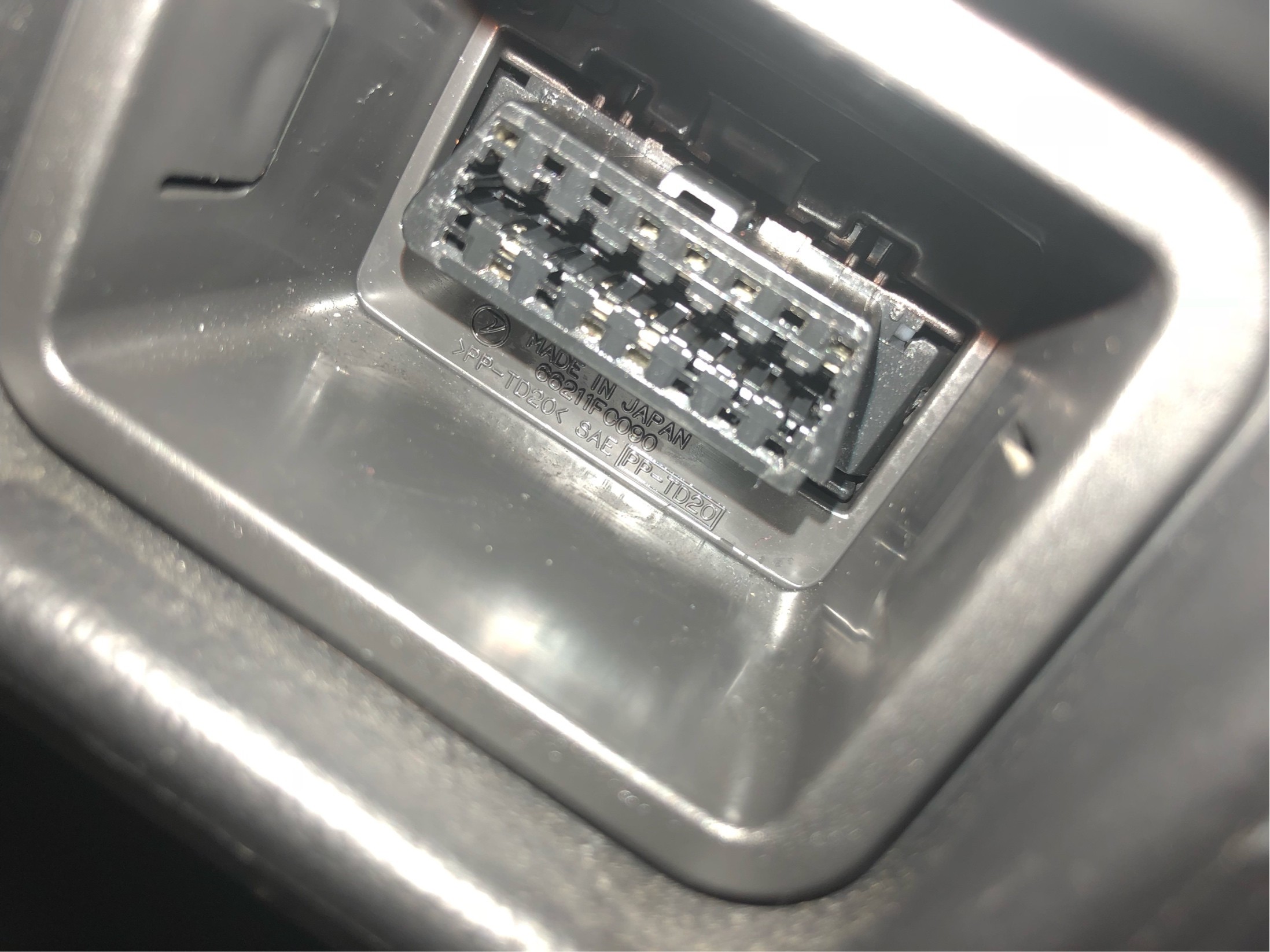 Close up of the OBD port
Close up of the OBD port