Unlock the secrets of your Mercedes-Benz. How To Use Obd2 scanners effectively to diagnose and maintain your vehicle with the help of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. This guide empowers you to understand fault codes, interpret live data, and perform essential maintenance, reducing repair costs and ensuring peak performance, ultimately improving your car ownership experience. With insights into vehicle diagnostics, automotive repair, and engine performance, you’ll gain the knowledge to keep your prized car running smoothly.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and Its Importance
- 2. Identifying Your Vehicle’s OBD2 Port Location
- 3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading OBD2 Fault Codes
- 5. Understanding Common OBD2 Fault Codes in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 6. Utilizing Live Data for Enhanced Diagnostics
- 7. Clearing OBD2 Fault Codes: When and How
- 8. Exploring Advanced Functions: Coding and Programming
- 9. OBD2 as an Essential Tool for Used Car Inspections
- Check your VIN
- 10. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Scanners
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 and Its Importance
What is OBD2 and why is it crucial for modern vehicle diagnostics? OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that provides access to the health information of your vehicle. It’s a game-changer because it allows you to quickly identify problems, monitor performance, and make informed decisions about maintenance, saving you time and money. Let’s explore why OBD2 is indispensable for today’s cars, especially Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
OBD2 is a standardized system implemented in virtually all cars sold in the United States after 1996 and in Europe after 2004. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated to monitor emission-related components and systems. This standardization means that any OBD2 scanner can communicate with any OBD2-compliant vehicle, regardless of make or model.
The primary purpose of OBD2 is to monitor the performance of the engine, transmission, and other related components to ensure they are operating within acceptable parameters. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which can be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner.
Beyond emissions monitoring, OBD2 provides valuable insights into a vehicle’s overall health. By reading live data, such as engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings, you can identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This proactive approach can save you from costly repairs and keep your car running smoothly.
For Mercedes-Benz owners, OBD2 is particularly important because these vehicles often have complex systems and advanced technology. Regular OBD2 scans can help you stay on top of maintenance needs, troubleshoot issues specific to Mercedes-Benz models, and optimize performance.
In summary, OBD2 is essential for modern vehicle diagnostics because it:
- Provides standardized access to vehicle health information
- Helps identify and troubleshoot problems quickly
- Allows for proactive maintenance and prevention of costly repairs
- Offers valuable insights into engine and system performance
2. Identifying Your Vehicle’s OBD2 Port Location
Where can you find the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz? The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, usually on the driver’s side. Its exact placement can vary slightly depending on the model year and trim, but it’s generally easily accessible. Finding this port is the first step to connecting your OBD2 scanner and unlocking a wealth of diagnostic information.
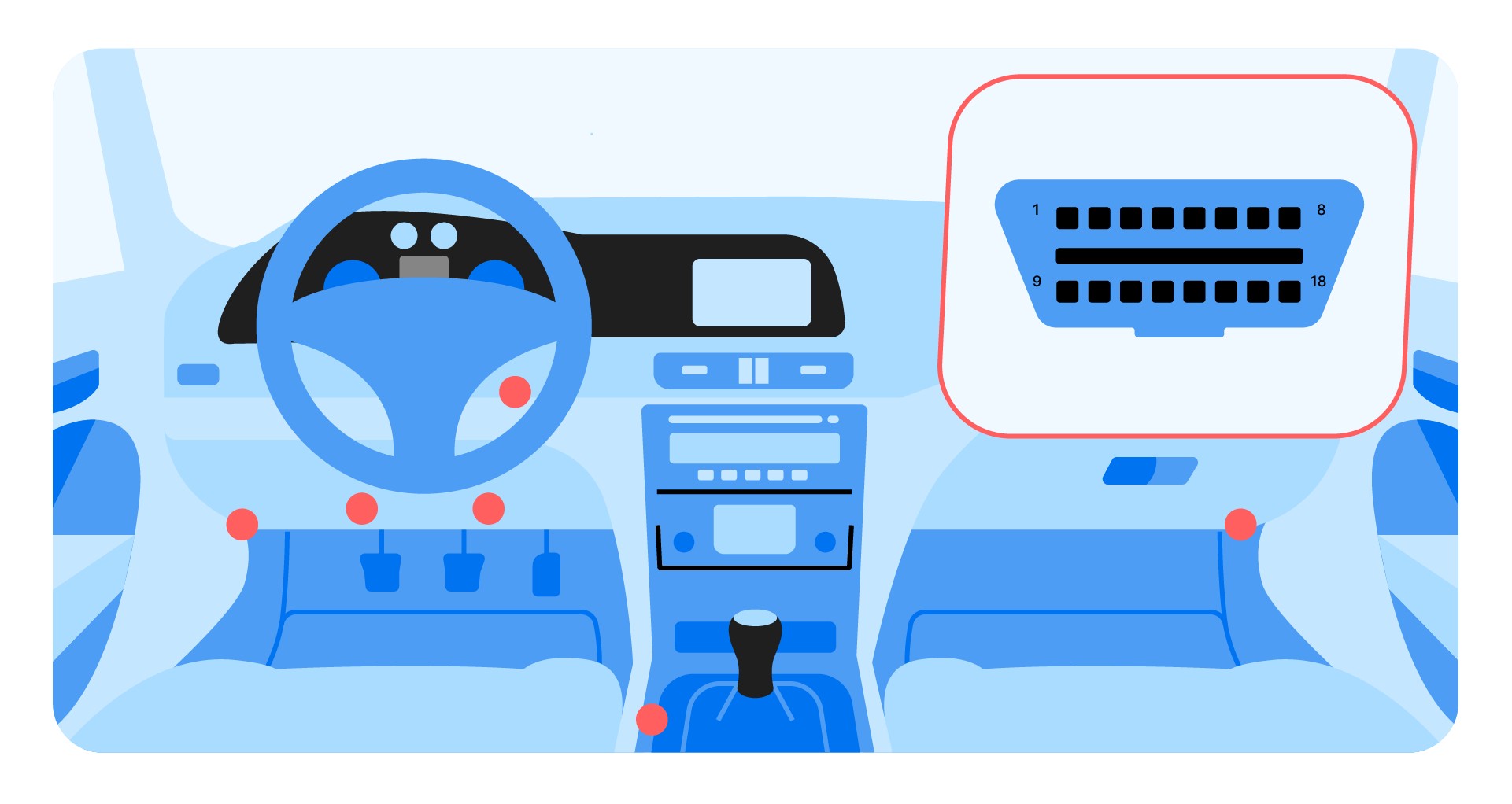 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
Knowing the precise location of the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz is essential for seamless diagnostics. Here’s a more detailed guide to help you find it:
-
Check Under the Dashboard: Start by looking under the dashboard on the driver’s side. In most Mercedes-Benz models, the OBD2 port is located in this area.
-
Look for a Trapezoidal Connector: The OBD2 port is typically a 16-pin trapezoidal connector. It’s usually black or blue and easily identifiable.
-
Check Near the Steering Column: In some models, the OBD2 port may be located near the steering column. Look for a small panel or cover that you can open to access the port.
-
Consult Your Owner’s Manual: If you’re having trouble finding the OBD2 port, consult your Mercedes-Benz owner’s manual. It should provide a diagram or description of the port’s location.
-
Use a Flashlight: If the area under the dashboard is dark, use a flashlight to help you locate the OBD2 port.
-
Common Locations by Model:
- C-Class: Often found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the center console.
- E-Class: Typically located under the dashboard, to the left of the steering column.
- S-Class: Usually positioned under the dashboard, near the driver’s side footwell.
- GLC: Commonly found under the dashboard, in the center or to the left of the steering column.
-
Accessibility: Ensure that the OBD2 port is easily accessible without requiring any tools or disassembly. It should be in a location where you can comfortably connect the scanner.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to quickly and easily locate the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz, enabling you to perform diagnostic scans and retrieve valuable vehicle health information.
3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
What are the different types of OBD2 scanners and which one is right for you? The market offers a variety of OBD2 scanners, ranging from basic Bluetooth code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. Selecting the right scanner depends on your budget, technical expertise, and diagnostic needs. Understanding the capabilities of each type will help you make an informed decision.
To help you choose the right OBD2 scanner for your needs, here’s a detailed breakdown of the different types available:
-
Basic Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers:
- Description: These are the most affordable and user-friendly options, typically pairing with your smartphone via Bluetooth.
- Features: They can read and clear basic diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and display basic live data, such as engine temperature and RPM.
- Pros: Low cost, easy to use, convenient for quick diagnostics.
- Cons: Limited functionality, may not support advanced features or specific Mercedes-Benz systems.
- Best For: Average drivers who want to quickly check and clear basic fault codes.
-
Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners:
- Description: These scanners offer a balance of features and affordability, providing more advanced diagnostic capabilities than basic code readers.
- Features: They can read and clear DTCs, display live data, reset service reminders, and perform basic servicing functions like brake pad replacement.
- Pros: More features than basic code readers, suitable for DIY repairs and maintenance.
- Cons: May not support all advanced functions or coding for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Best For: DIY enthusiasts and those who want to perform more in-depth diagnostics and maintenance.
-
Professional-Grade OBD2 Diagnostic Tools:
- Description: These are high-end, comprehensive diagnostic tools used by professional mechanics and technicians.
- Features: They offer advanced capabilities such as coding, programming, module resetting, and detailed live data analysis. They can also perform specialized functions specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Pros: Extensive functionality, supports advanced coding and programming, provides detailed diagnostic information.
- Cons: High cost, complex to use, requires technical expertise.
- Best For: Professional mechanics, automotive electricians, and advanced DIYers with extensive knowledge of Mercedes-Benz systems.
-
Smartphone Apps:
- Description: Many OBD2 scanners can be paired with smartphone apps that offer additional features and data analysis.
- Features: These apps can provide detailed fault code descriptions, repair tips, and access to online databases for troubleshooting.
- Pros: Enhanced functionality, user-friendly interface, access to additional resources.
- Cons: Requires a compatible OBD2 scanner, may have subscription fees for advanced features.
- Best For: Users who want a more interactive and informative diagnostic experience.
When choosing an OBD2 scanner for your Mercedes-Benz, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your Mercedes-Benz model and year.
- Features: Determine which features you need based on your diagnostic and maintenance goals.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Cost: Set a budget and find a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other Mercedes-Benz owners to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select an OBD2 scanner that meets your specific needs and helps you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, located at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading OBD2 Fault Codes
How do you read and interpret OBD2 fault codes? Reading fault codes is the cornerstone of OBD2 diagnostics, revealing the underlying issues triggering warning lights on your dashboard. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of connecting your scanner, accessing fault codes, and understanding what they mean.
To read OBD2 fault codes effectively, follow these detailed steps:
-
Prepare Your Vehicle:
- Park your Mercedes-Benz in a safe location and turn off the engine.
- Locate the OBD2 port, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
-
Connect the OBD2 Scanner:
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- If using a Bluetooth scanner, pair it with your smartphone or tablet according to the scanner’s instructions.
-
Turn On the Ignition:
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s systems and allows the scanner to communicate with the car’s computer.
- Ensure headlights, radio, and AC are turned off to minimize electricity consumption.
-
Select Your Vehicle:
- On the OBD2 scanner, select the make, model, and year of your Mercedes-Benz. Some advanced scanners offer an automatic VIN recognition feature that simplifies this step.
- If prompted, manually enter the VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
-
Initiate the Scan:
- Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Scan” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Choose whether to scan all control units or select specific modules (e.g., engine, transmission, ABS).
- Start the scanning process. The scanner will communicate with the vehicle’s computer to retrieve any stored fault codes.
-
Review the Fault Codes:
- Once the scan is complete, the OBD2 scanner will display a list of fault codes. Each code is a five-character alphanumeric identifier (e.g., P0171).
- Record each fault code for further investigation.
-
Interpret the Fault Codes:
- Use the OBD2 scanner’s built-in database or a reliable online resource to look up the meaning of each fault code.
- Understand that some fault codes are generic, while others are specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- For example:
P0171 - System Too Lean (Bank 1): Indicates that the engine is running lean, which could be caused by a vacuum leak, faulty sensor, or fuel delivery issue.P0300 - Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected: Suggests that one or more cylinders are misfiring, which could be due to faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
-
Additional Tips:
- Read the Code Descriptions: Pay close attention to the descriptions provided by the scanner, as they often offer valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
- Check Freeze Frame Data: Some scanners provide “freeze frame” data, which captures the vehicle’s operating conditions (e.g., engine speed, coolant temperature) when the fault code was triggered. This can help you pinpoint the cause of the issue.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After recording the fault codes, you can clear them using the scanner. However, it’s essential to address the underlying issue first. If the problem persists, the fault codes will reappear.
By following these steps, you can effectively read and interpret OBD2 fault codes, gaining valuable insights into your Mercedes-Benz’s health. For professional assistance and expert advice, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
5. Understanding Common OBD2 Fault Codes in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
What are some typical OBD2 fault codes found in Mercedes-Benz vehicles and what do they signify? While OBD2 provides standardized codes, certain issues are more prevalent in Mercedes-Benz cars. Knowing these common codes and their potential causes can help you diagnose problems more efficiently and take appropriate action.
Here’s a detailed overview of common OBD2 fault codes in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, along with their potential causes:
-
P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1):
- Description: Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is too lean on engine bank 1.
- Potential Causes:
- Vacuum leak
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty or failing mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Clogged fuel filter
- Failing fuel pump
- Faulty fuel injectors
-
P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 2):
- Description: Similar to P0171, but indicates a lean air-fuel mixture on engine bank 2.
- Potential Causes: Same as P0171.
-
P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected:
- Description: Indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring randomly.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Faulty fuel injectors
- Vacuum leak
- Low compression
- Timing issues
-
P0400 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Malfunction:
- Description: Indicates a problem with the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, which is designed to reduce emissions.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty EGR valve
- Clogged EGR passages
- Faulty EGR sensor
- Vacuum leak in the EGR system
-
P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1):
- Description: Indicates that the catalytic converter on engine bank 1 is not functioning efficiently.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Exhaust leak
- Engine running too rich or too lean
-
P0455 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large Leak):
- Description: Indicates a large leak in the evaporative emission control system (EVAP), which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
- Potential Causes:
- Loose or faulty fuel cap
- Cracked or damaged EVAP hoses
- Faulty EVAP vent valve
- Faulty EVAP purge valve
-
U0100 – Lost Communication With ECM/PCM:
- Description: Indicates a loss of communication with the engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control module (PCM).
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty ECM/PCM
- Wiring issues
- Loose connections
- CAN bus communication problems
-
B1000 – Control Unit Faulty:
- Description: Indicates a general fault with a control unit in the vehicle.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty control unit module
- Software issues
- Wiring problems
-
C1000 – Traction System Malfunction:
- Description: Indicates a malfunction in the traction control system, which helps prevent wheel slip and maintain stability.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty wheel speed sensors
- Faulty ABS module
- Hydraulic issues
-
P2006 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Closed (Bank 1):
- Description: Indicates that the intake manifold runner control is stuck in the closed position on engine bank 1.
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty intake manifold runner control actuator
- Sticking intake manifold runners
- Vacuum leak in the intake manifold runner control system
Additional Tips:
- Consult Mercedes-Benz Specific Resources: Refer to Mercedes-Benz service manuals and online forums for more detailed information about specific fault codes and their potential solutions.
- Check for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Review TSBs issued by Mercedes-Benz, as they often provide valuable insights into common issues and recommended repair procedures.
- Perform Thorough Diagnostics: Don’t rely solely on the fault code. Perform additional diagnostics, such as visual inspections, sensor testing, and live data analysis, to confirm the cause of the problem.
By understanding these common OBD2 fault codes and their potential causes, you can diagnose problems more effectively and take appropriate action to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert assistance and professional diagnostic services.
6. Utilizing Live Data for Enhanced Diagnostics
What is live data and how can it help you diagnose car problems more accurately? Live data refers to real-time information from your car’s sensors and modules, providing a snapshot of its current operating conditions. By monitoring parameters like engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings, you can identify subtle issues that may not trigger fault codes, leading to more precise diagnoses.
Live data is an invaluable tool for diagnosing complex car problems. Here’s how you can utilize it effectively:
-
Accessing Live Data:
- Connect your OBD2 scanner to your Mercedes-Benz and turn on the ignition.
- Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Select the parameters you want to monitor. Common parameters include:
- Engine RPM
- Engine Coolant Temperature
- Intake Air Temperature
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Reading
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim Values
- Throttle Position
- Vehicle Speed
-
Monitoring Key Parameters:
- Engine RPM: Monitor the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM) to ensure it is within the normal range. Irregularities can indicate issues with the engine’s performance.
- Engine Coolant Temperature: Check the engine coolant temperature to ensure it reaches and maintains the proper operating temperature. Overheating or undercooling can lead to engine damage.
- Intake Air Temperature: Monitor the intake air temperature to ensure it is within the expected range. High intake air temperatures can reduce engine performance.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Reading: Monitor the MAF sensor reading to ensure it is providing accurate data about the amount of air entering the engine. Faulty MAF sensors can cause lean or rich fuel mixtures.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Check the oxygen sensor readings to ensure they are fluctuating properly. Oxygen sensors provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) about the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Trim Values: Monitor the short-term and long-term fuel trim values to assess how the ECU is adjusting the air-fuel mixture. High fuel trim values can indicate vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, or fuel delivery issues.
- Throttle Position: Check the throttle position to ensure the throttle is opening and closing properly. Issues with the throttle can affect engine performance and fuel economy.
- Vehicle Speed: Monitor the vehicle speed to ensure it matches the speedometer reading. Discrepancies can indicate issues with the vehicle speed sensor or ABS system.
-
Analyzing Live Data:
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the live data readings to the specifications provided in your Mercedes-Benz service manual. This will help you identify any parameters that are out of range.
- Look for Trends: Monitor the live data over time to identify any trends or patterns. For example, a gradual increase in engine coolant temperature could indicate a cooling system problem.
- Correlate with Symptoms: Correlate the live data with the symptoms you are experiencing. For example, if you are experiencing poor fuel economy, check the oxygen sensor readings and fuel trim values.
-
Using Live Data for Specific Problems:
- Vacuum Leaks: Monitor the fuel trim values. High positive fuel trim values can indicate a vacuum leak.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Monitor the oxygen sensor readings. Slow or erratic readings can indicate a faulty oxygen sensor.
- MAF Sensor Issues: Monitor the MAF sensor reading. Inaccurate readings can indicate a faulty MAF sensor.
- Catalytic Converter Problems: Monitor the oxygen sensor readings before and after the catalytic converter. A significant difference in readings can indicate a faulty catalytic converter.
-
Additional Tips:
- Use a Graphing Scanner: A graphing scanner can help you visualize the live data and identify trends more easily.
- Consult Mercedes-Benz Resources: Refer to Mercedes-Benz service manuals and online forums for more information about interpreting live data for specific models.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about how to interpret the live data, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.
By utilizing live data effectively, you can gain valuable insights into your Mercedes-Benz’s health and diagnose problems more accurately. For expert assistance and professional diagnostic services, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
7. Clearing OBD2 Fault Codes: When and How
Is it okay to clear OBD2 fault codes and how do you do it properly? Clearing fault codes should only be done after you’ve properly diagnosed and resolved the underlying issue. While it can turn off the warning light, simply clearing the code without fixing the problem will only result in it reappearing. This section will guide you through the correct procedure and precautions.
Here’s a detailed guide on when and how to clear OBD2 fault codes:
-
When to Clear OBD2 Fault Codes:
- After Repairing the Underlying Issue: Only clear the fault codes after you have properly diagnosed and repaired the problem that triggered them. Clearing the codes without fixing the issue will only result in the warning light reappearing.
- Verifying the Repair: After performing the repair, clear the codes and drive the vehicle to see if the warning light stays off. This confirms that the repair was successful.
- During Diagnostic Testing: Sometimes, it may be necessary to clear the codes during diagnostic testing to see if a particular fault code reappears. This can help you isolate intermittent problems.
-
How to Clear OBD2 Fault Codes:
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port of your Mercedes-Benz.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Navigate to the “Clear Codes” Option: On the OBD2 scanner’s menu, find the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
- Confirm the Clearing Process: The scanner may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes. Follow the prompts to proceed.
- Wait for Confirmation: The scanner will take a few seconds to clear the codes. Wait until you receive confirmation that the process is complete.
- Turn Off the Ignition: After clearing the codes, turn off the ignition and remove the OBD2 scanner from the port.
-
Precautions and Considerations:
- Record the Fault Codes: Before clearing the codes, record all the fault codes and their descriptions. This information can be useful for future diagnostics if the problem recurs.
- Understand the Implications: Clearing the codes will erase the stored diagnostic information, including freeze frame data. This may make it more difficult to diagnose the problem if it reappears.
- Check for Readiness Monitors: After clearing the codes, the vehicle’s readiness monitors will be reset. These monitors need to run and complete their tests before the vehicle can pass an emissions inspection.
- Drive the Vehicle: After clearing the codes, drive the vehicle for a while to allow the readiness monitors to run. The amount of time required varies depending on the vehicle and the type of monitors.
- Re-Scan for Codes: After driving the vehicle, re-scan for codes to ensure that the problem has been resolved and no new codes have appeared.
-
When NOT to Clear OBD2 Fault Codes:
- Before Diagnosing the Issue: Never clear the codes before properly diagnosing the underlying problem. Clearing the codes will only mask the symptom and make it more difficult to find the root cause.
- If You Are Unsure: If you are unsure about the cause of the fault codes or how to repair the problem, do not clear the codes. Seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.
- Before an Emissions Inspection: Do not clear the codes shortly before an emissions inspection. Clearing the codes will reset the readiness monitors, and the vehicle may not pass the inspection until the monitors have completed their tests.
-
Using a Professional OBD2 Scanner:
- Advanced Features: Professional-grade OBD2 scanners offer advanced features such as the ability to view readiness monitor status, perform bi-directional tests, and access manufacturer-specific diagnostic information.
- Data Logging: Some scanners allow you to log live data and save it for later analysis. This can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems.
- Software Updates: Ensure that your OBD2 scanner has the latest software updates to support the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols.
By following these guidelines, you can clear OBD2 fault codes safely and effectively, ensuring that you address the underlying issues and maintain your Mercedes-Benz in good condition. For expert assistance and professional diagnostic services, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
8. Exploring Advanced Functions: Coding and Programming
What are the advanced functions of OBD2 scanners, such as coding and programming, and when are they necessary? Advanced OBD2 functions like coding and programming allow you to customize your car’s settings, replace modules, and update software. While these functions are typically used by professionals, understanding them can help you appreciate the full potential of OBD2 technology.
Advanced functions like coding and programming are essential for maintaining and customizing modern vehicles. Here’s an in-depth look at these features and when they are necessary:
-
Coding:
- Definition: Coding involves changing the software parameters of a vehicle’s control units to customize certain functions or enable new features.
- When It’s Necessary:
- Retrofitting Options: When adding new features to your Mercedes-Benz, such as installing a new navigation system or upgrading to LED headlights, coding is required to enable these features in the vehicle’s control units.
- Personalizing Settings: Coding can be used to customize various settings, such as adjusting the sensitivity of the parking sensors, changing the behavior of the automatic headlights, or enabling/disabling certain warning messages.
- Replacing Control Units: When replacing a faulty control unit, coding is necessary to ensure that the new unit is properly configured for your vehicle’s specific options and settings.
- Examples:
- Enabling cornering lights on a Mercedes-Benz C-Class
- Adjusting the ambient lighting settings on a Mercedes-Benz E-Class
- Activating the sport display on a Mercedes-Benz GLC
-
Programming:
- Definition: Programming involves updating the software of a vehicle’s control units to the latest version. This can improve performance, fix bugs, and add new features.
- When It’s Necessary:
- Software Updates: Manufacturers often release software updates to address known issues, improve performance, and add new features. Programming is required to install these updates.
- Replacing Control Units: When replacing a faulty control unit, programming is often required to ensure that the new unit has the correct software version and is compatible with the rest of the vehicle’s systems.
- Addressing Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): TSBs often recommend programming the control units to address specific issues.
- Examples:
- Updating the engine control unit (ECU) software to improve fuel economy
- Updating the transmission control unit (TCU) software to improve shifting performance
- Updating the ABS module software to address a known issue with the braking system
-
Tools and Equipment:
- Professional-Grade OBD2 Scanners: Coding and programming require professional-grade OBD2 scanners that support these advanced functions. These scanners are typically more expensive than basic code readers.
- Software Subscriptions: Some coding and programming functions require a subscription to the manufacturer’s diagnostic software.
- Knowledge and Expertise: Coding and programming require a deep understanding of vehicle systems and software. It is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician.
-
Risks and Precautions:
- Incorrect Coding/Programming: Incorrect coding or programming can cause serious problems, including engine damage, transmission failure, and electrical issues.
- Warranty Implications: Performing coding or programming may void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Power Supply: Ensure that the vehicle has a stable power supply during coding and programming. Interruptions in power can cause the process to fail and damage the control units.
-
Benefits of Coding and Programming:
- Improved Performance: Coding and programming can improve the performance of the engine, transmission, and other systems.
- Enhanced Features: Coding can enable new features and customize existing settings to suit your preferences.
- Extended Lifespan: Keeping the control units up-to-date with the latest software can help extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
By understanding the advanced functions of coding and programming, you can make informed decisions about maintaining and customizing your Mercedes-Benz. For expert assistance and professional diagnostic services, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
9. OBD2 as an Essential Tool for Used Car Inspections
Why is an OBD2 scan crucial when buying a used car? Before purchasing a used Mercedes-Benz, an OBD2 scan can reveal hidden problems, verify the seller’s claims, and provide valuable insights into the car’s maintenance history. This proactive step can save you from costly repairs and ensure you’re making a sound investment.
Performing an OBD2 scan is crucial when buying a used car. Here’s why:
-
Detecting Hidden Problems:
- Fault Codes: An OBD2 scan can reveal stored fault codes that indicate underlying problems with the engine, transmission, ABS, and other systems.
- Pending Codes: The scan can also reveal pending codes, which are fault codes that have not yet triggered the check engine light but indicate a potential issue.
- Hidden Issues: Some sellers may try to hide problems by clearing the fault codes just before showing the car to potential buyers. An OBD2 scan can reveal if the codes have been recently cleared, which is a red flag.
-
Verifying Seller’s Claims:
- Maintenance History: The seller may claim that the car has been well-maintained. An OBD2 scan can verify this claim by revealing any stored fault codes or issues that have been ignored.
- Mileage Discrepancies: Some advanced OBD2 scanners can read the mileage stored in the vehicle’s control units. This can help you verify that the mileage on the odometer is accurate.
- Accident History: An OBD2 scan can reveal if the car has been involved in an accident by detecting fault codes related to the airbag system or other safety features.
-
Evaluating Vehicle Health:
- Live Data Analysis: Analyzing live data, such as engine temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values, can provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s overall health and performance.
- Readiness Monitors: Checking the status of the readiness monitors can help you determine if the vehicle is ready to pass an emissions inspection.
- Performance Issues: An OBD2 scan can help you identify performance issues, such as engine misfires, poor fuel economy, or reduced power.
-
Negotiating a Fair Price:
- Identifying Repair Needs: By revealing hidden problems and potential issues, an OBD2 scan can help you identify any necessary repairs.
- Negotiating the Price: You can use the information from the OBD2 scan to negotiate a fair price for the used car, taking into account the cost of any necessary repairs.
- Avoiding Costly Surprises: Performing an OBD2 scan can help you avoid costly surprises and ensure that you are making a sound investment.
-
Steps to Perform an OBD2 Scan Before Buying a Used Car:
- Bring an OBD2 Scanner: Bring your own OBD2 scanner or ask the seller if you can use theirs.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port of the car.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Scan for Fault Codes: Scan for any stored or pending fault codes.
- Analyze Live Data: Analyze live data to evaluate the vehicle’s overall health and performance.
- Check Readiness Monitors: Check the status of the readiness monitors.
- Review the Results: Review the results of the OBD2 scan with a qualified mechanic or technician.
-
Additional Tips:
- Get a Vehicle History Report: In addition to performing an OBD2 scan, get a vehicle history report from a reputable provider such as Carfax or AutoCheck.
- Have the Car Inspected: Have the car inspected by a qualified mechanic before making a purchase.
- Take a Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to assess its performance and handling.
By following these steps, you can use an OBD2 scan to make an informed decision when buying a used car and avoid costly surprises. For expert assistance and professional diagnostic services, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle’s history. Get a report instantly!
10. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Scanners
How can OBD2 scanners assist with routine maintenance on your Mercedes-Benz? OBD2 scanners are not just for diagnosing problems; they’re also valuable tools for preventative maintenance. By regularly monitoring your car’s health and performing necessary maintenance tasks, you can extend its lifespan and optimize its performance.
OBD2 scanners can greatly assist with routine maintenance on your Mercedes-Benz. Here’s how:
-
Monitoring Vehicle Health:
- Regular Scans: Perform regular OBD2 scans to check for any stored or pending fault codes. This can help you identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Live Data Analysis: Monitor live data, such as engine temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values, to assess the overall health of the engine and other systems.
- **