Is My Car Obd2 compliant? Understanding OBD2 compliance is crucial for diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert insights into vehicle diagnostics. This guide will clarify OBD2 standards, helping you determine if your car meets these requirements, and introduces related concepts like scan tools, diagnostic information, and vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What is OBD2 and Why Does it Matter?
- 1.1. Historical Context of OBD2
- 1.2. Key Benefits of OBD2
- 1.3. How OBD2 Works in Modern Vehicles
- 2. Determining OBD2 Compliance for Your Car
- 2.1. Checking the Vehicle’s Model Year
- 2.2. Locating the OBD2 Port
- 2.3. Checking the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
- 2.4. Consulting the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
- 2.5. Using Online OBD2 Compliance Checkers
- 3. Understanding Global OBD2 Compliance Standards
- 3.1. OBD2 Standards in the United States
- 3.2. EOBD Standards in Europe
- 3.3. JOBD Standards in Japan
- 3.4. OBD2 Compliance in Other Regions
- 4. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Compliance
- 4.1. Myth: All Cars with a 16-Pin Connector are OBD2 Compliant
- 4.2. Myth: OBD2 Compliance Means Full Diagnostic Capability
- 4.3. Myth: OBD2 Scanners Can Fix Any Car Problem
- 5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 5.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners for Beginners
- 5.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners for Professionals
- 5.3. Smartphone-Based OBD2 Scanners
- 5.4. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 6. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 6.1. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD2 Port
- 6.2. Turning on the Ignition
- 6.3. Navigating the Scanner’s Menu
- 6.4. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 7. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
- 7.1. Reading Live Data Streams
- 7.2. Performing Component Tests
- 7.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
- 7.4. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
- 7.5. When to Seek Professional Help
- 8. OBD2 and Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 8.1. Specific OBD2 Requirements for Mercedes-Benz
- 8.2. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 8.3. Accessing Advanced Diagnostic Functions on Mercedes-Benz
- 9. Maintaining Your Car’s OBD2 System
- 9.1. Regularly Checking for Trouble Codes
- 9.2. Keeping Your Car’s Software Updated
- 9.3. Ensuring Proper Sensor Functionality
- 9.4. Maintaining the OBD2 Port
- 10. The Future of OBD2 and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 10.1. OBD3 and Enhanced Diagnostics
- 10.2. The Role of Telematics in Vehicle Diagnostics
- 10.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
- 10.4. The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs) on OBD Systems
- 11. FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2
- 11.1. What is the Best OBD2 Scanner for My Car?
- 11.2. How Do I Know If My Car is OBD2 Compliant?
- 11.3. Can an OBD2 Scanner Fix My Car?
- 11.4. Where is the OBD2 Port Located?
- 11.5. What Do OBD2 Codes Mean?
- 11.6. How Do I Clear OBD2 Codes?
- 11.7. Is EOBD the Same as OBD2?
- 11.8. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner on Any Car?
- 11.9. How Often Should I Check My Car for OBD2 Codes?
- 11.10. What is Freeze Frame Data?
- 12. Need Help with Your Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics?
- 12.1. Contact Us for Expert Assistance
- 12.2. Explore Our Diagnostic Tools and Services
- 12.3. Visit Our Website for More Information
1. What is OBD2 and Why Does it Matter?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics version 2, is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and manage engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. It matters because it allows mechanics and vehicle owners to access diagnostic information using a scan tool, aiding in identifying issues and ensuring vehicles meet emission standards. According to the EPA, OBD2 was mandated in the United States for all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996. This standardized system has made vehicle diagnostics more accessible and efficient.
1.1. Historical Context of OBD2
The journey to OBD2 began with early diagnostic systems in the 1960s, evolving into OBD by the 1980s, primarily in California, to monitor emissions components. OBD2 emerged in the mid-1990s, offering a standardized approach with specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and a universal connector. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) played a crucial role in defining OBD2 standards, ensuring consistency across different vehicle manufacturers.
1.2. Key Benefits of OBD2
OBD2 offers several benefits, including:
- Standardized Diagnostics: Uniform diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) make it easier to identify and address issues across different vehicle brands.
- Emissions Monitoring: Ensures vehicles meet environmental regulations by monitoring emissions-related components.
- Performance Tracking: Provides insights into engine and vehicle performance, helping identify potential problems early on.
- Data Accessibility: Allows mechanics and vehicle owners to access critical data using a scan tool, facilitating efficient troubleshooting.
1.3. How OBD2 Works in Modern Vehicles
In modern vehicles, OBD2 systems continuously monitor various sensors and components, such as the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and engine control unit (ECU). When a fault is detected, the system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and may illuminate the check engine light. Mechanics and vehicle owners can then use a scan tool to retrieve these codes and diagnose the issue. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper use of OBD2 tools can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve repair accuracy.
2. Determining OBD2 Compliance for Your Car
Knowing if your car is OBD2 compliant is the first step in utilizing diagnostic tools effectively. Here’s how to check:
2.1. Checking the Vehicle’s Model Year
In the United States, all cars and light trucks manufactured in 1996 or later are required to be OBD2 compliant. In Europe, gasoline vehicles from 2001 and diesel vehicles from 2004 are typically OBD2 compliant. Canada adopted OBD2 standards in 1998. Always verify compliance based on the country where the vehicle was originally sold.
2.2. Locating the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard, typically on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector. If you find this port, it’s a good sign, but not a guarantee, that your vehicle is OBD2 compliant.
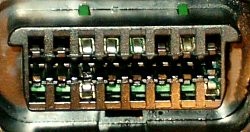 OBD2 Port Location
OBD2 Port Location
2.3. Checking the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) Label
Look under the hood for the Vehicle Emission Control Information (VECI) label. This label often states whether the vehicle is OBD2 compliant. It may also use terms like “OBD II,” “EOBD” (European OBD), or “JOBD” (Japanese OBD).
2.4. Consulting the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
The owner’s manual should provide information on whether the vehicle is OBD2 compliant. Look for sections discussing emissions control or diagnostics.
2.5. Using Online OBD2 Compliance Checkers
Several websites offer OBD2 compliance checkers where you can enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year to determine if it is OBD2 compliant. These tools can provide a quick and convenient way to verify your vehicle’s compliance.
3. Understanding Global OBD2 Compliance Standards
OBD2 standards vary by region. Knowing these differences is essential, especially if you own an imported vehicle.
3.1. OBD2 Standards in the United States
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandated OBD2 compliance for all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996. This includes specific requirements for monitoring emissions-related components and systems.
3.2. EOBD Standards in Europe
Europe’s equivalent of OBD2 is EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics). Gasoline vehicles from 2001 and diesel vehicles from 2004 are generally EOBD compliant. EOBD standards are similar to OBD2 but have some regional differences. Commission Directive 70/220/EEC outlines the specific requirements for EOBD compliance.
3.3. JOBD Standards in Japan
Japan’s OBD standard is JOBD (Japanese On-Board Diagnostics). While Japan adopted OBD-II-like standards later than the US and Europe, many vehicles manufactured for the Japanese market from 2008 onwards are OBD2 compliant.
3.4. OBD2 Compliance in Other Regions
Many other countries have adopted OBD2-like standards, often with variations. For example, Australia requires OBD2 compliance for petrol vehicles from 2006 and diesel vehicles from 2007. Brazil has similar standards for petrol vehicles from 2007 and diesel vehicles from 2015. Always check local regulations to confirm OBD2 compliance in your region.
4. Common Misconceptions About OBD2 Compliance
Several misconceptions exist regarding OBD2 compliance. Clearing these up can prevent confusion and ensure accurate diagnostics.
4.1. Myth: All Cars with a 16-Pin Connector are OBD2 Compliant
Not all cars with a 16-pin connector are OBD2 compliant. Some manufacturers used the same connector before implementing OBD2 systems. Always verify compliance using other methods, such as checking the VECI label or owner’s manual.
4.2. Myth: OBD2 Compliance Means Full Diagnostic Capability
OBD2 compliance ensures standardized access to emissions-related data, but it does not guarantee full diagnostic capability for all vehicle systems. Some advanced diagnostics may require specialized tools or manufacturer-specific software.
4.3. Myth: OBD2 Scanners Can Fix Any Car Problem
OBD2 scanners can identify problems by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), but they cannot fix the issues. The scanner provides information that helps diagnose the problem, but further inspection and repairs are necessary to resolve it.
5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and the complexity of the diagnostics you plan to perform.
5.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners for Beginners
Basic OBD2 scanners are ideal for beginners and DIY enthusiasts. These scanners can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and provide basic information about the vehicle’s status. They are typically inexpensive and easy to use.
5.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners for Professionals
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer more features, such as live data streaming, bidirectional control, and advanced diagnostic functions. These scanners are suitable for professional mechanics and experienced DIYers who need comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
5.3. Smartphone-Based OBD2 Scanners
Smartphone-based OBD2 scanners use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that connects to the OBD2 port and communicates with a smartphone app. These scanners offer a convenient and affordable way to access diagnostic information. Many apps provide additional features, such as performance monitoring and data logging.
5.4. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Functions: Determine if the scanner meets your diagnostic needs, such as reading and clearing codes, live data streaming, and bidirectional control.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and easy-to-understand instructions.
- Updates: Check if the scanner supports software updates to ensure compatibility with newer vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
6. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using an OBD2 scanner is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
6.1. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD2 Port
Locate the OBD2 port under the dashboard, usually on the driver’s side. Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure the connection is secure.
6.2. Turning on the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
6.3. Navigating the Scanner’s Menu
Follow the scanner’s instructions to navigate the menu. Select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
6.4. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The scanner will display any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Each code corresponds to a specific problem or fault in the vehicle’s system. Consult a DTC reference guide or online database to understand the meaning of each code.
6.5. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the DTCs using the scanner. Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the menu. Be aware that clearing codes does not fix the problem; it only removes the stored codes.
7. Advanced OBD2 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
For more complex issues, advanced OBD2 diagnostics may be necessary.
7.1. Reading Live Data Streams
Advanced OBD2 scanners can stream live data from various sensors and components in real-time. This data can help identify intermittent problems or diagnose performance issues. Monitor parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
7.2. Performing Component Tests
Some OBD2 scanners can perform component tests, such as activating solenoids or relays to verify their functionality. These tests can help isolate faulty components.
7.3. Using Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the vehicle’s operating conditions when a DTC was stored. This information can provide valuable clues about the circumstances leading to the fault.
7.4. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Here are some common OBD2 trouble codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, MAF sensor issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, oxygen sensor issue |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected | Loose gas cap, faulty purge valve, damaged vapor lines |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leak, throttle body issue |
7.5. When to Seek Professional Help
If you are unable to diagnose or repair the problem using an OBD2 scanner, or if the issue is complex, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
8. OBD2 and Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles, while OBD2 compliant, may require specialized diagnostic tools for advanced functions.
8.1. Specific OBD2 Requirements for Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz vehicles adhere to OBD2 standards, but they often incorporate proprietary diagnostic systems that require specific tools for in-depth analysis.
8.2. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, consider using scanners that offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, such as the iCarsoft MB II or the Autel MaxiCOM MK808. These scanners provide access to Mercedes-specific diagnostic functions.
8.3. Accessing Advanced Diagnostic Functions on Mercedes-Benz
To access advanced diagnostic functions on Mercedes-Benz vehicles, you may need to use a scanner with Mercedes-specific software or consult a mechanic with experience in Mercedes diagnostics.
9. Maintaining Your Car’s OBD2 System
Proper maintenance of your car’s OBD2 system ensures accurate and reliable diagnostics.
9.1. Regularly Checking for Trouble Codes
Regularly check for trouble codes using an OBD2 scanner. This can help identify potential problems early on, before they become more serious.
9.2. Keeping Your Car’s Software Updated
Ensure your car’s software is up-to-date. Manufacturers often release software updates that improve the performance and reliability of the OBD2 system.
9.3. Ensuring Proper Sensor Functionality
Regularly inspect and maintain your car’s sensors, such as oxygen sensors and MAF sensors. Faulty sensors can trigger false trouble codes and affect the accuracy of the OBD2 system.
9.4. Maintaining the OBD2 Port
Keep the OBD2 port clean and free from debris. A damaged or corroded port can prevent the scanner from connecting properly.
10. The Future of OBD2 and Vehicle Diagnostics
The future of OBD2 and vehicle diagnostics is evolving rapidly, with new technologies and standards emerging.
10.1. OBD3 and Enhanced Diagnostics
OBD3 is a proposed future standard that would enhance diagnostic capabilities and provide real-time emissions monitoring. OBD3 would automatically notify regulatory agencies of emissions violations.
10.2. The Role of Telematics in Vehicle Diagnostics
Telematics systems use wireless communication to transmit vehicle data to remote servers. These systems can provide real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, and remote vehicle monitoring.
10.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to analyze vehicle data and identify patterns that can predict potential problems. These technologies can improve the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics.
10.4. The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs) on OBD Systems
Electric vehicles (EVs) require different diagnostic approaches compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. OBD systems in EVs monitor battery health, motor performance, and charging system functionality. As EVs become more prevalent, OBD systems will need to adapt to these new technologies.
11. FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2:
11.1. What is the Best OBD2 Scanner for My Car?
The best OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. Basic scanners are suitable for simple tasks like reading and clearing codes, while advanced scanners offer more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
11.2. How Do I Know If My Car is OBD2 Compliant?
Check the vehicle’s model year, look for the OBD2 port, check the VECI label, and consult the owner’s manual.
11.3. Can an OBD2 Scanner Fix My Car?
No, an OBD2 scanner cannot fix your car. It can only identify problems by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
11.4. Where is the OBD2 Port Located?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, usually on the driver’s side.
11.5. What Do OBD2 Codes Mean?
OBD2 codes are standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that correspond to specific problems or faults in the vehicle’s system.
11.6. How Do I Clear OBD2 Codes?
Use an OBD2 scanner to select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the menu.
11.7. Is EOBD the Same as OBD2?
EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics) is Europe’s equivalent of OBD2. They are similar but have some regional differences.
11.8. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner on Any Car?
You can use an OBD2 scanner on any car that is OBD2 compliant.
11.9. How Often Should I Check My Car for OBD2 Codes?
You should check your car for OBD2 codes regularly, especially if you notice any performance issues or warning lights.
11.10. What is Freeze Frame Data?
Freeze frame data captures the vehicle’s operating conditions when a DTC was stored, providing valuable clues about the circumstances leading to the fault.
12. Need Help with Your Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics?
Navigating the complexities of OBD2 and Mercedes-Benz diagnostics can be challenging. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and support to help you diagnose, repair, and maintain your vehicle effectively.
12.1. Contact Us for Expert Assistance
Have questions about your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us today for expert assistance. Our team of experienced technicians is here to help you troubleshoot issues and find the right solutions.
12.2. Explore Our Diagnostic Tools and Services
Discover our range of diagnostic tools and services designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. From basic OBD2 scanners to advanced diagnostic systems, we have the tools you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
12.3. Visit Our Website for More Information
Visit MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information about our products, services, and expert resources. Learn how we can help you unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz.
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t let diagnostic challenges slow you down. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today and experience the difference expert support can make.