As a Model 3 owner, understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities is crucial, and the Model 3 Obd2 Port is key. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers the expert insights and resources you need to confidently diagnose and maintain your Tesla. Explore how our comprehensive tools and expert guidance can empower you to unlock hidden features, troubleshoot issues efficiently, and keep your Tesla running smoothly with vehicle diagnostics and Tesla maintenance information.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port in Your Model 3
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Port?
- 1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port Important for Model 3 Owners?
- 1.3 Challenges with the Model 3 OBD2 Port
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Model 3: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1 Preparing for the Search
- 2.2 Step-by-Step Instructions to Find the OBD2 Port
- 2.3 Visual Aids and Resources
- 3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Model 3
- 3.1 Understanding Compatibility Issues
- 3.2 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Model 3
- 3.3 Key Features to Look For in an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.4 Where to Buy OBD2 Scanners
- 4. Diagnosing Common Model 3 Issues Using the OBD2 Port
- 4.1 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.2 Common Issues Diagnosed via OBD2
- 4.3 Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- 4.4 Resources for DTC Lookup and Interpretation
- 5. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Model 3
- 5.1 Understanding Hidden Features
- 5.2 Tools and Software Required
- 5.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Features
- 5.4 Risks and Precautions
- 6. Maintaining Your Model 3: Tips and Best Practices
- 6.1 Regular Maintenance Tasks
- 6.2 Using the OBD2 Port for Maintenance
- 6.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 6.4 Resources for Model 3 Maintenance
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using the Model 3 OBD2 Port
- 7.1 Incorrect Scanner Selection
- 7.2 Neglecting Safety Precautions
- 7.3 Misinterpreting DTCs
- 7.4 Overlooking Software Updates
- 7.5 Ignoring Warning Signs
- 7.6 Unauthorized Modifications
- 7.7 Overlooking Physical Damage
- 7.8 Neglecting Data Backups
- 7.9 Forgetting to Disconnect
- 7.10 Lack of Professional Consultation
- 8. The Future of OBD2 and Diagnostics for Electric Vehicles
- 8.1 Advancements in OBD2 Technology
- 8.2 Adapting to Electric Vehicle Diagnostics
- 8.3 The Role of Wireless and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 8.4 The Future of DIY Diagnostics
- 8.5 The Integration of AI and Machine Learning
- 8.6 Cybersecurity Considerations
- 9. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Model 3 Diagnostics
- 9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
- 9.2 Expert Guidance and Support
- 9.3 Detailed Guides and Resources
- 9.4 Community Forum
- 9.5 Software and Firmware Updates
- 9.6 Custom Solutions
- 9.7 Training Programs
- 9.8 Remote Diagnostic Services
- 9.9 Secure Data Handling
- 9.10 Continuous Improvement
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the Model 3 OBD2 Port
- 10.1 What is the Model 3 OBD2 port used for?
- 10.2 Where is the OBD2 port located in the Model 3?
- 10.3 What type of OBD2 scanner is compatible with the Model 3?
- 10.4 Can I use a generic OBD2 scanner with my Model 3?
- 10.5 How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using the OBD2 port?
- 10.6 What are some common issues that can be diagnosed using the OBD2 port?
- 10.7 Can I unlock hidden features on my Model 3 using the OBD2 port?
- 10.8 What are the risks of unlocking hidden features?
- 10.9 How often should I perform maintenance on my Model 3?
- 10.10 Where can I find more information about Model 3 diagnostics and maintenance?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port in Your Model 3
1.1 What is an OBD2 Port?
An On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface used in most modern vehicles, including the Tesla Model 3. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was standardized in 1996 to monitor vehicle emissions and engine performance. This port allows technicians and vehicle owners to access a wealth of information about the car’s various systems using diagnostic tools. This access can be used to diagnose problems, monitor performance, and even unlock hidden features.
1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port Important for Model 3 Owners?
For Model 3 owners, the OBD2 port is especially valuable. Tesla vehicles, while advanced, can still experience issues that require diagnosis. Accessing the OBD2 port allows owners to:
- Diagnose Issues: Identify the cause of warning lights and potential problems.
- Monitor Performance: Track battery health, motor efficiency, and other critical metrics.
- Customize Settings: Unlock hidden features and customize vehicle behavior (with appropriate tools and knowledge).
- Perform Maintenance: Access data needed for routine maintenance and troubleshooting.
1.3 Challenges with the Model 3 OBD2 Port
Despite the benefits, there are challenges associated with the Model 3 OBD2 port:
- Location: The OBD2 port’s location is not as straightforward as in traditional cars.
- Compatibility: Not all OBD2 scanners are fully compatible with Tesla’s software and communication protocols.
- Risk of Damage: Incorrectly accessing or modifying the vehicle’s systems can lead to damage or void warranties.
- Information Overload: Interpreting the data from the OBD2 port can be overwhelming without the right expertise and resources.
2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Model 3: A Step-by-Step Guide
2.1 Preparing for the Search
Before you start looking for the OBD2 port, it’s crucial to prepare your Model 3 properly:
- Power Down: Ensure the vehicle is completely turned off. According to Tesla’s service manuals, proper shutdown can take up to 15 minutes. This prevents potential electrical issues during the process.
- Safety First: Park the car in a safe location and engage the parking brake.
- Gather Tools: You might need a small Allen wrench or L-shaped screwdriver and a flashlight.
- Consult Documentation: Always refer to your Tesla owner’s manual or trusted online resources for specific instructions related to your vehicle.
- Software Compatibility: Confirm that your diagnostic software is up-to-date and compatible with your Tesla model.
2.2 Step-by-Step Instructions to Find the OBD2 Port
- Adjust Front Seats: Slide both front seats all the way forward to maximize space in the back.
- Locate the Rear Center Console Panel: In the back seat, find the small plastic panel at the bottom of the center console between the two front seats.
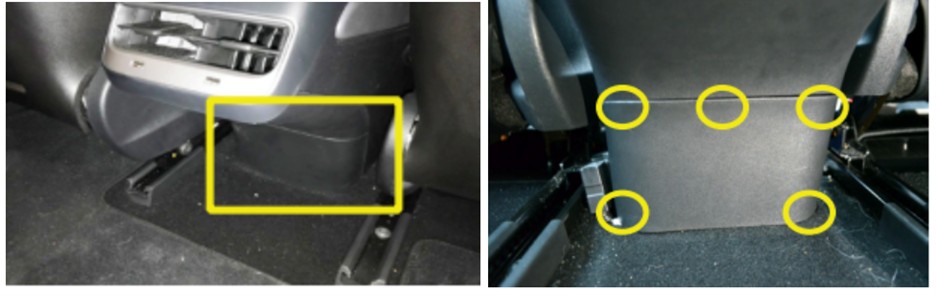 Rear Center Console Panel
Rear Center Console Panel
Alt text: Tesla Model 3 rear center console panel location, showing the plastic cover that needs to be removed to access the OBD2 port.
- Remove the Panel:
- The panel is held in place by five push-fit clips.
- Use an Allen wrench or L-shaped screwdriver to gently pry the panel open. Insert the short end of the tool under the panel on the right side.
- Rotate the tool so that the short end is vertical.
- Pull toward you, parallel to the floor. This should loosen the bottom right clip.
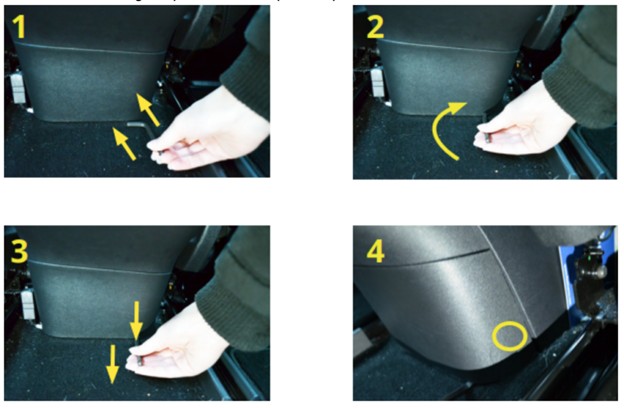 Loosening the Panel Clip
Loosening the Panel Clip
Alt text: Close-up view of using an Allen wrench to loosen the clip on the Tesla Model 3 rear center console panel, showing the correct tool placement and direction of force.
* Use your hands to pull the panel toward you and loosen the clip at the top right.
* Loosen and open the remaining three clips and pull the panel free. Removing the Panel
Removing the Panel
Alt text: Hands pulling the plastic panel away from the Tesla Model 3 center console, revealing the diagnostic connector behind it.
- Access the Diagnostic Connector: Inside the panel, you will find the Tesla Proprietary Diagnostic Connector. Press the clip that holds the white connector in place and slide to the left to release it.
- Connect the Cables: Plug the two white ends of the diagnostic cables into the corresponding connectors in the vehicle. Push until they click into place. The connectors only fit one way.
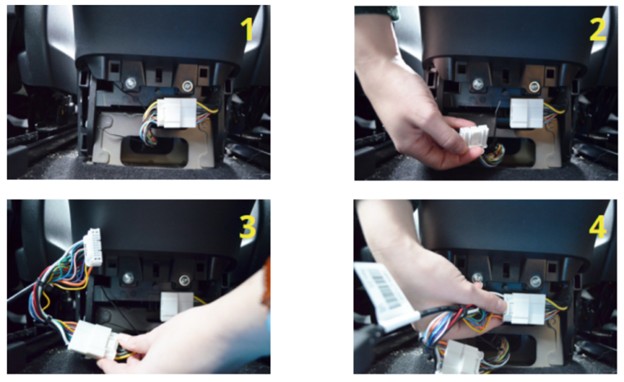 Connecting the OBD2 Cable
Connecting the OBD2 Cable
Alt text: Connecting the OBD2 cable to the Tesla Model 3 diagnostic connector, showing the proper alignment and secure connection of the white cable ends.
- Plug in the OBD2 Dongle: Then you can plug in the OBDLink dongle and connect it to your phone or tablet.
2.3 Visual Aids and Resources
If you’re having trouble locating the OBD2 port, consider these resources:
- Online Videos: Search YouTube for videos demonstrating the process.
- Tesla Forums: Consult online forums for tips and advice from other Model 3 owners.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Explore our website for detailed guides and support resources.
3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Model 3
3.1 Understanding Compatibility Issues
Not all OBD2 scanners are created equal, and compatibility issues can arise when using them with a Model 3. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), communication protocols can vary significantly between different car manufacturers. Tesla uses a proprietary communication protocol, which can make some generic OBD2 scanners ineffective or unreliable.
3.2 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Model 3
To ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics, choose an OBD2 scanner specifically recommended for Tesla vehicles:
- OBDLink MX+: This scanner is known for its compatibility with Tesla vehicles and supports advanced diagnostics.
- Scan My Tesla App: This app, when used with a compatible OBD2 dongle, provides detailed insights into your Model 3’s performance.
- TM-Spy App: Another popular app that offers real-time data and diagnostic capabilities.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: A professional-grade diagnostic tool offering comprehensive coverage for Tesla vehicles, including advanced functions such as ECU coding and programming.
3.3 Key Features to Look For in an OBD2 Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider these essential features:
- Tesla Compatibility: Ensure the scanner explicitly states compatibility with Tesla Model 3.
- Data Logging: The ability to record and analyze data over time.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Live data streams of critical parameters.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive app or software for easy navigation.
- Software Updates: Regular updates to support new Tesla software versions.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Wireless connection to your smartphone or tablet for added convenience.
- Bi-directional Control: Capability to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU for testing and calibration.
3.4 Where to Buy OBD2 Scanners
You can purchase OBD2 scanners from various sources:
- Online Retailers: Amazon, eBay, and other online marketplaces.
- Automotive Parts Stores: Local auto parts stores like AutoZone or Advance Auto Parts.
- Specialty Websites: Websites specializing in diagnostic tools, like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
4. Diagnosing Common Model 3 Issues Using the OBD2 Port
4.1 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of an OBD2 scanner is to read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes provide valuable information about potential issues within your Model 3. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), DTCs are standardized across the automotive industry, making it easier to identify and address problems.
- Understanding DTC Structure: DTCs typically consist of a five-character alphanumeric code (e.g., P0123). Each character provides specific information about the issue.
- Using a Scanner to Read DTCs: Connect your OBD2 scanner to the port and follow the instructions to read the stored DTCs.
- Interpreting the Codes: Refer to a DTC lookup table or use the scanner’s built-in database to understand the meaning of each code.
4.2 Common Issues Diagnosed via OBD2
Here are some common issues that can be diagnosed using the OBD2 port:
- Battery Health: Monitoring battery voltage, current, and temperature.
- Motor Performance: Tracking motor speed, torque, and efficiency.
- Charging Issues: Identifying problems with the charging system.
- Emissions System: Monitoring emissions-related components.
- Brake System: Detecting issues with the ABS or traction control systems.
- Airbag System: Diagnosing faults within the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) to ensure proper functionality in case of a collision.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): Reading sensor data to identify tire pressure discrepancies and potential issues.
4.3 Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- Case Study 1: Battery Degradation: A Model 3 owner noticed a decrease in range. Using an OBD2 scanner, they discovered that the battery voltage was lower than expected, indicating battery degradation.
- Case Study 2: Charging Issues: Another owner experienced intermittent charging failures. The OBD2 scanner revealed a DTC related to the charging system, leading them to replace a faulty charging module.
- Case Study 3: Motor Performance: A Model 3 driver noticed reduced acceleration. The OBD2 data showed that the motor torque was lower than expected, prompting them to investigate and repair a motor control issue.
4.4 Resources for DTC Lookup and Interpretation
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com offer comprehensive DTC lookup tools.
- Scanner Manuals: Refer to your OBD2 scanner’s manual for detailed information on DTC interpretation.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Explore our website for specific DTC guides related to Tesla vehicles.
5. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Model 3
5.1 Understanding Hidden Features
Tesla vehicles have numerous hidden features that can be unlocked using the OBD2 port and specialized software. These features can enhance your driving experience and customize your car to your preferences. According to Tesla enthusiast communities, common hidden features include:
- Enhanced Autopilot Features: Accessing advanced driver-assistance features.
- Performance Upgrades: Optimizing motor performance for increased acceleration.
- Customizable Lighting: Changing the interior and exterior lighting settings.
- Sound System Tweaks: Adjusting the audio system for optimal sound quality.
- Battery Management: Modifying battery charging and discharging parameters.
- Adjustable Suspension Settings: Modifying the air suspension settings (if equipped) for a more comfortable or sporty ride.
- Customizable Display Themes: Altering the appearance of the center display screen with unique themes.
5.2 Tools and Software Required
Unlocking hidden features requires specific tools and software:
- Compatible OBD2 Scanner: As mentioned earlier, choose a scanner known for Tesla compatibility.
- Specialized Software: Apps like Scan My Tesla or TM-Spy offer feature unlocking capabilities.
- Tesla Service Mode Access: Some features require accessing Tesla’s service mode.
- Knowledge and Expertise: Understanding the potential risks and consequences of modifying vehicle settings.
5.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Features
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Launch the Software: Open the Scan My Tesla or TM-Spy app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Access Service Mode (if required): Follow the instructions to enter Tesla’s service mode.
- Select the Feature: Choose the feature you want to unlock from the app’s menu.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the on-screen instructions to modify the vehicle’s settings.
- Test and Verify: After unlocking the feature, test it to ensure it functions correctly.
5.4 Risks and Precautions
Unlocking hidden features can be risky, and it’s essential to take precautions:
- Voiding Warranty: Modifying vehicle settings can void your Tesla warranty.
- Potential Damage: Incorrect modifications can damage the car’s systems.
- Software Glitches: Unlocking features can sometimes lead to software glitches or instability.
- Legal Implications: Some modifications may not be legal in your region.
- Always Backup: Create a backup of your original vehicle settings before making any modifications.
- Research Thoroughly: Ensure you fully understand the consequences of unlocking each feature.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re unsure about any step, consult a qualified Tesla technician.
6. Maintaining Your Model 3: Tips and Best Practices
6.1 Regular Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your Model 3 in top condition. Tesla recommends the following maintenance tasks:
- Tire Rotations: Rotate tires every 6,250 miles to ensure even wear.
- Brake Inspections: Inspect brake pads and rotors regularly.
- Fluid Checks: Check and top off windshield washer fluid.
- Cabin Filter Replacement: Replace the cabin filter every year or 12,500 miles.
- Battery Maintenance: Follow Tesla’s guidelines for battery care and charging.
- Coolant Flush: Perform a coolant flush every four years to maintain optimal thermal management of the battery pack and drivetrain.
- Brake Fluid Check: Inspect and replace brake fluid every two years to ensure proper braking performance and prevent corrosion.
6.2 Using the OBD2 Port for Maintenance
The OBD2 port can be used to monitor various parameters related to maintenance:
- Battery Health: Track battery degradation and charging cycles.
- Brake Wear: Monitor brake pad thickness and rotor condition.
- Motor Temperature: Ensure the motor is operating within the optimal temperature range.
- Software Updates: Check for available software updates.
6.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
The OBD2 port can also help troubleshoot common issues:
- Warning Lights: Identify the cause of warning lights on the dashboard.
- Performance Problems: Diagnose issues affecting acceleration, range, or handling.
- Charging Issues: Troubleshoot problems with the charging system.
6.4 Resources for Model 3 Maintenance
- Tesla Owner’s Manual: Refer to your Tesla owner’s manual for maintenance schedules and guidelines.
- Tesla Service Centers: Schedule maintenance appointments at a Tesla service center.
- Online Forums: Consult online forums for tips and advice from other Model 3 owners.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Explore our website for detailed maintenance guides and support resources.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using the Model 3 OBD2 Port
7.1 Incorrect Scanner Selection
Using an incompatible OBD2 scanner can lead to inaccurate readings or damage to the vehicle’s systems.
7.2 Neglecting Safety Precautions
Failing to power down the vehicle or take proper safety precautions can result in electrical issues or personal injury.
7.3 Misinterpreting DTCs
Incorrectly interpreting DTCs can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
7.4 Overlooking Software Updates
Using outdated software can result in compatibility issues or inaccurate data.
7.5 Ignoring Warning Signs
Ignoring warning signs or unusual behavior can lead to more significant problems down the road.
7.6 Unauthorized Modifications
Making unauthorized modifications to the vehicle’s systems can void the warranty or cause damage.
7.7 Overlooking Physical Damage
Failing to inspect the OBD2 port and cable for physical damage can lead to connection problems or inaccurate readings.
7.8 Neglecting Data Backups
Not backing up original vehicle settings before making modifications can make it difficult to revert to the original configuration if something goes wrong.
7.9 Forgetting to Disconnect
Leaving the OBD2 scanner connected for extended periods can drain the car’s battery.
7.10 Lack of Professional Consultation
Attempting complex diagnostics or modifications without professional guidance can lead to mistakes and potential damage.
8. The Future of OBD2 and Diagnostics for Electric Vehicles
8.1 Advancements in OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the needs of modern vehicles. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global OBD market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
8.2 Adapting to Electric Vehicle Diagnostics
As electric vehicles become more prevalent, OBD2 systems are adapting to monitor new parameters related to battery health, motor performance, and charging systems.
8.3 The Role of Wireless and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Wireless and cloud-based diagnostics are becoming increasingly common, allowing for remote monitoring and troubleshooting of vehicle issues.
8.4 The Future of DIY Diagnostics
With the right tools and knowledge, DIY diagnostics will continue to empower vehicle owners to take control of their car’s maintenance and repair.
8.5 The Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being integrated into diagnostic tools to provide more accurate and insightful data analysis.
8.6 Cybersecurity Considerations
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming a critical concern. Protecting the OBD2 port from unauthorized access is essential to prevent hacking or data breaches.
9. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Model 3 Diagnostics
9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Tesla vehicles, including the Model 3.
9.2 Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of experienced technicians provides expert guidance and support to help you diagnose and troubleshoot issues with your Model 3.
9.3 Detailed Guides and Resources
We offer detailed guides and resources on various topics related to Model 3 diagnostics, maintenance, and customization.
9.4 Community Forum
Our online forum provides a platform for Model 3 owners to connect, share tips, and ask questions.
9.5 Software and Firmware Updates
We provide access to the latest software and firmware updates for your OBD2 scanner and diagnostic tools.
9.6 Custom Solutions
We offer custom diagnostic solutions tailored to your specific needs and requirements.
9.7 Training Programs
We provide training programs for technicians and DIY enthusiasts who want to learn more about Model 3 diagnostics.
9.8 Remote Diagnostic Services
We offer remote diagnostic services to help you troubleshoot issues from the comfort of your home or office.
9.9 Secure Data Handling
We prioritize the security and privacy of your data, ensuring that your diagnostic information is protected.
9.10 Continuous Improvement
We are committed to continuously improving our products and services to meet the evolving needs of Model 3 owners.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the Model 3 OBD2 Port
10.1 What is the Model 3 OBD2 port used for?
The Model 3 OBD2 port is used for diagnosing vehicle issues, monitoring performance, and unlocking hidden features.
10.2 Where is the OBD2 port located in the Model 3?
The OBD2 port is located at the rear of the center console, under the air vents, and can be accessed from the rear legroom after removing the rear center console cover.
10.3 What type of OBD2 scanner is compatible with the Model 3?
Compatible OBD2 scanners include the OBDLink MX+, Scan My Tesla app, and TM-Spy app.
10.4 Can I use a generic OBD2 scanner with my Model 3?
While some generic OBD2 scanners may work, it’s best to use a scanner specifically recommended for Tesla vehicles.
10.5 How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using the OBD2 port?
Connect your OBD2 scanner to the port and follow the instructions to read the stored DTCs.
10.6 What are some common issues that can be diagnosed using the OBD2 port?
Common issues include battery health, motor performance, charging issues, and emissions system problems.
10.7 Can I unlock hidden features on my Model 3 using the OBD2 port?
Yes, but it requires specific tools, software, and knowledge, and it can be risky.
10.8 What are the risks of unlocking hidden features?
Risks include voiding the warranty, potential damage, software glitches, and legal implications.
10.9 How often should I perform maintenance on my Model 3?
Refer to your Tesla owner’s manual for maintenance schedules and guidelines.
10.10 Where can I find more information about Model 3 diagnostics and maintenance?
Explore MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for detailed guides and support resources.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your Model 3? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, comprehensive diagnostic tools, and personalized support. Our team is here to help you diagnose issues, unlock hidden features, and keep your Tesla running smoothly.
Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or connect via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and to explore our range of services. Let us empower you to take control of your Tesla’s diagnostics and maintenance.