The Obd2 Scanner Connector is your gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you demystify this essential tool, offering solutions for diagnosing issues and unlocking hidden features in your Mercedes. This guide explores the OBD2 port, diagnostic tools, and how they empower you to maintain your vehicle. Discover vehicle diagnostics, car diagnostic tools, and automotive diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 System
- 1.1 What is OBD2?
- 1.2 History and Evolution of OBD2
- 1.3 Why is OBD2 Important?
- 1.4 OBD2 vs OBD1: What’s the Difference?
- 2. The OBD2 Connector: Your Car’s Diagnostic Port
- 2.1 What is the OBD2 Connector?
- 2.2 Location of the OBD2 Connector
- 2.3 OBD2 Connector Pinout and Functionality
- 2.4 Types of OBD2 Connectors: A vs. B
- 3. OBD2 Scanners: Tools for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 3.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 3.2 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 3.3 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.4 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 3.5 How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 4. Using an OBD2 Scanner: Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 4.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3 Understanding OBD2 Codes
- 4.4 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.5 Reading Live Data and Sensor Information
- 4.6 Performing Other Diagnostic Tests
- 5. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
- 5.1 Bi-Directional Control
- 5.2 Module Programming
- 5.3 Accessing OEM-Specific Data
- 5.4 Unlocking Hidden Features
- 6. Common OBD2 Issues and Troubleshooting
- 6.1 Scanner Not Connecting
- 6.2 Inaccurate Readings
- 6.3 Clearing Codes That Immediately Return
- 6.4 Scanner Freezing or Crashing
- 7. OBD2 and Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 7.1 Specific OBD2 Considerations for Mercedes-Benz
- 7.2 Common Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 7.3 Unlocking Hidden Features on Mercedes-Benz
- 7.4 Choosing the Right Scanner for Mercedes-Benz
- 8. The Future of OBD: OBD3 and Beyond
- 8.1 What is OBD3?
- 8.2 Key Features of OBD3
- 8.3 Challenges and Concerns
- 8.4 The Role of OBD in Modern Automotive Technology
- 9. Resources and Further Learning
- 9.1 Online OBD2 Code Lookup Tools
- 9.2 OBD2 Forums and Communities
- 9.3 Educational Resources
- 9.4 Books and Publications
- 10. Contact Us for Expert Assistance
- FAQ: OBD2 Scanner Connector
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner connector?
- 2. Where is the OBD2 connector located in my car?
- 3. What types of OBD2 scanners are available?
- 4. How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using an OBD2 scanner?
- 5. What do OBD2 codes mean?
- 6. Can I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) with an OBD2 scanner?
- 7. What is live data and how can I access it with an OBD2 scanner?
- 8. What is bi-directional control and how is it used?
- 9. Can I unlock hidden features in my Mercedes-Benz using an OBD2 scanner?
- 10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my car?
1. Understanding the OBD2 System
1.1 What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system in vehicles that provides self-diagnostic and reporting capabilities. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated in all cars sold in the United States from 1996 onwards to monitor emission control systems. This system allows you to access a wealth of data about your vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues early on.
1.2 History and Evolution of OBD2
The OBD2 system evolved from earlier diagnostic systems in response to stricter emission regulations. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) was a major driver in the development of OBD standards. As noted by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 standardized the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and the connector interface across different manufacturers.
1.3 Why is OBD2 Important?
OBD2 is vital for several reasons:
- Emission Control: It ensures that vehicles meet emission standards by monitoring the performance of emission-related components.
- Early Issue Detection: It allows you to identify potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
- Data Accessibility: It provides access to real-time data about your vehicle’s performance.
- Standardization: It offers a standardized interface for diagnostics across different vehicle makes and models.
1.4 OBD2 vs OBD1: What’s the Difference?
OBD1 was the predecessor to OBD2 and had several limitations. OBD2 is more comprehensive, standardized, and offers more detailed diagnostic information. Key differences include:
- Standardization: OBD2 uses a standardized 16-pin connector (SAE J1962), while OBD1 connectors varied by manufacturer.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 employs standardized DTCs, making it easier to diagnose issues across different vehicles.
- Data Parameters: OBD2 provides access to a wider range of data parameters and sensors.
- Communication Protocol: OBD2 uses more advanced communication protocols like CAN (Controller Area Network).
2. The OBD2 Connector: Your Car’s Diagnostic Port
2.1 What is the OBD2 Connector?
The OBD2 connector, also known as the diagnostic port or Data Link Connector (DLC), is a 16-pin interface located inside your vehicle, typically under the dashboard. It allows you to connect an OBD2 scanner to your car’s computer system. This connector is standardized as per SAE J1962, ensuring compatibility across different vehicles.
2.2 Location of the OBD2 Connector
The OBD2 connector is usually found within a few feet of the steering wheel. Common locations include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the center console
- Behind an access panel
If you’re having trouble locating it, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
2.3 OBD2 Connector Pinout and Functionality
The OBD2 connector has 16 pins, each with a specific function. Some key pins include:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K Line
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L Line
- Pin 16: Battery Power
2.4 Types of OBD2 Connectors: A vs. B
There are two main types of OBD2 connectors: Type A and Type B. Type A is commonly found in cars and light-duty vehicles, while Type B is used in medium and heavy-duty vehicles. The primary difference is the voltage output, with Type A providing 12V and Type B providing 24V.
3. OBD2 Scanners: Tools for Vehicle Diagnostics
3.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a device that connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and retrieves diagnostic information. It reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), accesses real-time sensor data, and performs various diagnostic tests. These scanners range from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools.
3.2 Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, each with varying capabilities and features:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, inexpensive devices that read and clear DTCs.
- Handheld Scanners: These offer more advanced features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and O2 sensor testing.
- PC-Based Scanners: These connect to a laptop or desktop computer and offer extensive diagnostic capabilities through software.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter to connect to your smartphone and provide diagnostic information via an app.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are high-end tools used by mechanics and technicians, offering advanced features like bi-directional control, module programming, and comprehensive system diagnostics.
3.3 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Code Reading and Clearing: The ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Live Data Streaming: Real-time display of sensor data.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is triggered.
- O2 Sensor Testing: Tests the performance of oxygen sensors.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to control and test vehicle components.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner can be updated with the latest vehicle information.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
3.4 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
Several reputable brands offer high-quality OBD2 scanners. Some of the top brands include:
- Autel: Known for their professional-grade scanners with advanced features.
- Launch: Offers a wide range of scanners suitable for both DIYers and professionals.
- Innova: Popular for their user-friendly and reliable scanners.
- BlueDriver: Known for their smartphone-based scanners with comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Foxwell: Provides affordable and feature-rich scanners.
3.5 How to Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs and budget. If you’re a DIYer looking to perform basic diagnostics, a handheld or smartphone-based scanner may suffice. For more advanced diagnostics and professional use, consider a PC-based or professional-grade scanner.
4. Using an OBD2 Scanner: Step-by-Step Guide
4.1 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Connector: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle, usually under the dashboard.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically or may require you to press a power button.
4.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option on the scanner’s menu.
- View DTCs: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further investigation.
- Interpret the Codes: Use an OBD2 code lookup tool or database to interpret the meaning of each code.
4.3 Understanding OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are five-character alphanumeric codes that provide information about the nature and location of a problem. The first character indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The remaining three characters provide more specific information about the fault.
4.4 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Erase Codes”: Navigate to the “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Confirm the Erase: The scanner may ask you to confirm that you want to erase the codes.
- Verify the Clear: After clearing the codes, start the engine and check if the codes reappear. If they do, the underlying issue still needs to be addressed.
4.5 Reading Live Data and Sensor Information
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the scanner’s menu.
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and O2 sensor readings.
- View Live Data: The scanner will display real-time values for the selected parameters.
4.6 Performing Other Diagnostic Tests
Many OBD2 scanners offer additional diagnostic tests, such as:
- O2 Sensor Test: Evaluates the performance of oxygen sensors.
- EVAP System Test: Checks the integrity of the evaporative emission control system.
- Readiness Monitors: Shows the status of various emission-related monitors.
5. Advanced OBD2 Functions and Capabilities
5.1 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and control various components. This feature is useful for testing actuators, solenoids, and other devices.
5.2 Module Programming
Some professional-grade OBD2 scanners offer module programming capabilities, allowing you to reprogram or update the software in various vehicle modules.
5.3 Accessing OEM-Specific Data
Advanced scanners can access OEM-specific data and diagnostic routines, providing more in-depth information about your vehicle’s systems.
5.4 Unlocking Hidden Features
With the right OBD2 scanner and software, you can unlock hidden features in your vehicle, such as:
- Automatic Door Locking: Enable automatic door locking when the vehicle reaches a certain speed.
- Comfort Turn Signals: Adjust the number of flashes for comfort turn signals.
- Gauge Adjustments: Customize the appearance of your instrument cluster.
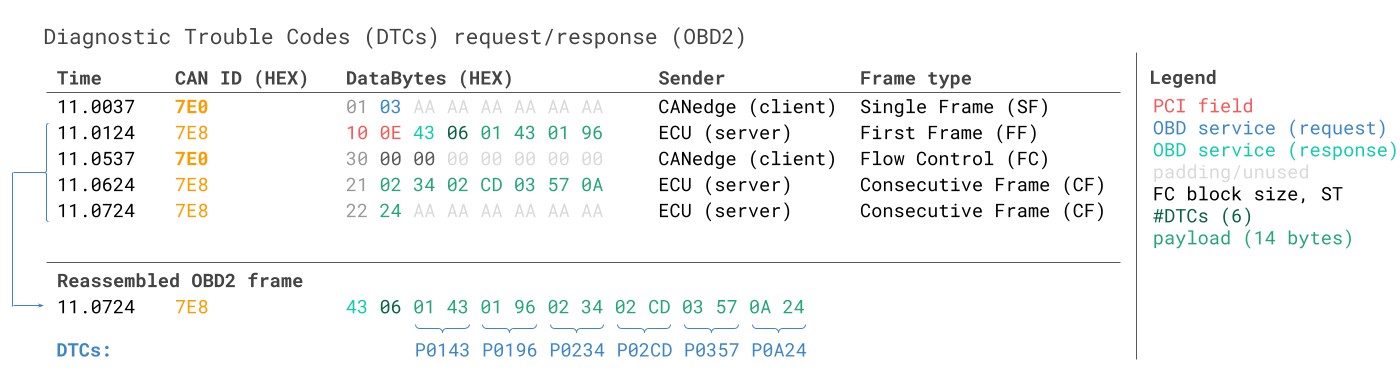 OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
6. Common OBD2 Issues and Troubleshooting
6.1 Scanner Not Connecting
If your OBD2 scanner is not connecting, try the following:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Power: Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
- Check the Scanner: Ensure the scanner is powered on and functioning correctly.
- Compatibility: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- OBD2 Port Issues: Check the OBD2 port for damaged or bent pins.
6.2 Inaccurate Readings
If you’re getting inaccurate readings from your OBD2 scanner, consider the following:
- Scanner Calibration: Calibrate the scanner according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Sensor Issues: Faulty sensors can cause inaccurate readings. Check the sensor data for anomalies.
- Wiring Problems: Check for damaged or corroded wiring that could affect sensor signals.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates.
6.3 Clearing Codes That Immediately Return
If you clear DTCs and they immediately return, the underlying issue still needs to be addressed. Investigate the cause of the code and repair the problem before clearing the codes again.
6.4 Scanner Freezing or Crashing
If your OBD2 scanner freezes or crashes, try the following:
- Restart the Scanner: Power off the scanner and then power it back on.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates.
- Contact Support: If the problem persists, contact the scanner manufacturer for support.
7. OBD2 and Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
7.1 Specific OBD2 Considerations for Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz vehicles adhere to the OBD2 standard but may also have manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes and routines. Advanced scanners that support Mercedes-Benz diagnostics are recommended for comprehensive troubleshooting.
7.2 Common Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Some common DTCs for Mercedes-Benz vehicles include:
- P0171/P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 1/Bank 2)
- P0300: Random Misfire Detected
- P0400: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunction
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- P0715: Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
7.3 Unlocking Hidden Features on Mercedes-Benz
Many Mercedes-Benz owners are interested in unlocking hidden features via OBD2. Common features include:
- AMG Menu in Instrument Cluster: Enable the AMG menu for performance data display.
- Cornering Lights: Activate cornering lights for improved visibility.
- Seatbelt Chime Deactivation: Disable the seatbelt chime for personal preference.
- Video in Motion: Allow video playback while the vehicle is in motion.
7.4 Choosing the Right Scanner for Mercedes-Benz
For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, consider OBD2 scanners that offer advanced diagnostic capabilities and support OEM-specific codes. Brands like Autel and Launch are popular choices among Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians.
8. The Future of OBD: OBD3 and Beyond
8.1 What is OBD3?
OBD3 is the next generation of on-board diagnostics, designed to provide more comprehensive and real-time monitoring of vehicle emissions. It aims to transmit diagnostic data wirelessly to regulatory agencies, allowing for remote monitoring of vehicle emissions compliance.
8.2 Key Features of OBD3
- Wireless Data Transmission: OBD3 will transmit diagnostic data wirelessly to a central server.
- Real-Time Monitoring: It will provide real-time monitoring of vehicle emissions.
- Remote Diagnostics: Regulatory agencies will be able to remotely diagnose emission-related issues.
8.3 Challenges and Concerns
OBD3 faces several challenges and concerns, including:
- Data Security: Ensuring the security and privacy of vehicle data.
- Implementation Costs: The cost of implementing the necessary hardware and infrastructure.
- Privacy Concerns: Concerns about government surveillance and data collection.
8.4 The Role of OBD in Modern Automotive Technology
OBD continues to play a crucial role in modern automotive technology, providing valuable diagnostic information and supporting the development of advanced vehicle systems. As vehicles become more complex, the importance of OBD will only continue to grow.
9. Resources and Further Learning
9.1 Online OBD2 Code Lookup Tools
- RepairPal: Offers a comprehensive OBD2 code chart with detailed descriptions and troubleshooting tips.
- OBD-Codes.com: Provides a database of OBD2 codes and related information.
- AutoCodes.com: Offers a searchable database of OBD2 codes and diagnostic information.
9.2 OBD2 Forums and Communities
- OBD2.com: A forum dedicated to OBD2 diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Automotive Forums: Various automotive forums offer sections dedicated to OBD2 diagnostics.
9.3 Educational Resources
- SAE International: The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) offers standards and resources related to OBD2 technology.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): Provides information on OBD regulations and compliance.
9.4 Books and Publications
- “OBD2 Automotive Code Encyclopedia and Cross-Reference Guide” by Mandy Concepcion
- “Automotive Diagnostic Systems: Understanding OBD-I & OBD-II” by Keith McCord
10. Contact Us for Expert Assistance
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we’re here to help you navigate the complexities of OBD2 diagnostics and unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz.
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Whether you’re seeking guidance on choosing the right OBD2 scanner, understanding diagnostic trouble codes, or unlocking hidden features, our team of experts is ready to assist you. Contact us today to discover how we can enhance your Mercedes-Benz ownership experience.
FAQ: OBD2 Scanner Connector
1. What is an OBD2 scanner connector?
An OBD2 scanner connector is a standardized 16-pin port in your vehicle that allows you to connect an OBD2 scanner for diagnostic purposes. It provides access to your car’s computer system, enabling you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests.
2. Where is the OBD2 connector located in my car?
The OBD2 connector is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering wheel. It may also be found near the center console or behind an access panel. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you’re having trouble locating it.
3. What types of OBD2 scanners are available?
There are several types of OBD2 scanners, including basic code readers, handheld scanners, PC-based scanners, smartphone-based scanners, and professional-grade scanners. Each type offers varying capabilities and features to suit different needs and budgets.
4. How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) using an OBD2 scanner?
To read DTCs, connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option on the scanner’s menu. The scanner will display any stored DTCs.
5. What do OBD2 codes mean?
OBD2 codes are five-character alphanumeric codes that provide information about the nature and location of a problem. The first character indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The remaining characters provide more specific information about the fault.
6. Can I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can clear DTCs using an OBD2 scanner. Navigate to the “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes” option on the scanner’s menu and confirm the erase. However, if the codes reappear after clearing them, the underlying issue still needs to be addressed.
7. What is live data and how can I access it with an OBD2 scanner?
Live data refers to real-time values for various parameters, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and O2 sensor readings. To access live data, connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port, turn the ignition to the “ON” position, and navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the scanner’s menu. Select the parameters you want to monitor.
8. What is bi-directional control and how is it used?
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and control various components. This feature is useful for testing actuators, solenoids, and other devices. It is typically available on professional-grade OBD2 scanners.
9. Can I unlock hidden features in my Mercedes-Benz using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, with the right OBD2 scanner and software, you can unlock hidden features in your Mercedes-Benz, such as enabling the AMG menu, activating cornering lights, deactivating the seatbelt chime, and enabling video in motion.
10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my car?
If your OBD2 scanner is not connecting, check the connection to ensure it is securely plugged into the OBD2 port. Verify that the vehicle’s ignition is turned on and that the scanner is powered on and functioning correctly. Also, ensure that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. If the problem persists, check the OBD2 port for damaged or bent pins.
We encourage you to reach out to MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for any further questions or assistance you may need.