OBD2 pin out is essential for accessing your Mercedes-Benz’s diagnostic data, and at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information and tools to understand and utilize this interface effectively. This guide explores the OBD2 connector, its pin out configurations, and how it facilitates vehicle diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Pin Out and Its Importance
- 1.1 The Role of OBD2 in Modern Vehicle Diagnostics
- 1.2 Benefits of Knowing Your Mercedes OBD2 Pin Out
- 1.3 Common Misconceptions About OBD2
- 2. Detailed OBD2 Pin Out Configuration for Mercedes-Benz
- 2.1 Identifying Communication Protocols via OBD2 Pin Out
- 2.2 Manufacturer-Specific Pins in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 2.3 Common Issues Related to Faulty OBD2 Pin Connections
- 3. Tools Needed to Read OBD2 Pin Out Data
- 3.1 Top OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 3.2 Using Multimeters and Oscilloscopes for Pin Out Testing
- 3.3 Diagnostic Software and Apps for Interpreting OBD2 Data
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Issues Using OBD2 Pin Out
- 4.1 Identifying Common Mercedes-Benz Issues via OBD2 Codes
- 4.2 Using Real-Time Data to Diagnose Performance Problems
- 4.3 Advanced Diagnostic Procedures Using OBD2
- 5. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Pin Out
- 5.1 Preventing Electrical Damage During OBD2 Testing
- 5.2 Best Practices for Handling OBD2 Connectors and Cables
- 5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
- 6. Upgrading Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Pin Out Access
- 6.1 Performance Tuning and ECU Remapping via OBD2
- 6.2 Activating Hidden Features Using OBD2
- 6.3 Risks and Benefits of Upgrading via OBD2
- 7. The Future of OBD2 Pin Out and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 7.1 OBD3 and Remote Diagnostics
- 7.2 The Role of AI in Interpreting OBD2 Data
- 7.3 Cybersecurity Concerns and OBD2 Access
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About OBD2 Pin Out
- 8.1 What is the OBD2 port location in a Mercedes-Benz?
- 8.2 Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my Mercedes-Benz?
- 8.3 What does it mean when the check engine light is on?
- 8.4 How do I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
- 8.5 Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
- 8.6 Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner?
- 8.7 What is the difference between OBD2 and OBD1?
- 8.8 How often should I scan my car for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
- 8.9 Can I use an OBD2 scanner to reset my car’s service light?
- 8.10 Where can I find more information about OBD2 pin out and vehicle diagnostics?
1. Understanding the OBD2 Pin Out and Its Importance
What is the OBD2 pin out, and why should Mercedes owners care? The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) pin out refers to the specific arrangement of pins on the OBD2 connector, a standardized interface used to access diagnostic information from a vehicle’s computer. This interface allows mechanics, technicians, and even car enthusiasts to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform various diagnostic tests, thus enhancing vehicle maintenance and repair processes. Understanding the OBD2 pin out is crucial for anyone looking to diagnose issues with their Mercedes-Benz efficiently.
The OBD2 standard, introduced in the mid-1990s, was designed to standardize vehicle diagnostics across different manufacturers. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defined the specifications for the OBD2 connector and communication protocols. The OBD2 system monitors various vehicle parameters, including engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. When a problem is detected, the system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which can be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner connected to the OBD2 port.
The OBD2 connector typically has 16 pins, each assigned a specific function. While some pins are standardized across all vehicles, others may be manufacturer-specific or used for different communication protocols. The standardized pins include those for power, ground, CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, and ISO 9141-2 communication. Non-standardized pins may be used for manufacturer-specific diagnostics or communication protocols.
1.1 The Role of OBD2 in Modern Vehicle Diagnostics
OBD2 plays a pivotal role in modern vehicle diagnostics. By providing a standardized interface, it enables technicians to quickly identify and address issues, reducing diagnostic time and costs. Here’s how OBD2 contributes to efficient vehicle maintenance:
- Standardized Diagnostics: OBD2 ensures that diagnostic tools and procedures are consistent across different vehicle makes and models. This standardization simplifies the diagnostic process, making it easier for technicians to work on a variety of vehicles.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: OBD2 allows technicians to monitor real-time data from various sensors and systems in the vehicle. This capability enables them to identify intermittent issues and assess the performance of different components under various operating conditions.
- Emission Control: One of the primary purposes of OBD2 is to monitor vehicle emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. The system monitors the performance of emission-related components, such as the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors, and alerts the driver if a problem is detected.
1.2 Benefits of Knowing Your Mercedes OBD2 Pin Out
Knowing the OBD2 pin out for your Mercedes-Benz can offer several benefits:
- DIY Diagnostics: With the right tools and knowledge, you can perform your own diagnostic checks, saving money on mechanic fees. By understanding the OBD2 pin out, you can use a scanner to read DTCs, monitor real-time data, and perform basic diagnostic tests.
- Informed Discussions with Mechanics: Understanding the basics of OBD2 can help you have more informed discussions with your mechanic, ensuring you’re both on the same page about the issue and potential solutions.
- Accessing Advanced Features: Some advanced diagnostic tools and software allow you to perform advanced functions, such as reprogramming control modules and customizing vehicle settings. Knowledge of the OBD2 pin out is essential for using these tools effectively.
- Vehicle Security: Understanding OBD2 can help you protect your vehicle from potential security threats. The OBD2 port can be a point of entry for hackers, so knowing how to secure it is crucial.
1.3 Common Misconceptions About OBD2
Several misconceptions surround OBD2 and its capabilities. Let’s debunk a few of them:
- OBD2 Can Fix Problems Automatically: OBD2 is a diagnostic tool; it identifies problems but doesn’t automatically fix them. The OBD2 system provides information about the issue, but it’s up to a technician or the vehicle owner to perform the necessary repairs.
- All OBD2 Scanners Are Created Equal: Different scanners offer different capabilities. Basic scanners can read and clear DTCs, while advanced scanners offer features like real-time data monitoring, bi-directional control, and programming capabilities.
- OBD2 Can Unlock Hidden Features: While some features can be accessed or modified through OBD2, this is not a standard function and may require specialized tools and knowledge. The ability to unlock hidden features depends on the vehicle’s software and the capabilities of the diagnostic tool.
- OBD2 Is Only for Mechanics: While mechanics use OBD2 extensively, car enthusiasts and DIYers can also benefit from understanding and using OBD2 tools for vehicle maintenance.
2. Detailed OBD2 Pin Out Configuration for Mercedes-Benz
What exactly do each of the pins in the OBD2 connector do in a Mercedes-Benz? The OBD2 connector has 16 pins, each serving a specific function. Not all pins are universally used across all vehicles, and some are specific to certain manufacturers or communication protocols. Here’s a detailed look at the typical OBD2 pin out configuration for Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
| Pin Number | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 2 | SAE J1850 Bus Positive (+) | Used for SAE J1850 communication protocol, common in older vehicles. |
| 3 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a ground connection to the vehicle’s chassis. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a ground connection for signal circuits. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | High signal wire for the CAN bus communication protocol. |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | Used for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000) communication protocols. |
| 8 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 9 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus Negative (-) | Used for SAE J1850 communication protocol, common in older vehicles. |
| 11 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 12 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 13 | Manufacturer Discretion | Can be used for manufacturer-specific purposes. Varies between different car models and manufacturers. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Low signal wire for the CAN bus communication protocol. |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | Used for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol. |
| 16 | Battery Power (+12V or +24V) | Provides power to the diagnostic tool, typically from the vehicle’s battery. |
2.1 Identifying Communication Protocols via OBD2 Pin Out
How can you use the OBD2 pin out to identify the communication protocols used by your Mercedes? Identifying the communication protocols used by your Mercedes-Benz is crucial for selecting the right diagnostic tools and procedures. Here’s how the OBD2 pin out can help you determine the protocols in use:
- CAN Bus (Controller Area Network): CAN bus is the most common communication protocol in modern vehicles. It uses pins 6 (CAN High) and 14 (CAN Low) for communication. If your Mercedes-Benz uses CAN bus, you’ll find these pins populated.
- ISO 9141-2: This protocol was used in older vehicles. It uses pin 7 (K-Line) and sometimes pin 15 (L-Line) for communication. If your vehicle uses ISO 9141-2, you’ll find pin 7 populated.
- SAE J1850 VPW and PWM: These protocols were common in older GM and Ford vehicles, respectively. SAE J1850 VPW uses pin 2, while SAE J1850 PWM uses pins 2 and 10. If your vehicle uses SAE J1850, you’ll find these pins populated.
2.2 Manufacturer-Specific Pins in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Are there any pins in the OBD2 connector that are specific to Mercedes-Benz, and what do they do? Mercedes-Benz, like other manufacturers, may use some of the undefined pins (1, 3, 8, 9, 11, 12, and 13) for proprietary diagnostic or communication purposes. These pins can be used for:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Accessing additional diagnostic data beyond the standardized OBD2 parameters.
- Programming and Configuration: Reprogramming control modules or configuring vehicle settings.
- Security Functions: Implementing security features or accessing vehicle immobilizer systems.
To understand the specific functions of these pins, you may need access to Mercedes-Benz’s technical documentation or specialized diagnostic tools. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer resources and tools that can help you interpret these manufacturer-specific signals.
2.3 Common Issues Related to Faulty OBD2 Pin Connections
What are some common issues that can arise from faulty OBD2 pin connections, and how can they be resolved? Faulty OBD2 pin connections can lead to various diagnostic and communication problems. Common issues include:
- No Communication: If the power or ground pins (4, 5, and 16) are faulty, the diagnostic tool may not power on or communicate with the vehicle.
- Intermittent Communication: Loose or corroded connections can cause intermittent communication issues, resulting in unreliable diagnostic data.
- Data Corruption: Faulty signal pins can lead to corrupted data, resulting in inaccurate diagnostic readings.
- ECU Damage: In rare cases, incorrect voltage or short circuits in the OBD2 connector can damage the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs).
To resolve these issues, you can:
- Inspect the Connector: Check the OBD2 connector for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose pins.
- Clean the Connections: Use a contact cleaner to clean the pins and ensure a good electrical connection.
- Test the Wiring: Use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage of the OBD2 pins.
- Replace the Connector: If the connector is severely damaged, consider replacing it with a new one.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed guides and resources to help you troubleshoot and resolve OBD2 connection issues.
3. Tools Needed to Read OBD2 Pin Out Data
What tools are essential for reading and interpreting data from the OBD2 pin out on a Mercedes-Benz? To effectively read and interpret data from the OBD2 pin out, you’ll need a combination of hardware and software tools. Here’s a list of essential tools:
- OBD2 Scanner: An OBD2 scanner is a handheld device or software application that connects to the OBD2 port and retrieves diagnostic information from the vehicle’s computer. Basic scanners can read and clear DTCs, while advanced scanners offer features like real-time data monitoring, bi-directional control, and programming capabilities.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is a versatile tool used to measure voltage, current, and resistance. It’s essential for testing the continuity and voltage of the OBD2 pins and diagnosing electrical issues.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope is used to visualize electrical signals over time. It can be helpful for analyzing the communication signals on the CAN bus or other communication lines.
- Diagnostic Software: Diagnostic software provides a user-friendly interface for accessing and interpreting OBD2 data. Some software applications offer advanced features like DTC lookup, repair information, and bi-directional control.
- OBD2 Adapter Cables: OBD2 adapter cables are used to connect the diagnostic tool to the OBD2 port. Different types of adapter cables are available for different vehicle makes and models.
- Pin Out Diagrams: Pin out diagrams provide detailed information about the function of each pin in the OBD2 connector. These diagrams are essential for troubleshooting and diagnosing OBD2 connection issues.
3.1 Top OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Which OBD2 scanners are best suited for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, considering their specific diagnostic needs? Choosing the right OBD2 scanner for your Mercedes-Benz can significantly impact your diagnostic capabilities. Here are some of the top OBD2 scanners for Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- Autel MaxiCOM MK906BT: The Autel MaxiCOM MK906BT is an advanced diagnostic scanner that offers comprehensive coverage for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It supports a wide range of functions, including DTC reading and clearing, real-time data monitoring, bi-directional control, and ECU programming.
- iCarsoft MB V3.0: The iCarsoft MB V3.0 is a professional-grade scanner specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It offers advanced diagnostic capabilities, including access to all vehicle systems, special functions, and coding.
- Launch X431 V+: The Launch X431 V+ is a versatile diagnostic scanner that supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models, including Mercedes-Benz. It offers advanced features like ECU programming, key programming, and online coding.
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: The Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis is the official diagnostic tool used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships. It offers the most comprehensive diagnostic and programming capabilities for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
3.2 Using Multimeters and Oscilloscopes for Pin Out Testing
How can multimeters and oscilloscopes be used to test the OBD2 pin out and identify potential issues? Multimeters and oscilloscopes are essential tools for testing the OBD2 pin out and diagnosing electrical issues. Here’s how you can use them:
- Testing Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the OBD2 pins. Continuity testing verifies that there is a complete electrical path between two points. This is useful for identifying broken or corroded wires.
- Measuring Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage of the OBD2 pins. Voltage testing verifies that the correct voltage is present at each pin. This is useful for identifying power supply issues.
- Analyzing Communication Signals: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the communication signals on the CAN bus or other communication lines. An oscilloscope displays the electrical signals over time, allowing you to identify signal distortions or other issues.
By using multimeters and oscilloscopes, you can effectively diagnose and resolve OBD2 pin out issues, ensuring reliable communication between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer.
3.3 Diagnostic Software and Apps for Interpreting OBD2 Data
What diagnostic software and mobile apps are available to help interpret OBD2 data from Mercedes-Benz vehicles? Diagnostic software and mobile apps can significantly enhance your ability to interpret OBD2 data from Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Here are some popular options:
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis Software: The official diagnostic software used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships. It provides comprehensive diagnostic and programming capabilities.
- Torque Pro (Android): A popular OBD2 app for Android devices. It allows you to monitor real-time data, read and clear DTCs, and customize dashboards.
- OBD Fusion (iOS and Android): A versatile OBD2 app for iOS and Android devices. It supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models and offers advanced features like data logging and graphing.
- DashCommand (iOS and Android): An OBD2 app that provides real-time data monitoring, DTC reading and clearing, and customizable dashboards. It also supports performance monitoring and fuel economy tracking.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed reviews and comparisons of diagnostic software and apps to help you choose the right tools for your needs.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Issues Using OBD2 Pin Out
How do you use the OBD2 pin out to diagnose common issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, step by step? Diagnosing issues using the OBD2 pin out involves a systematic approach to identify and resolve problems. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the OBD2 port of your Mercedes-Benz. Ensure the connection is secure and the scanner is powered on.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use the scanner to read the DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. Record the DTCs and their descriptions.
- Research the DTCs: Use a DTC lookup tool or online resources to research the meaning of each DTC. Understand the potential causes and symptoms associated with the DTCs.
- Inspect the OBD2 Connector: Check the OBD2 connector for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose pins. Clean the connector with a contact cleaner if necessary.
- Test the OBD2 Pin Out: Use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage of the OBD2 pins. Verify that the power and ground pins are functioning correctly.
- Analyze Real-Time Data: Use the scanner to monitor real-time data from various sensors and systems in the vehicle. Look for any abnormal readings or inconsistencies.
- Perform Bi-Directional Tests: If your scanner supports bi-directional control, perform tests to activate or deactivate specific components. This can help you isolate the source of the problem.
- Repair or Replace Faulty Components: Based on your diagnostic findings, repair or replace any faulty components. Clear the DTCs and retest the system to ensure the problem is resolved.
4.1 Identifying Common Mercedes-Benz Issues via OBD2 Codes
What are some common issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles that can be identified through specific OBD2 codes? Certain OBD2 codes are commonly associated with specific issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Here are a few examples:
- P0171 and P0174 (System Too Lean): These codes often indicate a vacuum leak, faulty mass airflow sensor, or fuel system issue.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold): This code typically indicates a faulty catalytic converter or oxygen sensor.
- P0300 (Random Misfire Detected): This code can be caused by a variety of issues, including faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
- P0715 (Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction): This code indicates a problem with the input or turbine speed sensor in the transmission.
By recognizing these common codes and their associated symptoms, you can quickly narrow down the potential causes of the problem and focus your diagnostic efforts.
4.2 Using Real-Time Data to Diagnose Performance Problems
How can monitoring real-time data from the OBD2 pin out help diagnose performance problems in a Mercedes-Benz? Monitoring real-time data from the OBD2 pin out can provide valuable insights into the performance of your Mercedes-Benz. Here are some examples:
- Engine Performance: Monitor parameters like engine RPM, coolant temperature, and throttle position to assess the overall performance of the engine.
- Fuel System: Monitor parameters like fuel trim, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel pressure to diagnose fuel system issues.
- Transmission: Monitor parameters like transmission temperature, input speed, and output speed to diagnose transmission problems.
- Emissions: Monitor parameters like oxygen sensor readings and catalytic converter temperature to assess the performance of the emissions system.
By analyzing these real-time data streams, you can identify abnormal readings or inconsistencies that may indicate a problem.
4.3 Advanced Diagnostic Procedures Using OBD2
What are some advanced diagnostic procedures that can be performed using the OBD2 interface on a Mercedes-Benz? Advanced diagnostic procedures can help you diagnose complex issues that may not be apparent through basic OBD2 scanning. These procedures include:
- ECU Programming: Reprogramming the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) to update software, fix bugs, or improve performance.
- Key Programming: Programming new keys or key fobs to the vehicle’s immobilizer system.
- Bi-Directional Control: Activating or deactivating specific components to test their functionality.
- Adaptation Reset: Resetting adaptation values for certain components after replacement or repair.
- Coding: Coding specific features or options to the vehicle’s control units.
These advanced procedures require specialized tools and knowledge and should be performed by qualified technicians. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide resources and training to help you understand and perform these advanced diagnostic procedures safely and effectively.
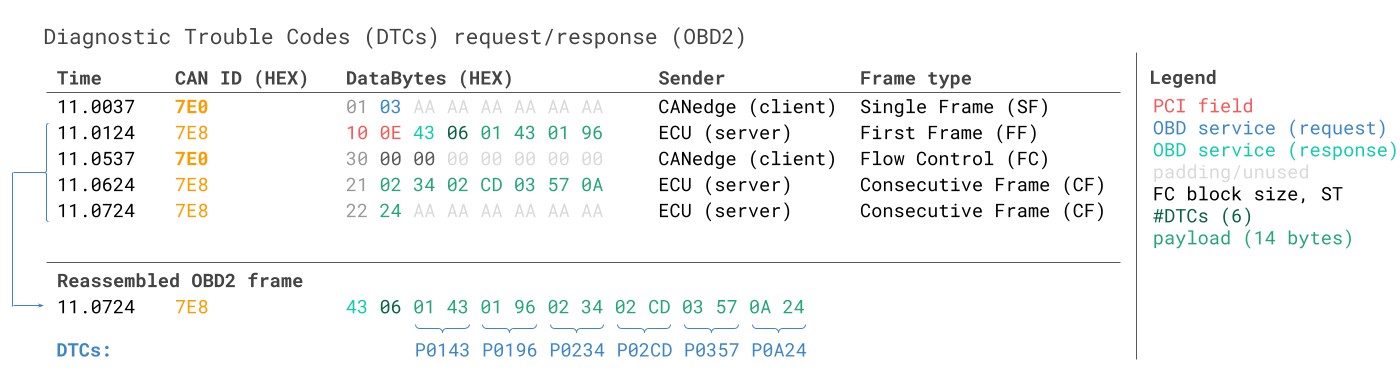 OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
5. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Pin Out
What safety precautions should be taken when working with the OBD2 pin out to avoid damage or injury? Working with the OBD2 pin out involves electrical connections, so it’s important to take certain safety precautions to avoid damage or injury:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before performing any electrical testing or repairs, disconnect the vehicle’s battery to prevent short circuits or electrical shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
- Avoid Short Circuits: Be careful not to create short circuits by accidentally touching the OBD2 pins with metal objects.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using diagnostic tools or performing diagnostic procedures.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris or sparks.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes or gases.
5.1 Preventing Electrical Damage During OBD2 Testing
How can you prevent electrical damage to your Mercedes-Benz or diagnostic tools during OBD2 testing? Preventing electrical damage is crucial when working with the OBD2 pin out. Here are some tips:
- Use the Correct Voltage: Ensure that the diagnostic tool is compatible with the vehicle’s voltage (typically 12V or 24V).
- Avoid Overloading the Circuit: Avoid overloading the OBD2 circuit by connecting multiple devices or drawing excessive current.
- Check for Short Circuits: Before connecting any diagnostic tools, check the OBD2 connector for any signs of short circuits.
- Use a Surge Protector: Use a surge protector to protect the diagnostic tool from voltage spikes or surges.
5.2 Best Practices for Handling OBD2 Connectors and Cables
What are the best practices for handling OBD2 connectors and cables to ensure their longevity and reliability? Proper handling of OBD2 connectors and cables can extend their lifespan and ensure reliable communication. Follow these best practices:
- Avoid Pulling on the Cable: When disconnecting the OBD2 connector, avoid pulling on the cable. Instead, grip the connector and gently pull it out.
- Store Cables Properly: Store OBD2 cables in a clean, dry place to prevent damage or corrosion.
- Protect Connectors from Moisture: Protect OBD2 connectors from moisture and humidity, which can cause corrosion.
- Inspect Cables Regularly: Inspect OBD2 cables regularly for any signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or exposed wires.
5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
When is it necessary to seek professional help from a qualified technician when diagnosing issues using the OBD2 pin out? While DIY diagnostics can be rewarding, there are situations where it’s best to seek professional help:
- Complex Issues: If you’re unable to diagnose the problem after performing basic OBD2 testing, it may be a complex issue that requires specialized knowledge and equipment.
- Electrical Problems: If you suspect an electrical problem, it’s best to seek professional help to avoid damaging the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Safety Concerns: If you’re uncomfortable working with electrical systems or performing certain diagnostic procedures, it’s best to leave it to a professional.
- ECU Programming: ECU programming requires specialized tools and knowledge and should be performed by qualified technicians.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you connect with qualified technicians in your area who can provide professional diagnostic and repair services.
6. Upgrading Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Pin Out Access
Can the OBD2 pin out be used to upgrade or enhance certain features in a Mercedes-Benz vehicle? Yes, the OBD2 pin out can be used to upgrade or enhance certain features in a Mercedes-Benz vehicle. Here are a few examples:
- Performance Tuning: Some tuners use the OBD2 interface to reprogram the engine control unit (ECU) and improve performance.
- Feature Activation: Certain features, such as daytime running lights or cornering lights, can be activated or deactivated using the OBD2 interface.
- Diagnostic Enhancements: Advanced diagnostic tools can provide access to additional diagnostic data and functions beyond the standard OBD2 parameters.
6.1 Performance Tuning and ECU Remapping via OBD2
How is the OBD2 pin out used for performance tuning and ECU remapping in Mercedes-Benz vehicles? Performance tuning and ECU remapping involve modifying the software in the engine control unit (ECU) to improve performance. The OBD2 interface is commonly used to upload the modified software to the ECU. Here’s how it works:
- Connect the Tuning Tool: Connect the tuning tool to the OBD2 port of your Mercedes-Benz.
- Read the Existing ECU Software: Use the tuning tool to read the existing software from the ECU.
- Modify the Software: Use specialized software to modify the ECU software, adjusting parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure.
- Upload the Modified Software: Use the tuning tool to upload the modified software to the ECU.
ECU remapping can improve engine performance, increase horsepower and torque, and improve fuel economy. However, it’s important to choose a reputable tuner and ensure that the modifications are safe and reliable.
6.2 Activating Hidden Features Using OBD2
What hidden features can be activated in Mercedes-Benz vehicles using the OBD2 pin out, and how is it done? Some Mercedes-Benz vehicles have hidden features that can be activated using the OBD2 interface. These features may include:
- Daytime Running Lights: Activating daytime running lights to improve visibility during the day.
- Cornering Lights: Activating cornering lights to improve visibility when turning corners.
- Comfort Features: Activating comfort features such as automatic door locking or automatic window closing.
To activate these features, you’ll need a diagnostic tool that supports coding and programming functions. The process typically involves accessing the vehicle’s control units and modifying certain parameters.
6.3 Risks and Benefits of Upgrading via OBD2
What are the potential risks and benefits of using the OBD2 pin out to upgrade or modify features in a Mercedes-Benz? Upgrading or modifying features using the OBD2 pin out can offer several benefits:
- Improved Performance: Performance tuning can improve engine performance and increase horsepower and torque.
- Enhanced Features: Activating hidden features can enhance the functionality and convenience of your vehicle.
- Customization: Upgrading via OBD2 allows you to customize your vehicle to suit your preferences.
However, there are also potential risks:
- Warranty Issues: Modifying the ECU or other control units can void your vehicle’s warranty.
- Reliability Issues: Incorrectly performed modifications can lead to reliability issues or damage to the vehicle.
- Safety Concerns: Some modifications can compromise the safety of the vehicle.
Before upgrading or modifying features using the OBD2 pin out, it’s important to weigh the risks and benefits and consult with a qualified technician.
7. The Future of OBD2 Pin Out and Vehicle Diagnostics
How is the OBD2 pin out evolving, and what does the future hold for vehicle diagnostics? The OBD2 pin out and vehicle diagnostics are constantly evolving. Here are some trends and future developments:
- Wireless OBD2 Adapters: Wireless OBD2 adapters are becoming increasingly popular. These adapters connect to the OBD2 port and transmit data wirelessly to a smartphone or tablet.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are emerging. These platforms allow technicians to access diagnostic data and perform remote diagnostics.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to analyze diagnostic data and provide more accurate and efficient diagnoses.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important in vehicle diagnostics. Measures are being taken to protect the OBD2 interface from hacking and unauthorized access.
7.1 OBD3 and Remote Diagnostics
What is OBD3, and how will it impact vehicle diagnostics and the use of the OBD2 pin out? OBD3 is the next generation of on-board diagnostics. It will require vehicles to transmit diagnostic data wirelessly to a central server. This will enable remote diagnostics and proactive maintenance. Here’s how OBD3 will impact vehicle diagnostics:
- Remote Monitoring: OBD3 will allow vehicle manufacturers and service providers to remotely monitor the health of vehicles.
- Proactive Maintenance: OBD3 will enable proactive maintenance by alerting vehicle owners and service providers to potential problems before they become major issues.
- Improved Emission Control: OBD3 will improve emission control by enabling remote monitoring of vehicle emissions and prompt detection of emission-related problems.
7.2 The Role of AI in Interpreting OBD2 Data
How will artificial intelligence (AI) enhance the interpretation of OBD2 data and improve diagnostic accuracy? AI can enhance the interpretation of OBD2 data and improve diagnostic accuracy in several ways:
- Data Analysis: AI can analyze large amounts of OBD2 data to identify patterns and trends that may not be apparent to human technicians.
- Fault Prediction: AI can use historical data to predict potential faults and alert technicians to take proactive measures.
- Diagnostic Guidance: AI can provide diagnostic guidance to technicians, helping them to quickly and accurately diagnose complex issues.
7.3 Cybersecurity Concerns and OBD2 Access
What are the cybersecurity concerns associated with OBD2 access, and how can vehicle owners protect themselves? The OBD2 interface can be a point of entry for hackers, so it’s important to be aware of the cybersecurity concerns:
- Unauthorized Access: Hackers can gain unauthorized access to the vehicle’s control units through the OBD2 interface.
- Malware Installation: Hackers can install malware on the vehicle’s control units, which can compromise the vehicle’s functionality and security.
- Data Theft: Hackers can steal sensitive data from the vehicle’s control units, such as personal information or vehicle identification numbers.
To protect yourself, take the following precautions:
- Use Reputable Diagnostic Tools: Use only reputable diagnostic tools from trusted vendors.
- Update Software Regularly: Keep the software on your diagnostic tools up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Secure Your OBD2 Port: Consider installing a lock or security device on your OBD2 port to prevent unauthorized access.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide resources and information to help you understand and address cybersecurity concerns related to OBD2 access.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About OBD2 Pin Out
8.1 What is the OBD2 port location in a Mercedes-Benz?
The OBD2 port in a Mercedes-Benz is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. However, the exact location may vary depending on the model and year of the vehicle. Refer to your owner’s manual for the specific location of the OBD2 port in your vehicle.
8.2 Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my Mercedes-Benz?
While most OBD2 scanners are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles, some scanners may offer more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities than others. Consider scanners specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles for optimal performance.
8.3 What does it mean when the check engine light is on?
The check engine light indicates that there is a problem with one or more of the vehicle’s systems. Use an OBD2 scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and identify the source of the problem.
8.4 How do I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
Use an OBD2 scanner to clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer. However, keep in mind that clearing the DTCs does not fix the underlying problem. The check engine light may come back on if the problem persists.
8.5 Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the severity of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention. In this case, it’s best to avoid driving the vehicle and seek professional help. If the check engine light is on but not flashing, it’s generally safe to drive the vehicle, but you should still have it checked by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
8.6 Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner correctly is generally safe and will not damage your car. However, it’s important to use a reputable scanner from a trusted vendor and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid using cheap or counterfeit scanners, as they may damage the vehicle’s electrical system.
8.7 What is the difference between OBD2 and OBD1?
OBD2 is the second generation of on-board diagnostics. It’s a standardized system that was introduced in the mid-1990s. OBD1 was the first generation of on-board diagnostics, and it was not standardized. OBD2 offers more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and is used in all modern vehicles.
8.8 How often should I scan my car for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
You should scan your car for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as a decrease in performance or fuel economy. Regular scanning can help you identify potential problems early and prevent costly repairs.
8.9 Can I use an OBD2 scanner to reset my car’s service light?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can be used to reset the car’s service light. However, not all scanners support this function. Check the scanner’s documentation to see if it’s compatible with your vehicle and supports service light reset.
8.10 Where can I find more information about OBD2 pin out and vehicle diagnostics?
You can find more information about OBD2 pin out and vehicle diagnostics at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. We offer a wide range of resources, including articles, guides, and tutorials, to help you understand and diagnose issues