Unlock the secrets hidden within your vehicle’s OBD2 codes with this comprehensive guide. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we empower you to understand and resolve these codes, saving you time and money. This guide explains what OBD2 codes are, how to read them, and how they impact your vehicle’s performance. Master your vehicle’s diagnostic language and keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly with enhanced diagnostic tools, error code solutions, and automotive maintenance tips.
Contents
- 1. What are OBD2 Codes?
- 1.1 Why are OBD2 Codes Important?
- 1.2 How Do OBD2 Codes Work?
- 1.3 Where is the OBD2 Port Located?
- 2. Types of OBD2 Codes
- 2.1 Powertrain Codes (P-Codes)
- 2.2 Body Codes (B-Codes)
- 2.3 Chassis Codes (C-Codes)
- 2.4 Network Communication Codes (U-Codes)
- 3. Decoding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
- 3.1 First Character: System Identification
- 3.2 Second Character: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific
- 3.3 Third Character: Subsystem Identification
- 3.4 Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Fault Code
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 4.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 4.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 4.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 4.4 P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- 4.5 P0507: Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
- 5. Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnosis
- 5.1 Connecting the Scanner
- 5.2 Reading the Codes
- 5.3 Interpreting the Results
- 5.4 Clearing the Codes
- 6. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
- 6.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 6.2 Safety-Related Codes
- 6.3 Persistent Codes
- 6.4 Lack of Mechanical Knowledge
- 7. Preventing OBD2 Codes Through Regular Maintenance
- 7.1 Oil Changes
- 7.2 Fluid Checks
- 7.3 Filter Replacements
- 7.4 Spark Plug Inspections
- 7.5 Tire Maintenance
- 8. OBD2 Code Scanners Available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 8.2 Advanced OBD2 Scanners
- 8.3 Professional-Grade Scanners
- 8.4 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 9. Understanding Manufacturer-Specific OBD2 Codes for Mercedes-Benz
- 9.1 Accessing Mercedes-Benz Service Information
- 9.2 Using Specialized Diagnostic Tools
- 9.3 Examples of Mercedes-Benz Specific Codes
- 9.4 Benefits of Understanding Specific Codes
- 10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 10.1 Enhanced Data Logging
- 10.2 Remote Diagnostics
- 10.3 Cloud Integration
- 10.4 Cybersecurity Measures
- FAQ: Decoding Your Vehicle’s Health – Common Questions About OBD2 Codes
- What is an OBD2 code?
- How do I read an OBD2 code?
- Can I fix my car myself after reading an OBD2 code?
- When should I consult a professional mechanic?
- What are the common types of OBD2 codes?
- How can I prevent OBD2 codes from appearing?
- What does the “Check Engine” light mean?
- Are OBD2 scanners universal?
- Can I clear an OBD2 code without fixing the problem?
- Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
1. What are OBD2 Codes?
OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes used to identify potential issues with a vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes act as a communication tool, alerting you to detected problems within various systems like the engine, transmission, and emissions. Think of them as your car’s way of saying, “Hey, something’s not quite right here.” According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these codes are a vital part of modern vehicle diagnostics. When you see a “Check Engine” light, it signifies that the car’s computer has detected something amiss. Using an OBD2 scanner from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can access the specific code and start diagnosing the problem.
1.1 Why are OBD2 Codes Important?
OBD2 codes offer several benefits, especially for Mercedes-Benz owners:
- Early Problem Detection: Identify issues before they become major repairs.
- Informed Decisions: Understand the problem to make informed decisions about repairs.
- Cost Savings: Potentially fix minor issues yourself, saving on mechanic fees.
- Performance Maintenance: Keep your car running efficiently and safely.
1.2 How Do OBD2 Codes Work?
Vehicles equipped with OBD2 systems constantly monitor various sensors and systems. When a sensor reading falls outside of the acceptable range, the car’s computer generates an OBD2 code. According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), this system helps ensure vehicles meet emissions standards. This code is stored in the computer’s memory and can be retrieved using an OBD2 scanner. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer scanners that are specifically designed to work with Mercedes-Benz vehicles, giving you accurate and reliable diagnostic information.
1.3 Where is the OBD2 Port Located?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. In most Mercedes-Benz models, you’ll find it near the steering column or in the footwell area. The port is a standard trapezoidal shape, making it easy to identify. Once you locate it, you can plug in your OBD2 scanner from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN and begin the diagnostic process.
2. Types of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are classified into four main categories: Powertrain (P), Body (B), Chassis (C), and Network Communication (U). Understanding these categories helps you narrow down the source of the problem. These classifications are based on standards set by the SAE. Each category covers different systems and components, providing a comprehensive diagnostic overview.
2.1 Powertrain Codes (P-Codes)
Powertrain codes (P-codes) relate to the engine, transmission, and related components. These are the most common type of OBD2 codes. For instance, P0300 indicates a random misfire in the engine, while P0171 suggests a lean fuel mixture. These codes provide crucial information about the engine’s performance. A faulty oxygen sensor or a malfunctioning fuel injector can trigger these codes. Regular maintenance and quality parts can help prevent powertrain issues.
2.2 Body Codes (B-Codes)
Body codes (B-codes) involve issues with the car’s body systems, such as airbags, power windows, and climate control. For example, B1001 could indicate a problem with the airbag system. These codes are vital for ensuring the safety and comfort features of your vehicle are functioning correctly. Issues with the car’s electrical system can often trigger these codes. Regularly checking and maintaining these systems can prevent such problems.
2.3 Chassis Codes (C-Codes)
Chassis codes (C-codes) pertain to the braking system, suspension, and steering. An example is C0040, which could signal a problem with the anti-lock braking system (ABS). These codes are critical for maintaining the vehicle’s handling and safety. Problems with sensors or hydraulic systems can lead to these codes. Ensuring your braking and suspension systems are in good condition is essential for safety.
2.4 Network Communication Codes (U-Codes)
Network communication codes (U-codes) indicate problems in the vehicle’s communication network, affecting how different modules interact. U0100, for example, suggests a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM). These codes can be complex and may require professional diagnosis. Faulty wiring or module malfunctions can cause these issues. Maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system is crucial for preventing communication problems.
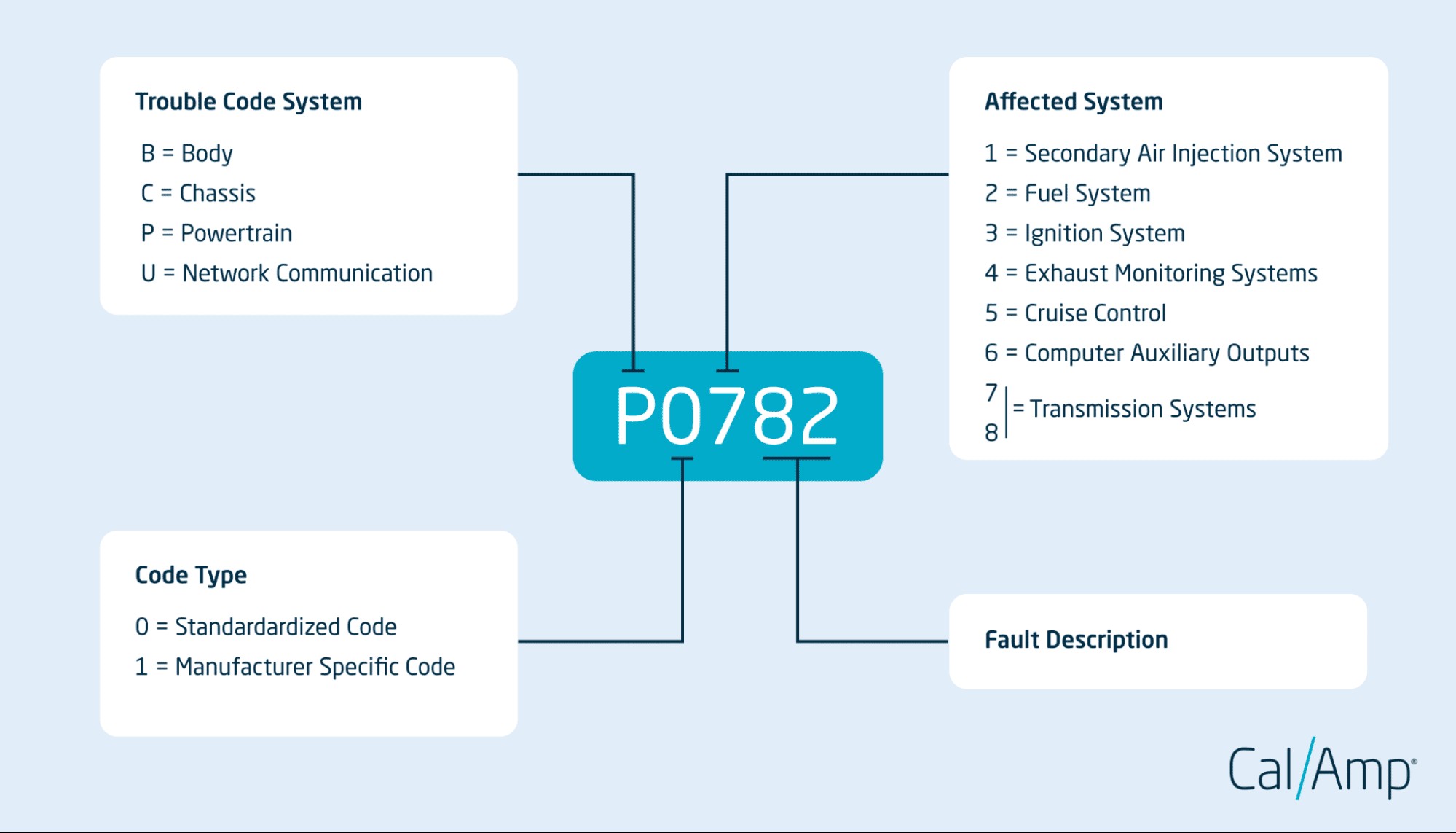
3. Decoding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes follow a standardized five-character format. The first character indicates the system, the second is either a 0 (standardized) or 1 (manufacturer-specific), and the remaining three characters specify the exact fault. The SAE provides detailed documentation on this structure, ensuring consistency across all vehicles. Understanding this structure helps you interpret the codes more effectively.
3.1 First Character: System Identification
The first character identifies the system: P (Powertrain), B (Body), C (Chassis), or U (Network). This is your starting point in understanding the code. For instance, if the code starts with “P,” you know the issue is related to the engine or transmission. This initial identification helps narrow down the diagnostic process.
3.2 Second Character: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific
The second character is “0” for standardized codes and “1” for manufacturer-specific codes. Standardized codes are the same across all vehicles, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular make or model. For example, a P0 code is a generic powertrain code, while a P1 code is specific to the manufacturer. Understanding this distinction helps you determine the level of detail the code provides.
3.3 Third Character: Subsystem Identification
The third character indicates the specific subsystem involved, such as fuel system, ignition system, or emissions system. There are eight common subsystems. Knowing the subsystem helps you focus your diagnostic efforts. For instance, a “2” in the third position often relates to the fuel system.
3.4 Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Fault Code
The fourth and fifth characters provide the specific fault code, detailing the exact problem. These characters offer the most precise information about the issue. For example, in the code P0420, the “20” indicates a problem with the catalytic converter. This detailed identifier is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair.
4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Certain OBD2 codes appear more frequently than others. Knowing these common codes can help you quickly diagnose and address common issues. These codes often relate to typical wear and tear or common component failures. Being familiar with these codes can save you time and money.
4.1 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
P0171 indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there’s too much air and not enough fuel. This can be caused by a vacuum leak, a faulty MAF sensor, or a clogged fuel filter. Addressing this issue promptly can improve fuel efficiency and prevent engine damage. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), vacuum leaks are a common cause of this code.
4.2 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
P0300 signals that the engine is misfiring, which can be due to faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors. Misfires can lead to reduced engine power and increased emissions. Replacing worn spark plugs and inspecting ignition components can resolve this issue. A misfire can cause serious engine damage if left unaddressed.
4.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0420 indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, which can result in increased emissions. This code often means the catalytic converter needs to be replaced. Ensuring your emissions system is functioning correctly is vital for environmental compliance. The EPA has strict regulations regarding catalytic converter efficiency.
4.4 P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
P0442 suggests a small leak in the evaporative emission control system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. This can be caused by a loose gas cap or a faulty EVAP system component. Tightening the gas cap is often the first step in addressing this issue. EVAP system leaks can lead to failed emissions tests.
4.5 P0507: Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
P0507 indicates that the engine’s idle speed is higher than normal, which can be caused by a faulty idle air control valve or a vacuum leak. This can lead to increased fuel consumption and rough idling. Cleaning or replacing the idle air control valve can often resolve this issue. Maintaining proper idle speed is crucial for efficient engine operation.
5. Using an OBD2 Scanner for Diagnosis
An OBD2 scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing vehicle problems. It allows you to read and clear OBD2 codes, providing valuable insights into your car’s health. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of high-quality OBD2 scanners specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These scanners provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information, helping you keep your car in top condition.
5.1 Connecting the Scanner
To use an OBD2 scanner, simply plug it into the OBD2 port located under the dashboard. Turn the ignition on, but don’t start the engine. The scanner will power on and begin communicating with the car’s computer. Ensure the connection is secure for accurate data retrieval.
5.2 Reading the Codes
Once connected, use the scanner’s interface to read the stored OBD2 codes. The scanner will display the codes along with a brief description of the issue. Record the codes for further diagnosis and research.
5.3 Interpreting the Results
Use the code definitions and your vehicle’s service manual to interpret the results. Understanding the code’s meaning is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. Consult online resources and forums for additional insights and tips.
5.4 Clearing the Codes
After addressing the underlying issue, you can use the scanner to clear the OBD2 codes. Clearing the codes resets the “Check Engine” light and allows you to monitor if the problem recurs. Be cautious when clearing codes, as it may erase valuable diagnostic data.
6. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
While an OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose many issues, some problems require the expertise of a professional mechanic. Complex or persistent codes, especially those related to safety systems, should be handled by a qualified technician. Ignoring these issues can lead to further damage and potential safety risks.
6.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
If you encounter multiple codes or codes that are difficult to interpret, it’s best to consult a mechanic. Complex diagnostic issues may require specialized tools and knowledge. A professional can accurately diagnose and repair these complex problems.
6.2 Safety-Related Codes
Codes related to safety systems, such as airbags or ABS, should always be addressed by a professional. These systems are critical for your safety, and any malfunction can have serious consequences. A qualified technician can ensure these systems are functioning correctly.
6.3 Persistent Codes
If a code reappears after you’ve attempted to fix the issue, it indicates a persistent problem that requires professional attention. Ignoring persistent codes can lead to further damage and potential safety risks. A mechanic can diagnose the root cause of the problem and implement a lasting solution.
6.4 Lack of Mechanical Knowledge
If you’re not comfortable working on your car or lack the necessary mechanical knowledge, it’s best to consult a mechanic. Attempting to fix complex issues without the proper knowledge can lead to further damage and potential safety risks. A professional can provide expert diagnosis and repair services.
7. Preventing OBD2 Codes Through Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is the best way to prevent OBD2 codes and keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule can help you identify and address potential issues before they trigger a code. Preventative maintenance is a cost-effective way to ensure the longevity and reliability of your vehicle.
7.1 Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are essential for engine health. Old or dirty oil can lead to increased friction and wear, triggering OBD2 codes related to engine performance. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
7.2 Fluid Checks
Regularly check and top off all fluids, including coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid. Low fluid levels can lead to system malfunctions and trigger OBD2 codes. Maintaining proper fluid levels is crucial for system performance and longevity.
7.3 Filter Replacements
Replace air filters, fuel filters, and cabin filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clogged filters can reduce engine performance and trigger OBD2 codes related to air and fuel delivery. Clean filters ensure efficient engine operation and optimal air quality.
7.4 Spark Plug Inspections
Inspect spark plugs regularly and replace them as needed. Worn spark plugs can cause misfires and trigger OBD2 codes related to ignition problems. New spark plugs improve engine performance and fuel efficiency.
7.5 Tire Maintenance
Maintain proper tire pressure and rotate tires regularly. Uneven tire wear can affect the vehicle’s handling and trigger OBD2 codes related to the ABS or traction control system. Proper tire maintenance ensures safe handling and prolongs tire life.
8. OBD2 Code Scanners Available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a variety of OBD2 scanners designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our scanners provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information, helping you keep your car in top condition. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, we have the right scanner for your needs.
8.1 Basic OBD2 Scanners
Our basic OBD2 scanners are perfect for reading and clearing codes. They provide essential diagnostic information and are easy to use. These scanners are ideal for DIY enthusiasts who want to perform basic troubleshooting.
8.2 Advanced OBD2 Scanners
Our advanced OBD2 scanners offer additional features, such as live data streaming, enhanced code definitions, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. These scanners are designed for professional mechanics and experienced DIYers.
8.3 Professional-Grade Scanners
Our professional-grade scanners provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, and programming functions. These scanners are ideal for professional mechanics who need the most advanced tools.
8.4 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Our wireless OBD2 adapters connect to your smartphone or tablet, allowing you to read and clear codes using a mobile app. These adapters offer convenience and portability. They are perfect for on-the-go diagnostics.
9. Understanding Manufacturer-Specific OBD2 Codes for Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz vehicles often have manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes that provide more detailed information than generic codes. Understanding these codes requires access to Mercedes-Benz service information and specialized diagnostic tools. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer scanners that support Mercedes-Benz specific codes, allowing you to accurately diagnose and repair your vehicle.
9.1 Accessing Mercedes-Benz Service Information
Accessing Mercedes-Benz service information is crucial for understanding manufacturer-specific codes. This information includes code definitions, diagnostic procedures, and repair instructions. You can access this information through Mercedes-Benz service portals or third-party databases.
9.2 Using Specialized Diagnostic Tools
Specialized diagnostic tools are necessary for reading and interpreting Mercedes-Benz specific codes. These tools provide advanced diagnostic capabilities and access to manufacturer-specific data. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of scanners that support Mercedes-Benz specific codes.
9.3 Examples of Mercedes-Benz Specific Codes
Examples of Mercedes-Benz specific codes include codes related to the Sensotronic Brake Control (SBC) system, the 7G-Tronic transmission, and the COMAND infotainment system. These codes provide detailed information about specific components and systems unique to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
9.4 Benefits of Understanding Specific Codes
Understanding Mercedes-Benz specific codes allows you to accurately diagnose and repair your vehicle, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. It also helps you avoid unnecessary repairs and save money.
10. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being developed. Future OBD2 systems will likely include enhanced data logging, remote diagnostics, and integration with cloud-based services. These advancements will provide even more valuable insights into vehicle health and performance.
10.1 Enhanced Data Logging
Future OBD2 systems will likely include enhanced data logging capabilities, allowing you to record and analyze vehicle data over time. This data can be used to identify trends, diagnose intermittent issues, and optimize vehicle performance.
10.2 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics will allow mechanics to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, using OBD2 data and telematics systems. This technology can reduce downtime and improve service efficiency.
10.3 Cloud Integration
Integration with cloud-based services will provide access to real-time diagnostic data, software updates, and remote support. This technology can enhance vehicle performance and reliability.
10.4 Cybersecurity Measures
Future OBD2 systems will include enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and unauthorized access. Cybersecurity is crucial for ensuring the safety and security of connected vehicles.
 OBD2 Scanner Connected
OBD2 Scanner Connected
FAQ: Decoding Your Vehicle’s Health – Common Questions About OBD2 Codes
What is an OBD2 code?
An OBD2 code is a standardized alphanumeric code that a vehicle’s onboard computer system uses to report detected issues within various systems, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions.
How do I read an OBD2 code?
You can read an OBD2 code using an OBD2 scanner, which plugs into the OBD2 port typically located under the dashboard. The scanner will display the code and a brief description of the issue.
Can I fix my car myself after reading an OBD2 code?
Depending on the issue, you may be able to fix your car yourself. Simple issues like a loose gas cap or a faulty sensor can often be resolved with basic tools and knowledge.
When should I consult a professional mechanic?
You should consult a professional mechanic for complex issues, safety-related codes, persistent codes, or if you lack the necessary mechanical knowledge to perform the repair yourself.
What are the common types of OBD2 codes?
The common types of OBD2 codes include Powertrain (P), Body (B), Chassis (C), and Network Communication (U) codes, each relating to different systems within the vehicle.
How can I prevent OBD2 codes from appearing?
You can prevent OBD2 codes from appearing by performing regular maintenance, using quality fuel and fluids, and addressing minor issues before they escalate.
What does the “Check Engine” light mean?
The “Check Engine” light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected an issue and stored an OBD2 code. It’s a signal that something is not functioning correctly and requires attention.
Are OBD2 scanners universal?
While OBD2 scanners use a standardized protocol, some scanners offer more advanced features and support manufacturer-specific codes, making them more suitable for certain vehicles.
Can I clear an OBD2 code without fixing the problem?
While you can clear an OBD2 code, it’s generally not advisable to do so without addressing the underlying issue, as the code will likely reappear.
Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
You can find reliable information about OBD2 codes in your vehicle’s service manual, online databases, and forums, and from professional mechanics.
Understanding OBD2 codes empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s health. With the right knowledge and tools, you can diagnose and resolve many issues yourself, saving time and money. For more complex problems, don’t hesitate to consult a professional mechanic. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice, premium OBD2 scanners, and unparalleled support. Our team at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States is here to help you understand and resolve any OBD2 code issues, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz performs at its best. Contact us via Whatsapp for immediate assistance and discover how our services can enhance your vehicle’s performance and longevity.