Finding your OBD2 port can be a breeze with the right guidance, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help you locate it swiftly and understand its importance for vehicle diagnostics, so you can diagnose and read diagnostic trouble codes. This guide will help you pinpoint the OBD II location, understand its pinout, and utilize it for effective car diagnostics, emission system checks, and more, ensuring your car meets required standards. Learn about vehicle computer access, onboard diagnostic tools, and car diagnostic scanners.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port
- 1.1. What is the primary function of OBD2 port?
- 1.2. Why is the OBD2 port important for vehicle maintenance?
- 1.3. How does the OBD2 port help in emission control?
- 2. Common OBD2 Port Locations in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 2.1. Why does the OBD2 port location vary among vehicle models?
- 2.2. What tools can help in locating the OBD2 port?
- 2.3. Are there any safety precautions to consider when locating the OBD2 port?
- 3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout Explained
- 3.1. What are the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 connectors?
- 3.2. How does the OBD2 connector facilitate data retrieval?
- 3.3. Can I use an adapter to connect an OBD1 scanner to an OBD2 port?
- 4. Detailed Overview of OBD2 Port Pinouts
- 4.1. What is the role of the ground pins (4 and 5) in the OBD2 port?
- 4.2. How do pins 6 and 14 (CAN bus) contribute to diagnostics?
- 4.3. What is the purpose of the ISO 9141-2 K Line (pin 7) and L Line (pin 15)?
- 5. Importance of the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 5.1. How does the OBD2 port provide insights into the car’s engine?
- 5.2. What role does the OBD2 port play in monitoring the emission system?
- 5.3. Can the OBD2 port help improve fuel efficiency?
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide on Using the OBD2 Port
- 7.1. What types of OBD2 scanners are available?
- 7.2. How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
- 7.3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when using an OBD2 scanner?
- 7. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
- 7.1. How does the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro enhance OBD2 diagnostics?
- 7.2. What are the benefits of using the CAN-FD protocol for vehicle diagnostics?
- 7.3. Are there any limitations to using advanced diagnostic tools with the OBD2 port?
- 8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for the OBD2 Port
- 8.1. What are the signs of a damaged OBD2 port?
- 8.2. How can I repair a damaged OBD2 port?
- 8.3. Can I use a faulty OBD2 port without causing further damage?
- 9. Utilizing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
- 9.1. What resources does MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for Mercedes-Benz diagnostics?
- 9.2. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me troubleshoot common Mercedes-Benz issues?
- 9.3. Is the information on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN reliable and accurate?
- 10. FAQs About the OBD2 Port
- Conclusion
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a standardized interface in your vehicle that provides access to the car’s computer. It acts as a gateway, allowing technicians and vehicle owners to connect diagnostic tools for accessing and reading vehicle data. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 in the United States are required to have an OBD2 port. This standardization simplifies vehicle diagnostics and helps ensure vehicles meet emissions standards.
1.1. What is the primary function of OBD2 port?
The primary function of the OBD2 port is to provide access to your vehicle’s diagnostic data. This data includes information related to the engine, transmission, emissions, and other critical systems. By connecting a diagnostic scanner to the OBD2 port, you can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform various diagnostic tests.
1.2. Why is the OBD2 port important for vehicle maintenance?
The OBD2 port is crucial for vehicle maintenance because it allows for quick and accurate identification of problems. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%. Early detection of issues through the OBD2 port can prevent costly repairs and ensure your vehicle operates efficiently.
1.3. How does the OBD2 port help in emission control?
The OBD2 port plays a vital role in emission control by monitoring the performance of emission-related components. It helps ensure that your vehicle meets the required emission standards by detecting malfunctions in systems such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and fuel system. Regular checks through the OBD2 port can help you maintain your vehicle’s emission compliance.
2. Common OBD2 Port Locations in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
While the OBD2 port is standardized, its exact location can vary among different vehicle models. However, it is typically found within the driver’s area. For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, here are some common locations:
- Under the Dashboard: Most commonly, the OBD2 port is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Check the area near the steering column or the center console.
- Near the Center Console: Some models may have the port located in the center console, often near the gear shifter or under a small cover.
- Inside the Glove Box: In rare cases, the OBD2 port might be found inside the glove box.
Always consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the precise location, or use an online OBD2 port finder specific to your Mercedes-Benz model.
2.1. Why does the OBD2 port location vary among vehicle models?
The variation in OBD2 port location is due to differences in vehicle design and manufacturing considerations. Automakers place the port in a location that is most accessible while also complying with safety and ergonomic standards. Factors such as the layout of the dashboard, the placement of other components, and the overall interior design can influence the final location of the OBD2 port.
2.2. What tools can help in locating the OBD2 port?
If you’re having trouble finding the OBD2 port, several tools can assist you:
- Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual: This is the first and most reliable resource. It typically includes a diagram or description of the OBD2 port location.
- Online OBD2 Port Finders: Websites and apps like OBD2 Port Locator offer databases of vehicle models and their corresponding OBD2 port locations.
- Flashlight: A simple flashlight can help you see under the dashboard and in other hard-to-reach areas.
- Smartphone Camera: Use your smartphone’s camera to take photos or videos of potential locations, which can help you inspect tight spaces more easily.
2.3. Are there any safety precautions to consider when locating the OBD2 port?
Yes, when searching for the OBD2 port, keep these safety precautions in mind:
- Park Safely: Ensure your vehicle is parked in a safe location, away from traffic.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Turn off the engine and remove the key from the ignition to prevent accidental starting.
- Use Proper Lighting: Use a flashlight or other suitable lighting to avoid straining your eyes or causing accidents.
- Avoid Obstructions: Make sure the area around the OBD2 port is clear of any obstructions that could cause injury or damage.
 Illustration of typical obd2 port locations in a common vehicle
Illustration of typical obd2 port locations in a common vehicle
3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout Explained
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin (2×8) J1962 connector that allows diagnostic tools to interface with your vehicle’s computer. Unlike older OBD1 connectors, the OBD2 connector is universally located within two feet of the steering wheel, making it easily accessible. Understanding the pinout of the OBD2 connector is essential for advanced diagnostics and customization.
3.1. What are the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 connectors?
The main differences between OBD1 and OBD2 connectors are standardization and functionality. OBD1 systems were not standardized, meaning each manufacturer could use different connectors and protocols. OBD2, on the other hand, is a standardized system that includes a universal connector and a set of diagnostic protocols. This standardization allows any OBD2-compliant scanner to work with any OBD2-compliant vehicle. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of vehicle diagnostics.
3.2. How does the OBD2 connector facilitate data retrieval?
The OBD2 connector facilitates data retrieval by providing a physical interface for diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s computer. When a scanner is plugged into the OBD2 port, it can request and receive data related to various vehicle systems. The data is transmitted through specific pins in the connector, each serving a unique purpose. This enables technicians and vehicle owners to read fault codes, monitor real-time data, and perform diagnostic tests.
3.3. Can I use an adapter to connect an OBD1 scanner to an OBD2 port?
While adapters exist that claim to connect OBD1 scanners to OBD2 ports, their effectiveness is often limited. Due to the significant differences in protocols and data formats between OBD1 and OBD2 systems, an adapter alone cannot ensure proper communication. Using an adapter may result in inaccurate data or even damage to the vehicle’s computer. It is always recommended to use a scanner specifically designed for the OBD2 system to ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics.
4. Detailed Overview of OBD2 Port Pinouts
The OBD2 port consists of 16 pins, each with a specific function. Here’s a detailed overview:
- Pin 1: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 2: SAE J1850 Bus+
- Pin 3: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (ISO 15765-4)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K Line
- Pin 8: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 9: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus-
- Pin 11: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 12: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 13: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 14: CAN Low (ISO 15765-4)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L Line
- Pin 16: Battery Power
Understanding these pinouts can help you troubleshoot connection issues and perform advanced diagnostics.
4.1. What is the role of the ground pins (4 and 5) in the OBD2 port?
Pins 4 and 5 provide grounding for the OBD2 port. Pin 4 is the chassis ground, which connects to the vehicle’s metal frame, and Pin 5 is the signal ground, which provides a stable reference point for the electrical signals. These ground pins ensure safe and accurate data transmission by preventing electrical noise and interference. Proper grounding is essential for reliable communication between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer.
4.2. How do pins 6 and 14 (CAN bus) contribute to diagnostics?
Pins 6 and 14 connect to the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, which is a critical communication network in modern vehicles. The CAN bus allows various electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other without a central host computer. Pin 6 is the CAN High line, and Pin 14 is the CAN Low line. These pins are essential for many diagnostic processes, as outlined by the ISO 15765-4 standard, which defines the communication protocol for OBD2 diagnostics over the CAN bus.
4.3. What is the purpose of the ISO 9141-2 K Line (pin 7) and L Line (pin 15)?
The ISO 9141-2 K Line (pin 7) and L Line (pin 15) are used for serial communication in some vehicles, particularly older models. The K Line is the primary communication line, while the L Line is used for initialization and diagnostic functions. These pins are part of the ISO 9141-2 communication protocol, which is one of the several protocols used in OBD2 systems. Although newer vehicles primarily use the CAN bus for communication, some still utilize the ISO 9141-2 protocol for specific diagnostic functions.
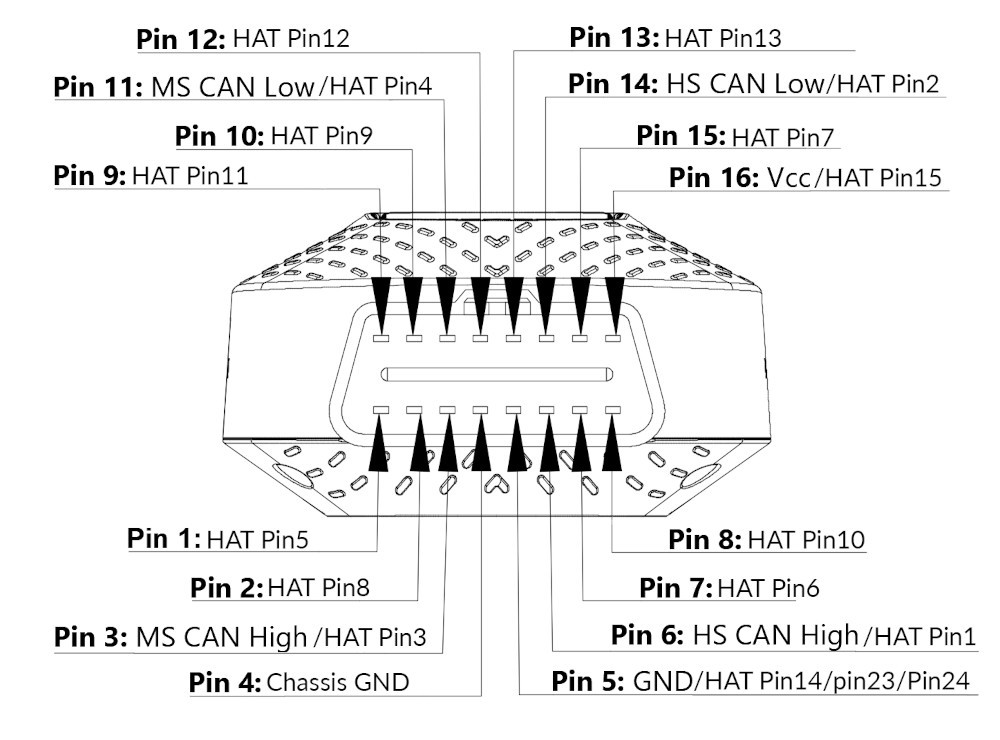 OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
5. Importance of the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
The OBD2 diagnostic port is essential for gaining insights into your car’s engine, emission system, and overall health. It allows for comprehensive self-diagnosis and reporting capabilities, aiding in troubleshooting and ensuring vehicles meet emission standards. According to a report by the EPA, OBD2 systems have significantly reduced vehicle emissions by enabling timely detection and correction of emission-related problems.
5.1. How does the OBD2 port provide insights into the car’s engine?
The OBD2 port provides insights into the car’s engine by allowing access to various engine-related parameters, such as engine speed, temperature, fuel consumption, and ignition timing. By monitoring these parameters, technicians and vehicle owners can identify potential issues, such as misfires, sensor failures, and fuel system problems. Real-time data from the OBD2 port can help diagnose engine problems quickly and accurately.
5.2. What role does the OBD2 port play in monitoring the emission system?
The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in monitoring the emission system by tracking the performance of emission-related components, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system. It detects malfunctions that could lead to increased emissions and alerts the driver through the check engine light. Regular monitoring through the OBD2 port helps ensure that the vehicle meets emission standards and reduces environmental impact.
5.3. Can the OBD2 port help improve fuel efficiency?
Yes, the OBD2 port can help improve fuel efficiency by providing data on fuel consumption, air-fuel ratio, and other parameters that affect fuel economy. By monitoring this data, you can identify issues that may be reducing fuel efficiency, such as a faulty oxygen sensor or a clogged air filter. Addressing these issues can improve fuel economy and save money on fuel costs.
6. Step-by-Step Guide on Using the OBD2 Port
Using the OBD2 port is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or an online OBD2 port finder to locate the port.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect a compatible OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read any stored fault codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a reliable source, such as the MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN database, to interpret the meaning of the codes.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): If you have addressed the issue, you can clear the codes using the scanner.
Remember, if your car was manufactured after 1996, it is required by law to have an OBD2 port.
7.1. What types of OBD2 scanners are available?
Various types of OBD2 scanners are available, each with different features and capabilities:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, inexpensive scanners that can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Enhanced Scanners: These scanners offer additional features, such as real-time data monitoring, freeze frame data, and advanced diagnostic tests.
- Professional Scanners: These are high-end scanners used by professional technicians. They offer advanced features like bi-directional control, programming capabilities, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These scanners connect to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi and use a mobile app to display diagnostic data.
7.2. How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. Consider the following factors:
- Features: Determine which features are important to you. Do you need real-time data monitoring, advanced diagnostic tests, or bi-directional control?
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: Set a budget and find a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
7.3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when using an OBD2 scanner?
To ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics, avoid these common mistakes:
- Not Consulting the Vehicle’s Manual: Always refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific information about the OBD2 system and diagnostic procedures.
- Ignoring Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of the vehicle’s parameters when the fault code was triggered. This data can be helpful in diagnosing intermittent problems.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Issue: Clearing codes without fixing the underlying problem will only result in the code reappearing.
- Using Incompatible Scanners: Using a scanner that is not compatible with your vehicle can lead to inaccurate data or even damage to the vehicle’s computer.
- Misinterpreting Codes: Always use a reliable source to interpret the meaning of diagnostic trouble codes.
 Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
7. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
While your car’s OBD2 port provides basic information, you can achieve deeper insights by using advanced tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro. This device connects to your OBD2 port to offer faster, more detailed information about your vehicle’s performance. According to Bosch, advanced diagnostic tools can improve diagnostic accuracy by up to 30%.
7.1. How does the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro enhance OBD2 diagnostics?
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro enhances OBD2 diagnostics by providing faster and more detailed access to vehicle data. It supports the CAN-FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-Rate) protocol, which allows for higher data transfer rates compared to standard CAN. This enables the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to gather more data in real-time, providing a more comprehensive view of your vehicle’s performance. Additionally, it offers advanced features such as remote diagnostics, data logging, and custom scripting, making it a powerful tool for advanced users.
7.2. What are the benefits of using the CAN-FD protocol for vehicle diagnostics?
The CAN-FD protocol offers several benefits for vehicle diagnostics:
- Higher Data Transfer Rates: CAN-FD allows for faster data transfer rates compared to standard CAN, enabling more data to be gathered in real-time.
- Increased Bandwidth: The increased bandwidth of CAN-FD allows for more data to be transmitted simultaneously, providing a more comprehensive view of the vehicle’s performance.
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: The higher data transfer rates and increased bandwidth of CAN-FD can improve diagnostic accuracy by providing more detailed and timely information.
- Support for Advanced Features: CAN-FD enables advanced features such as remote diagnostics, data logging, and custom scripting, making it a versatile tool for advanced users.
7.3. Are there any limitations to using advanced diagnostic tools with the OBD2 port?
While advanced diagnostic tools offer many benefits, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Cost: Advanced diagnostic tools can be more expensive than basic OBD2 scanners.
- Complexity: These tools can be more complex to use and may require specialized knowledge.
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Security: Be aware of potential security risks when connecting third-party devices to your vehicle’s OBD2 port. Always use reputable tools and follow security best practices.
8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for the OBD2 Port
Like any electronic component, the OBD2 port can experience issues. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Bent or Damaged Pins: Inspect the pins inside the OBD2 port for any signs of damage.
- Loose Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the port.
- No Power: Check the vehicle’s battery and fuses.
- Communication Errors: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle and that the ignition is turned on.
If you encounter persistent issues, consult a professional mechanic.
8.1. What are the signs of a damaged OBD2 port?
Signs of a damaged OBD2 port can include:
- Bent or Broken Pins: Visually inspect the pins inside the port for any signs of damage.
- Loose Connection: The scanner does not fit snugly into the port or easily falls out.
- Corrosion: Look for signs of rust or corrosion inside the port.
- No Power: The scanner does not power on when plugged into the port.
- Communication Errors: The scanner displays communication errors or cannot connect to the vehicle’s computer.
8.2. How can I repair a damaged OBD2 port?
Repairing a damaged OBD2 port can be challenging and may require specialized tools and knowledge. Here are some steps you can take:
- Inspect the Port: Visually inspect the port for any signs of damage, such as bent or broken pins.
- Straighten Bent Pins: If the pins are bent but not broken, you may be able to carefully straighten them using a small tool, such as a needle-nose plier.
- Clean the Port: Use a contact cleaner to clean the port and remove any corrosion.
- Replace the Port: If the port is severely damaged, you may need to replace it. This may require soldering and wiring skills.
If you are not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, it is best to consult a professional mechanic.
8.3. Can I use a faulty OBD2 port without causing further damage?
Using a faulty OBD2 port can potentially cause further damage to the vehicle’s computer or the diagnostic tool. A damaged port may not provide a stable connection, which can lead to communication errors and inaccurate data. In some cases, a faulty port can even short-circuit and damage the vehicle’s electrical system. It is always recommended to repair or replace a damaged OBD2 port before using it.
9. Utilizing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information and resources to help you diagnose and maintain your Mercedes-Benz vehicle. From detailed guides on using diagnostic tools to troubleshooting common issues, our website is your go-to source for all things Mercedes-Benz diagnostics. Our information is sourced from industry experts and reputable automotive resources, ensuring reliability and accuracy.
9.1. What resources does MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for Mercedes-Benz diagnostics?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a variety of resources for Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, including:
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step guides on using diagnostic tools and interpreting diagnostic trouble codes.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Tips and solutions for common issues related to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Diagnostic Tool Reviews: Reviews and comparisons of different diagnostic tools suitable for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Expert Advice: Access to expert advice from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians.
- Community Forum: A community forum where you can ask questions and share your experiences with other Mercedes-Benz owners.
9.2. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me troubleshoot common Mercedes-Benz issues?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you troubleshoot common Mercedes-Benz issues by providing:
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Database: A comprehensive database of DTCs specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles, along with detailed explanations and troubleshooting tips.
- Symptom-Based Diagnostics: Guidance on diagnosing issues based on specific symptoms, such as engine misfires, transmission problems, or electrical faults.
- Step-by-Step Procedures: Detailed step-by-step procedures for performing diagnostic tests and repairs.
- Video Tutorials: Video tutorials demonstrating how to use diagnostic tools and perform common repairs.
- Expert Support: Access to expert support from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians who can provide personalized advice and guidance.
9.3. Is the information on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN reliable and accurate?
Yes, the information on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is reliable and accurate. We source our information from industry experts, reputable automotive resources, and official Mercedes-Benz documentation. Our content is carefully reviewed and updated regularly to ensure it is accurate and up-to-date. We also encourage our users to provide feedback and report any inaccuracies they may find, so we can continuously improve the quality of our content.
10. FAQs About the OBD2 Port
Here are some frequently asked questions about the OBD2 port:
- What if I can’t find the OBD2 location? Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location.
- Are all OBD2 ports the same? Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization.
- How many OBD2 ports does a car have? Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
- Can I use the OBD2 port to monitor real-time data? Yes, many OBD2 scanners can display real-time data, such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel consumption.
- Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time? It is generally not recommended to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time, as it can drain the vehicle’s battery.
- Can I use the OBD2 port to program or reprogram my car’s computer? Some professional-grade scanners can be used to program or reprogram a car’s computer, but this requires specialized knowledge and should only be done by trained technicians.
- What does it mean when the check engine light comes on? The check engine light indicates that there is a problem with one or more of the vehicle’s systems. You can use an OBD2 scanner to read the diagnostic trouble code and determine the cause of the problem.
- How often should I check my car’s OBD2 port for diagnostic trouble codes? It is a good idea to check your car’s OBD2 port for diagnostic trouble codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as reduced performance or poor fuel economy.
- Can I use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose ABS or airbag problems? Some advanced OBD2 scanners can diagnose ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and airbag problems, but this requires a scanner that supports these systems.
- Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes? You can find reliable information about OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes on MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, as well as in your vehicle’s owner’s manual and reputable automotive repair websites.
Conclusion
The OBD2 port is more than just a plug in your car; it’s a portal to understanding your vehicle’s health and status. Next time you find yourself with a dashboard warning light, remember the power of the OBD2 port at your fingertips. Embrace the capabilities of the OBD2 port to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Explore our range of OBD2 tools and resources at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to keep your vehicle in top condition and start leveraging the power of advanced diagnostics today.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, located at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or call us on WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and support. Let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running at its best!
