Coding the TPMS system after installing new sensors ensures accurate tire pressure monitoring. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive solutions to properly code your TPMS, preventing inaccurate readings and system malfunctions. Our expert advice covers sensor replacement, TPMS reset procedures, and diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, giving you peace of mind and optimal performance. Whether you’re looking for TPMS relearn processes, TPMS programming tools, or troubleshooting TPMS issues, we have you covered.
Contents
- 2. Understanding TPMS and Sensor Replacement
- 2.1. What is TPMS?
- 2.2. Types of TPMS
- 2.3. Why Replace TPMS Sensors?
- 3. Identifying the Need for TPMS Coding
- 3.1. New Sensor Installation
- 3.2. Sensor Replacement
- 3.3. Tire Rotation
- 3.4. ECU Reset or Replacement
- 3.5. Winter/Summer Tire Swaps
- 4. Tools Required for TPMS Coding
- 4.1. TPMS Diagnostic Tool
- 4.2. OBD-II Scanner
- 4.3. Laptop with Diagnostic Software
- 4.4. Sensor Programming Tool
- 4.5. Tire Pressure Gauge
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to TPMS Coding
- 5.1. Preparation
- 5.2. Install New TPMS Sensors
- 5.3. Connect Diagnostic Tool
- 5.4. Read Existing Sensor Data
- 5.5. Program New Sensor IDs (If Necessary)
- 5.6. Perform TPMS Relearn Procedure
- 5.7. Verify TPMS Function
- 5.8. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6. Common TPMS Coding Issues and Troubleshooting
- 6.1. Sensor Not Recognized
- 6.2. TPMS Warning Light Remains On
- 6.3. Inaccurate Tire Pressure Readings
- 6.4. Diagnostic Tool Connection Issues
- 7. Advanced TPMS Coding Techniques
- 7.1. Customizing TPMS Thresholds
- 7.2. Programming Multiple Sensor Sets
- 7.3. Disabling TPMS (Not Recommended)
- 8. Choosing the Right TPMS Sensors
- 8.1. OEM vs. Aftermarket Sensors
- 8.2. Sensor Compatibility
- 8.3. Sensor Quality
- 8.4. Sensor Features
- 9. Maintaining Your TPMS System
- 9.1. Regular Tire Pressure Checks
- 9.2. Sensor Inspections
- 9.3. Valve Stem Maintenance
- 9.4. Professional Service
- 10. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 10.1. Expert Guidance
- 10.2. Comprehensive Solutions
- 10.3. High-Quality Products
- 10.4. Cost Savings
- 11. Real-World Examples of TPMS Coding
- 11.1. Example 1: Mercedes-Benz C-Class Sensor Replacement
- 11.2. Example 2: Mercedes-Benz E-Class Winter Tire Swap
- 11.3. Example 3: Mercedes-Benz S-Class Sensor Damage
- 12. The Future of TPMS Technology
- 12.1. Advanced Sensor Technology
- 12.2. Integration with ADAS
- 12.3. Remote Monitoring
- 12.4. Predictive Maintenance
- 13. TPMS and Vehicle Safety
- 14. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS Solutions
- 14.1. Contact Information
- 14.2. Why Contact Us?
- 15. FAQ: TPMS Coding and Maintenance
- 15.1. What is TPMS coding?
- 15.2. Why is TPMS coding necessary?
- 15.3. What tools are required for TPMS coding?
- 15.4. How often should I replace TPMS sensors?
- 15.5. Can I replace TPMS sensors myself?
- 15.6. What is a TPMS relearn procedure?
- 15.7. What are the different types of TPMS relearn procedures?
- 15.8. How can I troubleshoot TPMS coding issues?
- 15.9. What are the benefits of using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS solutions?
- 15.10. How can I contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS assistance?
2. Understanding TPMS and Sensor Replacement
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is a critical safety feature in modern vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz models. It monitors tire pressure in real-time, alerting the driver to significant pressure drops that could lead to accidents or tire damage. When a TPMS sensor fails or needs replacement, it’s essential to understand the system and the proper procedures for coding and calibration.
2.1. What is TPMS?
TPMS, or Tire Pressure Monitoring System, is an electronic system designed to monitor the air pressure inside the tires on a vehicle. The primary goal of TPMS is to enhance vehicle safety by providing real-time tire pressure information to the driver. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), TPMS has significantly reduced the number of accidents caused by underinflated tires.
2.2. Types of TPMS
There are two main types of TPMS: direct and indirect.
- Direct TPMS: Uses pressure sensors inside each tire to directly measure tire pressure. These sensors transmit data to the vehicle’s computer, providing accurate, real-time pressure readings.
- Indirect TPMS: Uses the vehicle’s ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) to monitor tire pressure. It detects changes in tire pressure by measuring the rotational speed of the wheels. If a tire loses pressure, its rotational speed increases, triggering an alert.
2.3. Why Replace TPMS Sensors?
TPMS sensors typically have a lifespan of 5 to 10 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions. Common reasons for replacing TPMS sensors include:
- Battery Failure: TPMS sensors are battery-powered, and the battery life is limited. Once the battery dies, the sensor needs replacement.
- Physical Damage: Sensors can be damaged during tire changes, accidents, or by road debris.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salts can corrode the sensor components.
- Valve Stem Issues: The valve stem, which is part of the sensor, can become damaged or corroded, leading to air leaks.
3. Identifying the Need for TPMS Coding
Coding the TPMS system is essential after installing new sensors to ensure the system functions correctly. Here are situations where TPMS coding is necessary:
3.1. New Sensor Installation
Whenever a new TPMS sensor is installed, the vehicle’s computer needs to recognize and communicate with the new sensor. Coding ensures that the system accurately monitors the tire pressure from the new sensor.
3.2. Sensor Replacement
If an existing TPMS sensor is replaced, the vehicle’s computer must be updated with the new sensor’s ID. This process is crucial for maintaining accurate tire pressure readings.
3.3. Tire Rotation
In some cases, tire rotation can necessitate TPMS coding, especially if the vehicle uses direct TPMS. Coding ensures that the system correctly identifies the location of each sensor after the tires have been moved.
3.4. ECU Reset or Replacement
If the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) has been reset or replaced, the TPMS system may need to be recoded to establish communication with the sensors.
3.5. Winter/Summer Tire Swaps
When swapping between winter and summer tires, which often have their own set of TPMS sensors, coding is required to ensure the system recognizes the sensors on the new set of tires.
4. Tools Required for TPMS Coding
To properly code the TPMS system, you’ll need specialized tools. Here are some essential tools for TPMS coding:
4.1. TPMS Diagnostic Tool
A TPMS diagnostic tool is essential for reading sensor data, programming new sensors, and performing TPMS resets. These tools can communicate with the vehicle’s computer and the TPMS sensors, allowing you to diagnose issues and perform necessary coding.
4.2. OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is needed to access the vehicle’s computer and perform various diagnostic and coding functions. Some TPMS tools may include OBD-II scanning capabilities.
4.3. Laptop with Diagnostic Software
For advanced TPMS coding, a laptop with diagnostic software specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles is required. This software allows you to access advanced TPMS functions and perform detailed coding procedures.
4.4. Sensor Programming Tool
If you’re using aftermarket TPMS sensors, you may need a sensor programming tool to program the sensor with the correct ID before installing it in the wheel.
4.5. Tire Pressure Gauge
A reliable tire pressure gauge is necessary to ensure that the tires are inflated to the correct pressure after sensor installation and coding.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to TPMS Coding
Coding the TPMS system involves several steps to ensure the new sensors are correctly recognized and monitored by the vehicle’s computer. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
5.1. Preparation
- Gather Tools: Ensure you have all the necessary tools, including the TPMS diagnostic tool, OBD-II scanner, laptop with diagnostic software, sensor programming tool (if needed), and tire pressure gauge.
- Vehicle Information: Have the vehicle’s make, model, and year readily available. You may also need the vehicle identification number (VIN).
- TPMS Sensor Information: Obtain the sensor IDs for the new TPMS sensors. This information is usually printed on the sensor or provided with the sensor packaging.
5.2. Install New TPMS Sensors
- Remove Old Sensors: If replacing existing sensors, carefully remove the old TPMS sensors from the wheels.
- Install New Sensors: Install the new TPMS sensors in the wheels, ensuring they are properly seated and tightened.
- Inflate Tires: Inflate the tires to the recommended pressure specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or on the tire placard.
5.3. Connect Diagnostic Tool
- Connect to OBD-II Port: Plug the TPMS diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Power On: Turn on the diagnostic tool and follow the on-screen instructions to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
5.4. Read Existing Sensor Data
- Access TPMS Menu: Navigate to the TPMS menu on the diagnostic tool.
- Read Sensor IDs: Use the tool to read the existing sensor IDs stored in the vehicle’s computer. This step helps identify which sensors need to be replaced or recoded.
5.5. Program New Sensor IDs (If Necessary)
- Select Sensor Programming: If using aftermarket sensors, select the sensor programming option on the diagnostic tool.
- Enter Sensor IDs: Enter the sensor IDs for the new TPMS sensors. Some tools can automatically detect the sensor IDs.
- Program Sensors: Follow the on-screen instructions to program the sensors with the correct IDs.
5.6. Perform TPMS Relearn Procedure
- Select Relearn Procedure: Choose the TPMS relearn procedure option on the diagnostic tool.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the relearn procedure. There are typically three types of relearn procedures:
- Auto Relearn: The vehicle automatically learns the new sensor IDs after driving for a certain period.
- Stationary Relearn: The vehicle learns the new sensor IDs while stationary, typically by using the diagnostic tool to activate each sensor.
- OBD Relearn: The diagnostic tool programs the new sensor IDs directly into the vehicle’s computer via the OBD-II port.
- Complete Relearn: Complete the relearn procedure according to the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool.
5.7. Verify TPMS Function
- Check Tire Pressure Readings: After completing the relearn procedure, check the tire pressure readings on the vehicle’s display or with the diagnostic tool to ensure the new sensors are communicating correctly.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a short test drive to confirm that the TPMS system is functioning properly and that no warning lights are illuminated.
5.8. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Access DTC Menu: Use the diagnostic tool to access the DTC menu.
- Clear Codes: Clear any TPMS-related DTCs that may have been stored during the sensor replacement and coding process.
6. Common TPMS Coding Issues and Troubleshooting
While TPMS coding is a straightforward process, some common issues can arise. Here’s a troubleshooting guide to help you resolve these issues:
6.1. Sensor Not Recognized
Issue: The vehicle’s computer does not recognize the new TPMS sensor after installation and coding.
Possible Causes:
- Incorrect sensor ID entered during programming.
- Faulty TPMS sensor.
- Incorrect relearn procedure.
- Communication issues between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Double-check the sensor ID and ensure it is entered correctly.
- Verify that the TPMS sensor is functioning properly by using the diagnostic tool to read its data.
- Repeat the relearn procedure, ensuring each step is followed correctly.
- Check the OBD-II port and diagnostic tool connections for any issues.
6.2. TPMS Warning Light Remains On
Issue: The TPMS warning light remains illuminated on the dashboard after sensor replacement and coding.
Possible Causes:
- Low tire pressure.
- Faulty TPMS sensor.
- Incorrect sensor programming.
- System malfunction.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure all tires are inflated to the correct pressure.
- Verify that the TPMS sensors are programmed correctly and communicating with the vehicle’s computer.
- Use the diagnostic tool to check for any DTCs and clear them.
- Inspect the TPMS system for any physical damage or corrosion.
6.3. Inaccurate Tire Pressure Readings
Issue: The tire pressure readings displayed by the TPMS system are inaccurate.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty TPMS sensor.
- Incorrect sensor calibration.
- Interference from other electronic devices.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Verify the accuracy of the TPMS sensors by comparing their readings with a reliable tire pressure gauge.
- Recalibrate the TPMS sensors using the diagnostic tool.
- Check for any electronic devices that may be interfering with the TPMS system.
6.4. Diagnostic Tool Connection Issues
Issue: The diagnostic tool is unable to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty OBD-II port.
- Incorrect diagnostic tool settings.
- Communication issues between the tool and the vehicle.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the OBD-II port for any damage or corrosion.
- Verify that the diagnostic tool is configured correctly for the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Try using a different diagnostic tool to rule out any issues with the tool itself.
7. Advanced TPMS Coding Techniques
For advanced users and professional technicians, there are several advanced TPMS coding techniques that can enhance the system’s performance and functionality.
7.1. Customizing TPMS Thresholds
Some diagnostic tools and software allow you to customize the TPMS pressure thresholds. This feature enables you to adjust the pressure levels at which the TPMS warning light is triggered, providing greater control over the system’s sensitivity.
7.2. Programming Multiple Sensor Sets
If you frequently switch between different sets of tires (e.g., winter and summer tires), you can program multiple sensor sets into the vehicle’s computer. This eliminates the need to recode the TPMS system each time you change tires.
7.3. Disabling TPMS (Not Recommended)
In some cases, you may want to disable the TPMS system temporarily. However, disabling TPMS is generally not recommended, as it compromises the vehicle’s safety. If you choose to disable TPMS, ensure you understand the potential risks and consequences.
8. Choosing the Right TPMS Sensors
Selecting the right TPMS sensors is crucial for ensuring the system’s reliability and accuracy. Here are some factors to consider when choosing TPMS sensors:
8.1. OEM vs. Aftermarket Sensors
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Sensors: These sensors are made by the vehicle manufacturer or an approved supplier. They are designed to meet the exact specifications of the vehicle and offer the best compatibility and reliability.
- Aftermarket Sensors: These sensors are made by third-party manufacturers. They are often more affordable than OEM sensors but may not offer the same level of quality and compatibility.
8.2. Sensor Compatibility
Ensure that the TPMS sensors you choose are compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or a TPMS compatibility guide to verify sensor compatibility.
8.3. Sensor Quality
Choose TPMS sensors from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Look for sensors that are made from durable materials and designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
8.4. Sensor Features
Consider the features offered by different TPMS sensors, such as battery life, pressure range, and communication frequency. Choose sensors that meet your specific needs and preferences.
9. Maintaining Your TPMS System
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of your TPMS system. Here are some maintenance tips:
9.1. Regular Tire Pressure Checks
Check your tire pressure regularly, using a reliable tire pressure gauge. Inflate your tires to the recommended pressure specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or on the tire placard.
9.2. Sensor Inspections
Inspect the TPMS sensors periodically for any signs of damage or corrosion. Replace any damaged or corroded sensors promptly.
9.3. Valve Stem Maintenance
Maintain the valve stems by keeping them clean and free of debris. Replace the valve stems if they become damaged or corroded.
9.4. Professional Service
Have your TPMS system serviced by a qualified technician at regular intervals. A professional technician can diagnose and repair any issues with the system and ensure it is functioning properly.
10. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of benefits for Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians, including:
10.1. Expert Guidance
We provide expert guidance on TPMS coding, sensor replacement, and system maintenance. Our team of experienced technicians can help you troubleshoot any issues and ensure your TPMS system is functioning correctly.
10.2. Comprehensive Solutions
We offer comprehensive solutions for all your TPMS needs, from diagnostic tools and software to sensor programming and relearn procedures. Our solutions are designed to be effective, reliable, and user-friendly.
10.3. High-Quality Products
We offer a wide selection of high-quality TPMS sensors, diagnostic tools, and software from reputable manufacturers. Our products are designed to meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
10.4. Cost Savings
By using our expert guidance and high-quality products, you can save money on TPMS repairs and maintenance. Our solutions are designed to be affordable and cost-effective.
11. Real-World Examples of TPMS Coding
To illustrate the importance and process of TPMS coding, here are a few real-world examples:
11.1. Example 1: Mercedes-Benz C-Class Sensor Replacement
A Mercedes-Benz C-Class owner noticed the TPMS warning light illuminated on the dashboard. Upon inspection, it was determined that one of the TPMS sensors had failed due to battery depletion. The owner purchased a new OEM TPMS sensor and followed the steps outlined above to install and code the new sensor. After completing the relearn procedure, the TPMS warning light was extinguished, and the system functioned correctly.
11.2. Example 2: Mercedes-Benz E-Class Winter Tire Swap
A Mercedes-Benz E-Class owner swaps between winter and summer tires each season. Each set of tires has its own set of TPMS sensors. To avoid having to recode the TPMS system each time the tires are changed, the owner programmed both sets of sensor IDs into the vehicle’s computer. This allows the TPMS system to automatically recognize the sensors on the current set of tires.
11.3. Example 3: Mercedes-Benz S-Class Sensor Damage
A Mercedes-Benz S-Class owner damaged a TPMS sensor while driving over a pothole. The sensor was physically damaged and needed to be replaced. The owner purchased an aftermarket TPMS sensor and used a sensor programming tool to program the new sensor with the correct ID. After installing and coding the new sensor, the TPMS system functioned correctly.
12. The Future of TPMS Technology
TPMS technology is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of the automotive industry. Here are some trends and developments in TPMS technology:
12.1. Advanced Sensor Technology
TPMS sensors are becoming more advanced, with features such as longer battery life, wider pressure ranges, and enhanced communication capabilities.
12.2. Integration with ADAS
TPMS is increasingly being integrated with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), such as lane departure warning and adaptive cruise control. This integration allows the vehicle to make more informed decisions based on tire pressure data.
12.3. Remote Monitoring
Some TPMS systems allow for remote monitoring of tire pressure via a smartphone app or other device. This feature enables drivers to check their tire pressure from anywhere, at any time.
12.4. Predictive Maintenance
TPMS data is being used for predictive maintenance, allowing vehicle owners and technicians to anticipate and address potential issues before they become major problems.
13. TPMS and Vehicle Safety
TPMS plays a critical role in vehicle safety by providing real-time tire pressure information to the driver. Proper tire inflation is essential for:
- Optimal Handling: Properly inflated tires provide the best handling and stability, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, which reduces fuel efficiency.
- Extended Tire Life: Properly inflated tires wear more evenly, extending their lifespan.
- Reduced Risk of Blowouts: Underinflated tires are more likely to overheat and blowout, which can lead to accidents.
14. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS Solutions
If you need assistance with TPMS coding, sensor replacement, or system maintenance, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced technicians is here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely.
14.1. Contact Information
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
14.2. Why Contact Us?
- Expert Advice: Get expert advice on TPMS coding and maintenance.
- Quality Products: Access high-quality TPMS sensors and diagnostic tools.
- Comprehensive Support: Receive comprehensive support for all your TPMS needs.
- Peace of Mind: Ensure your TPMS system is functioning correctly and safely.
15. FAQ: TPMS Coding and Maintenance
15.1. What is TPMS coding?
TPMS coding is the process of programming the vehicle’s computer to recognize and communicate with new TPMS sensors.
15.2. Why is TPMS coding necessary?
TPMS coding is necessary to ensure that the vehicle’s computer accurately monitors the tire pressure from the new sensors.
15.3. What tools are required for TPMS coding?
The tools required for TPMS coding include a TPMS diagnostic tool, OBD-II scanner, laptop with diagnostic software, sensor programming tool (if needed), and tire pressure gauge.
15.4. How often should I replace TPMS sensors?
TPMS sensors typically have a lifespan of 5 to 10 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
15.5. Can I replace TPMS sensors myself?
Yes, you can replace TPMS sensors yourself, but it is important to follow the proper procedures and use the correct tools.
15.6. What is a TPMS relearn procedure?
A TPMS relearn procedure is the process of teaching the vehicle’s computer the new sensor IDs after TPMS sensors are replaced or recoded.
15.7. What are the different types of TPMS relearn procedures?
The different types of TPMS relearn procedures include auto relearn, stationary relearn, and OBD relearn.
15.8. How can I troubleshoot TPMS coding issues?
You can troubleshoot TPMS coding issues by checking the sensor IDs, verifying sensor functionality, repeating the relearn procedure, and inspecting the TPMS system for any physical damage or corrosion.
15.9. What are the benefits of using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS solutions?
The benefits of using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS solutions include expert guidance, comprehensive solutions, high-quality products, and cost savings.
15.10. How can I contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS assistance?
You can contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS assistance by visiting our website, calling our WhatsApp number, or visiting our address in Miami, FL.
Navigating TPMS coding can be complex, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can ensure your Mercedes-Benz TPMS system operates flawlessly. Trust MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to provide the expertise and solutions you need for optimal vehicle safety and performance.
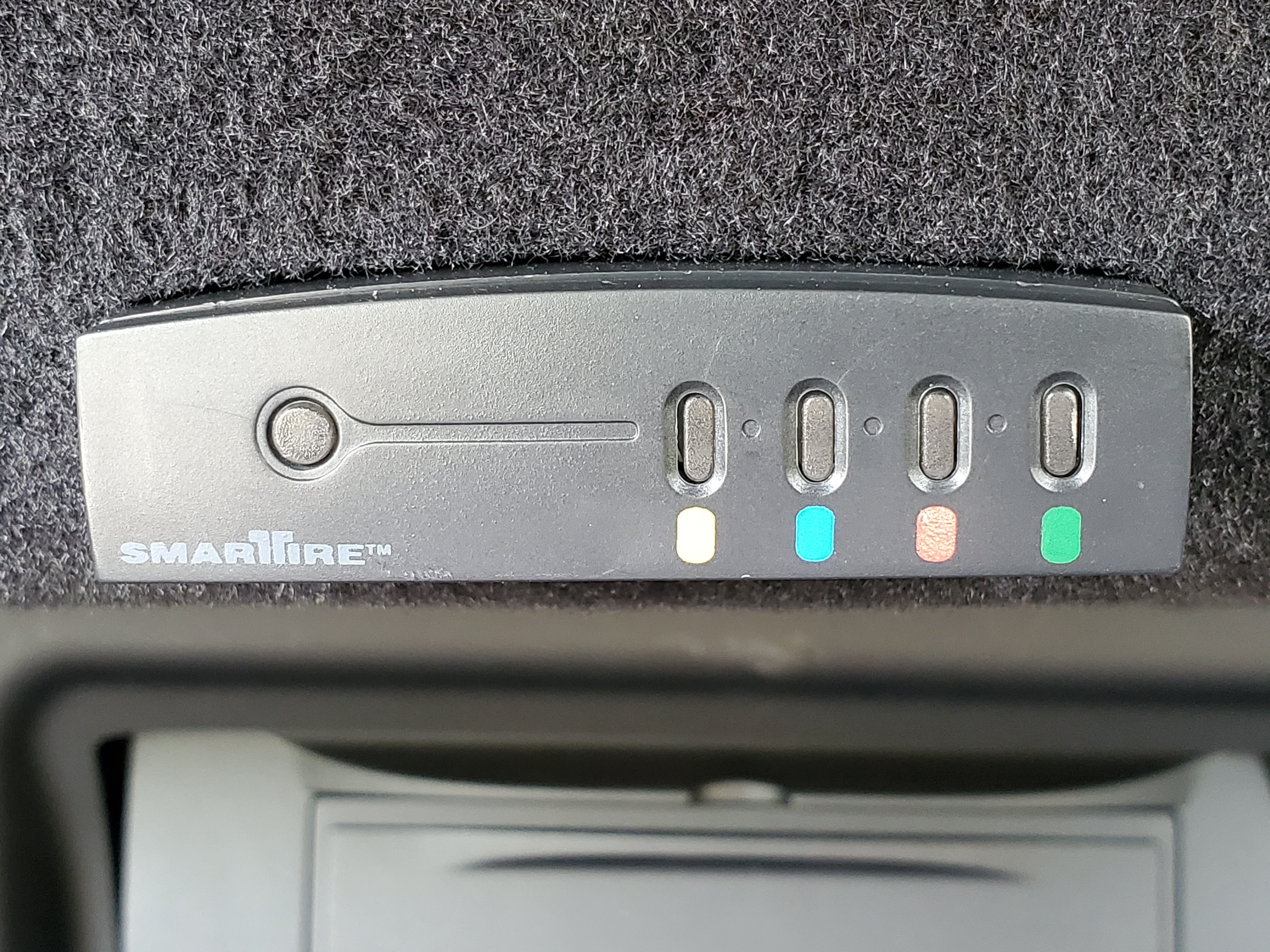 Aston Martin SmarTire TPMS Controller
Aston Martin SmarTire TPMS Controller
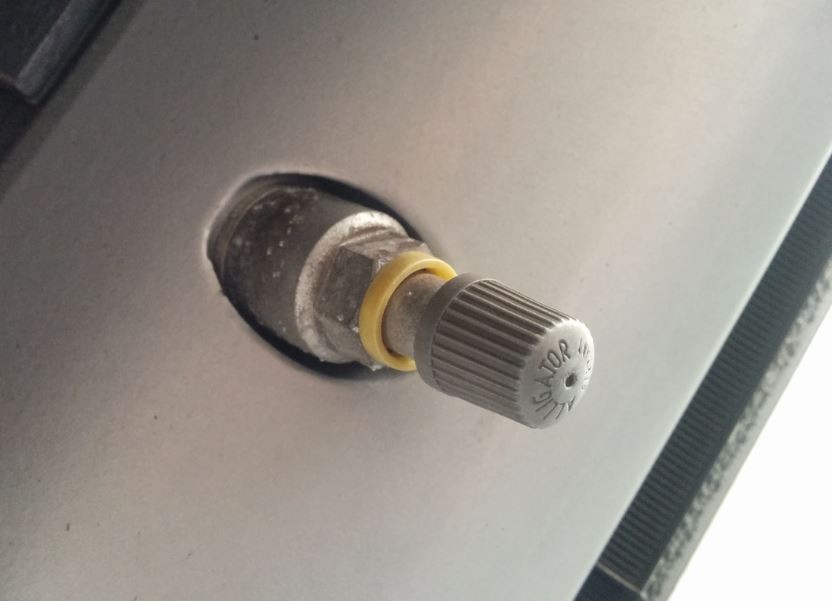 Close-up of TPMS sensor integrated into valve stem on Aston Martin DB9
Close-up of TPMS sensor integrated into valve stem on Aston Martin DB9
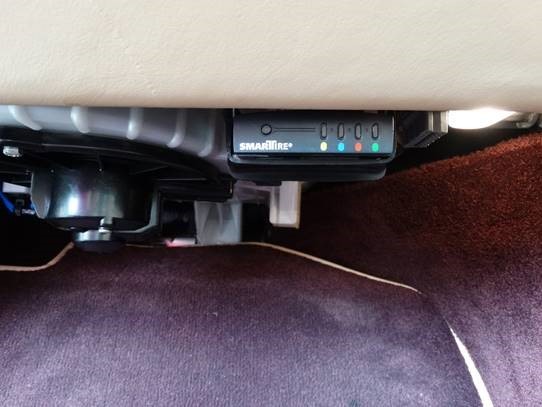 Later Aston Martin DB9 model showing under-dash SmarTire controller location
Later Aston Martin DB9 model showing under-dash SmarTire controller location
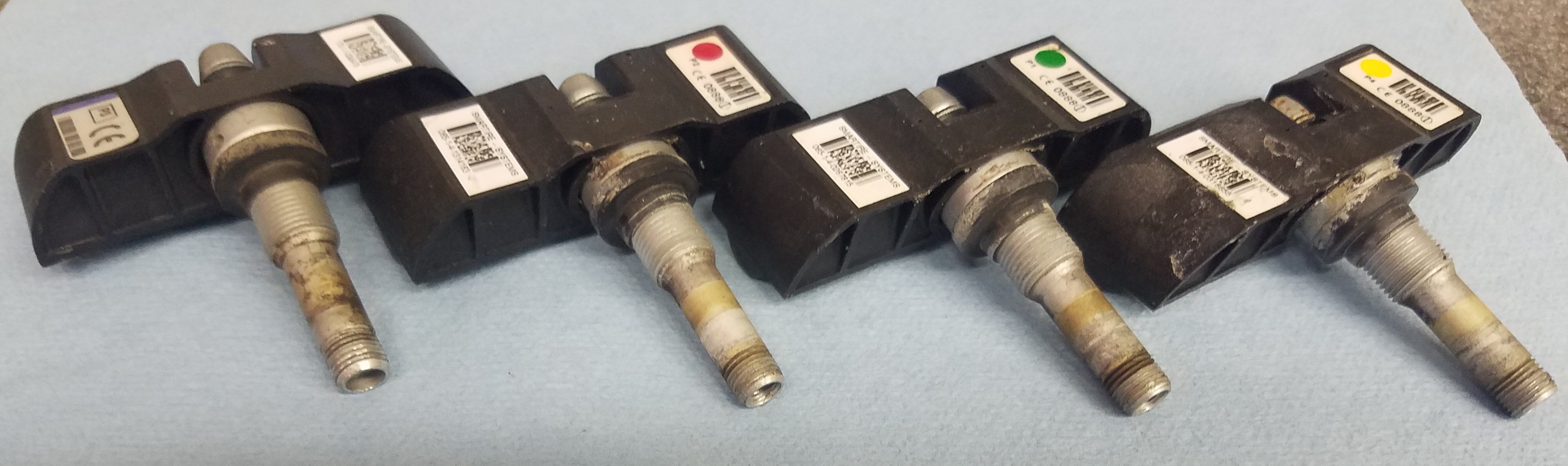 Dismantled SmarTire TPMS sensor revealing battery stack
Dismantled SmarTire TPMS sensor revealing battery stack
 Aston Martin DB9 dashboard displaying TPMS alert
Aston Martin DB9 dashboard displaying TPMS alert
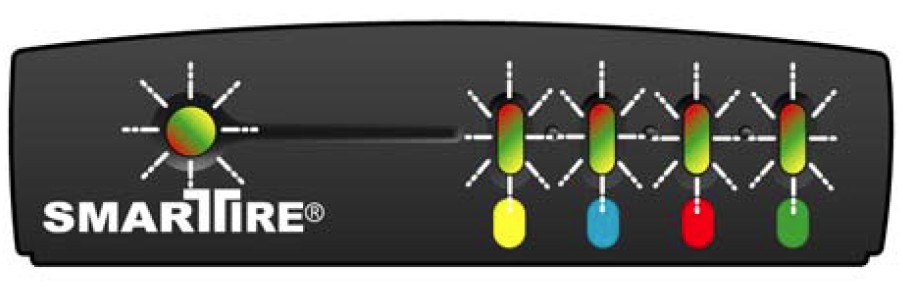 Aston Martin TPMS SmarTire system during startup diagnostics
Aston Martin TPMS SmarTire system during startup diagnostics
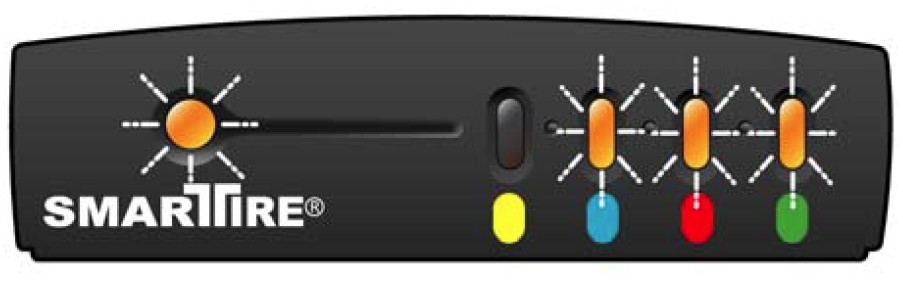 Aston Martin TPMS with first sensor communicating
Aston Martin TPMS with first sensor communicating
 Aston Martin TPMS showing normal operation with all tires okay
Aston Martin TPMS showing normal operation with all tires okay
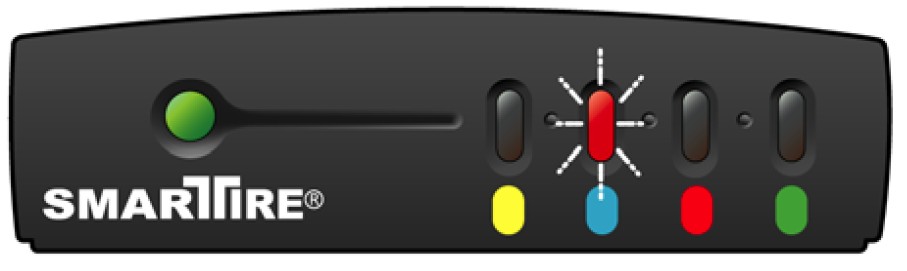 Aston Martin TPMS alert showing solid red for low tire pressure
Aston Martin TPMS alert showing solid red for low tire pressure
 Aston Martin dash displaying TPMS system fault warning
Aston Martin dash displaying TPMS system fault warning
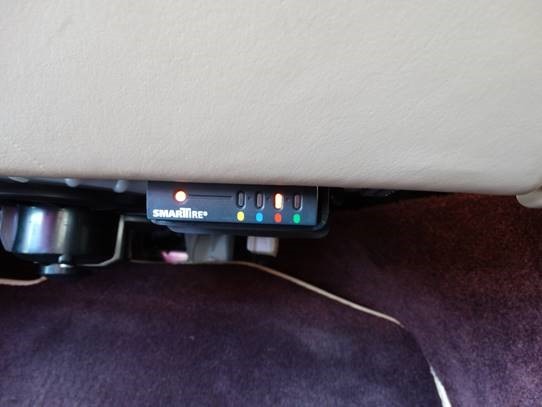 SmarTire controller showing communication loss with left front tire
SmarTire controller showing communication loss with left front tire
Are you having trouble coding your TPMS system after installing new sensors? Contact us now via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert assistance and solutions. Don’t let TPMS issues compromise your vehicle’s safety and performance. Reach out today and let us help you ensure your Mercedes-Benz is running smoothly. Our address is 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States.