Variant coding on the Head Unit (HU), also known as COMAND or MBUX in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, involves customizing the software to enable or disable specific features, tailoring the system to regional requirements, or activating optional equipment. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you understand and implement these customizations effectively. Variant coding includes tasks such as enabling navigation, activating smartphone integration, or adjusting audio settings and this ensures optimal vehicle functionality and personalization.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Variant Coding in Mercedes-Benz Head Units
- 1.1. What is Variant Coding?
- 1.2. Key Components Involved
- 1.3. Why is Variant Coding Necessary?
- 1.4. Common Terms and Acronyms
- 2. Examples of Variant Coding Applications
- 2.1. Enabling/Disabling Navigation Features
- 2.2. Activating Smartphone Integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto)
- 2.3. Adjusting Audio Settings and Equalization
- 2.4. Enabling/Disabling Specific Vehicle Functions (e.g., Lane Keeping Assist, Blind Spot Monitoring)
- 2.5. Adapting to Regional Requirements (Language, Units, Radio Frequencies)
- 2.6. Activating Performance Features (e.g., AMG Performance Displays)
- 3. Tools and Software for Variant Coding
- 3.1. Official Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tools (XENTRY/DAS)
- 3.2. Engineering Software (Vediamo, DTS Monaco)
- 3.3. Third-Party Tools and Interfaces
- 3.4. Hardware Interfaces (OBD-II)
- 3.5. Software Updates and Subscriptions
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Variant Coding
- 4.1. Preparation and Prerequisites
- 4.2. Connecting to the Vehicle’s ECU
- 4.3. Identifying the Correct Control Unit
- 4.4. Accessing Variant Coding Options
- 4.5. Modifying Parameters
- 4.6. Verifying the Changes
- 4.7. Finalizing the Coding Process
- 5. Potential Risks and Precautions
- 5.1. Incorrect Coding
- 5.2. Data Corruption
- 5.3. Warranty Issues
- 5.4. Precautions to Take
- 6. Advanced Variant Coding Techniques
- 6.1. Enabling Hidden Features
- 6.2. Customizing Vehicle Behavior
- 6.3. Optimizing Performance
- 6.4. Using Engineering Mode
- 6.5. Scripting and Automation
- 7. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
- 7.1. Retrofitting Options
- 7.2. Resolving Software Glitches
- 7.3. Enhancing Performance
- 7.4. Adapting to Aftermarket Modifications
- 7.5. Customer Success Stories
- 8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 8.1. Communication Errors
- 8.2. Incorrect Parameter Values
- 8.3. Software Freezes
- 8.4. ECU Not Responding
- 8.5. Error Codes After Coding
- 9. Staying Updated with the Latest Information
- 9.1. Official Mercedes-Benz Resources
- 9.2. Online Forums and Communities
- 9.3. Industry Publications
- 9.4. Training and Certification Programs
- 9.5. Networking with Professionals
- 10. The Future of Variant Coding
- 10.1. Increasing Vehicle Complexity
- 10.2. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 10.3. Cybersecurity Concerns
- 10.4. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 10.5. Integration with Cloud Services
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 1. What is variant coding?
- 2. Why is variant coding necessary?
- 3. What tools are used for variant coding?
- 4. What are the potential risks of variant coding?
- 5. How can I minimize the risks associated with variant coding?
- 6. Can variant coding void my vehicle’s warranty?
- 7. What is SCN coding?
- 8. What is engineering mode?
- 9. What is the future of variant coding?
- 10. Where can I find more information about variant coding?
1. Understanding Variant Coding in Mercedes-Benz Head Units
Variant coding, sometimes called parameterization, is a critical process in modern automotive systems, especially in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It involves modifying the software configuration of the Head Unit (HU), often referred to as COMAND or MBUX, to activate, deactivate, or adjust specific features and functions. This customization allows the vehicle to adapt to different regional requirements, optional equipment, and customer preferences. Variant coding ensures that the car’s electronic systems operate correctly and efficiently, providing an optimal driving experience.
1.1. What is Variant Coding?
Variant coding is the process of modifying the software parameters within a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) to tailor its functionality. In the context of Mercedes-Benz Head Units (HU), this means adjusting settings to enable or disable features, adapt to regional differences, or activate optional equipment. This process ensures that the vehicle operates according to specific requirements and preferences.
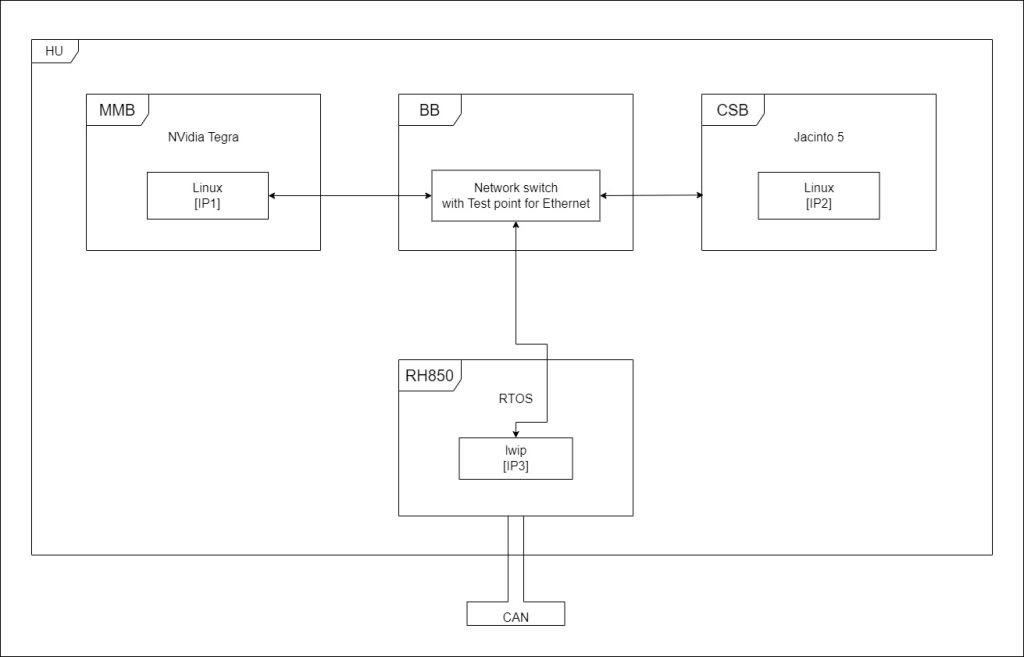
1.2. Key Components Involved
Several key components are involved in variant coding, including:
- Head Unit (HU): The central control unit for infotainment, navigation, and vehicle settings.
- Diagnostic Tools: Specialized software and hardware used to communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs. Examples include XENTRY/DAS, Vediamo, and DTS Monaco. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive information and support for selecting the right tools.
- ECUs (Electronic Control Units): Various control units within the vehicle that manage specific functions, such as engine control, transmission, and safety systems.
- Vehicle Communication Interfaces: Interfaces like CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, used for communication between ECUs.
1.3. Why is Variant Coding Necessary?
Variant coding is essential for several reasons:
- Regional Adaptation: Different regions have varying regulations and requirements. Variant coding allows manufacturers to adapt vehicles to comply with local laws, such as enabling specific language options or disabling certain features.
- Optional Equipment: Vehicles come with a range of optional features. Variant coding activates or deactivates these features based on the vehicle’s configuration.
- Customer Preferences: Some features can be customized to suit individual preferences, such as adjusting audio settings or display themes.
- Software Updates and Retrofitting: Variant coding is often required when installing new software updates or retrofitting components to ensure compatibility and proper functionality.
1.4. Common Terms and Acronyms
Understanding the terminology is crucial for anyone involved in variant coding. Here are some common terms and acronyms:
- HU: Head Unit, the main infotainment system.
- COMAND: Cockpit Management and Data system, a previous generation of Mercedes-Benz infotainment systems.
- MBUX: Mercedes-Benz User Experience, the latest generation infotainment system.
- ECU: Electronic Control Unit, a generic term for any of the car’s computers.
- CAN Bus: Controller Area Network, the communication network used by the car’s ECUs.
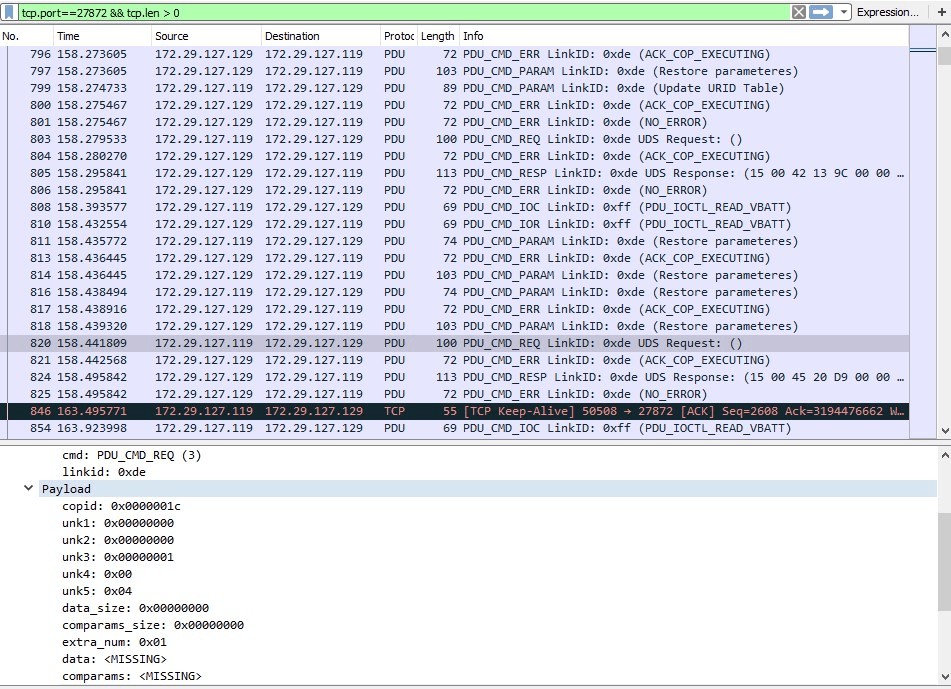
- UDS: Unified Diagnostic Services, a diagnostic protocol used to communicate with ECUs.
- SCN Coding: System Component Nomenclature coding, a specific type of variant coding used by Mercedes-Benz to ensure correct component matching and software compatibility.
- XENTRY/DAS: Mercedes-Benz diagnostic software.
- Vediamo: Engineering software used for advanced diagnostics and variant coding.
- DTS Monaco: Diagnostic Tool Set Monaco, another engineering tool used for ECU flashing and coding.
2. Examples of Variant Coding Applications
Variant coding in Mercedes-Benz vehicles covers a wide range of applications, each designed to enhance functionality, adapt to regional standards, or cater to specific customer needs. These examples demonstrate the flexibility and importance of variant coding in modern automotive systems.
2.1. Enabling/Disabling Navigation Features
One of the most common applications of variant coding is enabling or disabling navigation features. This is often necessary when a vehicle is sold without the navigation option pre-installed but the owner wishes to add it later.
- Activating Navigation: Variant coding can activate the navigation system by configuring the head unit to recognize and use GPS data. This may involve entering specific codes or parameters to unlock the navigation software.
- Updating Maps: Variant coding can also be used to update map data, ensuring that the navigation system has the latest road information and points of interest.
- Disabling Navigation in Certain Regions: In some regions, navigation features may be restricted due to legal or regulatory reasons. Variant coding can disable these features to comply with local laws.
2.2. Activating Smartphone Integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto)
Smartphone integration, such as Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, has become a standard feature in modern vehicles. Variant coding plays a crucial role in activating and configuring these systems.
- Enabling CarPlay/Android Auto: Variant coding can enable the head unit to recognize and communicate with smartphones via CarPlay or Android Auto. This involves configuring the USB ports and software settings to support these protocols.
- Adjusting Display Settings: Variant coding can also be used to adjust display settings for CarPlay and Android Auto, ensuring that the interface is properly sized and optimized for the vehicle’s screen.
- Resolving Compatibility Issues: Sometimes, compatibility issues may arise between the head unit and specific smartphone models. Variant coding can help resolve these issues by adjusting communication parameters and software settings.
2.3. Adjusting Audio Settings and Equalization
Audio settings and equalization are important for delivering an optimal listening experience. Variant coding allows technicians to fine-tune these settings to match the vehicle’s audio system and the owner’s preferences.
- Optimizing Sound Profiles: Variant coding can adjust sound profiles to match the vehicle’s speaker configuration and acoustic characteristics. This ensures that the audio system delivers balanced and clear sound.
- Adjusting Equalization: Variant coding allows technicians to adjust equalization settings to optimize sound quality for different music genres and listening preferences.
- Enabling Surround Sound: In vehicles equipped with surround sound systems, variant coding can activate and configure these features to create a more immersive audio experience.
2.4. Enabling/Disabling Specific Vehicle Functions (e.g., Lane Keeping Assist, Blind Spot Monitoring)
Many modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles come equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) such as lane keeping assist and blind spot monitoring. Variant coding can enable or disable these functions based on the vehicle’s configuration and the owner’s preferences.
- Activating ADAS Features: Variant coding can activate ADAS features by configuring the appropriate sensors and control units. This may involve calibrating the sensors and adjusting software settings to ensure proper functionality.
- Disabling ADAS Features: In some cases, owners may prefer to disable certain ADAS features. Variant coding allows technicians to deactivate these functions while maintaining the vehicle’s overall safety and performance.
- Adjusting Sensitivity Settings: Variant coding can also be used to adjust the sensitivity settings of ADAS features, such as lane keeping assist and blind spot monitoring, to match the driver’s preferences and driving style.
2.5. Adapting to Regional Requirements (Language, Units, Radio Frequencies)
Regional adaptation is a critical aspect of variant coding. Vehicles sold in different regions must comply with local regulations and standards, which may require adjustments to language settings, units of measurement, and radio frequencies.
- Changing Language Settings: Variant coding can change the language settings of the head unit to match the local language. This includes menus, voice prompts, and other user interface elements.
- Adjusting Units of Measurement: Variant coding can adjust units of measurement to match local standards, such as changing from miles to kilometers or from Fahrenheit to Celsius.
- Configuring Radio Frequencies: Different regions use different radio frequencies. Variant coding can configure the head unit to receive local radio stations and comply with local broadcasting standards.
2.6. Activating Performance Features (e.g., AMG Performance Displays)
For high-performance Mercedes-Benz models, such as those from AMG, variant coding can activate special performance features, such as AMG performance displays and track data logging.
- Enabling AMG Performance Displays: Variant coding can enable AMG performance displays, which provide real-time information on engine performance, G-forces, and other performance metrics.
- Activating Track Data Logging: Variant coding can activate track data logging features, which allow drivers to record and analyze their performance on the track. This may involve configuring sensors, data storage, and software settings to support these functions.
- Adjusting Performance Settings: Variant coding can also be used to adjust performance settings, such as throttle response, suspension settings, and transmission shift points, to optimize the vehicle’s performance for different driving conditions.
 Mercedes diagnostic tool interface
Mercedes diagnostic tool interface
3. Tools and Software for Variant Coding
Variant coding in Mercedes-Benz vehicles requires specialized tools and software to access and modify the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs). These tools enable technicians to read and write data to the ECUs, activate or deactivate features, and adapt the vehicle to specific requirements.
3.1. Official Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tools (XENTRY/DAS)
XENTRY/DAS (Diagnostic Assistance System) is the official diagnostic software used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships and authorized service centers. This comprehensive tool provides a wide range of functions, including:
- Vehicle Diagnostics: XENTRY/DAS can diagnose faults and issues in various vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, brakes, and airbags.
- Variant Coding: XENTRY/DAS allows technicians to perform variant coding, activating or deactivating features based on the vehicle’s configuration.
- Software Updates: XENTRY/DAS can update the software in various ECUs, ensuring that the vehicle has the latest bug fixes and performance improvements.
- SCN Coding: XENTRY/DAS supports SCN (System Component Nomenclature) coding, a specific type of variant coding used by Mercedes-Benz to ensure correct component matching and software compatibility.
3.2. Engineering Software (Vediamo, DTS Monaco)
In addition to XENTRY/DAS, there are also engineering software tools like Vediamo and DTS Monaco that are used for advanced diagnostics and variant coding. These tools offer more flexibility and control than XENTRY/DAS, but they also require a higher level of technical expertise.
- Vediamo: Vediamo (Vehicle Diagnostic and Measuring System) is a powerful engineering tool used for ECU flashing, coding, and parameterization. It allows technicians to access and modify ECU data directly, enabling them to perform advanced customizations and repairs.
- DTS Monaco: DTS Monaco (Diagnostic Tool Set Monaco) is another engineering tool used for ECU flashing and coding. It offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of functions, making it a popular choice among technicians and enthusiasts.
3.3. Third-Party Tools and Interfaces
Several third-party tools and interfaces are available for variant coding in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools offer a more affordable alternative to the official Mercedes-Benz tools, but they may not have the same level of functionality or support.
- iCarsoft MB II: The iCarsoft MB II is a handheld diagnostic tool that supports variant coding and other advanced functions. It offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of features, making it a popular choice among DIY enthusiasts and independent mechanics.
- Autel MaxiSys: The Autel MaxiSys is a professional-grade diagnostic tool that supports variant coding and ECU programming. It offers a wide range of functions and a comprehensive vehicle coverage, making it a popular choice among professional technicians.
- OBDSTAR Tools: OBDSTAR offers a range of diagnostic and programming tools that support variant coding in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them a popular choice among DIY enthusiasts and independent mechanics.
3.4. Hardware Interfaces (OBD-II)
To communicate with the vehicle’s ECUs, a hardware interface is required. The most common interface is the OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) port, which is a standardized port found in all modern vehicles.
- OBD-II Scanners: OBD-II scanners are used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and access basic vehicle information. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them a popular choice among DIY enthusiasts.
- OBD-II Interfaces with Variant Coding Support: Some OBD-II interfaces support variant coding and other advanced functions. These interfaces typically come with specialized software that allows technicians to access and modify ECU data.
- Multiplexers: Multiplexers are used to connect to multiple ECUs simultaneously. They are typically used in conjunction with diagnostic software like XENTRY/DAS and Vediamo.
3.5. Software Updates and Subscriptions
To keep the diagnostic tools and software up-to-date, regular software updates and subscriptions are required. These updates provide access to the latest vehicle data, bug fixes, and new features.
- Mercedes-Benz Updates: Mercedes-Benz provides regular software updates for XENTRY/DAS. These updates are typically available through a subscription service.
- Third-Party Updates: Third-party tool vendors also provide regular software updates for their diagnostic tools. These updates are typically available through a subscription service or as a one-time purchase.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Variant Coding
Performing variant coding on a Mercedes-Benz vehicle requires careful planning, the right tools, and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems. This step-by-step guide provides a general overview of the process.
4.1. Preparation and Prerequisites
Before starting the variant coding process, it is important to gather all the necessary information and tools.
- Vehicle Information: Collect the vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number), model year, and current software versions.
- Diagnostic Tool: Choose the appropriate diagnostic tool and ensure that it is properly installed and configured.
- Hardware Interface: Connect the hardware interface (e.g., OBD-II scanner) to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Battery Charger: Connect a battery charger to the vehicle to maintain a stable voltage during the coding process.
- Backup: Create a backup of the vehicle’s current ECU data in case something goes wrong.
4.2. Connecting to the Vehicle’s ECU
Once the preparation is complete, the next step is to connect to the vehicle’s ECU.
- Launch Diagnostic Software: Launch the diagnostic software (e.g., XENTRY/DAS, Vediamo, DTS Monaco).
- Select Vehicle: Select the correct vehicle model and year from the software’s menu.
- Establish Connection: Establish a connection to the vehicle’s ECU using the hardware interface. This may involve entering specific communication parameters or selecting a communication protocol.
4.3. Identifying the Correct Control Unit
After connecting to the vehicle, the next step is to identify the correct control unit for variant coding.
- Scan for ECUs: Use the diagnostic software to scan for all the ECUs in the vehicle.
- Identify Target ECU: Identify the ECU that controls the feature or function you want to modify. This may involve consulting the vehicle’s wiring diagrams or technical documentation.
- Verify ECU Information: Verify the ECU’s part number and software version to ensure that you have the correct information.
4.4. Accessing Variant Coding Options
Once you have identified the correct control unit, the next step is to access the variant coding options.
- Navigate to Coding Menu: Navigate to the coding menu within the diagnostic software. This may involve entering a specific access code or selecting a coding function.
- Select Variant Coding: Select the variant coding option from the menu.
- View Current Settings: View the current variant coding settings for the selected ECU.
4.5. Modifying Parameters
After accessing the variant coding options, the next step is to modify the parameters.
- Identify Parameters: Identify the parameters that control the feature or function you want to modify. This may involve consulting the vehicle’s technical documentation or experimenting with different settings.
- Enter New Values: Enter the new values for the selected parameters.
- Save Changes: Save the changes to the ECU. This may involve entering a security code or confirming the changes.
4.6. Verifying the Changes
After modifying the parameters, the next step is to verify the changes.
- Test Functionality: Test the functionality of the modified feature or function to ensure that it is working correctly.
- Read ECU Data: Read the ECU data to verify that the changes have been saved correctly.
- Check for Errors: Check for any error codes or warning messages that may have been triggered by the changes.
4.7. Finalizing the Coding Process
Once you have verified the changes, the final step is to finalize the coding process.
- Disconnect Diagnostic Tool: Disconnect the diagnostic tool from the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Remove Battery Charger: Remove the battery charger from the vehicle.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure that all the systems are working correctly.
5. Potential Risks and Precautions
Variant coding, while powerful, carries potential risks if not performed correctly. It’s crucial to understand these risks and take necessary precautions to avoid damaging the vehicle’s electronic systems.
5.1. Incorrect Coding
Incorrect coding can lead to a variety of problems, ranging from minor inconveniences to serious malfunctions.
- System Malfunctions: Incorrect coding can cause systems to malfunction, such as the engine, transmission, or brakes.
- Error Codes: Incorrect coding can trigger error codes, which can make it difficult to diagnose other problems.
- Vehicle Damage: In severe cases, incorrect coding can damage the vehicle’s electronic systems, requiring costly repairs.
5.2. Data Corruption
Data corruption can occur during the coding process, especially if there are power interruptions or communication errors.
- ECU Damage: Data corruption can damage the ECU, rendering it unusable.
- System Instability: Data corruption can cause system instability, leading to erratic behavior and unpredictable performance.
- Loss of Functionality: Data corruption can result in the loss of functionality, such as the navigation system, audio system, or ADAS features.
5.3. Warranty Issues
Performing variant coding can void the vehicle’s warranty, especially if it is done improperly or without authorization.
- Unauthorized Modifications: Manufacturers may void the warranty if the vehicle has been modified without their authorization.
- Damage Caused by Coding: Damage caused by incorrect coding may not be covered by the warranty.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all variant coding changes, including dates, parameters modified, and reasons for the changes.
5.4. Precautions to Take
To minimize the risks associated with variant coding, it is important to take the following precautions:
- Use Reliable Tools: Use reliable diagnostic tools and software from reputable vendors.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the instructions carefully and do not deviate from the recommended procedures.
- Backup Data: Always back up the vehicle’s current ECU data before making any changes.
- Stable Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply during the coding process to prevent data corruption.
- Expert Assistance: If you are not comfortable performing variant coding yourself, seek assistance from a qualified technician.
- Understand the System: Gain a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems and the parameters you are modifying.
- Double-Check Settings: Double-check all settings before saving them to the ECU.
- Test Thoroughly: Test the functionality of the modified feature or function thoroughly after making changes.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest information and best practices for variant coding.
6. Advanced Variant Coding Techniques
For advanced users and technicians, there are several advanced variant coding techniques that can be used to unlock hidden features, customize vehicle behavior, and optimize performance.
6.1. Enabling Hidden Features
Many Mercedes-Benz vehicles have hidden features that are not enabled by default. Variant coding can be used to unlock these features, providing access to additional functionality.
- AMG Performance Displays: Enable AMG performance displays on non-AMG models.
- Cornering Lights: Activate cornering lights for improved visibility in turns.
- Comfort Closing: Enable comfort closing of windows and sunroof with the remote key.
6.2. Customizing Vehicle Behavior
Variant coding can be used to customize vehicle behavior, tailoring it to the owner’s preferences and driving style.
- Throttle Response: Adjust throttle response for improved acceleration.
- Steering Feel: Customize steering feel for a more sporty or comfortable driving experience.
- Suspension Settings: Fine-tune suspension settings for improved handling and ride quality.
6.3. Optimizing Performance
Variant coding can be used to optimize performance, improving the vehicle’s power, efficiency, and overall driving experience.
- Engine Tuning: Adjust engine parameters for increased power and torque.
- Transmission Tuning: Optimize transmission shift points for improved acceleration and fuel economy.
- Fuel Efficiency: Adjust fuel parameters for improved fuel efficiency.
6.4. Using Engineering Mode
Engineering mode is a hidden menu within the head unit that provides access to advanced settings and diagnostic information.
- Accessing Engineering Mode: Access engineering mode by entering a specific key combination on the head unit.
- Advanced Settings: Explore the advanced settings within engineering mode to customize vehicle behavior and optimize performance.
- Diagnostic Information: View diagnostic information to troubleshoot problems and monitor system performance.
6.5. Scripting and Automation
Scripting and automation can be used to streamline the variant coding process, making it faster, more efficient, and less prone to errors.
- Coding Scripts: Create coding scripts to automate the variant coding process.
- Batch Coding: Use batch coding to apply the same coding changes to multiple vehicles.
- Remote Coding: Perform remote coding over the internet using specialized tools and interfaces.
 Mercedes diagnostic tool
Mercedes diagnostic tool
7. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Examining real-world examples and case studies can provide valuable insights into the practical applications of variant coding and the benefits it can offer.
7.1. Retrofitting Options
Variant coding is often used to retrofit options that were not originally installed on the vehicle.
- Navigation System: Retrofitting a navigation system to a vehicle that did not originally have one.
- Backup Camera: Adding a backup camera to a vehicle that did not originally have one.
- Parking Sensors: Installing parking sensors to a vehicle that did not originally have them.
7.2. Resolving Software Glitches
Variant coding can be used to resolve software glitches and compatibility issues.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Fixing Bluetooth connectivity issues with smartphones.
- Audio System Problems: Resolving audio system problems, such as distortion or loss of sound.
- Display Issues: Fixing display issues, such as flickering or incorrect colors.
7.3. Enhancing Performance
Variant coding can be used to enhance performance and improve the driving experience.
- Increased Horsepower: Increasing horsepower and torque through engine tuning.
- Improved Handling: Improving handling and ride quality through suspension tuning.
- Better Fuel Economy: Optimizing fuel economy through fuel parameter adjustments.
7.4. Adapting to Aftermarket Modifications
Variant coding can be used to adapt the vehicle’s systems to aftermarket modifications.
- Aftermarket Exhaust: Adjusting engine parameters to accommodate an aftermarket exhaust system.
- Aftermarket Wheels: Calibrating the speedometer and odometer for aftermarket wheels.
- Aftermarket Suspension: Fine-tuning the suspension settings for an aftermarket suspension system.
7.5. Customer Success Stories
Sharing customer success stories can demonstrate the value of variant coding and the benefits it can offer.
- Improved Functionality: Customers who have successfully retrofitted options or unlocked hidden features.
- Enhanced Performance: Customers who have experienced improved performance and a better driving experience.
- Resolved Issues: Customers who have had software glitches or compatibility issues resolved through variant coding.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful planning and execution, issues can arise during the variant coding process. Knowing how to troubleshoot these issues is essential for a successful outcome.
8.1. Communication Errors
Communication errors can occur when the diagnostic tool is unable to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Check Connections: Check all connections between the diagnostic tool, hardware interface, and vehicle.
- Verify Protocol: Verify that the diagnostic tool is using the correct communication protocol.
- Try Different Tool: Try a different diagnostic tool or hardware interface.
8.2. Incorrect Parameter Values
Entering incorrect parameter values can lead to system malfunctions and error codes.
- Double-Check Values: Double-check all parameter values before saving them to the ECU.
- Consult Documentation: Consult the vehicle’s technical documentation or seek advice from a qualified technician.
- Restore Backup: Restore the vehicle’s original ECU data from the backup.
8.3. Software Freezes
Software freezes can occur during the coding process, especially if there are power interruptions or communication errors.
- Restart Software: Restart the diagnostic software and try again.
- Check Connections: Check all connections between the diagnostic tool, hardware interface, and vehicle.
- Stable Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply during the coding process.
8.4. ECU Not Responding
In some cases, the ECU may not respond to the diagnostic tool.
- Check Power Supply: Check the power supply to the ECU.
- Verify Wiring: Verify the wiring to the ECU.
- Try Different Tool: Try a different diagnostic tool or hardware interface.
8.5. Error Codes After Coding
Error codes can appear after coding, indicating that something went wrong during the process.
- Read Error Codes: Read the error codes using the diagnostic tool.
- Consult Documentation: Consult the vehicle’s technical documentation or seek advice from a qualified technician.
- Clear Error Codes: Clear the error codes after resolving the underlying issue.
9. Staying Updated with the Latest Information
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and software updates being released regularly. Staying updated with the latest information is essential for anyone involved in variant coding.
9.1. Official Mercedes-Benz Resources
Mercedes-Benz provides a variety of resources for technicians and enthusiasts.
- XENTRY/DAS Updates: Keep XENTRY/DAS up-to-date with the latest software updates.
- Technical Documentation: Consult the vehicle’s technical documentation for detailed information on variant coding.
- Training Courses: Attend training courses offered by Mercedes-Benz to improve your skills and knowledge.
9.2. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities can be a valuable source of information and support.
- Mercedes-Benz Forums: Join online forums dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Coding Communities: Participate in coding communities to share knowledge and experiences.
- Social Media: Follow social media accounts and groups related to Mercedes-Benz and variant coding.
9.3. Industry Publications
Industry publications can provide insights into the latest trends and technologies.
- Automotive Magazines: Read automotive magazines to stay informed about new developments in the industry.
- Technical Journals: Consult technical journals for in-depth information on vehicle systems and coding techniques.
- Online News Sources: Follow online news sources for the latest updates on Mercedes-Benz and the automotive industry.
9.4. Training and Certification Programs
Training and certification programs can help you improve your skills and knowledge and gain recognition for your expertise.
- Automotive Training Centers: Attend training courses at automotive training centers.
- Certification Programs: Obtain certifications from industry organizations.
- Online Courses: Take online courses to learn about variant coding and other automotive topics.
9.5. Networking with Professionals
Networking with other professionals in the industry can provide valuable insights and opportunities.
- Industry Events: Attend industry events and conferences.
- Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations related to the automotive industry.
- Online Networking: Connect with other professionals on LinkedIn and other online platforms.
10. The Future of Variant Coding
The future of variant coding is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including increasing vehicle complexity, the rise of over-the-air (OTA) updates, and the growing importance of cybersecurity.
10.1. Increasing Vehicle Complexity
Vehicles are becoming increasingly complex, with more electronic systems and software than ever before. This complexity will likely lead to new challenges and opportunities for variant coding.
- More Parameters: There will be more parameters to code and customize.
- Advanced Techniques: Advanced coding techniques will be required to manage the complexity.
- Specialized Tools: Specialized tools and software will be needed to access and modify the vehicle’s systems.
10.2. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. These updates allow manufacturers to remotely update the vehicle’s software, without requiring a visit to the dealership.
- Remote Coding: OTA updates may enable remote coding, allowing technicians to perform variant coding from a remote location.
- Automatic Updates: OTA updates may automate some aspects of variant coding, making it easier to customize vehicle settings.
- Security Risks: OTA updates also pose security risks, as they could be used to remotely compromise the vehicle’s systems.
10.3. Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity is a growing concern in the automotive industry. Variant coding can be a potential attack vector, as it allows technicians to access and modify the vehicle’s electronic systems.
- Secure Coding Practices: Secure coding practices will be essential to prevent unauthorized access and modifications.
- Authentication: Strong authentication mechanisms will be needed to verify the identity of technicians and diagnostic tools.
- Encryption: Encryption will be used to protect the vehicle’s data and prevent tampering.
10.4. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is likely to play an increasing role in variant coding.
- Automated Coding: AI algorithms could be used to automate the variant coding process.
- Predictive Coding: AI could be used to predict the optimal coding settings for a given vehicle and driver.
- Troubleshooting: AI could be used to troubleshoot coding issues and provide solutions.
10.5. Integration with Cloud Services
Integration with cloud services will enable new possibilities for variant coding.
- Remote Diagnostics: Cloud services will enable remote diagnostics and coding.
- Data Analytics: Cloud services will provide data analytics for coding optimization.
- Personalized Settings: Cloud services will allow for personalized settings based on driver preferences.
Variant coding on Mercedes-Benz Head Units (HU) offers a powerful way to customize and optimize vehicle functionality. By understanding the tools, techniques, and potential risks involved, technicians and enthusiasts can unlock hidden features, adapt to regional requirements, and enhance the overall driving experience. Always follow best practices and stay updated with the latest information to ensure a successful and safe coding process.
Do you need expert advice on variant coding for your Mercedes-Benz? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for personalized assistance with diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and step-by-step repair and maintenance guidance. Reach us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is variant coding?
Variant coding is the process of modifying the software parameters within a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) to tailor its functionality.
2. Why is variant coding necessary?
Variant coding is necessary for regional adaptation, activating optional equipment, customer preferences, and software updates/retrofitting.
3. What tools are used for variant coding?
Official Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools (XENTRY/DAS), engineering software (Vediamo, DTS Monaco), and third-party tools are used for variant coding.
4. What are the potential risks of variant coding?
Potential risks include incorrect coding, data corruption, and warranty issues.
5. How can I minimize the risks associated with variant coding?
Use reliable tools, follow instructions carefully, back up data, ensure a stable power supply, and seek expert assistance if needed.
6. Can variant coding void my vehicle’s warranty?
Yes, performing variant coding can void the vehicle’s warranty, especially if it is done improperly or without authorization.
7. What is SCN coding?
SCN (System Component Nomenclature) coding is a specific type of variant coding used by Mercedes-Benz to ensure correct component matching and software compatibility.
8. What is engineering mode?
Engineering mode is a hidden menu within the head unit that provides access to advanced settings and diagnostic information.
9. What is the future of variant coding?
The future of variant coding is likely to be shaped by increasing vehicle complexity, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and cybersecurity concerns.
10. Where can I find more information about variant coding?
You can find more information about variant coding in official Mercedes-Benz resources, online forums and communities, industry publications, and training and certification programs.