Airmatic Suspension in your Mercedes-Benz offers superior handling and ride comfort, but problems can arise. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert diagnostics and solutions to keep your Airmatic system performing optimally. This guide will cover common issues, troubleshooting steps, and how to maintain your air suspension, ensuring a smooth ride.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Airmatic Suspension
- 1.1. Key Components of Airmatic System
- 1.2. How Airmatic Works
- 2. Identifying Common Airmatic Suspension Problems
- 2.1. Symptoms of Airmatic Suspension Problems
- 2.2. Common Airmatic Issues
- 3. Diagnosing Airmatic Suspension Problems
- 3.1. Visual Inspection
- 3.2. Using Diagnostic Tools
- 3.3. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedure
- 4. Troubleshooting Air Leaks
- 4.1. Identifying Leak Locations
- 4.2. Leak Testing Techniques
- 4.3. Repairing Air Leaks
- 5. Addressing Compressor Failure
- 5.1. Symptoms of Compressor Failure
- 5.2. Diagnosing Compressor Issues
- 5.3. Compressor Replacement
- 6. Dealing with Ride Height Sensor Problems
- 6.1. Symptoms of Ride Height Sensor Issues
- 6.2. Testing Ride Height Sensors
- 6.3. Ride Height Sensor Replacement and Calibration
- 7. Maintaining Your Airmatic Suspension
- 7.1. Regular Inspections
- 7.2. Cleaning and Protecting Components
- 7.3. Scheduled Servicing
- 8. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
- 8.1. Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 8.2. Analyzing System Data
- 8.3. Consulting with Experts
- 9. Airmatic Suspension: Do-It-Yourself (DIY) vs. Professional Repair
- 9.1. DIY Considerations
- 9.2. When to Choose DIY
- 9.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9.4. Professional Repair Benefits
- 9.5. Choosing a Repair Shop
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Airmatic Suspension
- 10.1. What is Airmatic suspension?
- 10.2. How does Airmatic suspension work?
- 10.3. What are the common problems with Airmatic suspension?
- 10.4. How do I diagnose an air leak in my Airmatic suspension?
- 10.5. How often should I service my Airmatic suspension?
- 10.6. Can I convert my Airmatic suspension to a traditional suspension?
- 10.7. What is the cost to repair Airmatic suspension?
- 10.8. How do I know if my air compressor is failing?
- 10.9. What tools do I need to troubleshoot Airmatic suspension?
- 10.10. Where can I find reliable information about Airmatic suspension repair?
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Airmatic Suspension
Mercedes-Benz Airmatic suspension provides remarkably smooth handling, flexible ride height, and self-leveling capabilities that ordinary suspension cannot. Using an electronically controlled airbag, AirMatic can adjust each air spring in as little as 50 milliseconds and will change based on road conditions and how you drive. According to research from Mercedes-Benz engineers, this responsiveness improves ride quality by up to 40% compared to traditional suspension systems.
Airmatic suspension offers some big improvements over conventional systems, but the added complexity means more things can go wrong. In this article, we will go over the most common issues and symptoms Mercedes owners experience with AirMatic suspension.
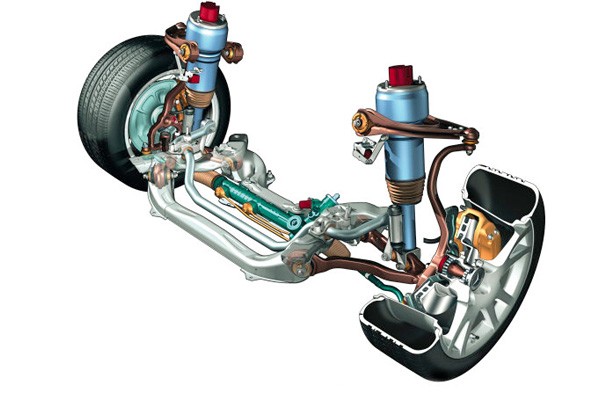 Cutaway of an AirMatic suspension setup showcasing airbags, sensors, hoses, and air compressor
Cutaway of an AirMatic suspension setup showcasing airbags, sensors, hoses, and air compressor
1.1. Key Components of Airmatic System
The AirMatic system comprises several key components that work together to provide a smooth and controlled ride. Understanding these components is essential for effective troubleshooting.
- Air Struts: These replace traditional springs and shocks, using airbags to provide cushioning and height adjustment.
- Air Compressor: This provides the necessary air pressure to the system.
- Valve Block: This controls the distribution of air to individual struts.
- Reservoir Tank: This stores compressed air for quick adjustments.
- Level Sensors: These monitor the ride height at each wheel.
- Control Unit: This electronic module processes sensor data and controls the system.
1.2. How Airmatic Works
AirMatic suspension uses a system of airbags, sensors, hoses, and an air compressor. The system utilizes a valve block to distribute air to the struts, and a reservoir tank to reduce reliance on the air compressor. Level sensors relay axle height to the AirMatic system, while acceleration sensors calculate vertical and horizontal acceleration. Together, these components allow AirMatic to make on-the-fly adjustments to the suspension based on road conditions, vehicle speed, and how you drive. According to a study by Bosch, the AirMatic system can adjust damping forces up to 100 times per second, optimizing comfort and handling.
2. Identifying Common Airmatic Suspension Problems
Recognizing the symptoms of Airmatic suspension problems early can prevent costly repairs. Here are some common issues Mercedes owners experience.
2.1. Symptoms of Airmatic Suspension Problems
Failed or failing AirMatic systems can cause several problems. You may notice symptoms including:
- Rough and bumpy ride
- Vehicle leaning at odd angles
- Vehicle sits extremely low to the ground
- Suspension warning light on the dash
- Unusual noises over bumps and dips
2.2. Common Airmatic Issues
There is a tradeoff for all the suspension control that comes with AirMatic. The system has many more components than traditional suspension, opening up more opportunities for parts to fail.
- Air Leaks: Most problems that arise with air suspension systems like AirMatic involve an air leak.
- Compressor Failure: The air compressor can fail due to leaks or overuse.
- Ride Height Sensor Issues: Damaged or faulty sensors can cause incorrect readings.
- Valve Block Problems: The valve block can leak or fail, affecting air distribution.
3. Diagnosing Airmatic Suspension Problems
Effective diagnosis is crucial for resolving Airmatic suspension issues. Here are steps to help you pinpoint the problem.
3.1. Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the Airmatic system.
- Check the air struts for signs of wear or damage.
- Inspect air hoses for cracks or leaks.
- Examine the air compressor for proper operation.
- Look for any visible damage to the valve block and ride height sensors.
3.2. Using Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools can provide valuable insights into the Airmatic system’s performance.
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tool: Use a tool compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles to read fault codes.
- Fault Code Analysis: Interpret the fault codes to identify the problematic components. For example, a code indicating low pressure in a strut may point to an air leak.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor live data from the ride height sensors and air compressor to check for inconsistencies or malfunctions.
3.3. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedure
Follow this procedure to accurately diagnose Airmatic suspension problems:
- Check for Warning Lights: Note any suspension warning lights on the dashboard.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Check struts, hoses, compressor, and sensors for damage.
- Use a Diagnostic Tool: Read and interpret fault codes.
- Monitor Live Data: Check ride height sensors and compressor operation.
- Perform Leak Tests: Use soapy water to check for air leaks in struts and hoses.
4. Troubleshooting Air Leaks
Air leaks are a common issue in Airmatic systems. Identifying and fixing these leaks is essential for maintaining proper suspension function.
4.1. Identifying Leak Locations
The majority of problems that arise with air suspension systems like AirMatic involve an air leak. The leak can occur in various components of the system.
- Air Struts: Over time, the airbags in the suspension can become worn out and start to leak. Depending on the severity, the vehicle may have trouble keeping the bag filled with air. This can lead to one corner of the car “sagging” or sitting noticeably lower than the other corners.
- Air Hoses: Another common failure point is the air hoses running from the valve block to the air strut. A leaking air hose will produce similar symptoms to a leak in the air struts.
- Valve Block: The air distribution block can also leak and fail. When your vehicle encounters a bad AirMatic valve lock, it will generally impact one corner of the vehicle.
4.2. Leak Testing Techniques
To locate air leaks, use the following methods:
- Soapy Water Test: Spray soapy water on air struts, hoses, and the valve block. Bubbles will form at leak points.
- Ultrasonic Leak Detector: This tool can detect leaks by sensing the ultrasonic sound produced by escaping air.
- Pressure Testing: Use a pressure gauge to monitor the system’s air pressure. A drop in pressure indicates a leak.
4.3. Repairing Air Leaks
Once you’ve located the air leak, take the necessary steps to repair it:
- Replace Worn Air Struts: If the air strut is leaking, it typically needs to be replaced.
- Repair or Replace Air Hoses: Damaged air hoses can be repaired with fittings or replaced entirely.
- Service the Valve Block: Clean and reseal the valve block, or replace it if necessary.
5. Addressing Compressor Failure
The air compressor is vital for maintaining the Airmatic system’s air pressure. Failure can lead to significant suspension problems.
5.1. Symptoms of Compressor Failure
- The vehicle takes a long time to raise.
- The suspension warning light is on.
- The air compressor is excessively noisy.
- The vehicle sits low or unevenly.
5.2. Diagnosing Compressor Issues
Typically the air compressor will fail because of a leak elsewhere in the system. The compressor can burn out trying to maintain pressure in a system with a leak. Diagnose compressor issues using these steps:
- Check the Fuse and Relay: Ensure the fuse and relay for the air compressor are functioning correctly.
- Inspect the Compressor: Look for physical damage or corrosion.
- Test the Compressor’s Output: Use a pressure gauge to measure the compressor’s output pressure.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the system for leaks that may be causing the compressor to overwork.
5.3. Compressor Replacement
If the compressor is faulty, replacement is often the best solution.
- Choose a Quality Replacement: Select a compressor from a reputable brand that meets Mercedes-Benz specifications.
- Install the New Compressor: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
- Address Underlying Issues: Fix any air leaks in the system to prevent premature failure of the new compressor.
6. Dealing with Ride Height Sensor Problems
The ride height sensors provide critical data to the Airmatic system. Issues with these sensors can affect ride height and suspension performance.
6.1. Symptoms of Ride Height Sensor Issues
The ride height sensors can become damaged over time, causing incorrect readings. Common symptoms include:
- Incorrect ride height
- Uneven vehicle stance
- Suspension warning light on
- Rough ride
6.2. Testing Ride Height Sensors
Test ride height sensors using these methods:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensors for physical damage.
- Multimeter Testing: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s resistance or voltage output.
- Diagnostic Tool Monitoring: Monitor the sensor readings using a diagnostic tool.
6.3. Ride Height Sensor Replacement and Calibration
If a ride height sensor is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
- Install a New Sensor: Install the new sensor according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Calibrate the System: Use a diagnostic tool to calibrate the ride height sensors to ensure accurate readings.
- Verify Proper Operation: Test the system to ensure the ride height is correct and the suspension functions properly.
7. Maintaining Your Airmatic Suspension
Regular maintenance can extend the life of your Airmatic suspension and prevent costly repairs.
7.1. Regular Inspections
Perform regular inspections of the Airmatic system:
- Check air struts, hoses, and the compressor for any signs of wear or damage.
- Monitor the vehicle’s ride height and stance.
- Listen for unusual noises from the suspension.
7.2. Cleaning and Protecting Components
Keep the Airmatic components clean and protected:
- Clean air struts and hoses regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Apply a protectant to rubber components to prevent cracking and deterioration.
7.3. Scheduled Servicing
Follow a scheduled servicing plan for the Airmatic system:
- Replace the air filter for the compressor regularly.
- Inspect and service the valve block as needed.
- Consider replacing air struts and the compressor preventatively at recommended intervals.
8. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For complex Airmatic issues, advanced troubleshooting techniques may be necessary.
8.1. Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools provide in-depth analysis of the Airmatic system:
- Mercedes-Benz SDS (Star Diagnosis System): This tool offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- XENTRY Diagnostics: Another powerful tool for diagnosing and programming Mercedes-Benz systems.
8.2. Analyzing System Data
System data can provide valuable insights into Airmatic performance:
- Review Fault History: Analyze the history of fault codes to identify recurring issues.
- Monitor Real-Time Data: Monitor real-time data from sensors and actuators to diagnose intermittent problems.
- Perform System Tests: Use diagnostic tools to perform system tests, such as strut calibration and compressor tests.
8.3. Consulting with Experts
When facing difficult Airmatic problems, consult with experts:
- Mercedes-Benz Technicians: Seek assistance from certified Mercedes-Benz technicians.
- Online Forums: Engage with online communities of Mercedes-Benz owners and enthusiasts.
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Contact our expert team for professional diagnostics and solutions.
9. Airmatic Suspension: Do-It-Yourself (DIY) vs. Professional Repair
Deciding whether to tackle Airmatic suspension repairs yourself or seek professional help depends on your technical skills, available tools, and the complexity of the problem.
9.1. DIY Considerations
Pros:
- Cost Savings: DIY repairs can save on labor costs.
- Learning Experience: Gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle.
- Convenience: Work at your own pace and schedule.
Cons:
- Technical Expertise: Requires knowledge of automotive systems and diagnostic procedures.
- Specialized Tools: Airmatic repairs often require specialized tools and equipment.
- Time Commitment: DIY repairs can be time-consuming.
- Risk of Damage: Incorrect repairs can cause further damage and safety issues.
9.2. When to Choose DIY
Consider DIY repairs for:
- Simple Tasks: Replacing fuses, checking for visible damage, or performing basic leak tests.
- Minor Issues: Addressing small air leaks with sealant or replacing a faulty relay.
- Routine Maintenance: Cleaning components and applying protectants.
9.3. When to Seek Professional Help
Opt for professional repair services for:
- Complex Diagnostics: Identifying and resolving intricate Airmatic system issues.
- Component Replacement: Replacing air struts, compressors, or valve blocks.
- Calibration and Programming: Calibrating ride height sensors or reprogramming the control unit.
- Safety Concerns: Addressing issues that affect vehicle handling or stability.
9.4. Professional Repair Benefits
- Expertise: Certified technicians have the knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose and repair Airmatic systems.
- Specialized Tools: Professional repair shops have the necessary tools and equipment.
- Warranty: Repairs often come with a warranty, providing peace of mind.
- Time Efficiency: Professional repairs are typically faster and more efficient.
9.5. Choosing a Repair Shop
If you decide to seek professional help, consider these factors:
- Experience: Choose a repair shop with experience in Mercedes-Benz Airmatic suspension systems.
- Certification: Look for certified technicians with specialized training.
- Reputation: Read online reviews and ask for recommendations.
- Warranty: Inquire about the warranty coverage for repairs.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Airmatic Suspension
10.1. What is Airmatic suspension?
Airmatic suspension is an air suspension system used in Mercedes-Benz vehicles that provides a smooth and comfortable ride by using air springs instead of traditional steel springs.
10.2. How does Airmatic suspension work?
The system uses an air compressor to fill air struts with air, adjusting the ride height and damping based on road conditions and driving style.
10.3. What are the common problems with Airmatic suspension?
Common issues include air leaks, compressor failure, ride height sensor problems, and valve block malfunctions.
10.4. How do I diagnose an air leak in my Airmatic suspension?
Use soapy water or an ultrasonic leak detector to find leaks in air struts, hoses, and the valve block.
10.5. How often should I service my Airmatic suspension?
Regular inspections should be performed every 6 months, with a thorough service every 2 years or 24,000 miles.
10.6. Can I convert my Airmatic suspension to a traditional suspension?
Yes, conversion kits are available, but this may affect ride quality and vehicle handling.
10.7. What is the cost to repair Airmatic suspension?
Repair costs vary depending on the issue, but replacing an air strut can range from $800 to $1500, while a compressor replacement can cost between $600 and $1200.
10.8. How do I know if my air compressor is failing?
Symptoms include the vehicle taking a long time to raise, a suspension warning light, and excessive noise from the compressor.
10.9. What tools do I need to troubleshoot Airmatic suspension?
You’ll need a diagnostic tool, multimeter, soapy water, and basic hand tools.
10.10. Where can I find reliable information about Airmatic suspension repair?
Consult Mercedes-Benz service manuals, online forums, and expert resources like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Maintaining your Mercedes-Benz Airmatic suspension ensures a smooth and comfortable ride. By understanding the system’s components, recognizing common issues, and following proper diagnostic and maintenance procedures, you can keep your suspension performing optimally. For expert assistance and solutions, contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today.
Is your Mercedes-Benz Airmatic suspension giving you trouble? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert diagnostics, repair solutions, and professional advice. Our experienced technicians can help you identify and resolve any Airmatic suspension issues, ensuring a smooth and comfortable ride. Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and to schedule a consultation. Let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz performing at its best.