The “Gateway” (CGW/ZGW) in a Mercedes network serves as the central communication hub, facilitating data exchange between various electronic control units (ECUs). At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we empower you to understand and address CGW-related issues effectively. This article clarifies the crucial role of the Central Gateway, its symptoms when failing, and how to diagnose and potentially resolve problems, ensuring your Mercedes operates at its peak performance. Unlock the full potential of your vehicle with central gateway diagnostics, Mercedes communication network insights, and ECU data exchange expertise.
Contents
- 1. What Does the “Gateway” (CGW/ZGW) Do in a Mercedes-Benz?
- 1.1 Understanding the Gateway’s Role
- 1.2 Key Responsibilities of the CGW
- 1.3 Why Is the Gateway Important?
- 1.4 The Central Gateway and Diagnostic Tools
- 2. What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
- 2.1 Communication Issues
- 2.2 Warning Lights and Error Messages
- 2.3 Electrical System Malfunctions
- 2.4 Comfort and Convenience System Problems
- 2.5 Transmission and Engine Issues
- 2.6 Other Potential Symptoms
- 2.7 Diagnosing Gateway Issues
- 3. How to Diagnose a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) Issue?
- 3.1 Preliminary Steps
- 3.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3 Communication Bus Testing
- 3.4 Power and Ground Testing
- 3.5 Component Testing (If Applicable)
- 3.6 Advanced Diagnostics
- 3.7 Common Causes of CGW Failure
- 3.8 Important Considerations
- 4. What Are the Potential Solutions for a Faulty Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
- 4.1 Addressing Minor Issues
- 4.2 Gateway Module Replacement
- 4.3 Cloning the Gateway Module
- 4.4 Addressing Water Damage
- 4.5 Important Considerations
- 4.6 After the Repair
- 5. Can I Replace the Gateway (CGW/ZGW) Myself, or Do I Need a Professional?
- 5.1 Factors to Consider
- 5.2 Steps Involved in DIY Replacement
- 5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
- 5.4 Benefits of Professional Replacement
- 5.5 Recommendations
- 6. What Is the Cost of Replacing a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
- 6.1 Factors Affecting the Cost
- 6.2 Estimated Cost Range
- 6.3 Getting an Accurate Quote
- 6.4 Cost-Saving Tips
- 6.5 Long-Term Cost Considerations
- 7. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Dealing With a Mercedes Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
- 7.1 Diagnostic Mistakes
- 7.2 Replacement Mistakes
- 7.3 Coding and Programming Mistakes
- 7.4 General Mistakes
1. What Does the “Gateway” (CGW/ZGW) Do in a Mercedes-Benz?
The “Gateway,” often referred to as the Central Gateway (CGW) or Zentrales Gateway (ZGW) in German, acts as the primary communication interface within a Mercedes-Benz vehicle’s complex network of electronic systems. It’s the central hub through which all data passes, ensuring seamless communication between various electronic control units (ECUs).
1.1 Understanding the Gateway’s Role
The CGW’s main function is to translate and route data between different communication protocols used by various ECUs in the car. Think of it as a multi-lingual translator and traffic controller for your car’s electronic systems.
1.2 Key Responsibilities of the CGW
- Communication Hub: It enables communication between diverse systems like the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), electronic stability program (ESP), climate control, infotainment, and more.
- Protocol Translation: Different ECUs may use different communication protocols (e.g., CAN, LIN, MOST). The CGW translates these protocols, ensuring that data can be exchanged seamlessly.
- Data Routing: It directs data packets to the intended recipient ECU, preventing information overload and ensuring efficient communication.
- Security Gateway: Modern CGWs often act as a security barrier, preventing unauthorized access to the vehicle’s network and protecting against hacking attempts. This is increasingly important with connected car features.
- Diagnostic Interface: The CGW serves as the primary access point for diagnostic tools. Technicians connect to the CGW to read fault codes, access live data, and perform diagnostic tests on various vehicle systems.
- Software Updates: The CGW facilitates software updates to various ECUs. New software versions are often loaded through the CGW and then distributed to the relevant modules.
- Vehicle Immobilization: In some Mercedes-Benz models, the CGW plays a role in the vehicle’s immobilization system, preventing unauthorized starting.
- Energy Management: The CGW can be involved in energy management functions, such as controlling the activation and deactivation of certain systems to conserve battery power.
1.3 Why Is the Gateway Important?
Without a properly functioning CGW, communication between critical systems would be impossible, leading to a cascade of problems. The engine might not communicate with the transmission, the ABS might not function correctly, or the infotainment system might fail to operate. The CGW is the keystone of the car’s electronic architecture.
1.4 The Central Gateway and Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools like the ones offered at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN connect directly to the CGW to access the entire vehicle’s electronic system. This allows technicians and knowledgeable owners to:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from all modules.
- View live data from various sensors and systems.
- Perform actuation tests to check the functionality of components.
- Program and code certain modules (requires specialized tools and knowledge).
By understanding the CGW’s role, you can better appreciate the importance of proper diagnostics and maintenance of your Mercedes-Benz’s electronic systems.
2. What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
A failing Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) can manifest in a wide array of symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. The symptoms can range from minor inconveniences to critical system failures. Here’s a comprehensive overview of potential indicators:
2.1 Communication Issues
- No Communication with Diagnostic Tools: This is a classic sign of a CGW problem. If a diagnostic tool cannot communicate with the CGW, it’s unable to access any other modules on the network.
- Intermittent Communication Loss: Communication may be possible sometimes but lost at other times. This can be due to loose connections, faulty wiring, or an overheating CGW.
- Module Not Responding Errors: When attempting to access specific modules (e.g., ECU, ABS) with a diagnostic tool, you may receive “Module Not Responding” or similar errors.
2.2 Warning Lights and Error Messages
- Multiple Warning Lights Illuminated: A faulty CGW can trigger a cascade of warning lights on the instrument cluster, including ABS, ESP, SRS (airbag), engine check light, and more. The specific lights will vary depending on the vehicle model and the severity of the CGW failure.
- Erroneous Error Messages: The instrument cluster or infotainment screen might display incorrect or nonsensical error messages. These messages may not accurately reflect the actual problem in the system.
- “Christmas Tree” Effect: A term used to describe a situation where numerous warning lights illuminate simultaneously, often flashing or flickering.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): While a CEL can indicate many issues, a CGW problem can cause it to illuminate, often accompanied by other symptoms.
2.3 Electrical System Malfunctions
- Battery Drain: A malfunctioning CGW can remain active even when the car is turned off, leading to excessive battery drain.
- Random Electrical Issues: Systems may work intermittently or fail without apparent reason. This can include problems with power windows, door locks, lights, wipers, and other electrical components.
- Engine Stalling: In some cases, a faulty CGW can cause the engine to stall unexpectedly, especially while driving. This is a serious safety concern.
- Starting Problems: The car may be difficult to start or fail to start altogether.
- Loss of Keyless Entry Functionality: The keyless entry system may stop working, requiring the use of the physical key to unlock the car.
- Alarm System Issues: The alarm system may trigger randomly or fail to disarm properly.
2.4 Comfort and Convenience System Problems
- Infotainment System Issues: The radio, navigation system, or other infotainment features may malfunction or fail completely.
- Climate Control Problems: The air conditioning or heating system may not work correctly.
- Seat Malfunctions: Power seats may not adjust properly, or heated/cooled seats may fail to operate.
- Sunroof Problems: The sunroof may not open or close correctly.
- Wiper Malfunctions: Wipers may not function, function intermittently, or fail to turn off.
2.5 Transmission and Engine Issues
- Limp Mode: The car may enter limp mode, restricting engine power and speed to protect the drivetrain.
- Transmission Problems: Shifting problems, rough shifting, or failure to shift can occur.
- Engine Performance Issues: Reduced engine power, poor fuel economy, or misfires can sometimes be linked to a CGW problem.
2.6 Other Potential Symptoms
- Incorrect Mileage Display: The displayed mileage may be incorrect or reset to zero.
- VIN Mismatch: The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) stored in the CGW may be incorrect, causing issues with diagnostics and programming.
- Component Protection Issues: Component protection, a security feature that prevents the use of stolen parts, may be activated incorrectly.
2.7 Diagnosing Gateway Issues
Diagnosing a CGW problem requires a systematic approach:
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool to scan all modules for DTCs. Pay close attention to codes related to communication errors or CGW-specific faults.
- Check Power and Ground Connections: Ensure that the CGW has proper power and ground connections. Check for corrosion or loose connections.
- Inspect Wiring Harness: Carefully inspect the wiring harness connected to the CGW for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, broken connectors, or water intrusion.
- Test Communication Bus: Use an oscilloscope or a specialized communication bus tester to verify the integrity of the CAN bus network.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Water damage is a common cause of CGW failure, especially in vehicles where the CGW is located in the trunk.
- Consult a Mercedes-Benz Specialist: If you are not comfortable performing these diagnostic steps, it’s best to consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
Remember, a malfunctioning CGW can have far-reaching effects on your Mercedes-Benz. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure safe operation. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers resources and tools to help you navigate these complex diagnostic challenges.
3. How to Diagnose a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) Issue?
Diagnosing a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) issue requires a systematic approach, combining visual inspection, diagnostic tools, and a solid understanding of Mercedes-Benz electrical systems. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
3.1 Preliminary Steps
-
Gather Information:
- Vehicle Information: Note the year, model, and VIN of the Mercedes-Benz.
- Symptoms: Document all the symptoms the vehicle is exhibiting. When did they start? Are they intermittent or constant?
-
Visual Inspection:
- CGW Location: Identify the location of the CGW in your specific Mercedes-Benz model. Common locations include under the dashboard, in the center console, or in the trunk.
- Physical Damage: Check the CGW for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, water stains, or corrosion.
- Wiring and Connectors: Inspect the wiring harness and connectors connected to the CGW. Look for frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion.
3.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
-
Connect Diagnostic Tool:
- Use a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool. Tools like the Autel MaxiSYS, iCarsoft MB II, or the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system (XENTRY/DAS) are recommended. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can assist you in selecting the right tool for your needs.
- Connect the tool to the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
-
Scan for DTCs:
- Perform a full system scan to retrieve DTCs from all modules.
- Pay close attention to codes related to:
- Communication errors (e.g., “No Communication,” “CAN Bus Error”)
- CGW-specific faults (e.g., “CGW Internal Fault”)
- Modules that are not responding
-
Interpret DTCs:
- Research the meaning of each DTC. Mercedes-Benz specific DTCs can be found in repair manuals or online databases.
- Note that some DTCs may be a consequence of a CGW failure, rather than the root cause.
3.3 Communication Bus Testing
-
Identify CAN Bus Wires:
- Locate the CAN High and CAN Low wires connected to the CGW. These are typically twisted pair wires. Refer to a wiring diagram for your specific model.
-
CAN Bus Voltage Measurement:
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage between CAN High and CAN Low.
- With the ignition on, you should typically see a voltage difference of around 2.5V. A significantly different voltage can indicate a problem with the CAN bus.
-
Oscilloscope Testing (Advanced):
- An oscilloscope can provide a more detailed view of the CAN bus signals.
- Connect the oscilloscope to the CAN High and CAN Low wires.
- Observe the waveform. A healthy CAN bus signal should have a distinct pattern with clear high and low states. Distorted or missing signals indicate a problem.
3.4 Power and Ground Testing
-
Identify Power and Ground Wires:
- Locate the power and ground wires connected to the CGW. Refer to a wiring diagram.
-
Voltage Testing:
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the power wire with the ignition on. You should see battery voltage (approximately 12V).
-
Ground Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check the resistance between the ground wire and a known good ground point on the vehicle chassis. The resistance should be very low (close to 0 ohms).
-
Load Testing:
- A voltage drop test can be performed to check the integrity of the power and ground circuits under load.
3.5 Component Testing (If Applicable)
-
CGW Relay (If Equipped):
- Some Mercedes-Benz models may have a relay that provides power to the CGW.
- Check the relay for proper operation. You can test the relay using a multimeter or a relay tester.
3.6 Advanced Diagnostics
-
Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis (XENTRY/DAS):
- This is the factory diagnostic system used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships.
- It provides advanced diagnostic capabilities, including:
- CGW-specific diagnostic tests
- Software updates and programming
- Guided fault finding
-
Data Logging:
- Some diagnostic tools allow you to log data from various sensors and modules.
- This can be helpful in identifying intermittent problems or unusual patterns.
-
Wiring Diagrams:
- A wiring diagram is essential for tracing circuits and identifying potential problems.
- You can find wiring diagrams in repair manuals or online databases.
3.7 Common Causes of CGW Failure
- Water Damage: This is a common problem, especially in vehicles where the CGW is located in the trunk. Check for blocked drain holes that can cause water to accumulate.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on connectors or wiring can cause communication problems.
- Voltage Spikes: Voltage spikes can damage the CGW.
- Software Glitches: Software glitches can sometimes cause the CGW to malfunction.
- Internal Failure: In some cases, the CGW may fail internally due to component failure.
3.8 Important Considerations
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job.
- Documentation: Keep a record of all tests performed and results obtained.
- Professional Help: If you are not comfortable performing these diagnostic steps, it’s best to consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
- Software Updates: Before replacing the CGW, check if a software update is available. A software update may resolve the problem.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) issues and determine the appropriate course of action. Remember that MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the tools and knowledge you need to tackle these challenges.
4. What Are the Potential Solutions for a Faulty Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
Once you’ve diagnosed a faulty Gateway (CGW/ZGW) in your Mercedes-Benz, it’s time to explore the potential solutions. The appropriate solution will depend on the nature and severity of the problem. Here’s a breakdown of common fixes:
4.1 Addressing Minor Issues
-
Loose Connections:
- Solution: Carefully inspect all connectors connected to the CGW. Disconnect and reconnect them to ensure a secure connection. Use electrical contact cleaner to remove any corrosion.
-
Corroded Terminals:
- Solution: Clean corroded terminals with a wire brush or terminal cleaning tool. Apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
-
Wiring Problems:
- Solution: Repair or replace any damaged wiring. Use proper splicing techniques and ensure that the wiring is properly insulated.
-
Software Glitches:
- Solution: Check for available software updates for the CGW. Use a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool to perform the update. This may resolve minor software glitches.
4.2 Gateway Module Replacement
-
When to Replace: If the CGW has suffered severe damage (e.g., water damage, internal failure) or if other solutions have failed, replacement is often necessary.
-
New vs. Used:
- New CGW: Purchasing a new CGW from a Mercedes-Benz dealer ensures that you get a genuine part that is guaranteed to work. However, it’s the most expensive option.
- Used CGW: A used CGW can be a more affordable option, but it’s important to source it from a reputable supplier. Ensure that the used CGW is compatible with your vehicle’s year, model, and VIN.
-
Coding and Programming:
- Required: A new or used CGW will typically need to be coded and programmed to your vehicle. This involves using a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool to:
- Enter the vehicle’s VIN into the CGW.
- Configure the CGW to match the vehicle’s options and equipment.
- Program the CGW with the latest software.
- Online vs. Offline Coding:
- Online Coding: This requires a connection to the Mercedes-Benz online server. It’s the most secure and reliable method, but it typically requires a subscription.
- Offline Coding: This can be done without an internet connection, but it may not be possible for all vehicles or all functions.
- Specialized Tools: Coding and programming the CGW requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s often best to have this done by a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician or a shop specializing in Mercedes-Benz electronics.
- Required: A new or used CGW will typically need to be coded and programmed to your vehicle. This involves using a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool to:
4.3 Cloning the Gateway Module
-
What is Cloning? Cloning involves transferring the data from the old CGW to the replacement CGW. This can be a faster and easier alternative to coding and programming, especially when using a used CGW.
-
How it Works: Specialized tools are used to read the data from the old CGW and write it to the replacement CGW. This transfers the VIN, configuration data, and other important information.
-
Advantages:
- Faster than coding and programming.
- May not require an online connection.
- Can be used with used CGWs.
-
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized tools.
- May not be possible if the old CGW is severely damaged.
- Potential legal and ethical concerns if the data is not properly handled.
4.4 Addressing Water Damage
- Identify the Source of the Leak: Locate the source of the water leak and repair it to prevent future damage. Common sources include blocked drain holes in the trunk, faulty seals, or damaged weather stripping.
- Dry the Affected Area: Thoroughly dry the affected area to prevent corrosion. Use a shop vacuum to remove any standing water.
- Clean Corroded Components: Clean any corroded components with a wire brush or terminal cleaning tool.
- Apply Corrosion Protection: Apply a corrosion protection spray to prevent future corrosion.
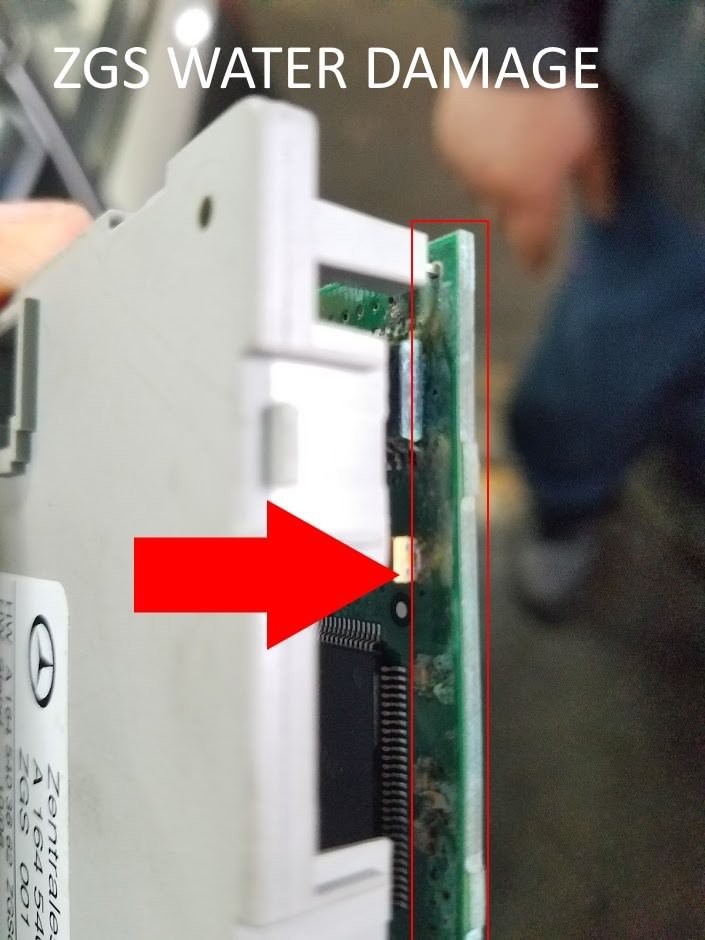 Mercedes Benz Central Gateway Water Damage, water damage to the central gateway module
Mercedes Benz Central Gateway Water Damage, water damage to the central gateway module
4.5 Important Considerations
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job.
- Documentation: Keep a record of all tests performed and results obtained.
- Professional Help: If you are not comfortable performing these repairs, it’s best to consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis (XENTRY/DAS): This is the factory diagnostic system used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships and is highly recommended for any coding, programming, or software updates.
4.6 After the Repair
- Clear DTCs: After completing the repair, clear all DTCs from all modules.
- Test the System: Thoroughly test all systems to ensure that they are functioning properly.
- Monitor for Recurrence: Keep an eye out for any recurrence of the symptoms.
By following these steps, you can effectively address a faulty Gateway (CGW/ZGW) in your Mercedes-Benz. Remember that MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the resources and support you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
5. Can I Replace the Gateway (CGW/ZGW) Myself, or Do I Need a Professional?
Deciding whether to replace the Gateway (CGW/ZGW) in your Mercedes-Benz yourself or seek professional help is a crucial decision. It depends on your technical skills, experience, available tools, and comfort level. Here’s a breakdown to help you make the right choice:
5.1 Factors to Consider
-
Technical Skills and Experience:
- DIY (Do-It-Yourself): If you have experience working on automotive electrical systems, are comfortable using diagnostic tools, and understand basic coding/programming concepts, you might consider replacing the CGW yourself.
- Professional: If you have limited experience with automotive electrical systems or are unfamiliar with diagnostic tools and coding/programming, it’s best to seek professional help.
-
Diagnostic Tools:
- DIY: You’ll need a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool that can read DTCs, access live data, and potentially perform coding/programming functions.
- Professional: Professional technicians have access to advanced diagnostic tools, including the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system (XENTRY/DAS), which provides comprehensive diagnostic and coding capabilities.
-
Coding and Programming Requirements:
- DIY: Replacing the CGW typically requires coding and programming to integrate it with your vehicle’s specific configuration. This can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and tools.
- Professional: Professional technicians have the expertise and tools to perform coding and programming accurately and efficiently.
-
Access to Information:
- DIY: You’ll need access to wiring diagrams, repair manuals, and technical information specific to your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Professional: Professional technicians have access to comprehensive databases and technical resources.
-
Risk Tolerance:
- DIY: There’s a risk of damaging the new CGW or other vehicle systems if the replacement is not done correctly.
- Professional: Professional technicians are trained to minimize the risk of damage.
-
Cost:
- DIY: Replacing the CGW yourself can save you money on labor costs, but you’ll need to factor in the cost of the diagnostic tool and the CGW itself.
- Professional: Professional labor costs can be significant, but you’ll be paying for expertise and peace of mind.
5.2 Steps Involved in DIY Replacement
If you decide to replace the CGW yourself, here’s a general outline of the steps involved:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on electrical components.
- Locate the CGW: Identify the location of the CGW in your specific Mercedes-Benz model.
- Remove the Old CGW: Carefully disconnect the wiring harness and remove the old CGW.
- Install the New CGW: Connect the wiring harness to the new CGW and install it in its location.
- Connect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Coding and Programming: Use a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool to code and program the new CGW to your vehicle.
- Clear DTCs: Clear all DTCs from all modules.
- Test the System: Thoroughly test all systems to ensure that they are functioning properly.
5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
- Lack of Experience: If you have limited experience with automotive electrical systems or are unfamiliar with diagnostic tools and coding/programming.
- Complex Coding Requirements: If the CGW requires complex coding or programming that you are not comfortable performing.
- Uncertainty About the Diagnosis: If you are not sure that the CGW is the actual problem.
- Lack of Tools: If you don’t have access to the necessary diagnostic tools or coding/programming equipment.
- Time Constraints: If you don’t have the time to dedicate to the replacement process.
5.4 Benefits of Professional Replacement
- Expertise: Professional technicians have the expertise and experience to diagnose and replace the CGW correctly.
- Proper Tools: They have access to advanced diagnostic tools and coding/programming equipment.
- Warranty: Professional repairs typically come with a warranty, providing you with peace of mind.
- Reduced Risk: Professional technicians are trained to minimize the risk of damage to your vehicle.
- Time Savings: Professional replacement can save you time and hassle.
5.5 Recommendations
- Consult a Mercedes-Benz Specialist: If you are unsure whether to replace the CGW yourself, consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician or a shop specializing in Mercedes-Benz electronics.
- Get a Quote: Get a quote from a professional repair shop to compare the cost with the DIY option.
- Weigh the Pros and Cons: Carefully weigh the pros and cons of DIY replacement versus professional replacement before making a decision.
In conclusion, replacing the Gateway (CGW/ZGW) in your Mercedes-Benz can be a DIY project if you have the necessary skills, tools, and experience. However, if you are unsure or uncomfortable with any aspect of the replacement process, it’s best to seek professional help. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you assess your options and connect you with qualified professionals in your area.
6. What Is the Cost of Replacing a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
The cost of replacing a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW) can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors will help you budget effectively and make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of the costs involved:
6.1 Factors Affecting the Cost
-
New vs. Used CGW:
- New CGW: A new CGW purchased from a Mercedes-Benz dealer is the most expensive option. The price can range from $800 to $2000 or more, depending on the model and year of your vehicle.
- Used CGW: A used CGW can be significantly cheaper, ranging from $200 to $800. However, it’s important to source it from a reputable supplier and ensure that it’s compatible with your vehicle.
-
Labor Costs:
- Professional Installation: Labor costs can vary depending on the shop’s hourly rate and the complexity of the job. Expect to pay between $200 and $800 for labor.
- DIY Installation: If you replace the CGW yourself, you’ll save on labor costs, but you’ll need to factor in the cost of any tools or equipment you need to purchase.
-
Coding and Programming:
- Required: Coding and programming the new CGW to your vehicle is essential. This can add $100 to $500 to the total cost.
- Dealer vs. Independent Shop: Mercedes-Benz dealerships typically charge more for coding and programming than independent shops specializing in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
-
Diagnostic Fees:
- Initial Diagnosis: If you take your car to a shop for diagnosis, you’ll likely be charged a diagnostic fee, typically ranging from $100 to $200.
- Post-Installation Testing: Some shops may charge an additional fee for testing the system after the CGW has been replaced.
-
Additional Parts:
- Wiring or Connectors: In some cases, you may need to replace damaged wiring or connectors, which will add to the overall cost.
-
Location:
- Geographic Location: Labor rates can vary depending on your geographic location. Expect to pay more in areas with a higher cost of living.
6.2 Estimated Cost Range
Based on these factors, here’s an estimated cost range for replacing a Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW):
- DIY Replacement (Used CGW): $300 – $1000 (including the cost of the used CGW, diagnostic tool, and coding/programming services if needed)
- Professional Replacement (Used CGW): $500 – $1500 (including the cost of the used CGW, labor, and coding/programming)
- Professional Replacement (New CGW): $1000 – $3000 (including the cost of the new CGW, labor, and coding/programming)
6.3 Getting an Accurate Quote
To get an accurate quote for replacing your Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW), follow these steps:
- Gather Vehicle Information: Provide the year, model, and VIN of your vehicle to the repair shop.
- Describe the Symptoms: Clearly describe the symptoms your vehicle is exhibiting.
- Ask for a Detailed Estimate: Ask for a detailed estimate that includes the cost of the CGW, labor, coding/programming, and any other potential charges.
- Inquire About Warranty: Ask about the warranty on the CGW and the labor.
- Compare Quotes: Get quotes from multiple repair shops to compare prices.
6.4 Cost-Saving Tips
- Consider a Used CGW: A used CGW can save you a significant amount of money.
- Shop Around for Labor: Get quotes from multiple repair shops to find the best price.
- Ask About Discounts: Ask if the shop offers any discounts for AAA members, seniors, or military personnel.
- DIY Some of the Work: If you’re comfortable, you can do some of the preliminary work yourself, such as removing the old CGW, to save on labor costs.
6.5 Long-Term Cost Considerations
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular maintenance can help prevent CGW failure. Check for water leaks and corrosion regularly.
- Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts to ensure long-term reliability.
By understanding the costs involved and taking steps to minimize them, you can effectively manage the expense of replacing your Mercedes-Benz Gateway (CGW/ZGW). Remember that MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the information and resources you need to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair.
7. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Dealing With a Mercedes Gateway (CGW/ZGW)?
Dealing with a Mercedes Gateway (CGW/ZGW) can be complex, and it’s easy to make mistakes that can lead to further problems or unnecessary expenses. Here’s a guide to common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
7.1 Diagnostic Mistakes
-
Misinterpreting DTCs:
- Mistake: Relying solely on DTCs without further investigation. DTCs can be misleading and may not always point to the root cause of the problem.
- Solution: Use DTCs as a starting point, but perform thorough testing to confirm the diagnosis. Check wiring, connections, and other components.
-
Failing to Perform a Full System Scan:
- Mistake: Only scanning the modules that are exhibiting symptoms.
- Solution: Perform a full system scan to identify any hidden DTCs that may be related to the problem.
-
Ignoring Communication Errors:
- Mistake: Dismissing communication errors as minor issues.
- Solution: Communication errors can be a sign of a CGW problem. Investigate these errors thoroughly.
-
Not Checking for Water Damage:
- Mistake: Overlooking the possibility of water damage, especially in vehicles where the CGW is located in the trunk.
- Solution: Carefully inspect the CGW and surrounding area for signs of water damage.
-
Assuming the CGW is Faulty:
- Mistake: Jumping to the conclusion that the CGW is faulty without proper testing.
- Solution: Perform thorough testing to rule out other potential causes, such as wiring problems or faulty sensors.
7.2 Replacement Mistakes
-
Buying the Wrong CGW:
- Mistake: Purchasing a CGW that is not compatible with your vehicle’s year, model, and VIN.
- Solution: Verify the part number of the CGW before purchasing it. Consult a Mercedes-Benz dealer or a reputable online parts supplier.
-
Not Coding/Programming the New CGW:
- Mistake: Installing the new CGW without coding and programming it to your vehicle.
- Solution: Coding and programming is essential for integrating the new CGW with your vehicle’s specific configuration.
-
Improper Installation:
- Mistake: Damaging the CGW or wiring during installation.
- Solution: Follow the installation instructions carefully. Use proper tools and techniques.
-
Using Incorrect Tools:
- Mistake: Using generic diagnostic tools that are not compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Solution: Use a Mercedes-Benz compatible diagnostic tool, such as the Autel MaxiSYS, iCarsoft MB II, or the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system (XENTRY/DAS).
-
Neglecting Wiring and Connections:
- Mistake: Only replacing the CGW without addressing any underlying wiring or connection issues.
- Solution: Inspect wiring and connections for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace as needed.
7.3 Coding and Programming Mistakes
-
Using Incorrect Software:
- Mistake: Using outdated or incompatible software for coding and programming.
- Solution: Use the latest version of the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system (XENTRY/DAS) or a comparable tool.
-
Interrupting the Coding Process:
- Mistake: Interrupting the coding process, which can damage the CGW.
- Solution: Ensure that the battery is fully charged and that there are no interruptions during the coding process.
-
Entering Incorrect Data:
- Mistake: Entering incorrect data during coding, such as the wrong VIN or configuration settings.
- Solution: Double-check all data before entering it.
-
Failing to Back Up Data:
- Mistake: Failing to back up the original CGW data before coding.
- Solution: Back up the original CGW data before coding, if possible.
7.4 General Mistakes
-
Ignoring Warning Signs:
- Mistake: Ignoring warning signs, such as multiple warning lights or communication errors.
- Solution: Address any warning signs promptly.
-
Delaying Repairs:
- Mistake: Delaying repairs, which can lead to further damage.
- Solution: Address any CGW issues promptly to prevent further damage.
-
Not Seeking Professional Help:
- Mistake: Attempting to diagnose or repair the CGW without the necessary skills, tools, or knowledge.
- Solution: Seek professional help from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
-
Using Aftermarket Parts:
- Mistake: Using low-quality aftermarket parts that are not reliable.
- Solution: Use genuine Mercedes-Benz parts or reputable aftermarket brands.
-
Neglecting Preventative Maintenance:
- Mistake: Neglecting preventative maintenance, such as checking for water leaks and corrosion.
- Solution: Perform regular maintenance to prevent CGW failure.
-
Not Documenting the Process:
- Mistake: Not documenting the diagnostic and repair process.