Can DTCs Be Generated By Failures In Cloud-connected Vehicle Services? Yes, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) can indeed be triggered by failures within cloud-connected vehicle services, impacting your Mercedes-Benz. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert insights and tools to diagnose and address these issues effectively, ensuring seamless vehicle operation. Understanding these codes, their causes, and the appropriate solutions will help you maintain your vehicle’s peak performance, incorporating elements of vehicle diagnostics, remote diagnostics, and cloud connectivity issues.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 1.1. The Evolution of DTCs
- 1.2. Standard Exchange Formats for DTCs
- 2. How DTCs are Generated
- 2.1. Application Software with Diagnostic Functions (Monitors)
- 2.2. Diagnostic Events and the Diagnostic Manager (DM)
- 2.3. Debouncing of Events
- 2.4. Function Deactivation and the Function Inhibition Manager (FIM)
- 2.5. The Operation Cycle
- 3. The Error Memory and Extended Data
- 3.1. DTC Snapshot Data (Freeze Frames)
- 3.2. Extended Data
- 4. Cloud-Connected Vehicle Services and DTCs
- 4.1. How Cloud Connectivity Impacts DTC Generation
- 4.2. Examples of Cloud-Related DTCs
- 4.3. Diagnosing Cloud-Related DTCs
- 5. Tools and Technologies for Diagnosing Mercedes-Benz DTCs
- 5.1. Diagnostic Tools
- 5.2. Software and Applications
- 5.3. Telematics and Remote Diagnostics
- 6. Preventative Measures and Maintenance
- 6.1. Regular Software Updates
- 6.2. Monitor Cloud Service Status
- 6.3. Check Connectivity
- 6.4. Security Best Practices
- 6.5. Regular Maintenance
- 7. Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- 7.1. Case Study 1: Loss of Connectivity
- 7.2. Case Study 2: Software Update Failure
- 7.3. Case Study 3: Security Breach
- 8. Addressing Customer Challenges
- 8.1. Difficulty in Finding Suitable Diagnostic Tools
- 8.2. Uncertainty About Unlocking Hidden Features
- 8.3. Need for Simple Repair Guides and Maintenance Tips
- 8.4. Concerns About High Repair Costs at Dealerships
- 9. Services Offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 9.1. Detailed Information on Diagnostic Tools
- 9.2. Step-by-Step Guides for Unlocking Hidden Features
- 9.3. Simple Repair Guides and Maintenance Tips
- 9.4. Expert Advice and Support
- 9.5. Remote Diagnostic Services
- 9.6. Software Updates and Programming
- 10. Call to Action
- 11. FAQ: Cloud Connected Vehicle Services
- 11.1. What Diagnostic Tool is Best for My Mercedes-Benz?
- 11.2. How Can I Unlock Hidden Features on My Mercedes-Benz?
- 11.3. How Often Should I Perform Maintenance on My Mercedes-Benz?
- 11.4. Can Cloud Connectivity Issues Really Trigger DTCs?
- 11.5. What are the Benefits of Remote Diagnostics?
- 11.6. How Can I Protect My Vehicle from Security Breaches?
- 11.7. What Should I Do if I Receive a DTC Related to Cloud Connectivity?
- 11.8. Are OTA Software Updates Safe?
- 11.9. How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help Me?
- 11.10. Where Can I Find Reliable Independent Repair Shops for My Mercedes-Benz?
- 12. Conclusion: Stay Informed and Proactive
1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes used in-vehicle diagnostics to identify potential issues within a vehicle’s systems. These codes are standardized across the automotive industry to help technicians and vehicle owners diagnose and repair problems efficiently. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), DTCs are an integral part of the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system, which monitors the performance of various components in a vehicle. DTCs are generated by the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) or other control modules when they detect a malfunction or a reading outside the expected parameters.
1.1. The Evolution of DTCs
Originally, DTCs relied on flashing codes from control units, which were manually counted to identify issues. However, with the increasing complexity of vehicle electronics, these rudimentary methods became insufficient. This led to the development of 2-byte DTCs (mandated by OBD regulations) and 3-byte DTCs (standardized by the Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS) protocol), providing more detailed and precise diagnostic information.
1.2. Standard Exchange Formats for DTCs
To streamline diagnostics and ensure compatibility, standard exchange formats like DEXT (used in AUTOSAR for embedded electronics) and ODX (used by ASAM for off-board diagnostics) have been developed. These formats facilitate cooperation between vehicle manufacturers and their suppliers by providing a common language for exchanging diagnostic data.
2. How DTCs are Generated
The generation of DTCs involves several key steps, from initial detection to final storage in the vehicle’s memory. Understanding this process is crucial for accurately diagnosing and resolving issues.
2.1. Application Software with Diagnostic Functions (Monitors)
Application software, often referred to as monitors, continuously checks vehicle signals against predefined limits. When a signal falls outside these limits, the monitor sends an event notification to the Diagnostic Manager (DM). For example, a battery monitoring system might have limits set at 11.2V and 15.2V. If the battery voltage drops below or exceeds these values, the monitor triggers an event.
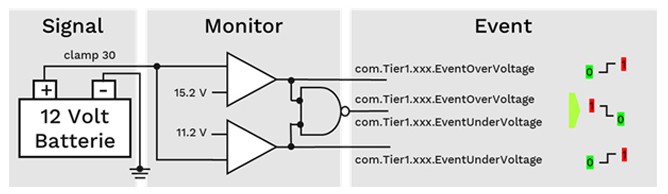 Battery monitoring with two events
Battery monitoring with two events
2.2. Diagnostic Events and the Diagnostic Manager (DM)
Diagnostic events are linked to specific DTCs and sent to the DM via middleware. The DM is responsible for processing these events and determining whether to store a DTC in the vehicle’s memory. Typically, the vehicle manufacturer determines which DTCs are uniformly used across its vehicles. Multiple events can be associated with a single DTC. For instance, both “EventOverVoltage” and “EventUnderVoltage” could trigger the same DTC, such as “PowerSupply”.
2.3. Debouncing of Events
To prevent minor, transient faults from triggering DTCs, a process called debouncing is used. Debouncing ensures that a fault must persist for a certain period or occur a certain number of times before a DTC is generated. There are three primary debouncing strategies:
- Time-based debouncing: An error must be present for a specific duration to be considered valid and trigger a DTC.
- Counter-based debouncing: An error counter increments or decrements based on the severity and frequency of the fault, triggering a DTC when the counter reaches a certain threshold.
- Internal debouncing: The monitor itself filters out transient faults, delivering only debounced events to the DM.
2.4. Function Deactivation and the Function Inhibition Manager (FIM)
When a DTC is confirmed, the vehicle must react appropriately to the fault. Vehicle manufacturers analyze potential faults and their effects using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) during vehicle development. The FIM then implements the necessary reactions in the control unit, such as deactivating certain functions to prevent further damage or ensure safety.
2.5. The Operation Cycle
The operation cycle is a defined sequence of events that governs the creation and clearing of DTCs. This cycle ensures that DTCs are generated and cleared under appropriate conditions, maintaining the accuracy of the diagnostic information. The dynamic status of each DTC is defined in the ISO 14229-1:2013 (UDS standard), with bits 0 to 6 of the StatusOfDTC indicating the DTC’s current stage in its lifecycle.
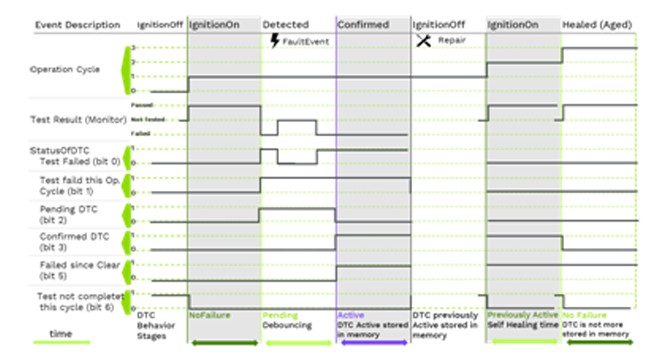 Dynamic behavior of DTC in the vehicle
Dynamic behavior of DTC in the vehicle
3. The Error Memory and Extended Data
For complex errors, a simple error code and status are insufficient. Additional information about the conditions under which the error occurred is needed for a more precise analysis.
3.1. DTC Snapshot Data (Freeze Frames)
Snapshot data, also known as freeze frames, captures the values of relevant parameters at the moment a DTC is triggered. This data can include speed, temperature, velocity, and other internal information, providing a comprehensive view of the conditions leading to the fault.
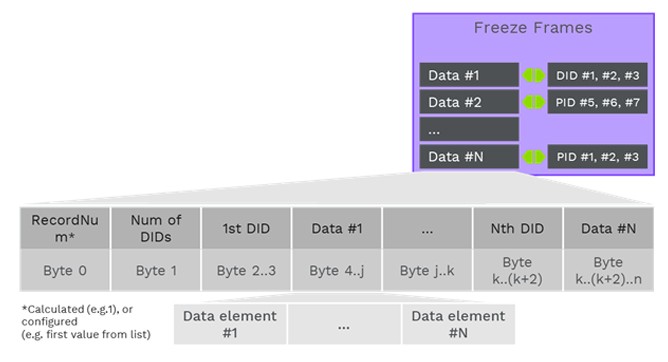 Details of DTC Snapshot Data
Details of DTC Snapshot Data
3.2. Extended Data
Extended data blocks contain additional information about a DTC, such as cycle counters, aging counters, the time of the last occurrence, and dynamic data from algorithms not included in the freeze frame data. Each extended data record is identified by a 1-byte record number, specifying the data structure.
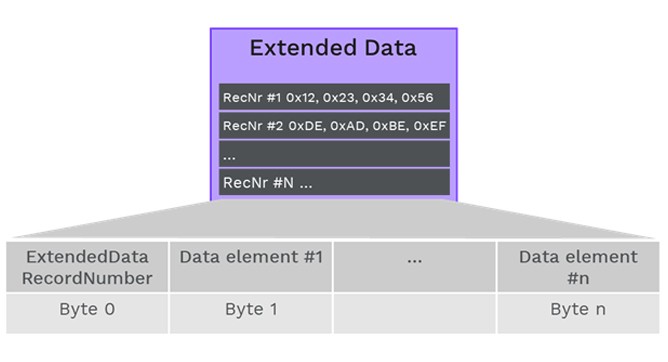 Details of DTC Extended Data
Details of DTC Extended Data
4. Cloud-Connected Vehicle Services and DTCs
With the rise of cloud-connected vehicle services, new possibilities and challenges have emerged in vehicle diagnostics. Cloud connectivity enables real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and over-the-air (OTA) updates, but it also introduces new potential failure points that can trigger DTCs.
4.1. How Cloud Connectivity Impacts DTC Generation
Cloud-connected vehicle services rely on a constant exchange of data between the vehicle and remote servers. Failures in this communication, or within the cloud services themselves, can lead to various issues, such as:
- Loss of Connectivity: If the vehicle loses its connection to the cloud, certain functions that depend on cloud services may fail, triggering DTCs related to communication errors or system malfunctions.
- Data Corruption: Errors in data transmission or processing can lead to corrupted data being sent to the vehicle, causing malfunctions and DTCs.
- Software Glitches: Issues within the cloud services, such as software bugs or server outages, can disrupt vehicle functions and trigger DTCs.
- Security Breaches: Unauthorized access to the vehicle’s systems through cloud connections can result in malicious actions that trigger DTCs.
4.2. Examples of Cloud-Related DTCs
Several types of DTCs can be directly related to failures in cloud-connected vehicle services. These include:
- Communication Errors: Codes indicating a loss of communication between the vehicle and the cloud, or between different modules within the vehicle that rely on cloud services.
- Software Update Failures: Codes triggered by failed or incomplete OTA software updates.
- Remote Diagnostics Issues: Codes indicating problems with remote diagnostic services, such as the inability to retrieve data or perform remote commands.
- Security-Related DTCs: Codes triggered by unauthorized access attempts or detected security breaches.
4.3. Diagnosing Cloud-Related DTCs
Diagnosing DTCs related to cloud-connected services requires a systematic approach. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we recommend the following steps:
- Initial Scan: Use a diagnostic tool to scan the vehicle for all stored DTCs. Note down the codes and any related freeze frame data.
- Research: Look up the DTCs in a comprehensive database or consult with a professional to understand their potential causes.
- Check Connectivity: Verify that the vehicle has a stable connection to the cloud. Check the vehicle’s network settings and ensure that the mobile data connection is active.
- Cloud Service Status: Check the status of the cloud services provided by the vehicle manufacturer. Look for any reported outages or known issues that might be affecting the vehicle.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the vehicle’s software is up to date. Install any pending OTA updates to address potential software glitches.
- Data Validation: If possible, validate the data being received from the cloud. Check for any inconsistencies or errors that might be causing malfunctions.
- Professional Assistance: If the issue persists, seek professional assistance from a qualified technician who specializes in Mercedes-Benz vehicles and cloud-connected services.
5. Tools and Technologies for Diagnosing Mercedes-Benz DTCs
Diagnosing DTCs in Mercedes-Benz vehicles requires specialized tools and technologies. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of diagnostic solutions tailored to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
5.1. Diagnostic Tools
- OBD-II Scanners: Basic OBD-II scanners can read and clear DTCs from the vehicle’s ECU. These tools are suitable for simple diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Advanced Diagnostic Systems: Advanced diagnostic systems, such as the Mercedes-Benz XENTRY Diagnosis system, provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including detailed DTC analysis, live data streaming, and component testing.
- Handheld Diagnostic Devices: Portable diagnostic devices offer a convenient way to diagnose DTCs on the go. These devices often include advanced features such as wireless connectivity and cloud-based data analysis.
5.2. Software and Applications
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Software: Mercedes-Benz provides proprietary diagnostic software that offers in-depth analysis of DTCs and vehicle systems. This software is essential for performing advanced diagnostics and repairs.
- Third-Party Diagnostic Apps: Several third-party diagnostic apps are available for smartphones and tablets. These apps can connect to the vehicle via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi and provide access to DTC information and diagnostic functions.
5.3. Telematics and Remote Diagnostics
- Telematics Systems: Telematics systems, such as Mercedes me connect, provide real-time vehicle data and remote diagnostic capabilities. These systems can alert the driver to potential issues and provide diagnostic information to the dealer or service provider.
- Remote Diagnostic Services: Remote diagnostic services allow technicians to remotely access the vehicle’s systems and perform diagnostics from a remote location. This can be useful for diagnosing issues that are difficult to replicate in a workshop environment.
6. Preventative Measures and Maintenance
Preventing DTCs related to cloud-connected vehicle services involves proactive maintenance and monitoring. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we recommend the following preventative measures:
6.1. Regular Software Updates
Ensure that your vehicle’s software is always up to date. Install OTA updates as soon as they become available to address potential software glitches and security vulnerabilities.
6.2. Monitor Cloud Service Status
Keep an eye on the status of the cloud services provided by Mercedes-Benz. Check for any reported outages or known issues that might be affecting your vehicle.
6.3. Check Connectivity
Regularly check your vehicle’s connectivity settings and ensure that the mobile data connection is stable. A weak or intermittent connection can lead to communication errors and DTCs.
6.4. Security Best Practices
Follow security best practices to protect your vehicle from unauthorized access. Use strong passwords for your Mercedes me connect account and be cautious about connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
6.5. Regular Maintenance
Perform regular maintenance on your vehicle to ensure that all systems are functioning properly. This includes checking the battery, electrical connections, and other components that can affect cloud connectivity.
7. Case Studies and Real-World Examples
To illustrate how failures in cloud-connected vehicle services can generate DTCs, let’s look at a few real-world examples:
7.1. Case Study 1: Loss of Connectivity
A Mercedes-Benz owner reported receiving a DTC related to the navigation system. After troubleshooting, it was discovered that the vehicle had lost its connection to the cloud, preventing the navigation system from accessing real-time traffic data. Once the connection was restored, the DTC cleared, and the navigation system functioned normally.
7.2. Case Study 2: Software Update Failure
Another Mercedes-Benz owner experienced a DTC related to the engine control unit after attempting an OTA software update. The update failed midway, leaving the ECU in an unstable state. A technician had to manually reflash the ECU with the correct software version to resolve the issue.
7.3. Case Study 3: Security Breach
In a more serious case, a Mercedes-Benz vehicle was targeted by a security breach. Hackers gained access to the vehicle’s systems through a vulnerability in the cloud-connected services and were able to remotely control certain functions. The vehicle’s security system detected the intrusion and triggered a DTC, alerting the owner and the authorities.
8. Addressing Customer Challenges
Understanding the challenges faced by Mercedes-Benz owners is crucial for providing effective solutions. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we address the following common challenges:
8.1. Difficulty in Finding Suitable Diagnostic Tools
Many Mercedes-Benz owners struggle to find the right diagnostic tools for their vehicles. We offer detailed information about various diagnostic tools, including their features, capabilities, and compatibility with different Mercedes-Benz models.
8.2. Uncertainty About Unlocking Hidden Features
Unlocking hidden features in Mercedes-Benz vehicles can be a complex process. We provide step-by-step guides and expert advice on how to safely and effectively unlock these features.
8.3. Need for Simple Repair Guides and Maintenance Tips
Many Mercedes-Benz owners prefer to perform simple repairs and maintenance tasks themselves. We offer easy-to-follow repair guides and maintenance tips to help owners keep their vehicles in top condition.
8.4. Concerns About High Repair Costs at Dealerships
Repair costs at authorized dealerships can be a concern for many Mercedes-Benz owners. We offer cost-effective diagnostic and repair solutions, as well as guidance on how to find reliable independent repair shops.
9. Services Offered by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide a comprehensive range of services to help you diagnose, repair, and maintain your Mercedes-Benz vehicle:
9.1. Detailed Information on Diagnostic Tools
We offer detailed information on various diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including OBD-II scanners, advanced diagnostic systems, and handheld diagnostic devices.
9.2. Step-by-Step Guides for Unlocking Hidden Features
We provide step-by-step guides on how to unlock hidden features in your Mercedes-Benz vehicle, such as AMG menu activation, video in motion, and more.
9.3. Simple Repair Guides and Maintenance Tips
We offer easy-to-follow repair guides and maintenance tips to help you perform simple repairs and maintenance tasks on your Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
9.4. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support on all aspects of Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, repair, and maintenance.
9.5. Remote Diagnostic Services
We offer remote diagnostic services to help you diagnose issues with your Mercedes-Benz vehicle from a remote location.
9.6. Software Updates and Programming
We provide software updates and programming services to ensure that your Mercedes-Benz vehicle is running the latest software versions.
10. Call to Action
Experiencing issues with your Mercedes-Benz due to cloud connectivity or other failures? Don’t let diagnostic trouble codes keep you off the road. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, reliable diagnostic tools, and comprehensive support. Our team is ready to assist you with:
- Selecting the right diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz model
- Step-by-step instructions for unlocking hidden features
- Easy-to-follow repair guides for common issues
- Professional advice on maintenance and troubleshooting
Reach out to us now and let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
Contact Information:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
11. FAQ: Cloud Connected Vehicle Services
11.1. What Diagnostic Tool is Best for My Mercedes-Benz?
The best diagnostic tool depends on your needs. For basic tasks, an OBD-II scanner may suffice. For advanced diagnostics, consider the Mercedes-Benz XENTRY Diagnosis system or a high-quality handheld device.
11.2. How Can I Unlock Hidden Features on My Mercedes-Benz?
Unlocking hidden features involves accessing the vehicle’s control units and modifying certain parameters. Follow our step-by-step guides or consult with a professional for assistance.
11.3. How Often Should I Perform Maintenance on My Mercedes-Benz?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, typically every 10,000 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first.
11.4. Can Cloud Connectivity Issues Really Trigger DTCs?
Yes, failures in cloud-connected vehicle services can indeed trigger DTCs related to communication errors, software update failures, and more.
11.5. What are the Benefits of Remote Diagnostics?
Remote diagnostics allow technicians to access your vehicle’s systems from a remote location, providing faster and more convenient troubleshooting.
11.6. How Can I Protect My Vehicle from Security Breaches?
Use strong passwords for your Mercedes me connect account, keep your software up to date, and be cautious about connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
11.7. What Should I Do if I Receive a DTC Related to Cloud Connectivity?
Check your vehicle’s connectivity settings, monitor the status of the cloud services, and install any pending software updates. If the issue persists, seek professional assistance.
11.8. Are OTA Software Updates Safe?
OTA software updates are generally safe, but it’s important to ensure that your vehicle has a stable internet connection and sufficient battery power before initiating the update.
11.9. How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help Me?
We offer detailed information on diagnostic tools, step-by-step guides for unlocking hidden features, simple repair guides, expert advice, remote diagnostic services, and software updates.
11.10. Where Can I Find Reliable Independent Repair Shops for My Mercedes-Benz?
Ask for recommendations from other Mercedes-Benz owners or check online reviews to find reputable independent repair shops in your area.
12. Conclusion: Stay Informed and Proactive
Understanding how failures in cloud-connected vehicle services can generate DTCs is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz. By staying informed, taking proactive measures, and utilizing the resources available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can ensure that your vehicle continues to provide a smooth and enjoyable driving experience. Contact us today for expert guidance and support.