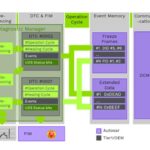
Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs), identified as Mode $0A, are not cleared by Mode $04 or disconnecting the battery. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guidance on how to properly manage and clear PDTCs, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz operates efficiently and complies with emission standards. Understanding the nuances of PDTCs, similar conditions windows, and the role of a scan tool is essential for effective vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What Are Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs)?
- 2. Why Were PDTCs Introduced?
- 3. How Do PDTCs Differ From Regular DTCs?
- 4. Can Mode $04 Clear PDTCs?
- 5. Does Disconnecting The Battery Clear PDTCs?
- 6. How Can PDTCs Be Cleared?
- 7. What Is A Similar Conditions Window (SCW)?
- 8. How Does SCW Help In Clearing PDTCs?
- 9. How Does California’s Smog Check Program Use PDTCs?
- 10. What Is The Universal Drive Cycle Pattern For Clearing PDTCs In California?
- 11. What Happens If Multiple PDTCs Are Present?
- 12. What Role Does Reprogramming The ECM Play In Clearing PDTCs?
- 13. How Does Freeze Frame Data (FFD) Relate To PDTCs?
- 14. What Tools Are Needed To Diagnose And Address PDTCs?
- 15. How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With PDTCs?
- 16. Understanding DTC Severity Levels
- 16.1. No DTC Present
- 16.2. Pending DTCs (Mode $07)
- 16.3. Stored DTCs (Mode $03)
- 16.4. Permanent DTCs (Mode $0A)
- 17. Diagnostic Tools for Mercedes-Benz
- 17.1. Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis System
- 17.2. Autel MaxiSys Elite
- 17.3. iCarsoft MB II
- 17.4. Launch Creader VII+
- 17.5. Foxwell NT510 Elite
- 18. Drive Cycle Procedures for Clearing PDTCs
- 18.1. General OBDII Drive Cycle
- 18.2. Mercedes-Benz Specific Drive Cycle
- 18.3. California Air Resources Board (CARB) Drive Cycle
- 19. Common Issues Leading to PDTCs in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 19.1. Misfires
- 19.2. Fuel System Problems
- 19.3. Oxygen Sensor Failures
- 19.4. Catalytic Converter Issues
- 19.5. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
- 20. Preventative Maintenance for Avoiding PDTCs
- 20.1. Regular Oil Changes
- 20.2. Spark Plug Replacement
- 20.3. Fuel Filter Replacement
- 20.4. Air Filter Replacement
- 20.5. Regular Inspections
- 21. The Role of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
- 21.1. MIL Activation
- 21.2. MIL Behavior
- 21.3. Reading DTCs
- 21.4. Addressing MIL Issues
- 22. Understanding Similar Conditions Window (SCW) Parameters
- 22.1. Engine Speed
- 22.2. Engine Load
- 22.3. Coolant Temperature
- 22.4. Other Parameters
- 23. Understanding OBDII Modes
- 23.1. Mode $01: Show Current Data
- 23.2. Mode $02: Show Freeze Frame Data
- 23.3. Mode $03: Show Stored DTCs
- 23.4. Mode $04: Clear DTCs
- 23.5. Mode $05: Oxygen Sensor Monitoring
- 23.6. Mode $06: Non-Continuous Monitoring Test Results
- 23.7. Mode $07: Show Pending DTCs
- 23.8. Mode $08: Request Control of On-Board System, Test or Component
- 23.9. Mode $09: Request Vehicle Information
- 23.10. Mode $0A: Show Permanent DTCs
- 24. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 25. How to Contact Us
- 26. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 26.1. What is the difference between a DTC and a PDTC?
- 26.2. Can I clear a PDTC by disconnecting the battery?
- 26.3. How do I clear a PDTC?
- 26.4. What is a drive cycle?
- 26.5. What is the California Air Resources Board (CARB)?
- 26.6. What is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)?
- 26.7. What is a Similar Conditions Window (SCW)?
- 26.8. What is OBDII?
- 26.9. What are OBDII modes?
- 26.10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me with PDTCs?
1. What Are Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs)?
Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs) are a specific type of diagnostic trouble code mandated in 2010 and fully implemented by the 2012 model year to prevent clearing of codes before emissions testing. These codes, represented as Mode $0A, remain in the vehicle’s computer memory even after a standard DTC (Mode $03) is erased. PDTCs ensure that vehicles with underlying issues cannot pass emissions tests simply by clearing the codes. This is achieved by storing PDTCs in non-volatile RAM (NVRAM), which retains data even when power is removed.
2. Why Were PDTCs Introduced?
PDTCs were introduced to combat the practice of clearing diagnostic trouble codes just before a vehicle undergoes an emissions test. This practice allowed vehicles that would typically fail due to emission-related issues to temporarily pass the test. By implementing PDTCs, regulatory bodies like the California Air Resources Board (CARB) aimed to ensure that vehicles genuinely meet emission standards before being certified.
3. How Do PDTCs Differ From Regular DTCs?
PDTCs differ from regular DTCs in their persistence and clearing conditions. Regular DTCs (Mode $03) can be cleared using a scan tool or by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery. However, PDTCs (Mode $0A) cannot be cleared using these methods. Instead, PDTCs require specific conditions to be met, such as the OBD system extinguishing the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or completing and passing the related monitor test on three consecutive trips.
4. Can Mode $04 Clear PDTCs?
No, Mode $04, which is the command to clear diagnostic information, cannot clear Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs). Mode $04 is designed to clear standard DTCs (Mode $03), freeze frame data, and other related diagnostic information. However, PDTCs are specifically designed to resist being cleared by this command to ensure compliance with emission standards.
5. Does Disconnecting The Battery Clear PDTCs?
No, disconnecting the vehicle’s battery will not clear PDTCs. PDTCs are stored in non-volatile RAM (NVRAM), which retains data even when power is removed. This is a key characteristic of PDTCs, ensuring they cannot be easily erased to bypass emission testing requirements.
6. How Can PDTCs Be Cleared?
PDTCs can only be cleared under specific conditions. The primary method involves the OBD system extinguishing the MIL because the underlying issue has been resolved. Alternatively, the ECM must see the related monitor test complete and pass on three consecutive trips. After these conditions are met, the PDTC will be removed from memory on the fourth key-on cycle. Using a scan tool to clear the memory will extinguish the MIL and clear the MODE $03 (Confirmed DTC) and MODE $02 (FFD), but the PDTC will remain until the successful completion of the drive cycle.
7. What Is A Similar Conditions Window (SCW)?
A Similar Conditions Window (SCW) is a set of specific conditions stored in the ECM’s memory when a Pending DTC (MODE $07) is set for misfire or fuel system issues. The SCW includes parameters such as engine speed (+/- 375 rpm), engine load (+/-20 %), and warmup condition (below or above 160°F). The ECM uses the SCW to monitor for a recurrence of the issue under the same driving conditions.
8. How Does SCW Help In Clearing PDTCs?
The SCW helps in accurately monitoring the conditions under which the initial fault occurred. By storing these specific parameters, the ECM can determine if the issue recurs under similar conditions. If the issue is resolved and does not reappear within the SCW parameters, the ECM can then clear the PDTC after the required number of successful trips.
9. How Does California’s Smog Check Program Use PDTCs?
California’s Smog Check Program uses PDTCs to fail vehicles that have recently had their diagnostic codes cleared. The program checks PID $30 (Warm-up Cycles Since Cleared) and PID $31 (Distance Traveled Since Cleared). If the Warm-Up Cycles are 14 or less, or the Distance Traveled is less than 200 miles, the vehicle will fail the inspection. This ensures that vehicles with unresolved issues cannot pass the test simply by clearing the codes.
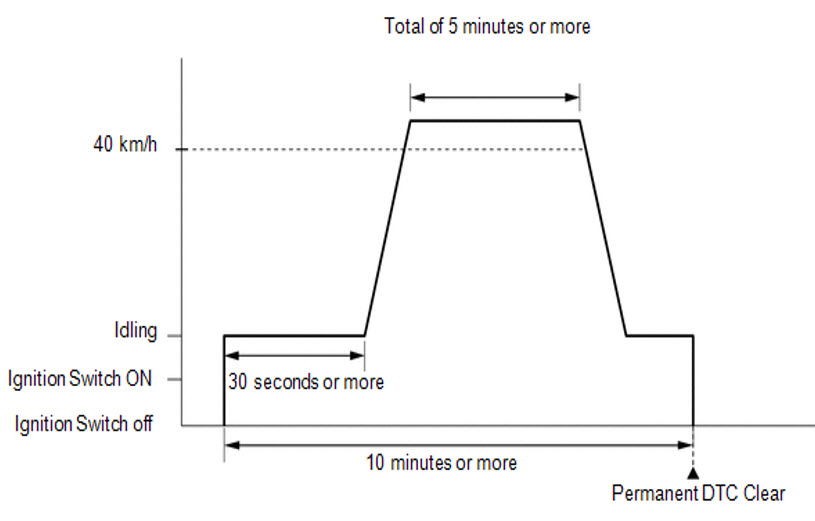
10. What Is The Universal Drive Cycle Pattern For Clearing PDTCs In California?
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has established a universal drive cycle pattern for clearing misfire and fuel system DTCs. This drive cycle requires specific conditions to be met:
- Cumulative time since engine start must be 600 seconds.
- Cumulative vehicle operation at or above 25 miles per hour must equal 300 seconds. (Medium-duty vehicles with diesel engines certified on an engine dynamometer may use cumulative operation at or above 15% calculated load instead of the 25 miles per hour).
- Continuous vehicle operation at idle (i.e., accelerator pedal released by driver and vehicle speed less than or equal to one mile per hour) for greater than or equal to 30 seconds.
- The ignition must be turned off for at least five seconds and then cycled on again.
11. What Happens If Multiple PDTCs Are Present?
If multiple PDTCs are present, clearing them from memory can take multiple trips and miles. Each PDTC must meet its specific clearing conditions, which can vary depending on the nature of the fault. If the stored MODE $03 DTC is no longer present, it should not affect driveability or emissions, but the PDTCs will remain until cleared according to the required procedures.
12. What Role Does Reprogramming The ECM Play In Clearing PDTCs?
Reprogramming the ECM can sometimes resolve PDTC issues. If a reflash update is designed to fix a PDTC issue, the PDTC will be erased during the update. However, if the reflash is unrelated to the PDTC, the update will not erase it. This is because the reflash process overwrites the existing software, potentially correcting the underlying cause of the PDTC.
13. How Does Freeze Frame Data (FFD) Relate To PDTCs?
Freeze Frame Data (FFD), stored in MODE $02, captures the operating conditions of the vehicle at the moment a DTC is set. This data includes parameters such as engine speed, engine load, and coolant temperature. FFD helps technicians diagnose the cause of the DTC by providing a snapshot of the conditions under which the fault occurred. When a second failure occurs within the same window, the MIL will turn on, and reviewable freeze frame data will be stored in MODE $02, allowing technicians to review the conditions that set the DTC.
14. What Tools Are Needed To Diagnose And Address PDTCs?
To diagnose and address PDTCs, a capable scan tool is essential. The scan tool should be able to read and display DTCs, including PDTCs (MODE $0A), as well as provide access to freeze frame data and other relevant diagnostic information. Some advanced scan tools can also perform the necessary tests and procedures to verify that the conditions for clearing the PDTC have been met.
15. How Can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With PDTCs?
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and resources to help you understand and address PDTCs in your Mercedes-Benz. We provide detailed information on the proper diagnostic tools, step-by-step instructions for troubleshooting common issues, and advice on how to ensure your vehicle complies with emission standards. Our goal is to empower Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians with the knowledge and tools they need to maintain their vehicles effectively.
16. Understanding DTC Severity Levels
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are not all created equal; they come in various severity levels, each indicating the seriousness of the detected issue and the potential impact on vehicle performance and emissions. Understanding these severity levels is essential for prioritizing repairs and ensuring vehicle safety.
16.1. No DTC Present
This is the ideal scenario where the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system has not detected any faults. All systems are functioning within acceptable parameters, and no corrective action is required. Regular maintenance and inspections can help maintain this state.
16.2. Pending DTCs (Mode $07)
Pending DTCs, also known as intermittent DTCs, indicate that a potential issue has been detected, but it has not yet been confirmed as a persistent problem. These codes are stored temporarily and may disappear if the fault does not recur within a certain number of drive cycles. Pending DTCs are a warning sign and should prompt further investigation to prevent the issue from escalating.
16.3. Stored DTCs (Mode $03)
Stored DTCs, or confirmed DTCs, indicate that a fault has been detected and verified by the onboard diagnostic system. These codes trigger the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), alerting the driver to the issue. Stored DTCs require immediate attention and should be diagnosed and repaired to prevent further damage to the vehicle.
16.4. Permanent DTCs (Mode $0A)
Permanent DTCs are the most severe type of DTC, indicating that a confirmed fault has occurred and cannot be cleared by traditional methods such as disconnecting the battery or using a scan tool. These codes are designed to prevent clearing DTCs before emissions testing and require specific conditions to be met before they can be cleared, such as completing a certain number of successful drive cycles.
17. Diagnostic Tools for Mercedes-Benz
Diagnosing and addressing DTCs in Mercedes-Benz vehicles requires specialized diagnostic tools that can access the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system and provide detailed information about detected faults. Here are some of the diagnostic tools commonly used for Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
17.1. Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis System
The Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis System is the official diagnostic tool used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships and authorized service centers. It provides comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including reading and clearing DTCs, accessing live data, performing component testing, and programming control units.
17.2. Autel MaxiSys Elite
The Autel MaxiSys Elite is a professional-grade diagnostic tool that offers advanced diagnostic capabilities for a wide range of vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz. It supports OE-level diagnostics, ECU programming, and advanced functions such as active testing and special functions.
17.3. iCarsoft MB II
The iCarsoft MB II is a diagnostic tool specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including reading and clearing DTCs, accessing live data, and performing special functions such as oil reset and electronic parking brake (EPB) reset.
17.4. Launch Creader VII+
The Launch Creader VII+ is a versatile diagnostic tool that supports OBDII diagnostics for a wide range of vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz. It can read and clear DTCs, access live data, and perform I/M readiness testing.
17.5. Foxwell NT510 Elite
The Foxwell NT510 Elite is a diagnostic tool that offers advanced diagnostic capabilities for a wide range of vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz. It supports OE-level diagnostics, ECU programming, and advanced functions such as active testing and special functions.
18. Drive Cycle Procedures for Clearing PDTCs
To clear Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs) in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, it is often necessary to perform a specific drive cycle procedure. A drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that must be met to allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system to run self-tests and verify that the issue has been resolved. Here are some common drive cycle procedures for Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
18.1. General OBDII Drive Cycle
The general OBDII drive cycle is a standardized procedure that can be used to clear PDTCs in most vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz. The procedure involves starting the engine and allowing it to warm up to normal operating temperature, then driving the vehicle at various speeds and loads to allow the onboard diagnostic system to run its self-tests.
18.2. Mercedes-Benz Specific Drive Cycle
Mercedes-Benz also has specific drive cycle procedures that are tailored to the specific vehicle model and engine type. These procedures can be found in the vehicle’s service manual or by consulting a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician. The Mercedes-Benz specific drive cycles often involve more precise driving conditions and may require the use of a diagnostic tool to monitor the progress of the self-tests.
18.3. California Air Resources Board (CARB) Drive Cycle
As mentioned earlier, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) has established a universal drive cycle pattern for clearing misfire and fuel system DTCs. This drive cycle requires specific conditions to be met:
- Cumulative time since engine start must be 600 seconds.
- Cumulative vehicle operation at or above 25 miles per hour must equal 300 seconds. (Medium-duty vehicles with diesel engines certified on an engine dynamometer may use cumulative operation at or above 15% calculated load instead of the 25 miles per hour).
- Continuous vehicle operation at idle (i.e., accelerator pedal released by driver and vehicle speed less than or equal to one mile per hour) for greater than or equal to 30 seconds.
- The ignition must be turned off for at least five seconds and then cycled on again.
19. Common Issues Leading to PDTCs in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
PDTCs can be triggered by a variety of issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ranging from minor problems to more serious mechanical failures. Here are some of the most common issues that can lead to PDTCs:
19.1. Misfires
Misfires occur when one or more of the engine’s cylinders fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. This can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or other issues in the ignition or fuel system. Misfires can lead to increased emissions and can trigger a PDTC.
19.2. Fuel System Problems
Fuel system problems can include issues with the fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel injectors, or other components in the fuel delivery system. These problems can cause the engine to run lean or rich, leading to increased emissions and potentially triggering a PDTC.
19.3. Oxygen Sensor Failures
Oxygen sensors are responsible for monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. Failures in the oxygen sensors can cause the engine control unit (ECU) to miscalculate the air-fuel mixture, leading to increased emissions and potentially triggering a PDTC.
19.4. Catalytic Converter Issues
The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions from the exhaust gases. Failures in the catalytic converter can lead to increased emissions and potentially triggering a PDTC.
19.5. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
EVAP leaks can occur in various components of the EVAP system, such as the fuel tank, fuel lines, or charcoal canister. These leaks can cause fuel vapors to escape into the atmosphere, leading to increased emissions and potentially triggering a PDTC.
20. Preventative Maintenance for Avoiding PDTCs
Preventative maintenance is essential for avoiding PDTCs and ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of your Mercedes-Benz. Here are some preventative maintenance measures that can help reduce the risk of PDTCs:
20.1. Regular Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are essential for maintaining engine health and preventing issues that can lead to PDTCs. Fresh oil helps lubricate engine components, reduce friction, and remove contaminants that can cause wear and damage.
20.2. Spark Plug Replacement
Spark plugs should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, leading to increased emissions and potentially triggering a PDTC.
20.3. Fuel Filter Replacement
The fuel filter should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals. A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow, leading to fuel system problems and potentially triggering a PDTC.
20.4. Air Filter Replacement
The air filter should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals. A dirty air filter can restrict airflow to the engine, leading to reduced performance and potentially triggering a PDTC.
20.5. Regular Inspections
Regular inspections by a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician can help identify potential issues before they escalate and lead to PDTCs. Inspections can include checking fluid levels, inspecting belts and hoses, and scanning for DTCs.
21. The Role of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), often referred to as the “check engine light,” plays a crucial role in alerting drivers to potential issues with their vehicle’s engine and emissions systems. When the MIL illuminates, it indicates that the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system has detected a fault that requires attention.
21.1. MIL Activation
The MIL is activated when the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system detects a fault that exceeds predetermined thresholds. The fault can be related to various systems, including the engine, transmission, emissions, and other critical components.
21.2. MIL Behavior
The MIL can exhibit different behaviors depending on the severity of the detected fault. In some cases, the MIL may illuminate steadily, indicating a non-critical issue that requires attention. In other cases, the MIL may flash, indicating a more severe issue that requires immediate attention.
21.3. Reading DTCs
When the MIL is illuminated, the first step is to read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. DTCs provide valuable information about the nature and location of the detected fault, helping technicians diagnose and repair the issue.
21.4. Addressing MIL Issues
Addressing MIL issues promptly is essential for preventing further damage to the vehicle and ensuring compliance with emissions regulations. Ignoring the MIL can lead to more serious problems and costly repairs down the road.
22. Understanding Similar Conditions Window (SCW) Parameters
The Similar Conditions Window (SCW) is a set of parameters stored in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system that capture the operating conditions at the time a fault is detected. These parameters provide valuable information about the context in which the fault occurred, helping technicians diagnose and repair the issue more effectively.
22.1. Engine Speed
Engine speed is one of the key parameters captured in the SCW. It indicates the rotational speed of the engine at the time the fault was detected. This information can help identify issues related to engine performance and stability.
22.2. Engine Load
Engine load is another important parameter captured in the SCW. It indicates the amount of power the engine is producing at the time the fault was detected. This information can help identify issues related to fuel delivery, ignition, and other engine systems.
22.3. Coolant Temperature
Coolant temperature is also captured in the SCW. It indicates the temperature of the engine coolant at the time the fault was detected. This information can help identify issues related to engine cooling and overheating.
22.4. Other Parameters
In addition to engine speed, engine load, and coolant temperature, the SCW may also capture other parameters such as vehicle speed, throttle position, and fuel trim. These parameters provide a more comprehensive picture of the operating conditions at the time the fault was detected.
23. Understanding OBDII Modes
OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in modern vehicles to monitor and diagnose various engine and emissions-related parameters. OBDII provides a set of modes that allow technicians to access and interpret diagnostic information. Here are some of the key OBDII modes:
23.1. Mode $01: Show Current Data
Mode $01 allows technicians to access real-time data from various sensors and systems in the vehicle. This data can include engine speed, engine load, coolant temperature, and other parameters.
23.2. Mode $02: Show Freeze Frame Data
Mode $02 allows technicians to access Freeze Frame Data, which captures the operating conditions at the time a DTC was set. This data can provide valuable insights into the cause of the fault.
23.3. Mode $03: Show Stored DTCs
Mode $03 allows technicians to access stored DTCs, which indicate confirmed faults that have been detected by the onboard diagnostic system.
23.4. Mode $04: Clear DTCs
Mode $04 allows technicians to clear DTCs from the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. However, as discussed earlier, this mode cannot clear Permanent DTCs (PDTCs).
23.5. Mode $05: Oxygen Sensor Monitoring
Mode $05 allows technicians to monitor the performance of the oxygen sensors in the exhaust system.
23.6. Mode $06: Non-Continuous Monitoring Test Results
Mode $06 allows technicians to access the results of non-continuous monitoring tests, which are tests that are not run continuously but are performed under specific conditions.
23.7. Mode $07: Show Pending DTCs
Mode $07 allows technicians to access pending DTCs, which indicate potential issues that have not yet been confirmed as persistent problems.
23.8. Mode $08: Request Control of On-Board System, Test or Component
Mode $08 allows technicians to request control of on-board systems, tests, or components for diagnostic purposes.
23.9. Mode $09: Request Vehicle Information
Mode $09 allows technicians to request vehicle information such as the vehicle identification number (VIN) and calibration identification.
23.10. Mode $0A: Show Permanent DTCs
Mode $0A allows technicians to access Permanent DTCs (PDTCs), which indicate confirmed faults that cannot be cleared by traditional methods.
24. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
Choosing the right resource for diagnosing and repairing your Mercedes-Benz is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive suite of services and expertise that sets us apart:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians and diagnostic specialists provides expert guidance and support to help you understand and address any issues with your vehicle.
- Comprehensive Resources: We offer a wide range of resources, including detailed diagnostic information, step-by-step repair guides, and technical articles, to empower you with the knowledge you need to maintain your Mercedes-Benz effectively.
- Specialized Tools: We provide access to specialized diagnostic tools and equipment that are specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ensuring accurate and efficient diagnostics and repairs.
- Commitment to Excellence: At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to excellence in all that we do. We strive to provide the highest quality services and support to our customers, ensuring their complete satisfaction.
25. How to Contact Us
If you have any questions or need assistance with diagnosing or repairing your Mercedes-Benz, please do not hesitate to contact us. Our team of experts is here to help you.
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
 Mercedes Diagnostic Tool
Mercedes Diagnostic Tool
Alt text: Mercedes-Benz CARB universal drive cycle illustration, showing time and speed requirements for clearing misfire and fuel system DTCs.
26. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
26.1. What is the difference between a DTC and a PDTC?
A DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) indicates a fault detected by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. A PDTC (Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Code) is a specific type of DTC that cannot be cleared by traditional methods, ensuring compliance with emissions regulations.
26.2. Can I clear a PDTC by disconnecting the battery?
No, disconnecting the battery will not clear a PDTC. PDTCs are stored in non-volatile memory, which retains data even when power is removed.
26.3. How do I clear a PDTC?
PDTCs can only be cleared by resolving the underlying issue and completing a specific drive cycle to allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system to verify that the fault has been corrected.
26.4. What is a drive cycle?
A drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that must be met to allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system to run self-tests and verify that a fault has been corrected.
26.5. What is the California Air Resources Board (CARB)?
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) is a regulatory agency responsible for developing and implementing programs to protect air quality and reduce emissions in California.
26.6. What is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)?
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), also known as the “check engine light,” is a warning light that illuminates when the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system detects a fault.
26.7. What is a Similar Conditions Window (SCW)?
A Similar Conditions Window (SCW) is a set of parameters stored in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system that capture the operating conditions at the time a fault is detected.
26.8. What is OBDII?
OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in modern vehicles to monitor and diagnose various engine and emissions-related parameters.
26.9. What are OBDII modes?
OBDII modes are a set of functions that allow technicians to access and interpret diagnostic information from the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system.
26.10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me with PDTCs?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert guidance, comprehensive resources, and specialized tools to help you understand and address PDTCs in your Mercedes-Benz.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and efficiently. Understanding Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes (PDTCs) and how to manage them is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and complying with emission standards. Remember, addressing PDTCs requires a thorough understanding of the underlying issues and proper diagnostic procedures.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us today for expert advice, diagnostic tools, and personalized assistance. Let MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in maintaining your vehicle’s performance and ensuring compliance with emission standards.
Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for immediate support.