Are you looking to diagnose powertrain issues in your vehicle? Understanding OBD-II Mode $03, the key to retrieving current powertrain Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), is essential for effective car maintenance. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert insights and resources to help you decode your vehicle’s health. This article dives deep into the functionality of Mode $03, including DTC encoding, reading sequences, and real-world examples, providing you with actionable knowledge. By learning about this diagnostic mode, you can ensure compliance with emission standards, improve engine efficiency, and increase vehicle reliability. Discover the importance of emission-related DTCs, confirmed DTCs, and OBD service.
Contents
- 1. What is OBD-II Mode $03 and Why is it Important?
- 1.1. Understanding DTCs: The Key to Vehicle Health
- 1.2. The Role of Service $03
- 1.3. Benefits of Knowing About Mode $03
- 2. Decoding DTCs: Understanding the Structure and Categories
- 2.1. Alphanumeric Prefixes: Identifying the System
- 2.2. Code Structure: Standardized and Proprietary Codes
- 2.3. DTC Categories: General Circuit, Range/Performance, and More
- 2.4. 2-Byte vs. 3-Byte DTCs: Decoding Processes
- 3. The Step-by-Step Process of Reading DTCs
- 3.1. Step 1: Query the Number of Stored DTCs
- 3.2. Step 2: Retrieve the DTCs
- 3.3. Handling Additional DTCs
- 4. Requesting the Number of DTCs: PID $01
- 4.1. Structure of the Request Message
- 4.2. Structure of the Response Message
- 4.3. Encoding the Number of DTCs in PID $01
- 4.4. Example of Request and Response Messages
- 5. Requesting Confirmed DTCs: Service $03
- 5.1. Structure of the Request Message
- 5.2. Structure of the Response Message
- 5.3. Example of Request and Response Messages
- 6. Real-World Examples of Reading DTCs
- 6.1. Example 1: Readiness Status and DTC Count
- 6.2. Example 2: Retrieving Specific DTCs with Service $03
- 7. Common Questions About OBD-II Mode $03
- 7.1. What is the best OBD-II scan tool for reading Mercedes DTCs?
- 7.2. How do I interpret DTCs retrieved using Mode $03?
- 7.3. Can I clear DTCs using Mode $03?
- 7.4. What if no DTCs are found using Mode $03?
- 7.5. Are all DTCs emission-related?
- 7.6. How often should I check for DTCs?
- 7.7. What does it mean if the MIL is on, but no DTCs are stored?
- 7.8. Can I rely solely on DTCs for diagnosing vehicle problems?
- 7.9. What are the limitations of OBD-II Mode $03?
- 7.10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with DTC diagnostics?
- 8. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Advanced Diagnostics
- 8.1. Expert Guidance and Support
- 8.2. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
- 8.3. Step-by-Step Repair Guides
- 8.4. Unlocking Hidden Features
- 8.5. Regular Maintenance Tips
- 9. Conclusion: Empowering You with Diagnostic Knowledge
1. What is OBD-II Mode $03 and Why is it Important?
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) Mode $03 is the service used to read emission-related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from a vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU). These DTCs signal problems related to the engine, transmission, and emissions systems, which can affect a vehicle’s compliance with emission regulations. According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), accurate DTC reading is crucial for maintaining vehicle emissions standards.
1.1. Understanding DTCs: The Key to Vehicle Health
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes that identify specific problems detected by a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. There are different types of DTCs, each providing unique information about the nature and status of the fault. Understanding these codes helps technicians and vehicle owners diagnose and address issues effectively.
- Pending DTCs: These are faults detected in the current driving cycle but not yet confirmed as actual problems. They become active only if they reoccur a certain number of times.
- Confirmed DTCs: These are faults verified over multiple driving cycles, meeting the conditions to be considered an actual issue.
- Permanent DTCs: These are confirmed DTCs retained in the ECU’s non-volatile memory until the appropriate monitor determines the malfunction is no longer present. They prevent vehicles from passing inspection by simply clearing DTCs prior to inspection.
 OBD-II Scantool Service Response
OBD-II Scantool Service Response
1.2. The Role of Service $03
The primary purpose of Service $03 is to enable external test equipment to read “confirmed” emission-related DTCs. This allows technicians to quickly identify and address issues affecting the vehicle’s emissions and performance.
1.3. Benefits of Knowing About Mode $03
- Improved Diagnostics: Quickly identify and address issues affecting vehicle emissions and performance.
- Cost Savings: Accurate diagnostics can prevent unnecessary repairs and reduce maintenance costs.
- Environmental Responsibility: Addressing emission-related issues helps maintain compliance with environmental regulations.
- Enhanced Vehicle Reliability: Timely identification and resolution of issues can improve the overall reliability and lifespan of the vehicle.
2. Decoding DTCs: Understanding the Structure and Categories
To effectively use Service $03, it’s essential to understand how DTCs are encoded. DTCs follow a specific structure, consisting of an alphanumeric prefix and a three-digit hexadecimal number. This structure identifies the category of the fault and provides detailed information about the issue.
2.1. Alphanumeric Prefixes: Identifying the System
The alphanumeric prefix consists of a letter and a digit, classifying the type of system or component affected:
- B0, B1, B2, B3: Codes for the Body system (e.g., airbags, climate control, lighting).
- C0, C1, C2, C3: Codes for the Chassis system (e.g., ABS, traction control).
- P0, P1, P2, P3: Codes for the Powertrain system (e.g., engine, transmission, emissions).
- U0, U1, U2, U3: Codes for Network and Vehicle Integration (e.g., communication between control modules).
2.2. Code Structure: Standardized and Proprietary Codes
The structure of the code is partially open-ended, meaning certain numeric sequences are reserved for standardized codes, while others are used by manufacturers for proprietary codes unique to their vehicles.
- Standardized Codes: Uniform codes assigned by regulatory bodies to ensure consistency across manufacturers.
- Proprietary Codes: Specialized codes used by manufacturers for unique vehicle-specific issues.
2.3. DTC Categories: General Circuit, Range/Performance, and More
Most DTCs fall into four basic categories:
- General Circuit/Open: Indicates an open circuit or general issue with connectivity.
- Range/Performance: Indicates a signal outside the expected range or poor performance.
- Circuit Low: Indicates a signal lower than expected.
- Circuit High: Indicates a signal higher than expected.
For example, the code P0143 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 3 can be broken down as follows:
- P: Powertrain system.
- 0143: Specific code indicating a low voltage issue with the O2 sensor in Bank 1, Sensor 3.
2.4. 2-Byte vs. 3-Byte DTCs: Decoding Processes
DTCs can be either 2 bytes or 3 bytes long. The decoding process depends on the length and format of the DTC.
- 2-byte DTCs: Decoded using a single, standardized list in SAE J2012DA.
- 3-byte DTCs: The two most significant bytes are decoded based on the DTC Format Identifier, and the least significant byte is decoded using the SAE J2012DA Failure Type Byte (FTB) Table.
For example, the DTC P0143 is transmitted on the communication bus as the hexadecimal value 0x0143.
3. The Step-by-Step Process of Reading DTCs
Understanding the sequence of steps involved in retrieving DTCs using Service $03 is critical for accurate diagnostics. The process involves querying the number of stored DTCs and then retrieving the DTCs themselves.
3.1. Step 1: Query the Number of Stored DTCs
The first step is to query the number of stored DTCs. This involves sending a Service $01, PID $01 request to all ECUs capable of reporting emission-related DTCs.
- ECU Response with DTCs: The response includes the count of stored DTCs.
- ECU Response with No DTCs: The response indicates zero stored DTCs.
3.2. Step 2: Retrieve the DTCs
The next step is to retrieve the DTCs. This involves sending a Service $03 request to each ECU to retrieve all stored emission-related DTCs.
- ECU Response with DTCs: ECUs with stored DTCs respond with one or more messages, each containing up to three DTCs per message.
- ECU Response with No DTCs: If no DTCs are stored, the ECU may choose not to respond.
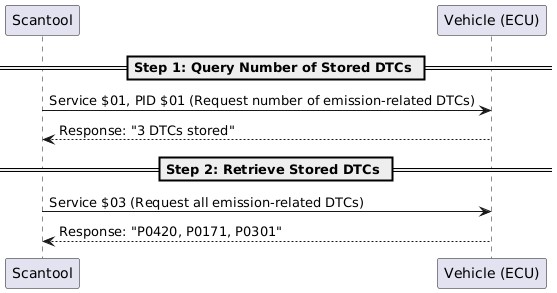 OBD-II Read DTC sequence
OBD-II Read DTC sequence
3.3. Handling Additional DTCs
If additional DTCs are logged between the initial count and the retrieval, the number of reported DTCs may exceed the expected count. In such cases, the cycle (Steps 1 and 2) must be repeated until the number of retrieved DTCs matches the count reported in the Service $01, PID $01 response.
4. Requesting the Number of DTCs: PID $01
To initiate the process of reading DTCs, a specific message must be sent to the ECU. This message, known as PID $01, requests the current powertrain diagnostic data, including the number of emission-related DTCs and the status of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL).
4.1. Structure of the Request Message
The request message consists of two data bytes:
- Data Byte #1: Service Identifier (SID) for the request. The byte value is
01, indicating Service $01 – Request Current Data. - Data Byte #2: Parameter Identifier (PID) that specifies what data is being requested. The byte value is
01, indicating PID $01 – Number of emission-related DTCs and MIL status.
4.2. Structure of the Response Message
The response message from the ECU includes:
- Data Byte #1: Response Service Identifier (SID) for the response. The byte value is
41, indicating a response to Service $01. - Data Byte #2: PID, matching the PID sent in the request. The byte value is
01. - Data Bytes #3–#6: Data Record, including the MIL status and the number of stored emission-related DTCs.
4.3. Encoding the Number of DTCs in PID $01
The number of stored DTCs is embedded into the PID $01. The first 6 bits of byte A provide the total number of stored DTCs. Byte A also indicates the status of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). Bytes B, C, and D provide additional status information about readiness tests and other diagnostic data.
4.4. Example of Request and Response Messages
- Request Example (from scantool to ECU):
01 01 - Response Example (from ECM to scantool):
41 01 83 33 FF 63
From the response message, we can determine that there are 3 stored and confirmed DTCs, and the MIL is ON.
5. Requesting Confirmed DTCs: Service $03
Once the number of stored DTCs is known, the next step is to request the DTCs themselves using Service $03. This service allows the tester (scantool) to request Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to emissions from the ECU.
5.1. Structure of the Request Message
The request message consists of a single data byte:
- Data Byte #1: Contains the Service Identifier (SID), which is
03(hex) for this request.
5.2. Structure of the Response Message
The response message from the ECU includes:
- Data Byte #1: Contains the Service Identifier for the response, which is
43(hex). - Data Bytes #2 to #7: Contain the emission-related DTCs. Each DTC is represented by two bytes: High Byte and Low Byte.
5.3. Example of Request and Response Messages
- Request Example (from the scantool to ECU):
03 - Response Example (from the ECM to scantool):
43 01 43 01 96 02 34
In this example, the response includes three DTCs: P0143, P0196, and P0234.
6. Real-World Examples of Reading DTCs
To illustrate the practical application of Service $03, let’s examine real-world examples of how DTCs are read and interpreted using an OBD-II scan tool.
6.1. Example 1: Readiness Status and DTC Count
The Readiness Status section from the OBD-II scan tool for Service $01 PID $01 reports the number of active emission-related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) status, and the readiness status of various onboard monitors.
In one scenario, the system reports 2 stored emission-related DTCs, but the MIL is off, suggesting the issues may not be currently active or critical. The Fuel System, Comprehensive Component, and EGR System tests are supported and have been successfully completed. Most non-continuous monitors (e.g., Catalyst, Oxygen Sensor) are not supported in this ECU configuration.
6.2. Example 2: Retrieving Specific DTCs with Service $03
Using an OBD-II scantool, Service $03 reports stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). In this example, two codes are retrieved: P1462 and P1461.
- P1462: Indicates a high voltage condition in the air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor circuit.
- P1461: Indicates a low voltage condition in the air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor circuit.
These codes are stored in the ECU and may represent past or persistent faults.
7. Common Questions About OBD-II Mode $03
To further clarify the use of OBD-II Mode $03, let’s address some frequently asked questions.
7.1. What is the best OBD-II scan tool for reading Mercedes DTCs?
The best OBD-II scan tool depends on your needs. For basic DTC reading, a simple handheld scanner will suffice. For advanced diagnostics, consider professional-grade tools with enhanced features like live data streaming and bidirectional control. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we can help you choose the right tool for your specific Mercedes model.
7.2. How do I interpret DTCs retrieved using Mode $03?
DTCs are interpreted by referring to a diagnostic code list. Each code corresponds to a specific issue. Online databases and repair manuals provide detailed descriptions of each code and recommended troubleshooting steps.
7.3. Can I clear DTCs using Mode $03?
No, Mode $03 is used for reading DTCs, not clearing them. To clear DTCs, you would typically use Service $04, which resets the diagnostic information. However, it’s essential to address the underlying issue before clearing the codes to prevent them from reappearing.
7.4. What if no DTCs are found using Mode $03?
If no DTCs are found, it could mean that there are no current issues detected by the ECU. However, it’s still advisable to perform a thorough inspection and monitor the vehicle for any potential problems.
7.5. Are all DTCs emission-related?
No, not all DTCs are emission-related. While Service $03 specifically retrieves emission-related DTCs, there are other DTCs related to various systems in the vehicle, such as the body, chassis, and network integration.
7.6. How often should I check for DTCs?
You should check for DTCs whenever you notice any unusual symptoms or performance issues with your vehicle. Regular checks can also be beneficial to identify potential problems early and prevent them from escalating.
7.7. What does it mean if the MIL is on, but no DTCs are stored?
If the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) is on, but no DTCs are stored, it could indicate a temporary or intermittent issue that has not been permanently logged. It’s advisable to monitor the vehicle and check for any recurring symptoms.
7.8. Can I rely solely on DTCs for diagnosing vehicle problems?
While DTCs provide valuable information, they should not be the sole basis for diagnosing vehicle problems. It’s essential to perform a comprehensive inspection, gather additional data, and use your expertise to accurately diagnose and address the issue.
7.9. What are the limitations of OBD-II Mode $03?
OBD-II Mode $03 primarily focuses on emission-related issues and may not provide detailed information about other systems in the vehicle. Additionally, some proprietary codes may require specialized tools or knowledge to interpret accurately.
7.10. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with DTC diagnostics?
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance, resources, and tools to help you accurately diagnose and address DTCs in your Mercedes vehicle. Whether you need help choosing the right scan tool, interpreting DTCs, or troubleshooting complex issues, our team is here to support you.
8. Leveraging MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Advanced Diagnostics
Understanding and utilizing OBD-II Mode $03 is just the beginning. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources and services to help you take your Mercedes diagnostics to the next level.
8.1. Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of experienced technicians and Mercedes experts provides personalized guidance and support to help you navigate the complexities of vehicle diagnostics. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we’re here to answer your questions and provide expert advice.
8.2. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools tailored to Mercedes vehicles, from basic OBD-II scanners to advanced professional-grade equipment. Our tools provide detailed DTC readings, live data streaming, bidirectional control, and other advanced features to help you accurately diagnose and address any issue.
8.3. Step-by-Step Repair Guides
Our step-by-step repair guides provide detailed instructions and illustrations to help you perform common repairs and maintenance tasks on your Mercedes. From replacing sensors to troubleshooting complex electrical issues, our guides provide the knowledge and confidence you need to tackle any project.
8.4. Unlocking Hidden Features
In addition to diagnostics and repairs, we also offer services to unlock hidden features in your Mercedes vehicle. From activating performance enhancements to customizing comfort settings, we can help you personalize your Mercedes to your exact preferences.
8.5. Regular Maintenance Tips
Our website features regular maintenance tips to help you keep your Mercedes in top condition. From oil changes to tire rotations, our tips provide valuable insights into proper vehicle care and preventative maintenance.
9. Conclusion: Empowering You with Diagnostic Knowledge
In conclusion, OBD-II Mode $03 is a vital tool for diagnosing powertrain issues by retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s memory. These DTCs offer essential insights into malfunctions, enabling technicians and vehicle owners to promptly identify and address potential problems, which is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and compliance with emission standards. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the expertise and resources needed to master Mercedes diagnostics.
We encourage you to take advantage of the comprehensive information and expert support available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes diagnostics? Contact us today for expert guidance, tool recommendations, and personalized support.
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let us help you ensure your Mercedes runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN now for a consultation and unlock the full potential of your vehicle!