Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are increasingly integrating with guided diagnostic procedures directly on scan tools or cloud platforms, enhancing the efficiency of vehicle maintenance. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive solutions to leverage these advancements, providing precise diagnostic information and streamlined repair processes. By understanding the integration of DTCs, technicians and Mercedes-Benz owners can significantly improve vehicle diagnostics and repairs, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools for proactive vehicle management. This integration offers better diagnostic accuracy, which results in improved vehicle performance and reduced repair times.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 1.1. The Role of DTCs in Vehicle Diagnostics
- 1.2. Evolution of DTC Standards: From OBD-I to OBD-II
- 1.3. Decoding DTCs: Structure and Interpretation
- 2. The Shift Towards Integrated Diagnostics
- 2.1. Benefits of Integrated Diagnostic Procedures
- 2.2. How Scan Tools Are Evolving
- 2.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostic Platforms
- 3. Key Players in Integrated Diagnostics
- 3.1. Scan Tool Manufacturers
- 3.2. Software and Platform Developers
- 3.3. Automotive OEMs
- 4. How Integration Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1. DTC Detection and Retrieval
- 4.2. Guided Diagnostic Procedures
- 4.3. Using Wiring Diagrams and Component Testing
- 4.4. Repair Verification and Code Clearing
- 5. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 5.1. Providing Access to Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 5.2. Expert Guidance and Support
- 5.3. Staying Updated with the Latest Technologies
- 6. Future Trends in Integrated Diagnostics
- 6.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
- 6.2. Augmented Reality (AR) in Diagnostics
- 6.3. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates and Diagnostics
- 7. Practical Applications and Examples
- 7.1. Diagnosing a Misfire in a Mercedes-Benz Engine
- 7.2. Troubleshooting an ABS Issue in a Mercedes-Benz Vehicle
- 7.3. Resolving an Airbag Warning Light in a Mercedes-Benz
- 8. Call to Action
- 9. FAQs
- 9.1. What is the best diagnostic tool for Mercedes-Benz?
- 9.2. How do I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes-Benz?
- 9.3. How often should I service my Mercedes-Benz?
- 9.4. Can I diagnose my Mercedes-Benz myself?
- 9.5. What are common DTCs for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
- 9.6. How do cloud platforms improve diagnostic accuracy?
- 9.7. What role does data logging play in vehicle maintenance?
- 9.8. What are the benefits of remote diagnostics?
- 9.9. How does integrated diagnostics reduce repair times?
- 9.10. What is the future of AI in vehicle diagnostics?
1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes used to identify malfunctions in a vehicle’s various systems. When a fault is detected, the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system generates a DTC, which can be read using a scan tool.
1.1. The Role of DTCs in Vehicle Diagnostics
DTCs play a crucial role in modern vehicle diagnostics. They provide technicians and vehicle owners with a starting point for identifying and addressing issues, saving time and reducing the complexity of the diagnostic process. By pinpointing the system and component at fault, DTCs enable targeted repairs.
1.2. Evolution of DTC Standards: From OBD-I to OBD-II
The evolution of DTC standards from OBD-I to OBD-II marked a significant advancement in vehicle diagnostics. OBD-I systems were manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization, making it difficult to interpret diagnostic information across different vehicle makes and models. OBD-II introduced a standardized set of DTCs and diagnostic protocols, ensuring consistency and ease of use for technicians.
Key Differences Between OBD-I and OBD-II:
| Feature | OBD-I | OBD-II |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized across all vehicles |
| DTC Codes | Proprietary | Standardized SAE codes |
| Diagnostic Port | Varied locations and connectors | Standardized 16-pin DLC |
| Data Parameters | Limited | Expanded range of parameters |
| Accessibility | Difficult to access and interpret | Easier access and interpretation |
| Implementation | Pre-1996 vehicles | 1996 and newer vehicles |
 OBD II Port
OBD II Port
1.3. Decoding DTCs: Structure and Interpretation
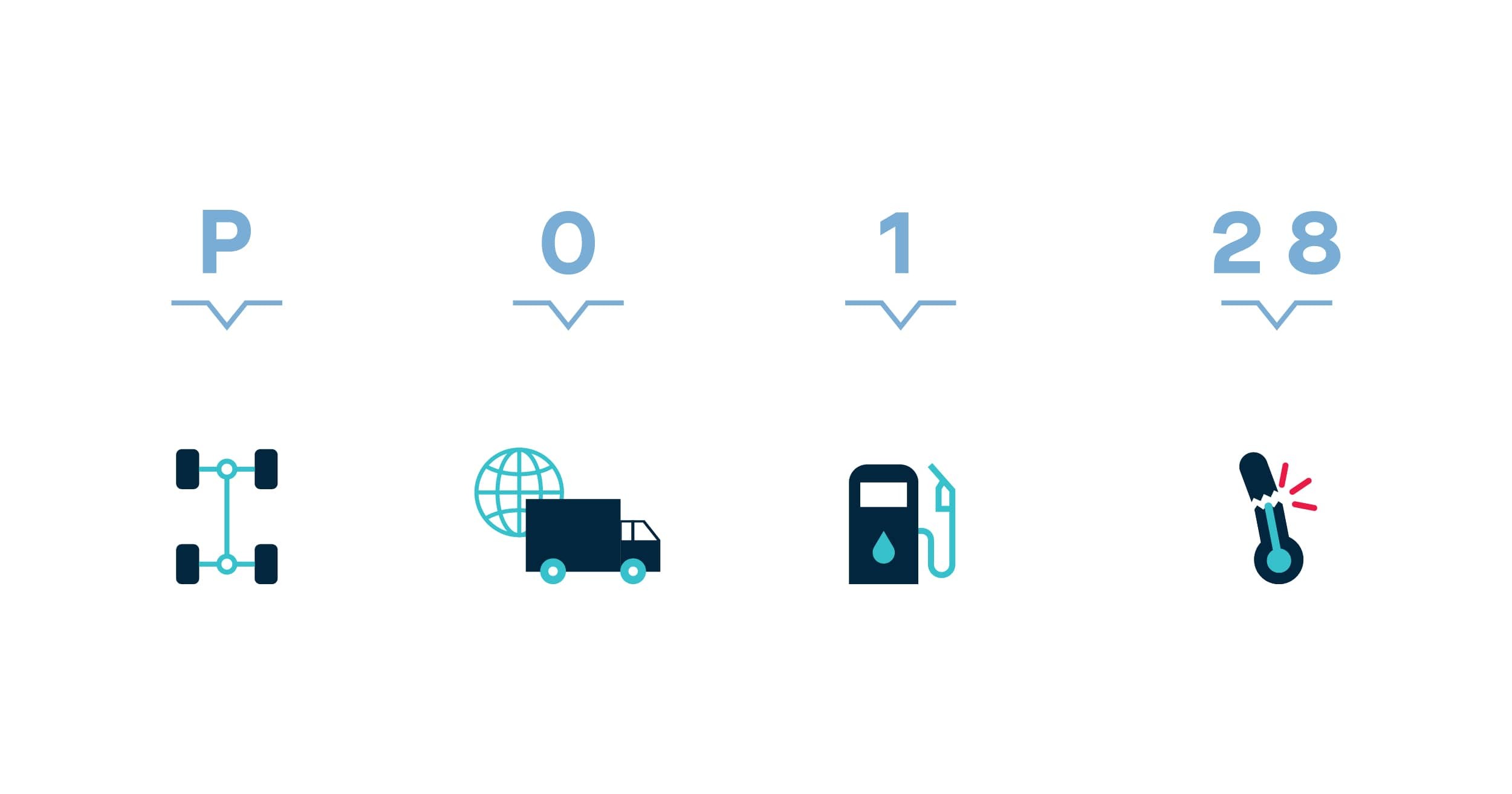
DTCs are typically five-character codes, each character providing specific information about the fault. Understanding the structure of a DTC is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Example of a DTC (P0128):
- First Character (P): Indicates the system affected (P = Powertrain).
- Second Character (0): Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character (1): Specifies the subsystem at fault (1 = Fuel and Air Metering).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters (28): Provide a specific fault index (28 = Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature).
2. The Shift Towards Integrated Diagnostics
The automotive industry is witnessing a shift towards integrated diagnostics, where DTCs are seamlessly integrated with guided diagnostic procedures directly on scan tools or cloud platforms. This integration enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces repair times, and improves overall efficiency.
2.1. Benefits of Integrated Diagnostic Procedures
Integrating DTCs with guided diagnostic procedures offers several key benefits:
- Improved Accuracy: Step-by-step guidance ensures technicians follow the correct diagnostic procedures, minimizing errors.
- Reduced Repair Times: Faster identification of the root cause leads to quicker repairs.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined diagnostic processes optimize workflow.
- Comprehensive Information: Access to detailed repair information and troubleshooting tips.
- Remote Diagnostics: Cloud platforms enable remote diagnostics and collaboration among technicians.
2.2. How Scan Tools Are Evolving
Modern scan tools are evolving to incorporate advanced features such as:
- DTC Code Lookup: Instant access to DTC definitions and possible causes.
- Guided Diagnostics: Step-by-step procedures for diagnosing and repairing faults.
- Wiring Diagrams: Integrated access to vehicle-specific wiring diagrams.
- Component Testing: Built-in tools for testing individual components.
- Data Logging: Ability to record and analyze vehicle data in real-time.
2.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostic Platforms
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are revolutionizing vehicle diagnostics by providing:
- Remote Access: Technicians can access diagnostic information and tools from any location.
- Data Storage: Diagnostic data is securely stored in the cloud, allowing for historical analysis and comparison.
- Collaboration: Technicians can collaborate with experts and share diagnostic information in real-time.
- Software Updates: Automatic software updates ensure technicians always have the latest diagnostic information.
- Integration with OEM Data: Access to OEM repair information and technical service bulletins.
3. Key Players in Integrated Diagnostics
Several key players are driving the adoption of integrated diagnostics, including scan tool manufacturers, software developers, and automotive OEMs.
3.1. Scan Tool Manufacturers
Scan tool manufacturers are developing advanced diagnostic tools that integrate DTCs with guided diagnostic procedures. These tools often include features such as:
- Autel: Offers a range of advanced scan tools with comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Snap-on: Provides high-end diagnostic tools with integrated repair information.
- Bosch: Delivers reliable scan tools with extensive vehicle coverage.
- Launch: Offers affordable scan tools with essential diagnostic functions.
3.2. Software and Platform Developers
Software and platform developers are creating cloud-based diagnostic platforms that provide technicians with access to a wealth of diagnostic information and tools.
- Mitchell 1: Offers a comprehensive suite of diagnostic and repair software.
- Alldata: Provides access to OEM repair information and diagnostic tools.
- Identifix: Delivers a vast database of diagnostic information and troubleshooting tips.
- Shop-Ware: Offers cloud-based shop management software with integrated diagnostics.
3.3. Automotive OEMs
Automotive OEMs are integrating diagnostic capabilities into their vehicles and providing access to OEM repair information and diagnostic tools.
- Mercedes-Benz: Offers specialized diagnostic tools and software for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- BMW: Provides access to BMW’s diagnostic and repair information through its service portal.
- Audi: Delivers diagnostic tools and software specifically designed for Audi vehicles.
- Volkswagen: Offers access to VW’s diagnostic and repair information through its service portal.
4. How Integration Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
The integration of DTCs with guided diagnostic procedures involves a series of steps, from initial DTC detection to final repair verification.
4.1. DTC Detection and Retrieval
The process begins with the detection of a fault by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system, which generates a DTC. The DTC can be retrieved using a scan tool connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
Steps for DTC Retrieval:
- Connect the scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port (typically located under the dashboard).
- Turn on the vehicle’s ignition.
- Select the appropriate vehicle make, model, and year on the scan tool.
- Navigate to the diagnostic menu and select “Read Codes” or a similar option.
- The scan tool will display any stored DTCs, along with their descriptions.
4.2. Guided Diagnostic Procedures
Once a DTC is retrieved, the scan tool or cloud platform provides guided diagnostic procedures to help technicians identify the root cause of the fault.
Components of Guided Diagnostic Procedures:
- DTC Definition: A detailed explanation of the DTC and its possible causes.
- Preliminary Checks: A list of initial checks to perform, such as visual inspections and basic component testing.
- Wiring Diagrams: Vehicle-specific wiring diagrams to aid in tracing circuits and identifying potential wiring issues.
- Component Testing: Step-by-step instructions for testing individual components using a multimeter or other diagnostic tools.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Common issues and solutions related to the DTC.
4.3. Using Wiring Diagrams and Component Testing
Wiring diagrams and component testing are essential parts of the guided diagnostic process.
- Wiring Diagrams: Provide a visual representation of the vehicle’s electrical circuits, allowing technicians to trace wires and identify potential shorts, opens, or other wiring issues.
- Component Testing: Involves using a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test the functionality of individual components, such as sensors, actuators, and modules.
Example: Testing a Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
- Locate the MAF sensor in the engine compartment.
- Disconnect the MAF sensor connector.
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage, resistance, and continuity of the sensor’s terminals, following the instructions in the guided diagnostic procedure.
- Compare the measured values to the specifications provided in the repair information.
- If the measured values are outside the specified range, the MAF sensor may be faulty and require replacement.
4.4. Repair Verification and Code Clearing
After performing the necessary repairs, it’s essential to verify that the fault has been resolved and clear the DTC from the vehicle’s computer.
Steps for Repair Verification and Code Clearing:
- Perform any necessary tests or procedures to verify that the fault has been resolved.
- Connect the scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Navigate to the diagnostic menu and select “Clear Codes” or a similar option.
- The scan tool will clear the DTC from the vehicle’s computer.
- Perform a test drive to ensure that the DTC does not return.
5. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN plays a crucial role in helping technicians and Mercedes-Benz owners leverage the benefits of integrated diagnostics.
5.1. Providing Access to Advanced Diagnostic Tools
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of advanced diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including:
- DTC Code Reading and Clearing: Quickly retrieve and clear DTCs from Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Guided Diagnostics: Step-by-step procedures for diagnosing and repairing faults.
- Wiring Diagrams: Access to vehicle-specific wiring diagrams.
- Component Testing: Built-in tools for testing individual components.
- Data Logging: Ability to record and analyze vehicle data in real-time.
5.2. Expert Guidance and Support
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert guidance and support to help technicians and Mercedes-Benz owners effectively use diagnostic tools and procedures. This includes:
- Technical Support: Access to experienced technicians who can answer questions and provide assistance.
- Training Programs: Comprehensive training programs on Mercedes-Benz diagnostics and repair.
- Online Resources: A wealth of online resources, including articles, videos, and troubleshooting guides.
- Community Forum: A forum where technicians and Mercedes-Benz owners can share information and ask questions.
5.3. Staying Updated with the Latest Technologies
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to staying updated with the latest diagnostic technologies and providing its customers with access to the most advanced tools and information. This includes:
- Regular Software Updates: Ensuring that diagnostic tools are always up-to-date with the latest vehicle coverage and diagnostic capabilities.
- New Product Releases: Introducing new diagnostic tools and technologies as they become available.
- Partnerships with OEMs: Collaborating with Mercedes-Benz and other OEMs to provide access to OEM repair information and diagnostic tools.
6. Future Trends in Integrated Diagnostics
The future of integrated diagnostics is expected to bring even more advanced technologies and capabilities, further enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of vehicle diagnostics.
6.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
AI is poised to play a significant role in the future of vehicle diagnostics. AI-powered diagnostic systems can analyze vast amounts of vehicle data to identify patterns and predict potential failures. This can help technicians diagnose issues more quickly and accurately, and even prevent failures before they occur.
Examples of AI Applications in Diagnostics:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze vehicle data to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Fault Diagnosis: AI systems can analyze DTCs, sensor data, and other information to identify the root cause of a fault.
- Automated Testing: AI can automate many of the manual steps involved in diagnostic testing, reducing the time and effort required.
6.2. Augmented Reality (AR) in Diagnostics
Augmented reality (AR) is another emerging technology that has the potential to revolutionize vehicle diagnostics. AR can overlay digital information onto the real world, providing technicians with visual guidance and assistance during the diagnostic process.
Examples of AR Applications in Diagnostics:
- Wiring Diagrams: AR can overlay wiring diagrams onto the vehicle, making it easier for technicians to trace wires and identify potential wiring issues.
- Component Identification: AR can identify components and provide information about their location and function.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: AR can provide step-by-step instructions for diagnostic procedures, guiding technicians through each step of the process.
6.3. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates and Diagnostics
Over-the-air (OTA) updates and diagnostics are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. OTA updates allow OEMs to remotely update vehicle software, fix bugs, and add new features. OTA diagnostics enable remote monitoring of vehicle health and performance, allowing OEMs to identify potential issues and proactively address them.
Benefits of OTA Updates and Diagnostics:
- Improved Vehicle Performance: OTA updates can improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Downtime: OTA diagnostics can identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns, reducing downtime.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: OTA updates and diagnostics can improve customer satisfaction by providing a more seamless and convenient ownership experience.
7. Practical Applications and Examples
To illustrate the benefits of integrated diagnostics, here are a few practical applications and examples:
7.1. Diagnosing a Misfire in a Mercedes-Benz Engine
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz owner experiences a misfire in their engine and receives a DTC indicating a misfire in cylinder 3.
Integrated Diagnostic Process:
- The technician connects a scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieves the DTC.
- The scan tool provides a guided diagnostic procedure for the DTC, including a list of possible causes, such as a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, or vacuum leak.
- The technician uses the guided diagnostic procedure to perform a series of tests, including:
- Inspecting the spark plug and ignition coil in cylinder 3.
- Testing the fuel injector in cylinder 3.
- Checking for vacuum leaks in the intake manifold.
- The technician identifies a faulty ignition coil as the cause of the misfire.
- The technician replaces the ignition coil and clears the DTC.
- The technician performs a test drive to ensure that the misfire has been resolved.
7.2. Troubleshooting an ABS Issue in a Mercedes-Benz Vehicle
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz owner experiences an ABS issue and receives a DTC indicating a problem with the ABS wheel speed sensor.
Integrated Diagnostic Process:
- The technician connects a scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieves the DTC.
- The scan tool provides a guided diagnostic procedure for the DTC, including a list of possible causes, such as a faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issue, or ABS module problem.
- The technician uses the guided diagnostic procedure to perform a series of tests, including:
- Inspecting the wheel speed sensor and wiring.
- Testing the wheel speed sensor signal.
- Checking the ABS module for proper operation.
- The technician identifies a faulty wheel speed sensor as the cause of the ABS issue.
- The technician replaces the wheel speed sensor and clears the DTC.
- The technician performs a test drive to ensure that the ABS issue has been resolved.
7.3. Resolving an Airbag Warning Light in a Mercedes-Benz
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz displays an airbag warning light, indicating a potential issue with the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS).
Integrated Diagnostic Process:
- Using a Mercedes-Benz compatible scan tool, a technician retrieves the specific DTC related to the SRS.
- The diagnostic tool provides a guided procedure, suggesting checks for the seatbelt pretensioners, airbag module connections, and individual airbag sensors.
- Following wiring diagrams, the technician verifies the integrity of the wiring and connections to the airbag module.
- The technician uses the scan tool to test the resistance and voltage of the airbag sensors.
- A faulty seat occupancy sensor is identified and replaced.
- After clearing the DTC and performing a system check, the airbag warning light is extinguished.
8. Call to Action
Ready to enhance your vehicle diagnostic capabilities? Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert consultation on advanced diagnostic tools, services for unlocking hidden features, and comprehensive repair and maintenance guidance for your Mercedes-Benz.
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Contact us now to elevate your Mercedes-Benz ownership experience!
9. FAQs
9.1. What is the best diagnostic tool for Mercedes-Benz?
The best diagnostic tool for Mercedes-Benz depends on your specific needs and budget. Options include:
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: The OEM diagnostic tool, offering the most comprehensive capabilities.
- Autel MaxiSys Elite: A high-end aftermarket tool with excellent Mercedes-Benz coverage.
- iCarsoft MB V3.0: An affordable option for DIY enthusiasts and small repair shops.
9.2. How do I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes-Benz?
Unlocking hidden features on your Mercedes-Benz requires specialized software and coding. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for professional assistance with unlocking hidden features.
9.3. How often should I service my Mercedes-Benz?
The recommended service interval for your Mercedes-Benz depends on the model and year. Refer to your owner’s manual or consult with a qualified technician for specific recommendations.
9.4. Can I diagnose my Mercedes-Benz myself?
Yes, with the right diagnostic tools and knowledge, you can diagnose your Mercedes-Benz yourself. However, for complex issues, it’s always best to consult with a qualified technician.
9.5. What are common DTCs for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
Common DTCs for Mercedes-Benz vehicles include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0300: Random Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large Leak)
9.6. How do cloud platforms improve diagnostic accuracy?
Cloud platforms offer access to vast databases of repair information, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting tips, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
9.7. What role does data logging play in vehicle maintenance?
Data logging allows technicians to record and analyze vehicle data in real-time, helping them identify intermittent issues and diagnose complex problems.
9.8. What are the benefits of remote diagnostics?
Remote diagnostics enable technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues from any location, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
9.9. How does integrated diagnostics reduce repair times?
Integrated diagnostics provides technicians with guided procedures and comprehensive information, reducing the time required to diagnose and repair vehicle issues.
9.10. What is the future of AI in vehicle diagnostics?
The future of AI in vehicle diagnostics includes predictive maintenance, automated testing, and more accurate fault diagnosis, further enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of vehicle maintenance.