Standardized Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) formats face increasing challenges as automotive systems become more proprietary; however, they will continue to be relevant. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can provide the expertise and tools necessary to navigate this complex landscape, ensuring accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs. With advanced diagnostic solutions, proprietary system integration, and Mercedes-Benz diagnostic support, we ensure you’re equipped to handle the evolving automotive technology.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 1.1. Historical Context of DTCs
- 1.2. Evolution of DTC Formats
- 1.3. The Role of Standardization
- 2. Proprietary Systems in Modern Vehicles
- 2.1. Examples of Proprietary Systems
- 2.2. How Proprietary Systems Challenge Standardized DTCs
- 2.3. The Rise of Encrypted and Secured Systems
- 3. The Continued Relevance of Standardized DTC Formats
- 3.1. Basic Diagnostics and Triage
- 3.2. Regulatory Requirements
- 3.3. Foundation for Advanced Diagnostics
- 3.4. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 4. Enhancing Standardized DTCs with Proprietary Information
- 4.1. Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
- 4.2. Enhanced Diagnostic Tools
- 4.3. Access to Manufacturer Databases
- 4.4. Data Logging and Analysis
- 4.5. Utilizing Freeze Frame Data and Extended Data
- 5. Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics
- 5.1. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 5.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 5.3. Remote Diagnostics
- 5.4. Predictive Diagnostics
- 5.5. Cybersecurity Measures
- 6. Best Practices for Working with DTCs in Proprietary Systems
- 6.1. Stay Updated with the Latest Information
- 6.2. Use High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
- 6.3. Follow Manufacturer Procedures
- 6.4. Document Your Work
- 6.5. Seek Expert Assistance
- 7. The Importance of Training and Certification
- 7.1. Understanding Complex Systems
- 7.2. Mastering Diagnostic Tools
- 7.3. Keeping Up with Technology
- 7.4. Industry Certifications
- 7.5. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Training Programs
- 8. Real-World Examples of DTCs in Action
- 8.1. Example 1: P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 8.2. Example 2: U0100 – Lost Communication With ECM/PCM “A”
- 8.3. Example 3: C1000 – Hydraulic Pump Motor Faulty
- 9. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Supports Your Diagnostic Needs
- 9.1. Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
- 9.2. Diagnostic Software
- 9.3. Technical Support
- 9.4. Training Programs
- 9.5. Remote Diagnostic Services
- 10. Addressing Customer Challenges
- 10.1. Difficulty in Finding Suitable Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2. Uncertainty About Unlocking Hidden Features
- 10.3. Need for Clear Repair and Maintenance Guidance
- 10.4. Concerns About High Repair Costs at Dealerships
- 10.5. Call to Action
- 11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes used in vehicle diagnostics to identify specific faults or malfunctions detected by the vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes provide technicians and vehicle owners with a standardized way to understand and address issues affecting the vehicle’s performance.
DTCs have evolved from simple flashing codes to complex alphanumeric codes that provide detailed information about the nature and location of the problem. As modern vehicles incorporate more advanced and proprietary systems, the role of standardized DTC formats is increasingly questioned. However, these standards remain essential for basic diagnostics and communication between different diagnostic tools and systems.
1.1. Historical Context of DTCs
The history of DTCs dates back to the early days of automotive diagnostics, where fault codes were simple flashing lights indicating a general problem. Over time, these evolved into more structured and detailed codes, particularly with the introduction of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems.
- Early Systems: Initial diagnostic systems used basic flashing codes to indicate general areas of concern.
- OBD-I: The first generation of OBD systems provided limited standardized diagnostic information.
- OBD-II: This standardized system, introduced in the mid-1990s, provided a more comprehensive set of DTCs and standardized diagnostic procedures. OBD-II mandated that all vehicles sold in the United States have a standardized port for accessing diagnostic information.
- Modern Systems: Current systems use 2-byte (OBD legislated codes) and 3-byte DTCs (UDS standardized), offering even more detailed diagnostic data.
1.2. Evolution of DTC Formats
DTC formats have undergone significant evolution to keep pace with advancements in automotive technology. The shift from simple flashing codes to alphanumeric codes has enabled more precise identification of faults and improved diagnostic accuracy.
- Flashing Codes: Early systems relied on mechanics counting flashes to interpret issues.
- Two-Byte DTCs: Standardized under OBD-II, these codes provided a more detailed description of the problem.
- Three-Byte DTCs: Used in modern systems, particularly those adhering to the Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS) standard, these codes offer even greater detail and specificity.
1.3. The Role of Standardization
Standardization of DTCs is crucial for several reasons, including:
- Consistency: Ensures that diagnostic tools and technicians can understand and interpret fault codes across different vehicle makes and models.
- Efficiency: Simplifies the diagnostic process, allowing technicians to quickly identify and address issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets requirements set by regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
2. Proprietary Systems in Modern Vehicles
Modern vehicles increasingly rely on proprietary systems developed by individual manufacturers. These systems often include unique software, hardware, and communication protocols that are not standardized across the industry. This trend presents challenges for standardized DTC formats, which may not fully capture the complexity and specificity of these proprietary systems.
2.1. Examples of Proprietary Systems
Many vehicle manufacturers have developed proprietary systems to enhance vehicle performance, safety, and convenience. Examples include:
- Engine Management Systems: Proprietary algorithms and control strategies optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Transmission Control Systems: Unique software manages gear shifting and transmission behavior.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Proprietary sensors and software enable features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking.
- Infotainment Systems: Custom software and hardware provide navigation, entertainment, and connectivity features.
2.2. How Proprietary Systems Challenge Standardized DTCs
Proprietary systems can challenge standardized DTCs in several ways:
- Limited Coverage: Standardized DTCs may not cover all the specific faults and conditions that can occur within proprietary systems.
- Inaccurate Interpretation: Standardized DTCs may provide a general description of the problem but lack the detailed information needed for accurate diagnosis and repair.
- Compatibility Issues: Diagnostic tools designed to work with standardized DTCs may not be fully compatible with proprietary systems, leading to communication errors or incomplete data.
2.3. The Rise of Encrypted and Secured Systems
The increasing use of encrypted and secured systems in modern vehicles further complicates the diagnostic process. Manufacturers employ encryption to protect their intellectual property and prevent unauthorized access to vehicle systems. This can make it difficult for aftermarket diagnostic tools and technicians to access and interpret DTCs and other diagnostic data.
3. The Continued Relevance of Standardized DTC Formats
Despite the challenges posed by proprietary systems, standardized DTC formats continue to play a vital role in automotive diagnostics. They provide a common language for identifying and addressing vehicle problems, enabling efficient communication between technicians, diagnostic tools, and vehicle owners.
3.1. Basic Diagnostics and Triage
Standardized DTCs are essential for basic diagnostics and triage. They provide a quick and easy way to identify the general area of the problem, allowing technicians to prioritize their work and focus on the most critical issues.
- Initial Assessment: Standardized DTCs provide a starting point for diagnosing vehicle problems.
- Prioritization: Help technicians prioritize their work by identifying the most critical issues.
- Communication: Facilitate communication between technicians, service advisors, and vehicle owners.
3.2. Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements mandate the use of standardized DTCs for emissions-related issues. Government agencies like the EPA and CARB require vehicles to have standardized diagnostic systems that can detect and report emissions-related faults. This ensures that vehicles comply with emissions standards and helps protect the environment.
3.3. Foundation for Advanced Diagnostics
Standardized DTCs serve as a foundation for more advanced diagnostic procedures. While they may not provide all the information needed to diagnose complex problems, they provide a starting point for further investigation. Technicians can use standardized DTCs to guide their diagnostic process and identify the specific systems or components that require further testing.
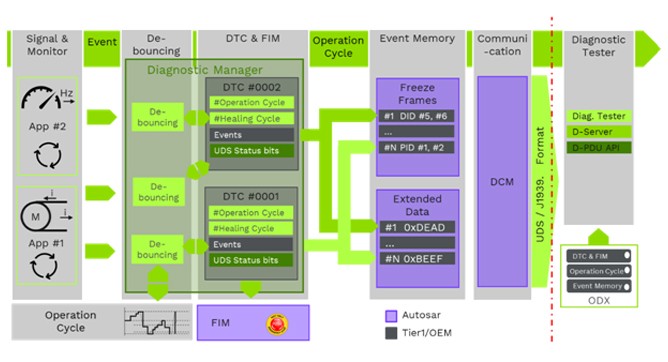 Process sequence of a DTC
Process sequence of a DTC
3.4. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN bridges the gap between standardized DTCs and proprietary systems, providing comprehensive diagnostic solutions for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our expertise and tools enable technicians and vehicle owners to accurately diagnose and repair even the most complex issues.
- Expertise: Deep understanding of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems.
- Advanced Tools: State-of-the-art diagnostic equipment for comprehensive vehicle analysis.
- Comprehensive Solutions: Tailored solutions for a wide range of diagnostic needs.
4. Enhancing Standardized DTCs with Proprietary Information
To overcome the limitations of standardized DTCs in the face of proprietary systems, it is necessary to enhance them with proprietary information. This can be achieved through several strategies, including:
4.1. Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
Many vehicle manufacturers supplement standardized DTCs with their own proprietary codes. These manufacturer-specific DTCs provide more detailed information about the faults and conditions that are unique to their vehicles. Diagnostic tools that can read and interpret these manufacturer-specific DTCs can provide a more accurate and comprehensive diagnosis.
4.2. Enhanced Diagnostic Tools
Enhanced diagnostic tools combine standardized DTC information with proprietary data to provide a more complete picture of the vehicle’s condition. These tools can access and interpret manufacturer-specific DTCs, as well as other diagnostic data that is not available through standardized channels.
4.3. Access to Manufacturer Databases
Access to manufacturer databases can provide technicians with valuable information about proprietary systems and their associated DTCs. These databases often contain detailed descriptions of DTCs, troubleshooting procedures, and repair information that is not available elsewhere.
4.4. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging and analysis can help technicians identify and understand complex problems that are not easily diagnosed with standardized DTCs alone. By recording and analyzing vehicle data over time, technicians can identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate underlying issues.
4.5. Utilizing Freeze Frame Data and Extended Data
Freeze frame data captures the operating conditions of the vehicle at the moment a DTC is triggered. Extended data provides additional information about the fault, such as the number of times it has occurred and the conditions under which it occurred. Both can provide a more detailed understanding of the issue.
5. Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics
The future of automotive diagnostics is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including:
5.1. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates allow vehicle manufacturers to remotely update vehicle software and firmware. This can be used to fix bugs, improve performance, and add new features. OTA updates can also be used to update diagnostic systems and DTC information, ensuring that technicians always have access to the latest diagnostic data.
5.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being used in automotive diagnostics. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze vast amounts of vehicle data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate underlying problems. ML algorithms can learn from historical diagnostic data to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic procedures.
5.3. Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allows technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely. This can be particularly useful for vehicles that are located in remote areas or for problems that are difficult to diagnose in person. Remote diagnostics tools typically use telematics data and video conferencing to allow technicians to interact with the vehicle and the vehicle owner.
5.4. Predictive Diagnostics
Predictive diagnostics uses data analysis and machine learning to predict when a vehicle component is likely to fail. This allows vehicle owners to proactively address potential problems before they lead to breakdowns or costly repairs. Predictive diagnostics can also help optimize maintenance schedules and reduce vehicle downtime.
5.5. Cybersecurity Measures
As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, cybersecurity becomes increasingly important. Diagnostic systems must be protected from unauthorized access and tampering to prevent malicious attacks. Manufacturers are implementing various cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection, to protect vehicle systems.
6. Best Practices for Working with DTCs in Proprietary Systems
Working with DTCs in proprietary systems requires a combination of knowledge, skill, and the right tools. Here are some best practices to follow:
6.1. Stay Updated with the Latest Information
Vehicle manufacturers are constantly updating their proprietary systems and DTC information. It is important to stay updated with the latest information by subscribing to manufacturer newsletters, attending training courses, and participating in online forums.
6.2. Use High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
High-quality diagnostic tools are essential for accurately diagnosing problems in proprietary systems. These tools should be able to read and interpret manufacturer-specific DTCs, access proprietary data, and perform advanced diagnostic procedures.
6.3. Follow Manufacturer Procedures
Always follow manufacturer procedures when diagnosing and repairing vehicles with proprietary systems. This will help ensure that you are using the correct diagnostic techniques and that you are not damaging the vehicle.
6.4. Document Your Work
Document your work thoroughly, including the DTCs that you found, the diagnostic procedures that you performed, and the repairs that you made. This will help you track your progress and provide a record of your work for future reference.
6.5. Seek Expert Assistance
If you are unsure about how to diagnose or repair a problem in a proprietary system, seek expert assistance. Contact the manufacturer’s technical support line or consult with a qualified technician who has experience working with the system.
7. The Importance of Training and Certification
Proper training and certification are essential for technicians working with modern vehicles and their complex diagnostic systems. Here’s why:
7.1. Understanding Complex Systems
Modern vehicles incorporate a vast array of electronic systems and sensors. Training programs provide technicians with the knowledge needed to understand these complex systems and how they interact.
7.2. Mastering Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools have become increasingly sophisticated, offering a wide range of features and capabilities. Training programs teach technicians how to effectively use these tools to diagnose and repair vehicle problems.
7.3. Keeping Up with Technology
Automotive technology is constantly evolving, with new systems and features being introduced regularly. Training programs help technicians stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices.
7.4. Industry Certifications
Certifications like those offered by ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) demonstrate a technician’s competence and commitment to quality. These certifications are often required by employers and can enhance a technician’s career prospects.
7.5. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Training Programs
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs designed to equip technicians with the skills and knowledge needed to diagnose and repair Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our programs cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Systems
- Proprietary DTC Interpretation
- Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- Use of Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tools
8. Real-World Examples of DTCs in Action
To illustrate the concepts discussed, let’s look at some real-world examples of DTCs in action:
8.1. Example 1: P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- Description: This standardized DTC indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in one or more cylinders.
- Proprietary Information: Manufacturer-specific data can provide more detail about the conditions under which the misfires are occurring, such as engine speed, load, and temperature.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check for any obvious mechanical problems, such as vacuum leaks or faulty spark plugs.
- Use a scan tool to monitor misfire counts for each cylinder.
- Perform a compression test to check for cylinder problems.
- Analyze freeze frame data to understand the conditions under which the misfire occurred.
- Solution: Based on the diagnostic findings, repair or replace the faulty components.
8.2. Example 2: U0100 – Lost Communication With ECM/PCM “A”
- Description: This standardized DTC indicates a loss of communication with the engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control module (PCM).
- Proprietary Information: Manufacturer-specific data can provide more detail about the specific communication bus that is affected and the other modules that are impacted.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check the wiring and connections to the ECM/PCM.
- Use a scan tool to check for other communication-related DTCs.
- Perform a network communication test to identify any problems with the vehicle’s communication bus.
- Consult the manufacturer’s service information for troubleshooting procedures.
- Solution: Based on the diagnostic findings, repair or replace the faulty wiring, connections, or modules.
8.3. Example 3: C1000 – Hydraulic Pump Motor Faulty
- Description: This code indicates a fault with the hydraulic pump motor, often related to braking or steering systems.
- Proprietary Information: Additional data might include specific voltage readings or resistance measurements that help pinpoint the electrical or mechanical failure.
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check the hydraulic fluid level and condition.
- Inspect the hydraulic pump motor for physical damage.
- Test the electrical connections and wiring to the pump motor.
- Use a diagnostic tool to monitor the pump motor’s performance.
- Solution: Depending on the diagnosis, either repair or replace the hydraulic pump motor.
9. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Supports Your Diagnostic Needs
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of diagnosing modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles. That’s why we offer a range of services and solutions to support your diagnostic needs:
9.1. Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
We provide a wide selection of high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our tools are capable of reading and interpreting both standardized and manufacturer-specific DTCs, as well as accessing proprietary data and performing advanced diagnostic procedures.
9.2. Diagnostic Software
Our diagnostic software provides access to the latest Mercedes-Benz diagnostic information, including DTC descriptions, troubleshooting procedures, and repair information. Our software is regularly updated to ensure that you always have access to the most current data.
9.3. Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide technical support and assistance with your diagnostic needs. We can help you troubleshoot complex problems, interpret DTCs, and perform advanced diagnostic procedures.
9.4. Training Programs
We offer specialized training programs designed to equip technicians with the skills and knowledge needed to diagnose and repair Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our programs cover a wide range of topics, including Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems, proprietary DTC interpretation, advanced diagnostic procedures, and the use of Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools.
9.5. Remote Diagnostic Services
Our remote diagnostic services allow you to access our expertise and diagnostic tools remotely. This can be particularly useful for vehicles that are located in remote areas or for problems that are difficult to diagnose in person.
10. Addressing Customer Challenges
Understanding the challenges faced by our customers is paramount to providing effective solutions. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we recognize these common difficulties:
10.1. Difficulty in Finding Suitable Diagnostic Tools
Many vehicle owners and technicians struggle to find diagnostic tools that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and capable of accessing proprietary data.
Our Solution: We offer a curated selection of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ensuring compatibility and access to proprietary data.
10.2. Uncertainty About Unlocking Hidden Features
The process of unlocking hidden features on Mercedes-Benz vehicles can be complex and risky, leading to uncertainty and hesitation.
Our Solution: We provide detailed, step-by-step guides and expert support to help you safely and effectively unlock hidden features on your Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
10.3. Need for Clear Repair and Maintenance Guidance
Many vehicle owners lack the knowledge and skills needed to perform basic repairs and maintenance on their Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
Our Solution: We offer clear, easy-to-follow repair and maintenance guides that empower you to perform basic tasks and save money on costly repairs.
10.4. Concerns About High Repair Costs at Dealerships
Repair costs at dealerships can be prohibitively expensive, leading many vehicle owners to seek alternative solutions.
Our Solution: We provide access to affordable diagnostic tools, repair guides, and technical support, enabling you to diagnose and repair your Mercedes-Benz vehicle at a fraction of the cost of dealership repairs.
10.5. Call to Action
Don’t let complex diagnostic challenges hold you back. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on selecting the right diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and performing essential repairs and maintenance on your Mercedes-Benz.
Contact Information:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)?
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a code used in vehicle diagnostics to identify specific faults or malfunctions detected by the vehicle’s onboard computer system.
2. Are standardized DTC formats still relevant?
Yes, standardized DTC formats are still relevant for basic diagnostics, regulatory compliance, and as a foundation for advanced diagnostics.
3. What are proprietary systems in modern vehicles?
Proprietary systems are unique software, hardware, and communication protocols developed by individual vehicle manufacturers.
4. How do proprietary systems challenge standardized DTCs?
Proprietary systems can challenge standardized DTCs by limiting coverage, providing inaccurate interpretations, and causing compatibility issues with diagnostic tools.
5. How can standardized DTCs be enhanced with proprietary information?
Standardized DTCs can be enhanced with manufacturer-specific DTCs, enhanced diagnostic tools, access to manufacturer databases, and data logging and analysis.
6. What are some future trends in automotive diagnostics?
Future trends in automotive diagnostics include over-the-air (OTA) updates, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), remote diagnostics, predictive diagnostics, and cybersecurity measures.
7. What are some best practices for working with DTCs in proprietary systems?
Best practices include staying updated with the latest information, using high-quality diagnostic tools, following manufacturer procedures, documenting your work, and seeking expert assistance.
8. What is the importance of training and certification for technicians?
Training and certification are essential for technicians to understand complex systems, master diagnostic tools, keep up with technology, and demonstrate competence.
9. How can MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN support my diagnostic needs?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers diagnostic tools and equipment, diagnostic software, technical support, training programs, and remote diagnostic services.
10. How do I contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for assistance?
You can contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or through our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
By addressing these questions, we aim to provide clarity and build trust with our audience, positioning MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN as a reliable source of information and support.
In conclusion, while proprietary systems present challenges to standardized DTC formats, the latter remain crucial for basic diagnostics and regulatory compliance. By enhancing standardized DTCs with proprietary information and utilizing advanced diagnostic tools, technicians and vehicle owners can effectively diagnose and repair even the most complex problems. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing the expertise, tools, and support needed to navigate this complex landscape and keep your Mercedes-Benz vehicle running smoothly. Embrace the future of automotive diagnostics with confidence and precision, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and longevity.