What Are Typical Live Data Values For Mercedes Brake Pad Wear Sensor Parameters? Understanding these values is critical for diagnosing brake issues effectively. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed insights into Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, helping you interpret live data and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Enhance your diagnostic capabilities with our resources, focusing on sensor readings, brake system analysis, and Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Brake Pad Wear Sensors in Mercedes Vehicles
- 1.1. The Role of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
- 1.2. Types of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
- 1.3. Importance of Monitoring Sensor Data
- 2. Typical Live Data Values for Brake Pad Wear Sensors
- 2.1. Understanding Resistance Values
- 2.2. Voltage Readings
- 2.3. Interpreting Digital Signals
- 3. Factors Affecting Live Data Values
- 3.1. Vehicle Model and Year
- 3.2. Sensor Type
- 3.3. Environmental Conditions
- 3.4. Brake System Condition
- 4. Using Diagnostic Tools to Read Live Data
- 4.1. OBD-II Scanners
- 4.2. Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Tools
- 4.3. Steps to Read Live Data
- 5. Diagnosing Common Issues Using Live Data
- 5.1. Identifying Worn Brake Pads
- 5.2. Detecting Uneven Wear
- 5.3. Troubleshooting Sensor Malfunctions
- 5.4. Case Studies
- 6. Maintenance and Prevention
- 6.1. Regular Inspections
- 6.2. Proper Installation
- 6.3. Use Quality Parts
- 6.4. Cleaning and Lubrication
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 7.1. Oscilloscope Testing
- 7.2. Voltage Drop Testing
- 7.3. Insulation Testing
- 8. The Future of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
- 8.1. Wireless Sensors
- 8.2. Predictive Maintenance
- 8.3. Integration with ADAS
- 9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- 9.1. Case Study 1: The Mysterious Warning Light
- 9.2. Case Study 2: The Overzealous Sensor
- 9.3. Case Study 3: The Silent Failure
- 10. The Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 10.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Information
- 10.2. Expert Support
- 10.3. Community Forum
- 10.4. Up-to-Date Information
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: What is the typical lifespan of brake pad wear sensors in Mercedes vehicles?
- Q2: Can I replace brake pad wear sensors myself?
- Q3: How do I reset the brake pad wear sensor warning light after replacing the sensors?
- Q4: Are there any aftermarket brake pad wear sensors that you recommend?
- Q5: What should I do if my diagnostic tool is not compatible with my Mercedes vehicle?
- Q6: How can I test the brake pad wear sensor to see if it is functioning correctly?
- Q7: Can incorrect tire pressure affect brake pad wear sensor readings?
- Q8: What are the symptoms of a failing brake pad wear sensor?
- Q9: How often should I check my brake pad wear sensor?
- Q10: Where can I find reliable information about specific live data values for my Mercedes model?
1. Understanding Brake Pad Wear Sensors in Mercedes Vehicles
Brake pad wear sensors in Mercedes-Benz vehicles are essential components designed to alert drivers when their brake pads are nearing the end of their service life. These sensors are integrated into the brake system and provide real-time data about the condition of the brake pads. Monitoring this data is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and preventing potential damage to the braking system.
1.1. The Role of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
The primary role of brake pad wear sensors is to monitor the thickness of the brake pads and send a signal to the vehicle’s onboard computer when the pads reach a predetermined wear limit. This signal triggers a warning light on the dashboard, alerting the driver to replace the brake pads.
1.2. Types of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
Mercedes-Benz vehicles typically use two types of brake pad wear sensors:
- Mechanical Sensors: These sensors use a simple electrical circuit that is completed when the brake pad wears down to a point where the sensor comes into contact with the brake rotor.
- Electronic Sensors: These more advanced sensors continuously monitor the resistance in the sensor circuit, providing more accurate and nuanced wear data.
1.3. Importance of Monitoring Sensor Data
Monitoring the live data from brake pad wear sensors allows technicians and vehicle owners to:
- Identify Wear Patterns: Detect uneven wear on brake pads, which can indicate other underlying issues in the braking system.
- Predict Maintenance Needs: Accurately predict when brake pad replacement will be necessary, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Ensure Safety: Maintain optimal braking performance and prevent potential safety hazards associated with worn brake pads.
2. Typical Live Data Values for Brake Pad Wear Sensors
Interpreting live data from Mercedes brake pad wear sensors requires an understanding of the expected values under normal operating conditions. These values can vary depending on the type of sensor and the specific vehicle model.
2.1. Understanding Resistance Values
Electronic brake pad wear sensors operate by measuring the resistance in an electrical circuit. The typical resistance values can be interpreted as follows:
- High Resistance (Open Circuit): Indicates that the brake pad is in good condition and has not worn down to the sensor.
- Low Resistance (Closed Circuit): Indicates that the brake pad has worn down to the sensor, and the warning light has been triggered.
- Fluctuating Resistance: May indicate a faulty sensor or an intermittent connection.
2.2. Voltage Readings
In some Mercedes models, the brake pad wear sensor data is presented as voltage readings. Typical voltage ranges are:
- Normal Condition: A voltage close to the system voltage (e.g., 12V) indicates that the brake pad is in good condition.
- Worn Condition: A significant drop in voltage, often to near 0V, indicates that the brake pad has worn down and the sensor is making contact with the rotor.
2.3. Interpreting Digital Signals
Some advanced systems use digital signals to communicate the brake pad wear status. These signals can be interpreted as follows:
- Active Signal: Indicates that the brake pad is within the acceptable wear range.
- Inactive Signal: Indicates that the brake pad has reached the wear limit and needs replacement.
3. Factors Affecting Live Data Values
Several factors can influence the live data values reported by Mercedes brake pad wear sensors. Understanding these factors is essential for accurate diagnostics.
3.1. Vehicle Model and Year
The specific values and types of sensors used can vary significantly between different Mercedes-Benz models and model years. Always consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable diagnostic database like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for accurate information.
3.2. Sensor Type
As mentioned earlier, the type of sensor (mechanical or electronic) will affect the type of data provided. Mechanical sensors typically provide a simple on/off signal, while electronic sensors offer more detailed resistance or voltage readings.
3.3. Environmental Conditions
Extreme temperatures and moisture can affect the performance of brake pad wear sensors. Corrosion and damage to the sensor can also lead to inaccurate readings.
3.4. Brake System Condition
The overall condition of the braking system, including the brake rotors and calipers, can impact sensor readings. For example, a warped rotor can cause uneven brake pad wear, leading to premature sensor activation.
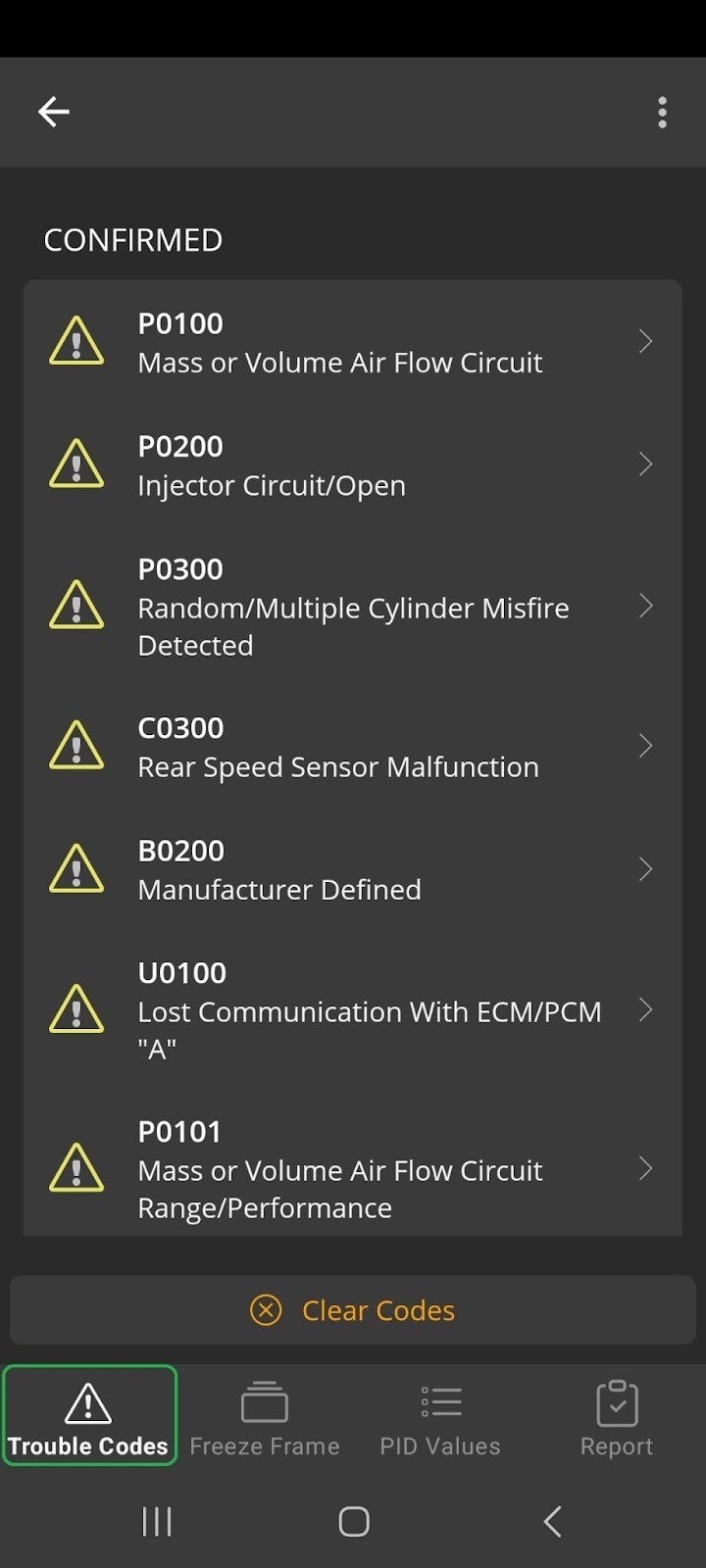
4. Using Diagnostic Tools to Read Live Data
To effectively monitor brake pad wear sensor data, it is necessary to use appropriate diagnostic tools. These tools allow you to access the vehicle’s onboard computer and view the live data stream from the sensors.
4.1. OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanners are widely used tools for accessing vehicle diagnostic information. While basic OBD-II scanners can read generic fault codes, more advanced scanners are required to access specific sensor data for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
4.2. Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Tools
Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools, such as the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system, offer more comprehensive access to vehicle data. These tools can read live data from all sensors, perform advanced diagnostics, and even program control units. You can find more information about suitable tools at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
4.3. Steps to Read Live Data
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Power On: Turn on the vehicle’s ignition without starting the engine.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the vehicle’s make, model, and year into the diagnostic tool.
- Access Live Data: Navigate to the live data or parameter identification (PID) section of the diagnostic tool.
- Select Brake Pad Wear Sensor: Choose the brake pad wear sensor from the list of available sensors.
- Monitor Data: Observe the live data values, paying attention to resistance, voltage, or digital signal readings.
5. Diagnosing Common Issues Using Live Data
Live data from brake pad wear sensors can be used to diagnose a variety of common issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
5.1. Identifying Worn Brake Pads
The most common use of live data is to confirm whether the brake pads have worn down to the replacement limit. A low resistance or voltage reading, or an inactive digital signal, indicates that the brake pads need to be replaced.
5.2. Detecting Uneven Wear
By comparing the live data from the brake pad wear sensors on different wheels, you can identify uneven wear patterns. This can indicate issues such as:
- Sticking Caliper: A caliper that is not releasing properly can cause excessive wear on one brake pad.
- Faulty Brake Hose: A restricted brake hose can prevent proper brake engagement, leading to uneven wear.
- Suspension Issues: Worn suspension components can affect wheel alignment, causing uneven brake pad wear.
5.3. Troubleshooting Sensor Malfunctions
If the live data from a brake pad wear sensor is erratic or inconsistent, it may indicate a sensor malfunction. Common causes of sensor failure include:
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can corrode the sensor and its wiring.
- Physical Damage: The sensor can be damaged by debris or during brake maintenance.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or disconnected wiring can prevent the sensor from transmitting accurate data.
5.4. Case Studies
Consider these examples to illustrate how live data can be used in diagnostics:
- Case Study 1: Premature Warning Light: A Mercedes-Benz C-Class owner reported that the brake pad warning light came on prematurely. Live data showed that the front left brake pad sensor was indicating a worn condition, while the other sensors showed normal readings. Upon inspection, it was found that the front left caliper was sticking, causing excessive wear on that brake pad.
- Case Study 2: Intermittent Warning Light: A Mercedes-Benz E-Class owner experienced an intermittent brake pad warning light. Live data showed fluctuating resistance values from the rear right brake pad sensor. Further investigation revealed that the sensor wiring was corroded, causing an intermittent connection.
- Case Study 3: No Warning Light: A Mercedes-Benz S-Class owner noticed that the brake pads were severely worn, but the warning light never came on. Live data showed that all brake pad sensors were reporting normal readings, even though the pads were dangerously thin. It was determined that the sensors had been disconnected during a previous brake service and were never reconnected.
 Brake Pad Wear Sensor
Brake Pad Wear Sensor
6. Maintenance and Prevention
Proper maintenance and preventative measures can help ensure the accuracy and reliability of Mercedes brake pad wear sensors.
6.1. Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect the brake pads and sensors for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Check the wiring and connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
6.2. Proper Installation
When replacing brake pads or sensors, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Ensure that the sensors are properly installed and connected to the wiring harness.
6.3. Use Quality Parts
Use high-quality brake pads and sensors that are designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Inferior parts may not provide accurate data and can lead to premature failure. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN recommends using OEM or equivalent quality parts for optimal performance.
6.4. Cleaning and Lubrication
Clean the brake pad wear sensors and their connections periodically to remove dirt, debris, and corrosion. Apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the connections to prevent future corrosion.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For complex brake system issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to accurately identify the root cause.
7.1. Oscilloscope Testing
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the electrical signals from the brake pad wear sensors. This can help identify intermittent faults or signal distortions that may not be apparent with a standard diagnostic tool.
7.2. Voltage Drop Testing
Voltage drop testing can be used to identify excessive resistance in the sensor wiring. This involves measuring the voltage drop across the wiring while the circuit is active. A high voltage drop indicates excessive resistance, which can affect sensor performance.
7.3. Insulation Testing
Insulation testing can be used to identify shorts to ground in the sensor wiring. This involves applying a high voltage to the wiring and measuring the leakage current. A high leakage current indicates a short to ground.
8. The Future of Brake Pad Wear Sensors
The technology behind brake pad wear sensors is constantly evolving. Future sensors are likely to be more accurate, reliable, and integrated with advanced vehicle systems.
8.1. Wireless Sensors
Wireless brake pad wear sensors are being developed to eliminate the need for physical wiring. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to the vehicle’s onboard computer, reducing the risk of wiring damage and corrosion.
8.2. Predictive Maintenance
Future brake pad wear sensors may be integrated with predictive maintenance systems that use machine learning algorithms to predict when brake pad replacement will be necessary. These systems will take into account factors such as driving habits, environmental conditions, and vehicle usage patterns.
8.3. Integration with ADAS
Brake pad wear sensors may be integrated with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to provide real-time information about brake system performance. This information can be used to enhance the performance of ADAS features such as automatic emergency braking and adaptive cruise control.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
To further illustrate the importance of understanding live data values for Mercedes brake pad wear sensor parameters, let’s delve into some real-world case studies. These examples highlight common issues, diagnostic approaches, and effective solutions.
9.1. Case Study 1: The Mysterious Warning Light
- Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz C300
- Complaint: The owner reported that the brake pad warning light illuminated intermittently, even though the brake pads appeared to have sufficient thickness.
- Diagnostic Approach: Using a Mercedes-specific diagnostic tool, the technician accessed the live data for all four brake pad wear sensors. The readings from three sensors were consistent, indicating normal pad thickness. However, the front passenger side sensor showed fluctuating resistance values.
- Findings: Upon closer inspection, the technician discovered that the sensor wiring was chafing against the wheel well, causing an intermittent short circuit.
- Solution: The technician repaired the damaged wiring and secured it properly to prevent future chafing. The brake pad warning light issue was resolved, and the owner was spared the unnecessary expense of replacing the brake pads.
9.2. Case Study 2: The Overzealous Sensor
- Vehicle: 2020 Mercedes-Benz E350
- Complaint: The owner received a brake pad replacement notification from the vehicle’s onboard system, despite having recently replaced the brake pads.
- Diagnostic Approach: The technician connected a diagnostic tool and reviewed the live data from the brake pad wear sensors. The readings indicated that all sensors were reporting a “worn” condition, which was inconsistent with the recent replacement.
- Findings: The technician discovered that the sensors had not been properly reset after the brake pad replacement.
- Solution: The technician used the diagnostic tool to reset the brake pad wear sensors. The system then recognized the new brake pads, and the warning message disappeared. This saved the owner from a potential misdiagnosis and unnecessary service.
9.3. Case Study 3: The Silent Failure
- Vehicle: 2016 Mercedes-Benz S550
- Complaint: The owner noticed a grinding noise while braking but received no warning from the vehicle’s system.
- Diagnostic Approach: The technician inspected the brake pads and found that they were severely worn, with minimal friction material remaining. The technician then accessed the live data from the brake pad wear sensors.
- Findings: All sensors reported normal readings, indicating that they were not functioning correctly. Further inspection revealed that the sensors had been installed incorrectly during a previous brake service, preventing them from making contact with the rotors when the pads wore down.
- Solution: The technician replaced the brake pads and properly installed new brake pad wear sensors. The grinding noise disappeared, and the system was now able to accurately monitor the condition of the brake pads.
10. The Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Understanding the nuances of Mercedes-Benz diagnostics can be challenging, but MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help.
10.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Information
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems, including detailed explanations of live data values, troubleshooting guides, and repair procedures.
10.2. Expert Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance. Whether you have a question about a specific diagnostic code or need help troubleshooting a complex issue, we are here to assist you.
10.3. Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and technicians. Share your experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
10.4. Up-to-Date Information
We are committed to providing the latest information on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic systems. Our content is regularly updated to reflect the latest technologies and repair procedures.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions related to Mercedes brake pad wear sensor parameters and their live data values:
Q1: What is the typical lifespan of brake pad wear sensors in Mercedes vehicles?
The lifespan of brake pad wear sensors typically matches the lifespan of the brake pads themselves. Generally, they should be replaced whenever the brake pads are replaced to ensure accurate readings.
Q2: Can I replace brake pad wear sensors myself?
Yes, you can replace brake pad wear sensors yourself if you have the necessary tools and experience. However, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take necessary safety precautions. If you’re not comfortable performing the replacement, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
Q3: How do I reset the brake pad wear sensor warning light after replacing the sensors?
The procedure for resetting the warning light varies depending on the Mercedes model. Some models require a diagnostic tool to reset the system, while others can be reset through the vehicle’s onboard computer. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for specific instructions.
Q4: Are there any aftermarket brake pad wear sensors that you recommend?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN recommends using OEM or equivalent quality brake pad wear sensors to ensure accurate readings and reliable performance. Some reputable aftermarket brands include Bosch, ATE, and Brembo.
Q5: What should I do if my diagnostic tool is not compatible with my Mercedes vehicle?
Ensure that your diagnostic tool is designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles and supports the specific model and year of your car. If your tool is not compatible, consider upgrading to a Mercedes-specific diagnostic tool like the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
Q6: How can I test the brake pad wear sensor to see if it is functioning correctly?
You can test the sensor using a multimeter to check for continuity. A functioning sensor should show an open circuit when the brake pad is not worn and a closed circuit when the pad is worn.
Q7: Can incorrect tire pressure affect brake pad wear sensor readings?
While incorrect tire pressure primarily affects tire wear, it can indirectly impact brake pad wear. Uneven tire wear can lead to imbalances in the braking system, potentially causing one brake pad to wear more quickly than the others. Regularly check and maintain proper tire pressure to promote even brake wear.
Q8: What are the symptoms of a failing brake pad wear sensor?
Symptoms of a failing brake pad wear sensor include:
Illuminated brake pad warning light
Intermittent warning light
Inaccurate readings
No warning light when brake pads are worn
Q9: How often should I check my brake pad wear sensor?
You should check your brake pad wear sensors during every routine brake inspection, which should be performed at least once a year or every 10,000 to 12,000 miles.
Q10: Where can I find reliable information about specific live data values for my Mercedes model?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is an excellent resource for finding reliable information about specific live data values for your Mercedes model. Additionally, consult your vehicle’s service manual or a trusted Mercedes-Benz technician.
Understanding typical live data values for Mercedes brake pad wear sensor parameters is crucial for effective diagnostics and maintenance. By using the information and resources provided by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz vehicle’s braking system remains in optimal condition. For expert assistance and personalized advice, contact us today!
Contact us:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t wait until it’s too late—ensure your Mercedes-Benz is performing at its best with our diagnostic expertise!