The 1998 Ford Explorer Obd2 Location is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side; MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert guidance for locating and utilizing your OBD2 port effectively. Understanding its location helps streamline diagnostics, promoting efficient vehicle maintenance and repair. Explore OBD II protocols, diagnostic troubleshooting, and automotive computer systems for comprehensive car care.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) System
- The Role of OBD2 in Modern Vehicles
- Key Components Monitored by OBD2
- Benefits of Using the OBD2 System
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 1998 Ford Explorer
- Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
- Common Locations and Identifying Features
- Tips for Easy Access
- 3. Why is the OBD2 Port Location Important?
- Facilitating Vehicle Diagnostics
- Reading Trouble Codes
- Ensuring Proper Maintenance
- Benefits of Knowing the Location
- 4. How to Use the OBD2 Port with a Diagnostic Scanner
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Diagnostic Scanner
- Types of Diagnostic Scanners
- Interpreting the Data
- Tips for Accurate Diagnostics
- 5. Common Issues Diagnosed via the OBD2 Port
- Engine Misfires
- Oxygen Sensor Failures
- Catalytic Converter Problems
- Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) System Issues
- Transmission Problems
- Other Common Issues
- 6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Your 1998 Ford Explorer
- Top OBD2 Scanners for the 1998 Ford Explorer
- Features to Look for in a Scanner
- Benefits of Using a Quality Scanner
- 7. Interpreting OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Understanding the Structure of DTCs
- Using a Code Database
- Troubleshooting Steps
- Example DTC Interpretation
- 8. Advanced Diagnostics and the OBD2 Port
- Bi-Directional Control
- Component Testing
- Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- Using Live Data
- Benefits of Advanced Diagnostics
- 9. DIY vs. Professional Diagnostics: Making the Right Choice
- When to Consider DIY Diagnostics
- When to Seek Professional Help
- Benefits of Professional Diagnostics
- DIY Diagnostic Tools You Might Need
- 10. Maintaining Your 1998 Ford Explorer’s OBD2 System
- Keeping the OBD2 Port Clean
- Checking for Software Updates
- Addressing Issues Promptly
- Regular Scanning
- Benefits of Maintaining the OBD2 System
- 11. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
- Enhanced Data Analytics
- Remote Diagnostics
- Integration with Smart Devices
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Benefits of Future Diagnostic Systems
- 12. FAQ about the 1998 Ford Explorer OBD2 Port
- Where is the OBD2 port located on a 1998 Ford Explorer?
- What type of OBD2 scanner should I use for my 1998 Ford Explorer?
- How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) on my 1998 Ford Explorer?
- Can I clear the check engine light using an OBD2 scanner?
- What are some common issues that can be diagnosed via the OBD2 port?
- Is it safe to drive my 1998 Ford Explorer with the check engine light on?
- How often should I scan my vehicle for diagnostic trouble codes?
- Can I use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner with my 1998 Ford Explorer?
- What is bi-directional control, and why is it useful?
- Where can I find more information about OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes?
- 13. Need Expert Assistance? Contact Us
- How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
- Contact Information
Table of Contents
- Understanding the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) System
- Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 1998 Ford Explorer
- Why is the OBD2 Port Location Important?
- How to Use the OBD2 Port with a Diagnostic Scanner
- Common Issues Diagnosed via the OBD2 Port
- OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Your 1998 Ford Explorer
- Interpreting OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Advanced Diagnostics and the OBD2 Port
- DIY vs. Professional Diagnostics: Making the Right Choice
- Maintaining Your 1998 Ford Explorer’s OBD2 System
- The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
- FAQ about the 1998 Ford Explorer OBD2 Port
- Need Expert Assistance? Contact Us
1. Understanding the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) System
What is the OBD2 system, and why is it important for your 1998 Ford Explorer? The On-Board Diagnostics version 2 (OBD2) system is a standardized system implemented in vehicles in 1996 for monitoring and diagnosing various vehicle systems, mandated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to ensure vehicles meet emissions standards. This system is essential for modern car maintenance because it provides real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that can help identify issues early, which can prevent costly repairs and improve vehicle performance.
The Role of OBD2 in Modern Vehicles
OBD2’s primary function is to monitor the performance of the engine, transmission, and other systems related to emissions. When the system detects a problem, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and may illuminate the check engine light on the dashboard. This alerts the driver to a potential issue that needs attention.
Key Components Monitored by OBD2
The OBD2 system monitors a wide range of components, including:
- Engine: Monitors sensors such as the oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensor, and crankshaft position sensor.
- Transmission: Monitors the transmission’s performance, including gear shifting and fluid temperature.
- Emissions System: Checks components like the catalytic converter, EGR valve, and EVAP system.
- Fuel System: Monitors fuel injectors, fuel pressure, and fuel trim levels.
Benefits of Using the OBD2 System
Using the OBD2 system offers several benefits:
- Early Issue Detection: Identifies problems before they become severe, reducing the risk of major breakdowns.
- Cost Savings: Allows for timely repairs, preventing more expensive damage in the future.
- Improved Performance: Helps maintain optimal vehicle performance by ensuring all systems are functioning correctly.
- Emissions Compliance: Ensures your vehicle meets environmental regulations, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
2. Locating the OBD2 Port in Your 1998 Ford Explorer
Where can you find the OBD2 port in a 1998 Ford Explorer? The OBD2 port in a 1998 Ford Explorer is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. This standardized location makes it easily accessible for technicians and vehicle owners to plug in diagnostic scanners and retrieve valuable data about the vehicle’s performance. Knowing the precise location helps in quickly diagnosing issues, ensuring timely and effective repairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBD2 Port
Follow these steps to locate the OBD2 port in your 1998 Ford Explorer:
- Check Under the Dashboard: Kneel down and look under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Locate the Port: The OBD2 port is usually near the steering column or slightly to the left.
- Identify the Shape: The port is a 16-pin trapezoidal connector.
- Use a Flashlight: If the area is dark, use a flashlight to illuminate the space and make the port more visible.
Common Locations and Identifying Features
- Typical Placement: Under the dashboard, driver’s side
- Shape: 16-pin trapezoidal connector
- Color: Usually black, but can vary
- Accessibility: Generally easy to access without tools
Tips for Easy Access
- Clear the Area: Remove any obstructions that might be blocking access to the port.
- Good Lighting: Ensure the area is well-lit to easily see the port.
- Flexible Neck Flashlight: Use a flashlight with a flexible neck to direct light exactly where you need it.
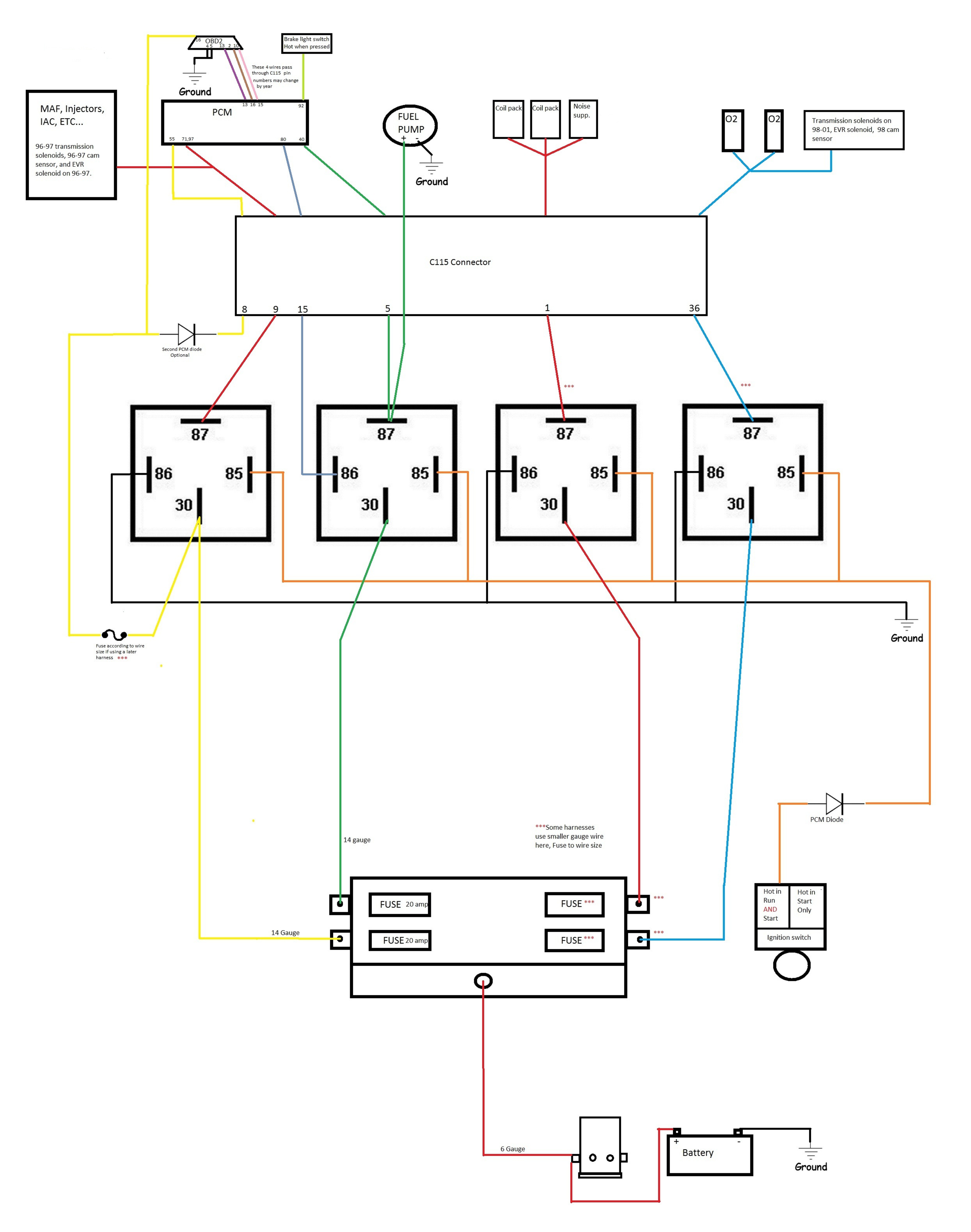 Ford Explorer OBD2 Port Location
Ford Explorer OBD2 Port Location
3. Why is the OBD2 Port Location Important?
Why is it essential to know the OBD2 port location in your 1998 Ford Explorer? Knowing the OBD2 port location is crucial for performing vehicle diagnostics, reading trouble codes, and ensuring proper maintenance, which can help prevent minor issues from escalating into major, costly repairs. Quick access to this port saves time and enables timely interventions, keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Facilitating Vehicle Diagnostics
The OBD2 port serves as the gateway to your vehicle’s computer system. Knowing its location allows you to quickly connect a diagnostic scanner and retrieve data about your vehicle’s performance.
Reading Trouble Codes
When your check engine light comes on, the OBD2 system stores diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Accessing the OBD2 port allows you to read these codes, providing valuable information about the nature of the problem.
Ensuring Proper Maintenance
Regularly checking your vehicle’s diagnostics through the OBD2 port can help you stay on top of maintenance needs. Early detection of issues can prevent minor problems from turning into major, costly repairs.
Benefits of Knowing the Location
- Time-Saving: Quickly locate the port without needing to search, saving time during diagnostics.
- Convenience: Perform diagnostics at home, avoiding trips to the mechanic for simple issues.
- Cost-Effective: Identify and address problems early, preventing expensive repairs.
4. How to Use the OBD2 Port with a Diagnostic Scanner
How do you effectively use the OBD2 port with a diagnostic scanner on your 1998 Ford Explorer? To use the OBD2 port, plug a compatible diagnostic scanner into the port, turn on the ignition without starting the engine, and follow the scanner’s prompts to read and interpret any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Understanding this process allows for quick and accurate vehicle diagnostics, facilitating timely maintenance and repairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Diagnostic Scanner
Follow these steps to use the OBD2 port with a diagnostic scanner:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the diagnostic scanner to the OBD2 port. Ensure it is securely plugged in.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the diagnostic scanner. It should power up and connect to the vehicle’s computer.
- Follow Prompts: Follow the scanner’s prompts to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and view live data.
Types of Diagnostic Scanners
There are several types of diagnostic scanners available:
- Basic Code Readers: These scanners read and clear DTCs, providing basic diagnostic information.
- Mid-Range Scanners: Offer additional features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and enhanced code definitions.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: Provide advanced diagnostics, including bi-directional control, component testing, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
Interpreting the Data
After scanning your vehicle, the diagnostic scanner will display any stored DTCs. These codes provide information about the specific problem detected by the OBD2 system. Refer to a code database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code and the potential causes of the issue.
Tips for Accurate Diagnostics
- Use a Reliable Scanner: Invest in a high-quality diagnostic scanner for accurate and reliable results.
- Consult Repair Manuals: Use repair manuals and online resources to understand DTCs and troubleshooting steps.
- Clear Codes Carefully: After addressing the identified issues, clear the DTCs and monitor if they return.
5. Common Issues Diagnosed via the OBD2 Port
What common issues can be diagnosed using the OBD2 port in your 1998 Ford Explorer? The OBD2 port is instrumental in diagnosing various common issues, including engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, catalytic converter problems, and issues with the evaporative emission control (EVAP) system. Early detection and diagnosis of these issues through the OBD2 port can prevent further damage and ensure your vehicle runs efficiently.
Engine Misfires
Engine misfires occur when one or more cylinders fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly. This can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks.
Oxygen Sensor Failures
Oxygen sensors monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. Faulty oxygen sensors can lead to poor fuel economy, increased emissions, and engine performance issues.
Catalytic Converter Problems
The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less toxic substances. Issues with the catalytic converter can result in increased emissions and reduced engine performance.
Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) System Issues
The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Problems with the EVAP system can trigger the check engine light and may indicate leaks or faulty components.
Transmission Problems
While less common, the OBD2 system can also detect issues with the transmission, such as incorrect gear ratios or solenoid failures.
Other Common Issues
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Problems: Affects the air-fuel mixture and engine performance.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Issues: Impacts throttle response and engine idle.
- Fuel Injector Problems: Can cause poor fuel economy and engine misfires.
 Diagnosing Car Issues with OBD2 Port
Diagnosing Car Issues with OBD2 Port
6. OBD2 Scanner Recommendations for Your 1998 Ford Explorer
Which OBD2 scanners are best recommended for use with your 1998 Ford Explorer? For a 1998 Ford Explorer, recommended OBD2 scanners include the Innova 3100j, known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, and the BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool, which offers advanced features and real-time data monitoring via a smartphone app. Choosing a reliable scanner ensures accurate and efficient vehicle diagnostics, helping maintain optimal performance.
Top OBD2 Scanners for the 1998 Ford Explorer
- Innova 3100j: A popular choice known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: Offers advanced features and real-time data monitoring via a smartphone app.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A professional-grade scanner with bi-directional control and advanced diagnostic functions.
- ScanTool OBDLink MX+: Provides fast and accurate data, compatible with various devices and software.
- Actron CP9600: An affordable option that reads and clears codes, displays live data, and offers code definitions.
Features to Look for in a Scanner
- Code Reading and Clearing: Essential for diagnosing and resolving issues.
- Live Data Streaming: Allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is triggered, helping diagnose intermittent problems.
- Enhanced Code Definitions: Provides detailed explanations of DTCs.
- Bi-Directional Control: Enables you to control and test vehicle components.
- Compatibility: Ensures the scanner is compatible with your 1998 Ford Explorer.
Benefits of Using a Quality Scanner
- Accurate Diagnostics: Provides reliable and accurate diagnostic information.
- Time Savings: Helps you quickly identify and address issues, saving time on repairs.
- Cost-Effective: Prevents costly repairs by detecting problems early.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy to use, even for beginners.
7. Interpreting OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
How do you interpret OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) retrieved from your 1998 Ford Explorer? Interpreting OBD2 DTCs involves using a diagnostic scanner to read the codes, consulting a reliable code database to understand their meanings, and then systematically troubleshooting the potential causes. Proper interpretation of these codes is vital for accurately diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues, ensuring effective and timely repairs.
Understanding the Structure of DTCs
OBD2 DTCs are five-character codes that provide information about the nature and location of a problem. The structure of a DTC is as follows:
- First Character: Indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the subsystem (e.g., 1 for Fuel and Air Metering, 2 for Fuel and Air Metering – Injector Circuit).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specify the particular fault within the subsystem.
Using a Code Database
A code database is an essential tool for interpreting DTCs. These databases provide detailed descriptions of each code, potential causes, and troubleshooting steps. Some popular code databases include:
- OBD-Codes.com
- AutoCodes.com
- RepairPal.com
Troubleshooting Steps
After identifying the meaning of a DTC, follow these steps to troubleshoot the issue:
- Verify the Code: Confirm that the code is accurate and relevant to your vehicle.
- Gather Information: Research the potential causes of the code.
- Inspect Components: Visually inspect the related components for damage or wear.
- Test Components: Use diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the components.
- Repair or Replace: Repair or replace any faulty components.
- Clear the Code: Clear the DTC and monitor if it returns.
Example DTC Interpretation
Let’s consider the DTC P0171, which indicates “System Too Lean (Bank 1).”
- P: Powertrain
- 0: Generic Code
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 71: Specific Fault (System Too Lean)
Potential causes for P0171 include vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, MAF sensor problems, and fuel delivery issues.
8. Advanced Diagnostics and the OBD2 Port
How can you use advanced diagnostics with the OBD2 port on your 1998 Ford Explorer? Advanced diagnostics via the OBD2 port involves using professional-grade scanners to perform bi-directional control, component testing, and access manufacturer-specific codes, providing a deeper understanding of complex vehicle issues. Utilizing these advanced techniques ensures precise and thorough diagnostics, facilitating effective and targeted repairs.
Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and control specific components. This can be useful for testing actuators, solenoids, and other devices to verify their functionality.
Component Testing
Component testing involves using the diagnostic scanner to perform specific tests on individual components. This can help you identify whether a component is functioning correctly or needs to be replaced.
Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
In addition to generic OBD2 codes, manufacturers often have their own set of diagnostic codes that provide more detailed information about specific issues. Accessing these codes requires a professional-grade scanner that supports manufacturer-specific diagnostics.
Using Live Data
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components. This can be helpful for identifying intermittent problems or diagnosing issues that only occur under certain conditions.
Benefits of Advanced Diagnostics
- Precise Diagnostics: Provides a deeper understanding of complex vehicle issues.
- Targeted Repairs: Allows you to focus on the specific components that are causing problems.
- Time Savings: Reduces the time required to diagnose and repair vehicle issues.
- Cost-Effective: Prevents unnecessary repairs by accurately identifying the root cause of the problem.
 Advanced Car Diagnostics with OBD2 Port
Advanced Car Diagnostics with OBD2 Port
9. DIY vs. Professional Diagnostics: Making the Right Choice
When should you perform DIY diagnostics versus seeking professional help for your 1998 Ford Explorer? DIY diagnostics are suitable for reading and clearing basic codes and performing simple troubleshooting steps, while professional diagnostics are recommended for complex issues, manufacturer-specific codes, and advanced component testing. Making the right choice ensures accurate diagnostics and effective repairs, saving time and preventing potential damage.
When to Consider DIY Diagnostics
- Reading and Clearing Basic Codes: If your check engine light comes on and you want to read the code and understand the issue.
- Simple Troubleshooting Steps: If the code indicates a simple problem, such as a loose gas cap or a faulty sensor that you can easily replace.
- Performing Basic Maintenance: If you want to monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues early.
When to Seek Professional Help
- Complex Issues: If the code indicates a complex problem that requires advanced diagnostic skills and equipment.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: If the scanner displays manufacturer-specific codes that require specialized knowledge.
- Advanced Component Testing: If you need to perform bi-directional control, component testing, or other advanced diagnostic procedures.
- Uncertainty: If you are unsure about the cause of the problem or how to repair it.
Benefits of Professional Diagnostics
- Expertise: Professional technicians have the knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose and repair complex vehicle issues.
- Advanced Equipment: Professional shops have access to advanced diagnostic equipment and tools.
- Time Savings: Professionals can quickly diagnose and repair issues, saving you time and effort.
- Warranty: Many professional shops offer warranties on their repairs, providing peace of mind.
DIY Diagnostic Tools You Might Need
- OBD2 Scanner
- Multimeter
- Socket Set
- Wrench Set
- Repair Manual
10. Maintaining Your 1998 Ford Explorer’s OBD2 System
How do you maintain your 1998 Ford Explorer’s OBD2 system to ensure optimal performance? To maintain the OBD2 system, regularly check for software updates for your diagnostic scanner, keep the OBD2 port clean and free from debris, and address any detected issues promptly to prevent further damage. Regular maintenance ensures accurate and reliable diagnostics, helping keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Keeping the OBD2 Port Clean
Ensure the OBD2 port is clean and free from dirt, dust, and debris. Use a small brush or compressed air to gently clean the port if necessary.
Checking for Software Updates
Keep your diagnostic scanner’s software up to date. Manufacturers regularly release updates that improve functionality, add new features, and fix bugs.
Addressing Issues Promptly
Address any detected issues promptly to prevent further damage to your vehicle. Ignoring DTCs can lead to more expensive repairs in the future.
Regular Scanning
Regularly scan your vehicle for DTCs, even if the check engine light is not illuminated. This can help you identify potential problems early.
Benefits of Maintaining the OBD2 System
- Accurate Diagnostics: Ensures that your diagnostic scanner provides accurate and reliable information.
- Preventive Maintenance: Helps you identify and address potential problems early.
- Improved Performance: Keeps your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
- Cost Savings: Prevents costly repairs by addressing issues promptly.
11. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
What does the future hold for automotive diagnostics and the OBD2 system? The future of automotive diagnostics involves enhanced data analytics, remote diagnostics, and integration with smart devices, leading to more proactive and efficient vehicle maintenance. These advancements promise to improve vehicle performance, reduce downtime, and enhance the overall ownership experience.
Enhanced Data Analytics
Future diagnostic systems will leverage advanced data analytics to provide more detailed and accurate insights into vehicle performance. This will enable predictive maintenance, where potential problems are identified before they occur.
Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics will allow technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues remotely. This can be particularly useful for fleet management and roadside assistance.
Integration with Smart Devices
Future diagnostic systems will be seamlessly integrated with smartphones, tablets, and other smart devices. This will provide vehicle owners with real-time data and diagnostic information at their fingertips.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI will play a significant role in future diagnostic systems. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential issues.
Benefits of Future Diagnostic Systems
- Proactive Maintenance: Identifies potential problems before they occur.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: Optimizes vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Downtime: Minimizes downtime by quickly diagnosing and repairing issues.
- Enhanced Ownership Experience: Provides vehicle owners with greater control and insights into their vehicle’s performance.
12. FAQ about the 1998 Ford Explorer OBD2 Port
Where is the OBD2 port located on a 1998 Ford Explorer?
The OBD2 port on a 1998 Ford Explorer is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
What type of OBD2 scanner should I use for my 1998 Ford Explorer?
You can use a basic code reader, a mid-range scanner, or a professional-grade scanner, depending on your diagnostic needs.
How do I read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) on my 1998 Ford Explorer?
Plug a diagnostic scanner into the OBD2 port, turn on the ignition without starting the engine, and follow the scanner’s prompts to read the DTCs.
Can I clear the check engine light using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, most OBD2 scanners allow you to clear the check engine light after addressing the underlying issues.
What are some common issues that can be diagnosed via the OBD2 port?
Common issues include engine misfires, oxygen sensor failures, catalytic converter problems, and EVAP system issues.
Is it safe to drive my 1998 Ford Explorer with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that requires immediate attention. If the light is steady, you can usually drive the vehicle, but it’s best to diagnose and address the problem as soon as possible.
How often should I scan my vehicle for diagnostic trouble codes?
You should scan your vehicle whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any performance issues. Regular scanning can help you identify potential problems early.
Can I use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner with my 1998 Ford Explorer?
Yes, you can use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner with your 1998 Ford Explorer, provided it is compatible with the OBD2 protocols used by your vehicle.
What is bi-directional control, and why is it useful?
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and control specific components, which can be useful for testing actuators and solenoids.
Where can I find more information about OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes?
You can find more information about OBD2 DTCs on websites like OBD-Codes.com, AutoCodes.com, and RepairPal.com.
13. Need Expert Assistance? Contact Us
Are you having trouble diagnosing issues with your 1998 Ford Explorer? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert assistance with diagnostics, repairs, and maintenance. Our team of experienced technicians can provide the guidance and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of services to help you maintain and repair your Mercedes-Benz:
- Expert Diagnostics: Our experienced technicians can accurately diagnose complex vehicle issues.
- OBD2 System Support: We provide support for all aspects of the OBD2 system, from reading codes to performing advanced diagnostics.
- Repair Services: We offer comprehensive repair services for a wide range of vehicle issues.
- Maintenance Services: We provide routine maintenance services to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
- Consultation: We offer expert consultation to help you make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair needs.
Contact Information
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Contact us today for all your diagnostic and repair needs! We are here to help you keep your vehicle in top condition.

