The 2002 Ford Ranger Obd2 Fuse Location is a common concern for vehicle owners. This article, brought to you by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, offers a comprehensive guide to help you locate and troubleshoot fuse issues, ensuring your Ranger’s diagnostic system functions correctly. We’ll explore the specific fuse locations, diagnostic procedures, and maintenance tips to keep your Ford Ranger running smoothly. You will discover more about Ford Ranger diagnostics, electrical troubleshooting, and automotive maintenance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of Fuses in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
- 1.1. Why Fuses Matter for OBD2 Functionality
- 1.2. Common Symptoms of a Blown Fuse Related to the OBD2 Port
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
- 2.1. Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location
- 2.2. Power Distribution Box Location
- 2.3. Identifying the Correct Fuse for the OBD2 Port
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking and Replacing Fuses
- 3.1. Gathering the Necessary Tools
- 3.2. Visual Inspection of the Fuse
- 3.3. Using a Test Light or Multimeter for Fuse Testing
- 3.4. Replacing a Blown Fuse
- 3.5. Post-Replacement Check
- 4. Common Fuse-Related Issues in the 2002 Ford Ranger
- 4.1. Short Circuits
- 4.2. Overloads
- 4.3. Faulty Wiring
- 4.4. Component Malfunctions
- 5. Advanced Troubleshooting for OBD2 Fuse Issues
- 5.1. Identifying the Root Cause of Repeated Fuse Blows
- 5.2. Using Wiring Diagrams to Trace Electrical Faults
- 5.3. Checking for Damaged or Corroded Wiring
- 5.4. Testing Individual Components on the OBD2 Circuit
- 6. Preventing Future Fuse Problems in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
- 6.1. Regular Electrical System Maintenance
- 6.2. Avoiding Overloads on Electrical Circuits
- 6.3. Proper Installation of Aftermarket Electrical Components
- 6.4. Using Quality Replacement Fuses
- 7. Understanding Fuse Ratings and Types
- 7.1. AMP Ratings Explained
- 7.2. Common Fuse Types (ATO, Mini, Maxi)
- 7.3. Color Coding and What It Signifies
- 8. When to Seek Professional Help
- 8.1. Recurring Fuse Problems Despite Troubleshooting
- 8.2. Complex Electrical System Issues
- 8.3. Ensuring Safety and Avoiding Further Damage
- 9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Diagnosing Electrical Issues
- 9.1. How OBD2 Scanners Help Identify Electrical Problems
- 9.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to Fuses
- 9.3. Using Live Data to Monitor Electrical System Performance
- 10. Maintaining Your 2002 Ford Ranger’s Electrical System for Longevity
- 10.1. Regular Inspection of Wiring and Connections
- 10.2. Protecting Wiring from Environmental Factors
- 10.3. Keeping Fuse Boxes Clean and Dry
- 10.4. Following Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
- 11. Additional Resources for 2002 Ford Ranger Owners
- 11.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 11.2. Repair Manuals and Guides
- 11.3. Local Auto Parts Stores
- 12. Case Studies: Real-World OBD2 Fuse Issues in 2002 Ford Rangers
- 12.1. Case Study 1: Repeatedly Blowing OBD2 Fuse Due to a Short in the Wiring Harness
- 12.2. Case Study 2: Intermittent OBD2 Port Failure Caused by a Corroded Fuse Box
- 12.3. Case Study 3: Aftermarket Stereo Installation Causing Fuse Overload
- 13. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and Fuse Technology
- 13.1. Advancements in Fuse Technology
- 13.2. Integration of OBD2 Systems with Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 13.3. The Role of AI in Automotive Troubleshooting
- 14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the 2002 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse Location
- 15. Conclusion: Keeping Your 2002 Ford Ranger Running Smoothly with Proper Fuse Maintenance
1. Understanding the Importance of Fuses in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
Fuses are essential components in your 2002 Ford Ranger’s electrical system, protecting it from overloads. When an electrical component malfunctions, the fuse is designed to blow, preventing damage to other parts of the system. Knowing the fuse locations and how to check them is vital for maintaining your vehicle’s health. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent more significant electrical issues.
1.1. Why Fuses Matter for OBD2 Functionality
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is crucial for monitoring your vehicle’s performance. A blown fuse can disrupt the OBD2 system, preventing it from reporting issues. This can lead to increased emissions and potential engine damage. Ensuring the OBD2 fuse is intact is vital for accurate diagnostics and timely repairs. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a functional OBD2 system is essential for detecting and addressing emissions-related problems.
1.2. Common Symptoms of a Blown Fuse Related to the OBD2 Port
Several symptoms indicate a blown fuse related to the OBD2 port:
- The check engine light does not illuminate.
- The diagnostic scanner fails to connect.
- The vehicle experiences performance issues.
- Electrical components connected to the same circuit malfunction.
If you notice any of these symptoms, checking the OBD2 fuse should be one of your first steps in troubleshooting.
2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
Finding the OBD2 fuse in your 2002 Ford Ranger involves checking two main fuse box locations. The primary fuse panel is located inside the passenger compartment, while the power distribution box is under the hood. Knowing these locations can save you time and effort during troubleshooting.
2.1. Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location
The passenger compartment fuse panel is typically located on the left end of the instrument panel.
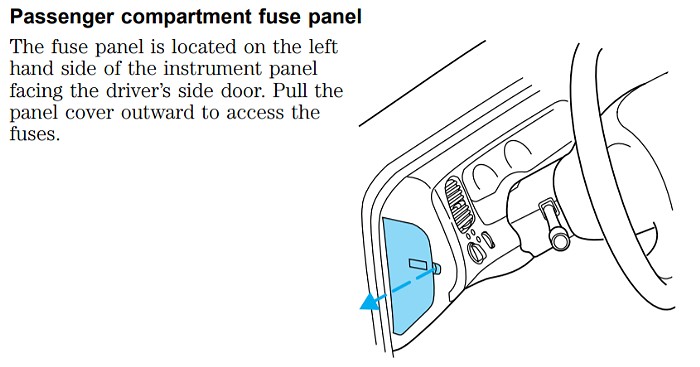 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location in a Ford Ranger
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location in a Ford Ranger
To access it, insert your finger into the divot and pull the cover off. The inside of the cover usually contains a diagram indicating the location of each fuse.
2.2. Power Distribution Box Location
The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment on the driver’s side, near the fender.
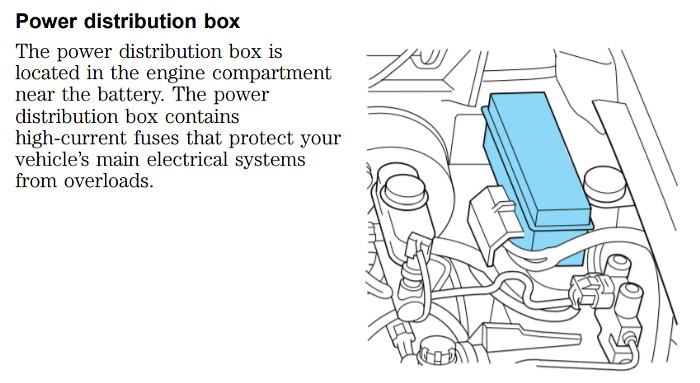 Power Distribution Box in a Ford Ranger Engine Compartment
Power Distribution Box in a Ford Ranger Engine Compartment
This box contains several fuses and relays that protect various systems, including the OBD2.
2.3. Identifying the Correct Fuse for the OBD2 Port
The specific fuse number for the OBD2 port can vary. Consult your owner’s manual for the exact fuse number. In many cases, it is Fuse 17, a 20-amp fuse, which also protects the cigar lighter and data link connector (DLC).
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking and Replacing Fuses
Once you’ve located the fuse panels, follow these steps to check and replace a blown fuse:
3.1. Gathering the Necessary Tools
Before you begin, gather these tools:
- Fuse puller (usually found in the fuse box)
- Replacement fuses (with the correct amperage)
- A test light or multimeter
- Your 2002 Ford Ranger owner’s manual
3.2. Visual Inspection of the Fuse
Remove the fuse using the fuse puller. Visually inspect the fuse. If the metal wire inside is separated or the fuse looks burnt, it’s blown and needs replacement.
3.3. Using a Test Light or Multimeter for Fuse Testing
For a more accurate test, use a test light or multimeter. With the test light, touch the probe to the metal contacts on top of the fuse while it’s still in the circuit. If the light illuminates, the fuse is good. A multimeter can be used to check for continuity. A reading of 0 ohms indicates a good fuse.
3.4. Replacing a Blown Fuse
Replace the blown fuse with a new one of the same amperage. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage, as this can cause severe wire damage and potentially start a fire.
3.5. Post-Replacement Check
After replacing the fuse, check the OBD2 port by plugging in a diagnostic scanner. If the scanner powers up and connects, the issue is resolved. If the fuse blows again immediately, there may be a short circuit in the system.
4. Common Fuse-Related Issues in the 2002 Ford Ranger
Several common issues can cause fuses to blow repeatedly in your 2002 Ford Ranger. Understanding these can help you diagnose and fix the underlying problems.
4.1. Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when a wire comes into contact with the vehicle’s metal chassis, creating a low-resistance path for electricity. This can cause a surge in current, blowing the fuse.
4.2. Overloads
An overload happens when too many electrical devices are drawing power from the same circuit, exceeding the fuse’s capacity.
4.3. Faulty Wiring
Damaged or corroded wiring can also cause fuses to blow. Regularly inspect the wiring for any signs of wear or damage.
4.4. Component Malfunctions
A failing electrical component, such as a sensor or motor, can draw excessive current, leading to a blown fuse.
5. Advanced Troubleshooting for OBD2 Fuse Issues
If you continue to experience OBD2 fuse problems, more advanced troubleshooting steps may be necessary.
5.1. Identifying the Root Cause of Repeated Fuse Blows
To identify the root cause of repeated fuse blows, use a multimeter to check for shorts in the wiring. Disconnect the OBD2 port and test for continuity between the port’s pins and the vehicle’s chassis. Any continuity indicates a short circuit.
5.2. Using Wiring Diagrams to Trace Electrical Faults
Wiring diagrams are invaluable for tracing electrical faults. These diagrams show the path of each wire in the system, making it easier to identify potential problem areas.
5.3. Checking for Damaged or Corroded Wiring
Inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage or corrosion. Pay close attention to areas where the wiring passes through metal panels or is exposed to the elements.
5.4. Testing Individual Components on the OBD2 Circuit
Test each component on the OBD2 circuit individually to identify any that may be drawing excessive current. Use a multimeter to measure the current draw of each component.
6. Preventing Future Fuse Problems in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
Preventing future fuse problems involves regular maintenance and proactive measures to protect your vehicle’s electrical system.
6.1. Regular Electrical System Maintenance
Regularly inspect your vehicle’s electrical system, including the wiring, fuses, and connections. Look for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
6.2. Avoiding Overloads on Electrical Circuits
Avoid overloading electrical circuits by not plugging too many devices into the same circuit at once. Use a power strip with a built-in circuit breaker to protect against overloads.
6.3. Proper Installation of Aftermarket Electrical Components
When installing aftermarket electrical components, such as stereos or lights, ensure they are properly wired and fused. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
6.4. Using Quality Replacement Fuses
Always use high-quality replacement fuses with the correct amperage rating. Avoid using cheap or generic fuses, as they may not provide adequate protection.
7. Understanding Fuse Ratings and Types
Knowing the different fuse ratings and types is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
7.1. AMP Ratings Explained
The amp rating of a fuse indicates the amount of current it can handle before blowing. Using the correct amp rating is crucial for protecting the electrical system.
7.2. Common Fuse Types (ATO, Mini, Maxi)
- ATO fuses: Standard-size fuses commonly used in older vehicles.
- Mini fuses: Smaller than ATO fuses, used in more compact fuse boxes.
- Maxi fuses: Larger fuses used for high-current circuits.
7.3. Color Coding and What It Signifies
Fuses are color-coded to indicate their amp rating. For example, a red fuse is typically 10 amps, while a blue fuse is 15 amps. Refer to the fuse color chart in your owner’s manual.
 Fuse Color Ratings Chart
Fuse Color Ratings Chart
8. When to Seek Professional Help
While many fuse-related issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting, some situations require professional help.
8.1. Recurring Fuse Problems Despite Troubleshooting
If you’ve tried troubleshooting and the fuse continues to blow repeatedly, there may be a more complex electrical problem that requires professional diagnosis.
8.2. Complex Electrical System Issues
Complex electrical system issues, such as shorts in the wiring harness or malfunctioning control modules, often require specialized tools and expertise to diagnose and repair.
8.3. Ensuring Safety and Avoiding Further Damage
If you’re not comfortable working with electrical systems or unsure about any of the troubleshooting steps, it’s best to seek professional help to ensure safety and avoid further damage.
9. The Role of OBD2 Scanners in Diagnosing Electrical Issues
OBD2 scanners are valuable tools for diagnosing electrical issues in your 2002 Ford Ranger.
9.1. How OBD2 Scanners Help Identify Electrical Problems
OBD2 scanners can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that indicate electrical problems, such as sensor failures or circuit faults.
9.2. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to Fuses
Some DTCs specifically indicate fuse-related problems, such as “Fuse B Circuit Malfunction.”
9.3. Using Live Data to Monitor Electrical System Performance
OBD2 scanners can also provide live data, allowing you to monitor the performance of various electrical components in real-time.
10. Maintaining Your 2002 Ford Ranger’s Electrical System for Longevity
Proper maintenance of your 2002 Ford Ranger’s electrical system is essential for its longevity and reliability.
10.1. Regular Inspection of Wiring and Connections
Regularly inspect the wiring and connections for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Clean corroded connections with a wire brush and apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
10.2. Protecting Wiring from Environmental Factors
Protect wiring from environmental factors, such as heat, moisture, and abrasion. Use wire loom or electrical tape to protect exposed wires.
10.3. Keeping Fuse Boxes Clean and Dry
Keep fuse boxes clean and dry to prevent corrosion. Use a vacuum cleaner to remove any dust or debris from the fuse box.
10.4. Following Manufacturer’s Recommended Maintenance Schedule
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your 2002 Ford Ranger. This schedule includes regular checks of the electrical system.
11. Additional Resources for 2002 Ford Ranger Owners
Several additional resources are available to help 2002 Ford Ranger owners maintain and troubleshoot their vehicles.
11.1. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities, such as FordRangerForum.com, provide a wealth of information and support from other Ranger owners.
11.2. Repair Manuals and Guides
Repair manuals and guides, such as those from Haynes and Chilton, offer detailed instructions and diagrams for repairing your Ranger.
11.3. Local Auto Parts Stores
Local auto parts stores, such as AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts, can provide replacement fuses, wiring, and other electrical components.
12. Case Studies: Real-World OBD2 Fuse Issues in 2002 Ford Rangers
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into common OBD2 fuse issues in 2002 Ford Rangers.
12.1. Case Study 1: Repeatedly Blowing OBD2 Fuse Due to a Short in the Wiring Harness
A 2002 Ford Ranger owner experienced a repeatedly blowing OBD2 fuse. After troubleshooting, it was discovered that a wire in the wiring harness had rubbed against the chassis, causing a short circuit. Repairing the damaged wire resolved the issue.
12.2. Case Study 2: Intermittent OBD2 Port Failure Caused by a Corroded Fuse Box
Another owner experienced intermittent OBD2 port failure. The problem was traced to a corroded fuse box. Cleaning the corrosion and applying dielectric grease restored the OBD2 port’s functionality.
12.3. Case Study 3: Aftermarket Stereo Installation Causing Fuse Overload
A third owner installed an aftermarket stereo, which caused the OBD2 fuse to blow. The stereo was drawing too much current from the same circuit as the OBD2 port. Installing a separate fused circuit for the stereo resolved the issue.
13. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and Fuse Technology
The future of automotive diagnostics and fuse technology is evolving rapidly, with new innovations and advancements on the horizon.
13.1. Advancements in Fuse Technology
Advancements in fuse technology include smart fuses that can reset themselves after an overload and electronic fuses that provide more precise protection.
13.2. Integration of OBD2 Systems with Cloud-Based Diagnostics
The integration of OBD2 systems with cloud-based diagnostics allows for remote monitoring and diagnosis of vehicle problems.
13.3. The Role of AI in Automotive Troubleshooting
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in automotive troubleshooting, with AI-powered diagnostic tools that can quickly identify and resolve complex problems.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the 2002 Ford Ranger OBD2 Fuse Location
14.1. What Does the OBD2 Fuse Control?
The OBD2 fuse controls the power supply to the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port, which is used to connect diagnostic scanners to the vehicle’s computer.
14.2. Where Can I Find the Fuse Box Diagram for My 2002 Ford Ranger?
The fuse box diagram is usually located on the inside of the fuse box cover or in your owner’s manual.
14.3. What Size Fuse Does the OBD2 Port Use?
The OBD2 port typically uses a 20-amp fuse. However, always consult your owner’s manual for the correct size.
14.4. Can I Use a Higher Amp Fuse If I Keep Blowing Fuses?
No, never use a higher amp fuse. This can cause severe wire damage and potentially start a fire.
14.5. How Do I Know If My OBD2 Port Is Working?
You can check if your OBD2 port is working by plugging in a diagnostic scanner. If the scanner powers up and connects, the port is working.
14.6. What Causes a Fuse to Blow Repeatedly?
A fuse that blows repeatedly is usually caused by a short circuit, overload, or faulty wiring.
14.7. Is It Safe to Drive with a Blown OBD2 Fuse?
It is generally safe to drive with a blown OBD2 fuse, but you will not be able to diagnose any problems with your vehicle until the fuse is replaced.
14.8. How Often Should I Check My Fuses?
You should check your fuses regularly, especially if you notice any electrical problems with your vehicle.
14.9. Can a Bad OBD2 Port Affect My Vehicle’s Performance?
Yes, a bad OBD2 port can prevent you from diagnosing and addressing performance issues, potentially leading to further damage.
14.10. Where Can I Buy Replacement Fuses for My 2002 Ford Ranger?
You can buy replacement fuses at most auto parts stores, such as AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts.
15. Conclusion: Keeping Your 2002 Ford Ranger Running Smoothly with Proper Fuse Maintenance
Maintaining the fuses in your 2002 Ford Ranger is essential for the smooth operation of its electrical system. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent more significant issues and keep your vehicle running efficiently. By understanding the fuse locations, troubleshooting steps, and preventive measures outlined in this guide, you can ensure your Ranger remains a reliable and enjoyable vehicle for years to come.
If you’re facing persistent issues with your Mercedes-Benz or need expert advice on diagnostic tools, advanced repairs, or unlocking hidden features, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced technicians is ready to provide tailored solutions and support. Contact us today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.