The 91 Gmc Obd2 Codes refer to the diagnostic trouble codes that can be retrieved from a 1991 GMC truck equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics system. Understanding these codes is crucial for diagnosing and repairing your vehicle, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the expertise and resources you need. By mastering the interpretation and resolution of these codes, you will be able to effectively troubleshoot your GMC, ensuring its performance and longevity, and leveraging advanced diagnostic tools and comprehensive support to keep your vehicle running smoothly with fault code identification, engine performance optimization, and automotive diagnostic solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD1 and the 1991 GMC
- 1.1. OBD1 vs. OBD2: What’s the Difference?
- 1.2. How OBD1 Works on a 1991 GMC
- 1.3. Accessing OBD1 Codes on Your 1991 GMC
- 1.4. Interpreting the Flashing Codes
- 2. Common 91 GMC OBD1 Codes and Their Meanings
- 2.1. Code 12: No Distributor Reference Pulse
- 2.2. Code 13: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Open
- 2.3. Code 14: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
- 2.4. Code 15: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High
- 2.5. Code 21: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High
- 2.6. Code 22: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low
- 3. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing 91 GMC OBD1 Codes
- 3.1. OBD1 Scanner or Code Reader
- 3.2. Multimeter
- 3.3. Wiring Diagrams
- 3.4. Scan Tools
- 3.5. Professional Diagnostic Software
- 4. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures for Common Issues
- 4.1. Diagnosing Code 13: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Open
- 4.2. Diagnosing Code 14: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
- 4.3. Diagnosing Code 21: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High
- 4.4. Clear the Code
- 5. Tips for Maintaining Your 1991 GMC’s Diagnostic System
- 5.1. Regular Inspections
- 5.2. Keep Electrical Connections Clean
- 5.3. Follow Maintenance Schedules
- 5.4. Monitor Vehicle Performance
- 5.5. Stay Informed
- 6. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in GMC Diagnostics
- 6.1. Diagnostic Guides and Information
- 6.2. Expert Advice and Support
- 6.3. Access to Diagnostic Tools
- 6.4. Community Forum and Support
- 6.5. Educational Resources
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for 91 GMC Trucks
- 7.1. Data Logging and Analysis
- 7.2. Actuator Testing
- 7.3. Wiring Harness Testing
- 7.4. Vacuum Leak Testing
- 7.5. Compression Testing
- 8. Case Studies: Real-World 91 GMC OBD1 Code Diagnoses
- 8.1. Case Study 1: Code 13 – Oxygen Sensor Issue
- 8.2. Case Study 2: Code 22 – Throttle Position Sensor Problem
- 9. Preventing Future Issues: Proactive Maintenance
- 9.1. Regular Tune-Ups
- 9.2. Fuel System Maintenance
- 9.3. Cooling System Service
- 9.4. Regular Oil Changes
- 9.5. Battery Maintenance
- 10. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and 1991 GMCs
- 10.1. Advancements in Diagnostic Technology
- 10.2. The Role of Telematics
- 10.3. The Impact of Electric Vehicles
- 10.4. The Importance of Training and Education
- 10.5. Resources at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
1. Understanding OBD1 and the 1991 GMC
While the term “OBD2” is in the keyword, it’s essential to clarify that 1991 GMC trucks used the earlier OBD1 system. Let’s explore the differences and how OBD1 works on your vehicle.
1.1. OBD1 vs. OBD2: What’s the Difference?
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) was the first generation of standardized diagnostic systems in vehicles, while OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics 2) is the more advanced system used in vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards in the United States. The primary differences lie in the diagnostic capabilities, the connector type, and the way codes are retrieved. OBD2 offers a more comprehensive range of diagnostic data and uses a standardized 16-pin connector.
1.2. How OBD1 Works on a 1991 GMC
On a 1991 GMC, the OBD1 system monitors various sensors and components to detect malfunctions. When a fault is detected, the system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in the vehicle’s computer. To retrieve these codes, you typically need to use a paper clip or a specialized OBD1 scanner to access the ALDL (Assembly Line Diagnostic Link) connector.
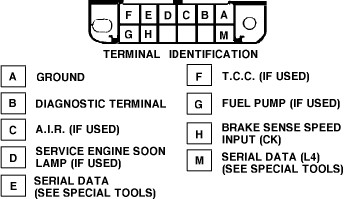
1.3. Accessing OBD1 Codes on Your 1991 GMC
Here’s how to access the OBD1 codes on your 1991 GMC:
- Locate the ALDL connector, usually found under the dashboard.
- Use a paper clip to connect terminals A and B on the connector.
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
- Observe the “Check Engine” light. It will flash a series of codes.
The “Check Engine” light will first flash Code 12 (one flash, a pause, then two flashes) three times. This indicates that the system is in diagnostic mode. After displaying Code 12, any stored trouble codes will be flashed three times each. Each code consists of two sets of flashes, representing the digits of the code. For example, Code 21 would be two flashes, a pause, then one flash.
 GM ALDL Connector
GM ALDL Connector
1.4. Interpreting the Flashing Codes
Once you have retrieved the codes, you need to interpret them to identify the problem. Common OBD1 codes for GMC vehicles include:
- Code 12: No distributor reference pulse (system in diagnostic mode)
- Code 13: Oxygen sensor circuit open
- Code 14: Coolant temperature sensor circuit low
- Code 15: Coolant temperature sensor circuit high
- Code 21: Throttle position sensor circuit high
- Code 22: Throttle position sensor circuit low
Refer to a comprehensive OBD1 code chart specific to GMC vehicles to understand the meaning of each code.
2. Common 91 GMC OBD1 Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding the common OBD1 codes for your 1991 GMC can help you diagnose and fix issues more efficiently. Here’s a breakdown of some frequently encountered codes and their possible causes.
2.1. Code 12: No Distributor Reference Pulse
Meaning: This code indicates that the system is in diagnostic mode and is normal when you are retrieving codes.
Possible Causes: None, as this is a diagnostic indicator, not a fault.
How to Address: No action is needed. It simply means the system is ready to display other stored codes.
2.2. Code 13: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Open
Meaning: This code indicates an issue with the oxygen sensor circuit, which can affect the air-fuel mixture and engine performance.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Wiring issues (open, short, or corrosion)
- Poor connection at the sensor
How to Address:
- Inspect the oxygen sensor and its wiring for damage.
- Check the sensor’s connector for corrosion or loose connections.
- Test the sensor’s resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the oxygen sensor if necessary.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), a faulty oxygen sensor can decrease fuel efficiency by up to 40%.
2.3. Code 14: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
Meaning: This code indicates that the engine coolant temperature sensor is reporting a low temperature, which can affect engine performance and fuel economy.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty coolant temperature sensor
- Wiring issues (open, short, or corrosion)
- Poor connection at the sensor
How to Address:
- Inspect the coolant temperature sensor and its wiring for damage.
- Check the sensor’s connector for corrosion or loose connections.
- Test the sensor’s resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the coolant temperature sensor if necessary.
2.4. Code 15: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High
Meaning: This code indicates that the engine coolant temperature sensor is reporting a high temperature.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty coolant temperature sensor
- Wiring issues (open, short, or corrosion)
- Poor connection at the sensor
How to Address:
- Inspect the coolant temperature sensor and its wiring for damage.
- Check the sensor’s connector for corrosion or loose connections.
- Test the sensor’s resistance using a multimeter.
- Replace the coolant temperature sensor if necessary.
2.5. Code 21: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High
Meaning: This code indicates that the throttle position sensor (TPS) is reporting a high voltage, which can affect engine idle and acceleration.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty throttle position sensor
- Wiring issues (short to voltage)
- Poor connection at the sensor
How to Address:
- Inspect the throttle position sensor and its wiring for damage.
- Check the sensor’s connector for corrosion or loose connections.
- Test the sensor’s voltage output using a multimeter.
- Adjust or replace the throttle position sensor if necessary.
2.6. Code 22: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low
Meaning: This code indicates that the throttle position sensor (TPS) is reporting a low voltage.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty throttle position sensor
- Wiring issues (short to ground or open circuit)
- Poor connection at the sensor
How to Address:
- Inspect the throttle position sensor and its wiring for damage.
- Check the sensor’s connector for corrosion or loose connections.
- Test the sensor’s voltage output using a multimeter.
- Adjust or replace the throttle position sensor if necessary.
3. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing 91 GMC OBD1 Codes
Having the right tools and equipment can significantly simplify the process of diagnosing OBD1 codes on your 1991 GMC. Here are some essential items to consider.
3.1. OBD1 Scanner or Code Reader
While you can retrieve codes using a paper clip, an OBD1 scanner or code reader can provide a more user-friendly interface and additional diagnostic information. These devices plug into the ALDL connector and display the codes on a screen.
Benefits:
- Easy to read codes
- May provide code descriptions
- Some models offer advanced features like data logging
3.2. Multimeter
A multimeter is a versatile tool for testing electrical circuits and components. It can be used to check voltage, resistance, and continuity, helping you identify wiring issues and faulty sensors.
Uses:
- Testing sensor voltage and resistance
- Checking for shorts or open circuits
- Verifying ground connections
3.3. Wiring Diagrams
Having access to wiring diagrams specific to your 1991 GMC can be invaluable when troubleshooting electrical issues. These diagrams show the layout of the vehicle’s electrical system, including the location of sensors, connectors, and wiring harnesses.
Benefits:
- Helps trace circuits and identify wiring problems
- Shows the location of components
- Reduces the risk of damaging the electrical system
3.4. Scan Tools
For more in-depth diagnostics, consider using a scan tool. These advanced devices can access a wide range of diagnostic data, perform tests, and even program certain vehicle functions.
Features:
- Reads and clears DTCs
- Displays live sensor data
- Performs actuator tests
- Provides access to advanced diagnostic functions
3.5. Professional Diagnostic Software
Professional diagnostic software provides comprehensive information, including repair procedures, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and wiring diagrams.
Benefits:
- Access to up-to-date information
- Step-by-step repair instructions
- Helps diagnose complex issues
4. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures for Common Issues
Let’s walk through the diagnostic procedures for some common OBD1 codes, providing a practical guide to troubleshooting your 1991 GMC.
4.1. Diagnosing Code 13: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Open
- Visual Inspection: Check the oxygen sensor and its wiring for any visible damage. Look for frayed wires, corroded connectors, or signs of physical stress.
- Connector Check: Disconnect the oxygen sensor connector and inspect the terminals for corrosion or damage. Clean the terminals with electrical contact cleaner if necessary.
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the oxygen sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct resistance range.
- Wiring Continuity Test: Check the continuity of the wiring between the oxygen sensor connector and the vehicle’s computer. Use a multimeter to verify that there are no open circuits or shorts to ground.
- Sensor Replacement: If the sensor fails the resistance test or the wiring is damaged, replace the oxygen sensor.
4.2. Diagnosing Code 14: Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
- Visual Inspection: Check the coolant temperature sensor and its wiring for any visible damage. Look for frayed wires, corroded connectors, or signs of coolant leakage.
- Connector Check: Disconnect the sensor connector and inspect the terminals for corrosion or damage. Clean the terminals with electrical contact cleaner if necessary.
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the coolant temperature sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct resistance values at different temperatures.
- Wiring Continuity Test: Check the continuity of the wiring between the sensor connector and the vehicle’s computer. Use a multimeter to verify that there are no open circuits or shorts to ground.
- Sensor Replacement: If the sensor fails the resistance test or the wiring is damaged, replace the coolant temperature sensor.
4.3. Diagnosing Code 21: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High
- Visual Inspection: Check the throttle position sensor (TPS) and its wiring for any visible damage. Look for frayed wires, corroded connectors, or signs of physical stress.
- Connector Check: Disconnect the sensor connector and inspect the terminals for corrosion or damage. Clean the terminals with electrical contact cleaner if necessary.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the TPS. With the throttle closed, the voltage should be around 0.5 volts. With the throttle fully open, the voltage should be around 4.5 volts.
- Wiring Continuity Test: Check the continuity of the wiring between the sensor connector and the vehicle’s computer. Use a multimeter to verify that there are no open circuits or shorts to ground.
- Sensor Adjustment or Replacement: If the voltage output is not within the specified range, try adjusting the TPS. If adjustment is not possible or the sensor is faulty, replace the TPS.
4.4. Clear the Code
After addressing the issue, clear the diagnostic trouble code to see if it returns.
5. Tips for Maintaining Your 1991 GMC’s Diagnostic System
Preventive maintenance can help keep your 1991 GMC’s diagnostic system in good working order, reducing the likelihood of future problems.
5.1. Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect your vehicle’s sensors, wiring, and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
5.2. Keep Electrical Connections Clean
Keep electrical connections clean and free of corrosion. Use electrical contact cleaner to clean terminals and connectors, and apply dielectric grease to protect them from moisture and corrosion.
5.3. Follow Maintenance Schedules
Adhere to the vehicle’s maintenance schedule for replacing components such as oxygen sensors and spark plugs. These components can affect the performance of the diagnostic system if they are not functioning correctly.
5.4. Monitor Vehicle Performance
Pay attention to your vehicle’s performance and watch for any warning signs, such as a rough idle, poor acceleration, or decreased fuel economy. These symptoms can indicate a problem with the diagnostic system or other vehicle components.
5.5. Stay Informed
Stay informed about common issues and diagnostic procedures for your 1991 GMC. Knowing the potential problems and how to address them can help you maintain your vehicle and prevent costly repairs.
6. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in GMC Diagnostics
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of resources and support to help you diagnose and repair your 1991 GMC, even though we specialize in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our expertise in automotive diagnostics can be applied to a variety of vehicles, providing valuable assistance.
6.1. Diagnostic Guides and Information
We provide comprehensive diagnostic guides and information that can help you understand OBD1 codes and troubleshoot issues on your 1991 GMC. Our resources cover a wide range of topics, including code definitions, diagnostic procedures, and repair tips.
6.2. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert advice and support to help you diagnose and repair your 1991 GMC. Whether you have a question about a specific code or need help troubleshooting a complex issue, we are here to assist you.
6.3. Access to Diagnostic Tools
While we specialize in Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools, we can provide recommendations for OBD1 scanners and code readers that are compatible with your 1991 GMC. We can also offer guidance on how to use these tools effectively.
6.4. Community Forum and Support
Engage with other GMC owners and enthusiasts, share your experiences, and learn from others. Our community is a valuable resource for troubleshooting issues and finding solutions to common problems.
6.5. Educational Resources
Access our library of articles, videos, and tutorials to deepen your understanding of automotive diagnostics and repair. Learn how to use diagnostic tools, interpret codes, and perform repairs on your 1991 GMC.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for 91 GMC Trucks
For complex issues or intermittent problems, advanced diagnostic techniques may be required. These techniques can help you pinpoint the root cause of the problem and ensure a successful repair.
7.1. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording live sensor data while the vehicle is in operation. This data can then be analyzed to identify anomalies or patterns that may indicate a problem.
How to Use:
- Connect a scan tool or data logger to the ALDL connector.
- Record data while driving the vehicle under various conditions.
- Analyze the data to identify sensor readings that are out of range or inconsistent.
7.2. Actuator Testing
Actuator testing involves using a scan tool to activate specific vehicle components, such as fuel injectors or solenoids. This can help you verify that the components are functioning correctly.
How to Use:
- Connect a scan tool to the ALDL connector.
- Use the scan tool to activate specific actuators.
- Observe the component’s response to verify that it is functioning correctly.
7.3. Wiring Harness Testing
Wiring harness testing involves checking the integrity of the vehicle’s wiring harnesses. This can help you identify shorts, open circuits, or high resistance connections.
How to Use:
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity and resistance of individual wires.
- Inspect wiring harnesses for signs of damage or corrosion.
- Repair or replace damaged wiring harnesses as necessary.
7.4. Vacuum Leak Testing
Vacuum leaks can cause a variety of problems, including a rough idle, poor acceleration, and decreased fuel economy. Vacuum leak testing involves using a smoke machine or other device to identify vacuum leaks in the engine.
How to Use:
- Connect a smoke machine to the engine’s vacuum system.
- Introduce smoke into the system and look for leaks.
- Repair or replace any leaking components.
7.5. Compression Testing
Compression testing involves measuring the compression in each cylinder of the engine. This can help you identify problems such as worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket.
How to Use:
- Remove the spark plugs from each cylinder.
- Insert a compression tester into each cylinder.
- Crank the engine and record the compression reading for each cylinder.
- Compare the readings to the vehicle’s specifications to identify any problems.
8. Case Studies: Real-World 91 GMC OBD1 Code Diagnoses
Let’s look at a couple of real-world case studies that illustrate how to diagnose OBD1 codes on a 1991 GMC.
8.1. Case Study 1: Code 13 – Oxygen Sensor Issue
Problem: A 1991 GMC truck was experiencing poor fuel economy and a rough idle. The “Check Engine” light was on, and the OBD1 system was displaying Code 13 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Open).
Diagnosis:
- The technician performed a visual inspection of the oxygen sensor and its wiring. No obvious damage was found.
- The technician disconnected the sensor connector and inspected the terminals for corrosion. Some corrosion was found, which was cleaned with electrical contact cleaner.
- The technician used a multimeter to measure the resistance of the oxygen sensor. The resistance was out of the specified range.
- The technician replaced the oxygen sensor.
Resolution: After replacing the oxygen sensor, the “Check Engine” light went off, and the truck’s fuel economy and idle improved.
8.2. Case Study 2: Code 22 – Throttle Position Sensor Problem
Problem: A 1991 GMC truck was experiencing erratic acceleration and occasional stalling. The “Check Engine” light was on, and the OBD1 system was displaying Code 22 (Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low).
Diagnosis:
- The technician performed a visual inspection of the throttle position sensor (TPS) and its wiring. No obvious damage was found.
- The technician disconnected the sensor connector and inspected the terminals for corrosion. The terminals were clean.
- The technician used a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the TPS. The voltage was below the specified range with the throttle closed.
- The technician attempted to adjust the TPS, but it was not possible to bring the voltage within the specified range.
- The technician replaced the TPS.
Resolution: After replacing the TPS, the “Check Engine” light went off, and the truck’s acceleration and idling issues were resolved.
9. Preventing Future Issues: Proactive Maintenance
Taking a proactive approach to maintenance can help prevent future issues with your 1991 GMC’s diagnostic system. Here are some tips to keep in mind.
9.1. Regular Tune-Ups
Regular tune-ups, including spark plug replacement and ignition system maintenance, can help keep your engine running smoothly and reduce the likelihood of diagnostic trouble codes.
9.2. Fuel System Maintenance
Keep your fuel system clean and well-maintained by using quality fuel and fuel additives. Replace the fuel filter regularly to prevent contaminants from clogging the fuel injectors.
9.3. Cooling System Service
Proper cooling system maintenance is essential for preventing overheating and other engine problems. Flush and refill the cooling system regularly, and inspect the radiator, hoses, and water pump for leaks or damage.
9.4. Regular Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are essential for keeping your engine lubricated and preventing wear and tear. Use the correct type of oil and change it according to the vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
9.5. Battery Maintenance
Keep your battery terminals clean and free of corrosion. Check the battery’s voltage regularly and replace the battery if it is weak or not holding a charge.
10. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics and 1991 GMCs
While the 1991 GMC uses an older OBD1 system, understanding the evolution of automotive diagnostics can provide valuable insights into how vehicles are maintained and repaired.
10.1. Advancements in Diagnostic Technology
Diagnostic technology has come a long way since the introduction of OBD1. Modern vehicles use advanced OBD2 systems with enhanced capabilities, including:
- Comprehensive sensor monitoring
- Real-time data logging
- Remote diagnostics
- Integration with mobile devices
10.2. The Role of Telematics
Telematics systems collect and transmit data about a vehicle’s performance and location. This data can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting
- Predictive maintenance
- Fleet management
- Stolen vehicle recovery
10.3. The Impact of Electric Vehicles
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming the automotive industry. EVs have different diagnostic requirements compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, including:
- Monitoring battery health and performance
- Diagnosing electric motor and inverter issues
- Troubleshooting charging system problems
10.4. The Importance of Training and Education
As diagnostic technology becomes more complex, it is essential for technicians to stay up-to-date with the latest tools and techniques. Training and education programs can help technicians develop the skills they need to diagnose and repair modern vehicles.
10.5. Resources at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Despite specializing in Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN aims to provide valuable information and assistance for a wide range of automotive diagnostic needs.
By understanding the 91 GMC OBD1 codes and following the diagnostic procedures outlined in this guide, you can keep your truck running smoothly and reliably for years to come.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or WhatsApp us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to learn more.