Global OBD2 DTC Clearing is a powerful function that allows you to erase all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) system simultaneously. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we empower car enthusiasts and professionals with the knowledge and tools to efficiently maintain their vehicles. This article explores the concept of global DTC clearing, its applications, and the benefits it offers for diagnosing and resolving vehicle issues.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 DTCs and the Need for Clearing
- 1.1 What Are OBD2 DTCs?
- 1.2 Why Clear DTCs?
- 1.3 The Importance of Accurate Diagnostics
- 2. What is Global DTC Clearing?
- 2.1 Defining Global DTC Clearing
- 2.2 Benefits of Global DTC Clearing
- 2.3 Understanding the Scope of Global DTC Clearing
- 3. How to Perform Global DTC Clearing
- 3.1 Tools Required
- 3.2 Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 4.1 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
- 4.2 Live Data Monitoring
- 4.3 Performing Component Tests
- 4.4 Using a Multimeter and Other Tools
- 5. Common OBD2 DTCs and Their Meanings
- 5.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 5.2 P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
- 5.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 5.4 P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- 5.5 P0505 – Idle Air Control System Malfunction
- 6. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 6.2 Recurring DTCs
- 6.3 Safety Concerns
- 6.4 Lack of Experience or Tools
- 7. Maximizing the Use of Diagnostic Tools
- 7.1 Choosing the Right Scan Tool
- 7.2 Understanding the Scan Tool’s Features
- 7.3 Following the Scan Tool’s Instructions
- 7.4 Keeping the Scan Tool Updated
- 8. The Role of Telematics in DTC Management
- 8.1 Real-Time DTC Monitoring
- 8.2 Remote Diagnostics
- 8.3 Predictive Maintenance
- 8.4 Fleet Management Benefits
- 9. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz: A Proactive Approach
- 9.1 Regular Maintenance Schedules
- 9.2 Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
- 9.3 Using High-Quality Parts
- 9.4 Keeping Accurate Records
- 10. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 11. FAQs About Global OBD2 DTC Clearing
- 11.1 What is the best OBD2 scan tool for clearing DTCs?
- 11.2 How do I know if my vehicle is OBD2 compliant?
- 11.3 Can I clear DTCs without a scan tool?
- 11.4 Will clearing DTCs affect my vehicle’s performance?
- 11.5 How often should I check for DTCs?
- 11.6 What does it mean when a DTC keeps coming back after clearing it?
- 11.7 Can clearing DTCs help me pass an emissions test?
- 11.8 What are the risks of clearing DTCs without fixing the problem?
- 11.9 How do I find out what a specific DTC means?
- 11.10 What should I do if I am not comfortable clearing DTCs myself?
- 12. The Future of Vehicle Diagnostics
- 12.1 Advancements in OBD Technology
- 12.2 The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 12.3 The Role of Connected Car Technologies
- 12.4 The Importance of Training and Education
- 13. Conclusion: Empowering Your Mercedes-Benz Ownership Experience
- 14. More Advanced Code Information Table
1. Understanding OBD2 DTCs and the Need for Clearing
1.1 What Are OBD2 DTCs?
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes stored in a vehicle’s onboard computer system when a malfunction or anomaly is detected by the vehicle’s sensors and systems. These codes provide vital clues about the nature and location of the problem, helping technicians diagnose and repair issues efficiently. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States after 1996 are required to support OBD-II diagnostics. This standardization allows for consistent diagnostic procedures across different vehicle makes and models.
1.2 Why Clear DTCs?
Clearing DTCs can be necessary in several situations:
- After Repairs: Once a fault has been repaired, clearing the corresponding DTC is crucial. This ensures that the check engine light is turned off and the OBD system can accurately monitor for new issues.
- Diagnostic Purposes: Clearing codes can help determine if a problem is recurring or if it was a one-time anomaly. If the code reappears after clearing, it indicates a persistent issue that requires further investigation.
- Performance Tuning: During performance modifications or tuning, clearing DTCs can help reset the system and ensure optimal performance.
- Emission Testing: Clearing historical codes before an emissions test can ensure that only current and relevant faults are reported.
1.3 The Importance of Accurate Diagnostics
Accurate diagnostics are essential for effective vehicle maintenance and repair. Misinterpreting DTCs or failing to address underlying issues can lead to further damage, increased repair costs, and potential safety hazards. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper training and diagnostic tools are critical for technicians to accurately identify and resolve vehicle problems.
2. What is Global DTC Clearing?
2.1 Defining Global DTC Clearing
Global DTC clearing is the process of simultaneously erasing all Diagnostic Trouble Codes stored in a vehicle’s OBD2 system using a diagnostic tool or scan tool. Unlike selective clearing, where individual codes are erased one at a time, global clearing provides a quick and efficient way to reset the entire system.
2.2 Benefits of Global DTC Clearing
- Time-Saving: Global clearing saves significant time compared to selectively erasing codes, especially when multiple DTCs are present.
- Comprehensive Reset: It ensures that all historical and pending codes are cleared, providing a clean slate for monitoring new issues.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the diagnostic process by quickly resetting the OBD2 system after repairs or modifications.
2.3 Understanding the Scope of Global DTC Clearing
It’s important to note that global DTC clearing only erases the stored codes and does not fix the underlying problems that triggered those codes. It is a tool for resetting the system after repairs or for diagnostic purposes, not a solution for vehicle malfunctions.
3. How to Perform Global DTC Clearing
3.1 Tools Required
To perform global DTC clearing, you will need:
- OBD2 Scan Tool: A compatible OBD2 scan tool is essential for accessing and clearing DTCs. These tools range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic scanners.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that the scan tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- User Manual: Refer to the scan tool’s user manual for specific instructions on performing global DTC clearing.
3.2 Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s a general guide on how to perform global DTC clearing:
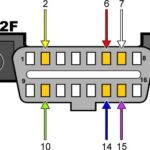
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the OBD2 scan tool into the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the vehicle’s ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Access the OBD2 Menu: Navigate to the OBD2 menu on the scan tool.
- Select “Clear Codes” or “Erase DTCs”: Look for an option labeled “Clear Codes,” “Erase DTCs,” or similar.
- Confirm the Clearing: The scan tool may prompt you to confirm the clearing operation. Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Wait for Confirmation: Allow the scan tool to complete the clearing process. It will typically display a confirmation message once finished.
- Disconnect the Scan Tool: Once the codes are cleared, disconnect the scan tool from the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Verify the Clearing: Start the engine and check if the check engine light is off. If the light reappears, it indicates that the underlying issue persists and requires further attention.
3.3 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Underlying Issue: Always diagnose and repair the root cause of the DTCs before clearing them.
- Using Incompatible Scan Tools: Ensure that the scan tool is compatible with your vehicle to avoid communication errors or damage to the OBD2 system.
- Ignoring Warning Messages: Pay attention to any warning messages or prompts displayed by the scan tool during the clearing process.
- Clearing Codes Before Emission Testing: Some vehicles require a certain number of drive cycles after clearing codes before they are ready for emission testing. Check your local regulations.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
4.1 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered. This data can provide valuable insights into the circumstances surrounding the fault, helping technicians diagnose intermittent or elusive problems.
4.2 Live Data Monitoring
Live data monitoring allows technicians to observe real-time sensor readings and system parameters while the vehicle is running. This can help identify anomalies or inconsistencies that may not trigger a DTC but could indicate a developing issue.
4.3 Performing Component Tests
Component tests involve activating or deactivating specific vehicle components using a scan tool to verify their functionality. This can help isolate faulty sensors, actuators, or modules.
4.4 Using a Multimeter and Other Tools
In addition to scan tools, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and other specialized tools can be used to further diagnose electrical and electronic issues. These tools allow technicians to measure voltage, current, resistance, and signal waveforms to pinpoint problems.
5. Common OBD2 DTCs and Their Meanings
5.1 P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running with too little fuel or too much air. Possible causes include:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty or faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Low fuel pressure
5.2 P0300 – Random Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires. Possible causes include:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Vacuum leaks
- Low fuel pressure
- Clogged fuel injectors
5.3 P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. Possible causes include:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Exhaust leaks
- Engine misfires
5.4 P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
This code indicates that there is a small leak in the evaporative emission control system. Possible causes include:
- Loose or faulty fuel cap
- Cracked or damaged fuel lines
- Faulty purge valve
- Faulty vent valve
5.5 P0505 – Idle Air Control System Malfunction
This code indicates that there is a problem with the idle air control system. Possible causes include:
- Faulty idle air control valve
- Vacuum leaks
- Dirty throttle body
- Wiring issues
6. When to Seek Professional Help
6.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
If you encounter complex diagnostic issues that you are unable to resolve on your own, it is best to seek professional help from a qualified technician.
6.2 Recurring DTCs
If a DTC reappears shortly after clearing it, it indicates a persistent issue that requires professional attention.
6.3 Safety Concerns
If you suspect that a vehicle problem may pose a safety risk, such as brake issues or steering problems, it is crucial to seek professional help immediately.
6.4 Lack of Experience or Tools
If you lack the experience, tools, or knowledge to diagnose and repair a vehicle problem, it is best to entrust the job to a professional technician.
7. Maximizing the Use of Diagnostic Tools
7.1 Choosing the Right Scan Tool
Selecting the right scan tool is essential for effective diagnostics. Consider factors such as:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the scan tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Features: Look for features such as DTC reading and clearing, live data monitoring, freeze frame data, and component testing.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scan tool with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Updates: Ensure that the scan tool can be updated with the latest software and vehicle coverage.
7.2 Understanding the Scan Tool’s Features
Familiarize yourself with all of the features and functions of your scan tool. This will enable you to use it more effectively and efficiently.
7.3 Following the Scan Tool’s Instructions
Always follow the scan tool’s instructions carefully to avoid errors or damage to the vehicle’s OBD2 system.
7.4 Keeping the Scan Tool Updated
Regularly update the scan tool with the latest software and vehicle coverage to ensure that it can accurately diagnose and repair the latest vehicles.
8. The Role of Telematics in DTC Management
8.1 Real-Time DTC Monitoring
Telematics systems can provide real-time DTC monitoring, allowing fleet managers and vehicle owners to identify and address issues proactively.
8.2 Remote Diagnostics
Some telematics systems offer remote diagnostic capabilities, enabling technicians to diagnose vehicle problems without being physically present at the vehicle.
8.3 Predictive Maintenance
Telematics data can be used to predict potential vehicle problems and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and repair costs.
8.4 Fleet Management Benefits
Telematics can provide valuable insights into fleet performance, enabling fleet managers to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce fuel consumption, and improve driver safety.
9. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz: A Proactive Approach
9.1 Regular Maintenance Schedules
Adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is essential for keeping your Mercedes-Benz in top condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil changes, filter replacements, fluid checks, and other maintenance tasks.
9.2 Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more serious problems. Pay attention to warning lights, unusual noises, and changes in vehicle performance, and seek professional help when needed.
9.3 Using High-Quality Parts
Using high-quality parts can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz performs optimally and lasts longer. Choose genuine Mercedes-Benz parts or reputable aftermarket brands.
9.4 Keeping Accurate Records
Keeping accurate records of all maintenance and repairs can help you track your vehicle’s history and identify potential issues early on.
10. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Are you struggling with DTCs on your Mercedes-Benz? Do you need help understanding how to use diagnostic tools or perform repairs? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice and assistance. Our team of experienced technicians can provide guidance on everything from choosing the right scan tool to diagnosing complex issues.
Contact Information:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted partner for all things Mercedes-Benz diagnostics and repair. Reach out today and let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
11. FAQs About Global OBD2 DTC Clearing
11.1 What is the best OBD2 scan tool for clearing DTCs?
The best OBD2 scan tool depends on your needs and budget. Basic code readers are suitable for simple DTC clearing, while advanced diagnostic scanners offer more features and capabilities. Popular brands include Autel, Launch, and Bosch.
11.2 How do I know if my vehicle is OBD2 compliant?
All cars and light trucks manufactured for sale in the United States after 1996 are required to be OBD2 compliant. You can also check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or look for an OBD2 port under the dashboard.
11.3 Can I clear DTCs without a scan tool?
Some vehicles may allow you to clear DTCs by disconnecting the battery for a period of time. However, this method is not recommended as it can also erase other important system settings and may not be effective for all DTCs. Using a scan tool is the preferred method.
11.4 Will clearing DTCs affect my vehicle’s performance?
Clearing DTCs will not directly affect your vehicle’s performance, but it can reset the OBD2 system and turn off the check engine light. If the underlying issue persists, the DTC will likely reappear, and performance may be affected.
11.5 How often should I check for DTCs?
You should check for DTCs whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual changes in vehicle performance. Regular DTC checks can help you identify potential problems early on.
11.6 What does it mean when a DTC keeps coming back after clearing it?
If a DTC keeps coming back after clearing it, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been resolved. Further diagnosis and repair are needed to address the root cause of the problem.
11.7 Can clearing DTCs help me pass an emissions test?
Clearing DTCs may help you pass an emissions test if the check engine light is on due to a minor issue that has been resolved. However, some vehicles require a certain number of drive cycles after clearing codes before they are ready for emission testing.
11.8 What are the risks of clearing DTCs without fixing the problem?
Clearing DTCs without fixing the underlying problem can mask the symptoms and delay necessary repairs. This can lead to further damage, increased repair costs, and potential safety hazards.
11.9 How do I find out what a specific DTC means?
You can use an OBD2 scan tool to read the DTC and display its definition. You can also search for the DTC online or consult with a qualified technician.
11.10 What should I do if I am not comfortable clearing DTCs myself?
If you are not comfortable clearing DTCs yourself, it is best to seek professional help from a qualified technician. They can accurately diagnose and repair the problem and ensure that the OBD2 system is properly reset.
12. The Future of Vehicle Diagnostics
12.1 Advancements in OBD Technology
OBD technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added to diagnostic systems. These advancements include:
- Enhanced Data Logging: Improved data logging capabilities allow for more detailed analysis of vehicle performance and diagnostic information.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic capabilities enable technicians to diagnose vehicle problems from anywhere in the world.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered diagnostic systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential problems.
- Cloud Connectivity: Cloud connectivity enables seamless data sharing and collaboration between technicians, manufacturers, and vehicle owners.
12.2 The Impact of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming the landscape of vehicle diagnostics. EVs have different diagnostic requirements than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, with a greater emphasis on battery management, electric motor performance, and charging system diagnostics.
12.3 The Role of Connected Car Technologies
Connected car technologies are enabling new diagnostic capabilities, such as over-the-air software updates, remote monitoring of vehicle health, and predictive maintenance alerts. These technologies are empowering vehicle owners to take a more proactive approach to vehicle maintenance and repair.
12.4 The Importance of Training and Education
As vehicle technology becomes more complex, the importance of training and education for technicians is growing. Technicians need to stay up-to-date on the latest diagnostic techniques, tools, and technologies to effectively diagnose and repair modern vehicles. Organizations such as ASE and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) offer training and certification programs for automotive technicians.
13. Conclusion: Empowering Your Mercedes-Benz Ownership Experience
Understanding and managing OBD2 DTCs is an essential aspect of Mercedes-Benz ownership. Global DTC clearing is a powerful tool for resetting the OBD2 system after repairs or for diagnostic purposes. By following the guidelines outlined in this article and seeking professional help when needed, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz remains in top condition.
Remember, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to support you with expert advice, diagnostic tools, and repair services. Contact us today and let us help you make the most of your Mercedes-Benz ownership experience. With our guidance, you can proactively address issues, maintain your vehicle’s performance, and enjoy the open road with confidence.
14. More Advanced Code Information Table
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Low oil level, faulty camshaft position actuator, timing chain issues |
| P0014 | “B” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Same as P0011 |
| P0030 | HO2S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, wiring issues, blown fuse |
| P0031 | HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Same as P0030 |
| P0032 | HO2S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Same as P0030 |
| P0100 | Mass Air Flow Circuit Malfunction | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, wiring issues |
| P0102 | Mass Air Flow Circuit Low Input | Same as P0100 |
| P0103 | Mass Air Flow Circuit High Input | Same as P0100 |
| P0112 | Intake Air Temperature Circuit Low Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input | Same as P0112 |
| P0117 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low Input | Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input | Same as P0117 |
| P0121 | Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Range/Performance | Dirty throttle body, faulty TPS sensor, wiring issues |
| P0122 | Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Low Input | Same as P0121 |
| P0123 | Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit High Input | Same as P0121 |
| P0131 | O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, wiring issues |
| P0132 | O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Same as P0131 |
| P0133 | O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Same as P0131 |
| P0134 | O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Same as P0131 |
| P0137 | O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2) | Faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, wiring issues |
| P0138 | O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2) | Same as P0137 |
| P0139 | O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 2) | Same as P0137 |
| P0140 | O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 2) | Same as P0137 |
| P0170 | Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty MAF sensor, low fuel pressure |
| P0172 | System Too Rich (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty MAF sensor, high fuel pressure |
| P0200 | Injector Circuit Malfunction | Faulty fuel injector, wiring issues, PCM problems |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression, vacuum leaks |
| P0302 | Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected | Same as P0301, but for cylinder 2 |
| P0303 | Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected | Same as P0301, but for cylinder 3 |
| P0304 | Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected | Same as P0301, but for cylinder 4 |
| P0325 | Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) | Faulty knock sensor, wiring issues, PCM problems |
| P0327 | Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) | Same as P0325 |
| P0328 | Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) | Same as P0325 |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Faulty EGR valve, clogged EGR passages, vacuum leaks, faulty EGR sensor |
| P0402 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive Detected | Same as P0401 |
| P0410 | Secondary Air Injection System Malfunction | Faulty air pump, check valve, vacuum leaks, wiring issues |
| P0411 | Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect Flow Detected | Same as P0410 |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, engine misfires |
| P0440 | Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction | Leaks in EVAP system, faulty gas cap, purge valve, vent valve, charcoal canister |
| P0441 | Evaporative Emission Control System Incorrect Purge Flow | Same as P0440 |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Same as P0440 |
| P0446 | Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Malfunction | Same as P0440 |
| P0500 | Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction | Faulty VSS sensor, wiring issues, ABS module problems |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Dirty throttle body, faulty IAC valve, vacuum leaks, wiring issues |
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Faulty transmission sensors, solenoid issues, wiring problems, low transmission fluid |
| P0705 | Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty TRS sensor, wiring issues, shift linkage problems |
| P0715 | Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty ISS/TSS sensor, wiring issues, transmission problems |
| P1101 | Mass Air Flow Sensor Out of Self Test Range | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks |
| P1345 | Crankshaft Position – Camshaft Position Correlation | Faulty crank sensor, cam sensor, timing chain issues, misaligned sensors |
| P1491 | EGR Valve Insufficient Lift Detected | Clogged EGR passages, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leaks |
| P1504 | Idle Air Control Circuit Open | Faulty IAC valve, wiring issues |
| P1635 | Tire/Axle Ratio Out of Acceptable Range | Incorrect tire size, faulty ABS module, PCM problems |