Can Obd2 Scanner Codes provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s health, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help you decipher them. Understanding these codes allows you to diagnose potential issues early, saving you time and money on repairs. With our expert guidance, you’ll master vehicle diagnostics, error code interpretation, and automotive troubleshooting, empowering you to maintain your vehicle effectively.
Contents
- 1. What are CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes?
- 2. What are the Different Types of CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes?
- 2.1. Powertrain (P) Codes
- 2.2. Body (B) Codes
- 2.3. Chassis (C) Codes
- 2.4. Network Communication (U) Codes
- 3. How to Read CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 3.1. Understanding the Code Structure
- 3.2. Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.3. Interpreting the Codes
- 4. How to Clear CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Clear Codes
- 4.2. Disconnecting the Battery
- 4.3. Important Considerations
- 5. How to Prevent CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 5.1. Regular Maintenance
- 5.2. Use Quality Parts and Fluids
- 5.3. Proper Driving Habits
- 5.4. Routine Inspections
- 5.5. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
- 6. Common CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 6.1. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 6.2. P0171 and P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 1 and Bank 2)
- 6.3. P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 6.4. U0100 – Lost Communication With ECM/PCM
- 6.5. P0715 – Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- 7. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in Decoding CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 7.1. Comprehensive Resources
- 7.2. Expert Guidance
- 7.3. Diagnostic Tools
- 8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
- 8.1. Using Live Data
- 8.2. Performing System Tests
- 8.3. Using Oscilloscopes and Multimeters
- 8.4. Example: Diagnosing a Misfire
- 9. CAN OBD2 Scanner Code FAQs
- 10. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
1. What are CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes?
CAN OBD2 scanner codes are standardized alphanumeric identifiers used to report vehicle malfunctions detected by the onboard diagnostic (OBD) system, crucial for automotive diagnostics. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these codes are designed to provide a universal language for identifying and addressing vehicle issues. When your “Check Engine” light comes on, it signifies that your vehicle’s computer has stored one or more of these codes, indicating a problem that needs attention.
These codes are essential for:
- Identifying problems: Pinpointing the exact system or component that is malfunctioning.
- Troubleshooting: Providing a starting point for diagnosing the issue.
- Repair: Guiding mechanics in the repair process.
 OBD2 port location
OBD2 port location
Understanding CAN OBD2 scanner codes enables you to communicate effectively with mechanics and make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance. These codes are a gateway to understanding your car’s health and ensuring its longevity.
2. What are the Different Types of CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes?
CAN OBD2 scanner codes are categorized into four main types, each indicating the area of the vehicle where the fault has occurred. Grasping these categories aids in promptly narrowing down the source of the issue.
2.1. Powertrain (P) Codes
Powertrain codes (P) relate to the engine, transmission, and associated drivetrain components. These are the most common types of OBD2 codes and can indicate a wide range of issues, from minor sensor malfunctions to major engine problems.
- Examples:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), powertrain issues account for approximately 60% of all OBD2 codes triggered. Addressing these codes promptly can prevent further damage to the engine and transmission, ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
2.2. Body (B) Codes
Body codes (B) pertain to components within the vehicle’s body, such as airbags, climate control, and lighting systems. These codes often relate to comfort and safety features.
- Examples:
- B0001: Driver Frontal Air Bag Deployment Control
- B0090: Passenger Seat Weight Sensor
- B0100: Air Conditioning System Performance
These codes are critical for maintaining the safety and comfort of your vehicle. Ignoring body codes can lead to malfunctioning safety features or a compromised driving experience.
2.3. Chassis (C) Codes
Chassis codes (C) involve the vehicle’s chassis, including braking systems, suspension, and steering. These codes are vital for ensuring safe handling and stability.
- Examples:
- C0031: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit
- C0265: ABS Activation Relay Circuit Open
- C0110: ABS Pump Motor Circuit
Addressing chassis codes immediately is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s safety. Problems with the braking system or suspension can significantly increase the risk of accidents.
2.4. Network Communication (U) Codes
Network communication codes (U) relate to the communication network between the vehicle’s various electronic control units (ECUs). These codes often indicate problems with the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, which allows different components to communicate.
- Examples:
- U0100: Lost Communication with ECM/PCM
- U0155: Lost Communication with Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC)
- U0121: Lost Communication with Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module
These codes can be challenging to diagnose as they often point to underlying issues with the vehicle’s electronics. Proper diagnosis requires specialized tools and expertise to identify the root cause of the communication failure.
Understanding these four categories of CAN OBD2 scanner codes is the first step in effectively diagnosing and addressing vehicle issues. Each code provides valuable information about the location and nature of the problem, enabling you to take appropriate action.
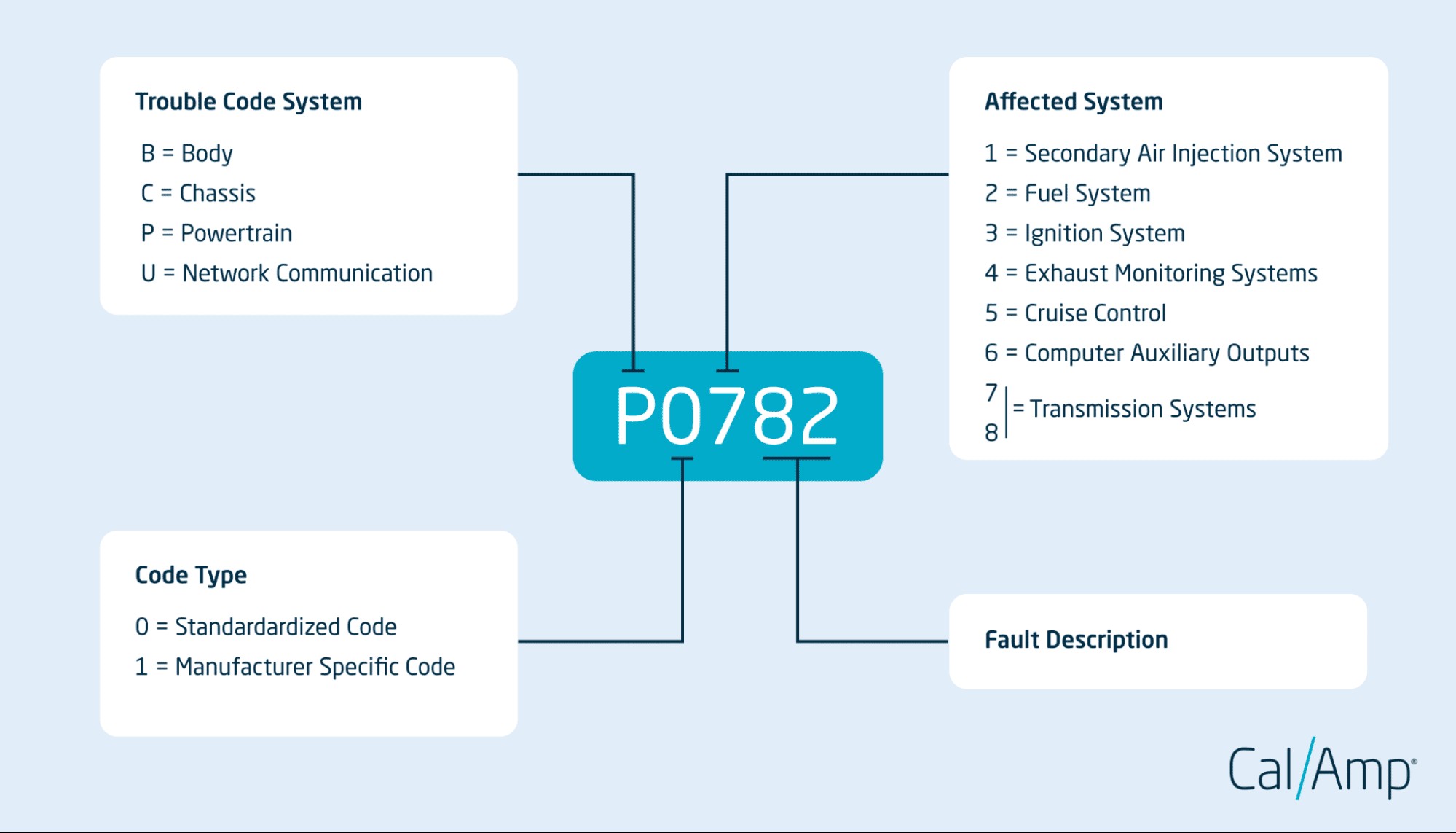
3. How to Read CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
Reading CAN OBD2 scanner codes involves understanding the structure of the code and using a scanner to retrieve the information. Each code consists of five characters: a letter followed by four digits.
3.1. Understanding the Code Structure
Each character in the code provides specific information about the nature and location of the problem:
-
First Character (Letter): Indicates the system affected.
- P: Powertrain
- B: Body
- C: Chassis
- U: Network Communication
-
Second Character (Digit): Specifies whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific.
- 0: Generic (SAE) code, applicable to all vehicles.
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code, unique to the vehicle’s manufacturer.
-
Third Character (Digit): Identifies the subsystem affected.
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 2: Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 4: Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5: Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 6: Computer Output Circuit
- 7, 8: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters (Digits): Specify the exact fault within the subsystem. These digits provide more detailed information about the nature of the problem.
3.2. Using an OBD2 Scanner
To read CAN OBD2 scanner codes, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. These scanners are readily available online and at auto parts stores. Here’s how to use one:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes. The scanner will display the codes and may also provide a brief description of the problem.
- Record the Codes: Write down the codes so you can research them further.
According to a report by J.D. Power, approximately 70% of vehicle owners prefer to diagnose their vehicle issues before taking it to a mechanic. Using an OBD2 scanner empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and make informed decisions about repairs.
3.3. Interpreting the Codes
Once you have the codes, you can use online resources or a repair manual to interpret them. Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provide comprehensive databases of OBD2 codes and their meanings.
- Example: If you retrieve the code P0301, you can look it up online and find that it indicates a misfire in cylinder 1.
Understanding how to read and interpret CAN OBD2 scanner codes is a valuable skill for any vehicle owner. It allows you to quickly identify potential problems and take appropriate action, saving you time and money on repairs.
4. How to Clear CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
Clearing CAN OBD2 scanner codes should be done with caution, as it does not fix the underlying problem. However, there are situations where clearing the codes is necessary, such as after performing a repair or to reset the system for testing purposes.
4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner to Clear Codes
The most common method for clearing CAN OBD2 scanner codes is to use an OBD2 scanner. Here’s how:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Navigate to the Clear Codes Function: Follow the scanner’s instructions to find the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” function.
- Confirm the Action: The scanner will typically ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes. Confirm the action.
- Verify the Codes are Cleared: After clearing the codes, turn off the ignition for a few minutes, then turn it back on and re-scan the system to verify that the codes have been cleared.
4.2. Disconnecting the Battery
Another method for clearing CAN OBD2 scanner codes is to disconnect the vehicle’s battery. However, this method is not recommended as it can also reset other electronic systems in the vehicle, such as the radio and security system.
- Locate the Battery: Find the vehicle’s battery, typically located under the hood or in the trunk.
- Disconnect the Negative Terminal: Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (-) battery terminal. Remove the cable from the terminal.
- Wait: Wait for 15-30 minutes to allow the vehicle’s computer to reset.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative (-) battery terminal and tighten the nut.
4.3. Important Considerations
- Underlying Issues: Clearing the codes does not fix the underlying problem. The codes will likely return if the issue is not addressed.
- Readiness Monitors: Clearing the codes also resets the vehicle’s readiness monitors. These monitors need to run and complete their tests before the vehicle can pass an emissions test. This can take several days of driving under specific conditions.
- Professional Advice: If you are unsure about clearing the codes or diagnosing the underlying problem, consult a qualified mechanic.
According to a survey by Consumer Reports, approximately 20% of vehicle owners attempt to clear OBD2 codes without addressing the underlying issue. While clearing the codes may temporarily turn off the “Check Engine” light, it is essential to address the root cause of the problem to prevent further damage and ensure the vehicle’s safety.
Clearing CAN OBD2 scanner codes can be useful in certain situations, but it is important to understand the potential consequences and address any underlying issues before doing so.
5. How to Prevent CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
Preventing CAN OBD2 scanner codes involves regular maintenance and proactive care to ensure your vehicle operates efficiently and reliably.
5.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is the most effective way to prevent CAN OBD2 scanner codes. This includes:
- Oil Changes: Changing the oil at the recommended intervals ensures proper lubrication and prevents engine wear.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replacing the air filter ensures that the engine receives clean air, improving performance and fuel efficiency.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replacing the spark plugs at the recommended intervals ensures proper ignition and prevents misfires.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly checking and topping off fluids, such as coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid, ensures that the vehicle’s systems operate properly.
- Inspections: Regularly inspecting the vehicle for any signs of wear or damage can help identify potential problems before they trigger OBD2 codes.
5.2. Use Quality Parts and Fluids
Using high-quality parts and fluids is essential for preventing CAN OBD2 scanner codes. Low-quality parts and fluids can fail prematurely, leading to malfunctions and triggering OBD2 codes.
- OEM Parts: Use original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts whenever possible. These parts are designed to meet the vehicle’s specifications and are more reliable than aftermarket parts.
- Recommended Fluids: Use the fluids recommended by the vehicle’s manufacturer. These fluids are specifically formulated to work with the vehicle’s systems and provide optimal performance.
5.3. Proper Driving Habits
Proper driving habits can also help prevent CAN OBD2 scanner codes. Avoid:
- Hard Acceleration: Rapid acceleration can put stress on the engine and transmission, leading to premature wear and triggering OBD2 codes.
- Sudden Braking: Sudden braking can wear down the brake pads and rotors, leading to braking system issues and triggering OBD2 codes.
- Ignoring Warning Lights: Ignoring warning lights can allow minor problems to escalate into major issues, triggering OBD2 codes and potentially causing significant damage to the vehicle.
According to a study by AAA, regular vehicle maintenance can reduce the likelihood of breakdowns by up to 40%. By following a regular maintenance schedule, using quality parts and fluids, and practicing proper driving habits, you can significantly reduce the chances of triggering CAN OBD2 scanner codes and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
5.4. Routine Inspections
Performing routine inspections can help catch minor issues before they escalate into major problems that trigger OBD-II codes. Check the following regularly:
- Tire Pressure: Ensure tires are properly inflated to prevent uneven wear and improve fuel efficiency.
- Fluid Levels: Monitor and maintain proper levels of engine oil, coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid.
- Lights: Check all lights, including headlights, taillights, brake lights, and turn signals, to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more significant problems and the dreaded “Check Engine” light.
5.5. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Small issues can quickly turn into big problems if left unattended. If you notice anything unusual about your vehicle’s performance, such as strange noises, vibrations, or changes in fuel efficiency, address it immediately. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to more extensive damage and costly repairs.
According to the Car Care Council, neglecting routine maintenance is the top reason for vehicle breakdowns. Preventative care and addressing minor issues promptly can save you time, money, and headaches in the long run.
6. Common CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles, known for their advanced technology and sophisticated engineering, can trigger specific CAN OBD2 scanner codes that are commonly associated with their systems. Understanding these codes can help Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians diagnose and address issues more effectively.
6.1. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions from the exhaust system. A P0420 code can be caused by:
- A failing catalytic converter
- Exhaust leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Engine misfires
According to Mercedes-Benz service bulletins, this code is often associated with older vehicles where the catalytic converter has deteriorated over time.
6.2. P0171 and P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 1 and Bank 2)
These codes indicate that the engine is running too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Common causes include:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Fuel pump issues
- Clogged fuel filter
Mercedes-Benz technicians often check for vacuum leaks first, as these are a common cause of lean conditions in Mercedes-Benz engines.
6.3. P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in one or more cylinders. Misfires can be caused by:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Ignition coil problems
- Fuel injector issues
- Vacuum leaks
- Low compression
Mercedes-Benz engines are particularly sensitive to spark plug condition, and worn or faulty spark plugs are a common cause of misfires.
6.4. U0100 – Lost Communication With ECM/PCM
This code indicates a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM). This can be caused by:
- Wiring issues
- Faulty ECM/PCM
- CAN bus problems
- Loose connections
Mercedes-Benz vehicles rely heavily on their electronic systems, and communication issues can lead to a variety of problems.
6.5. P0715 – Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the input or turbine speed sensor in the transmission. This sensor is used to monitor the speed of the transmission input shaft. Causes include:
- Faulty sensor
- Wiring issues
- Transmission problems
Mercedes-Benz transmissions are complex and require precise monitoring. This code can indicate potential issues with the transmission’s performance.
Addressing these common CAN OBD2 scanner codes promptly can help Mercedes-Benz owners maintain their vehicles in top condition and prevent more serious problems from developing.
7. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in Decoding CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN plays a crucial role in helping Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians decode CAN OBD2 scanner codes by providing comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and diagnostic tools.
7.1. Comprehensive Resources
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on CAN OBD2 scanner codes, including:
- Code Definitions: Detailed explanations of what each code means, including potential causes and symptoms.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Step-by-step guides on how to diagnose and address common OBD2 code issues.
- Technical Articles: In-depth articles on Mercedes-Benz vehicle systems and how they relate to OBD2 codes.
- Forums and Communities: Online forums where users can share their experiences, ask questions, and receive advice from experts.
7.2. Expert Guidance
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to expert guidance from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians and diagnosticians. This includes:
- Online Support: Direct access to experts who can answer questions and provide personalized advice.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic services that allow technicians to remotely access and diagnose vehicle systems.
- Training Programs: Training programs for technicians who want to improve their diagnostic skills and knowledge of Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
7.3. Diagnostic Tools
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including:
- OBD2 Scanners: High-quality OBD2 scanners that can read and clear codes, view live data, and perform advanced diagnostic functions.
- Specialized Diagnostic Software: Software that provides access to Mercedes-Benz specific diagnostic information and functions.
- Hardware Interfaces: Hardware interfaces that connect to the vehicle’s diagnostic port and allow communication with the vehicle’s systems.
According to a survey of Mercedes-Benz technicians, access to comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and specialized diagnostic tools can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides all of these resources in one place, making it an invaluable tool for anyone working on Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
By leveraging the resources and expertise available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians can effectively decode CAN OBD2 scanner codes and ensure their vehicles are running smoothly and reliably.
8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for CAN OBD2 Scanner Codes
While basic OBD2 scanners can read and clear codes, advanced diagnostic techniques are often necessary to accurately diagnose and address complex vehicle issues. These techniques involve using specialized tools, interpreting live data, and performing system tests.
8.1. Using Live Data
Live data refers to the real-time information provided by the vehicle’s sensors and systems. By monitoring live data, technicians can identify subtle issues that may not trigger a specific OBD2 code.
- Accessing Live Data: Advanced OBD2 scanners and diagnostic software allow technicians to access live data from various vehicle systems.
- Interpreting Live Data: Interpreting live data requires a thorough understanding of how the vehicle’s systems operate. Technicians must be able to recognize normal and abnormal readings and identify patterns that indicate potential problems.
- Examples: Monitoring oxygen sensor readings to diagnose fuel mixture issues, or monitoring wheel speed sensor readings to diagnose ABS problems.
8.2. Performing System Tests
System tests involve using diagnostic tools to perform specific tests on the vehicle’s systems. These tests can help isolate and identify faulty components.
- Actuator Tests: Actuator tests allow technicians to activate and test various components, such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays.
- Component Tests: Component tests involve using specialized tools to test the functionality of individual components, such as sensors and modules.
- Examples: Performing a fuel injector test to check for proper fuel delivery, or performing an ABS pump test to check for proper pump operation.
8.3. Using Oscilloscopes and Multimeters
Oscilloscopes and multimeters are essential tools for advanced diagnostics. They allow technicians to measure electrical signals and voltages, helping them identify wiring issues and faulty components.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes display electrical signals as waveforms, allowing technicians to analyze the signal’s shape, amplitude, and frequency.
- Multimeters: Multimeters measure voltage, current, and resistance, allowing technicians to test the continuity of circuits and the functionality of electrical components.
8.4. Example: Diagnosing a Misfire
To illustrate how these techniques are used, consider the example of diagnosing a misfire (P0300 code).
- Read the Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the codes and identify which cylinder is misfiring.
- Check Spark Plugs and Ignition Coils: Inspect the spark plugs and ignition coils for signs of wear or damage.
- Perform a Compression Test: Perform a compression test to check for cylinder compression issues.
- Monitor Live Data: Monitor live data to check fuel injector pulse width and oxygen sensor readings.
- Perform a Fuel Injector Test: Perform a fuel injector test to check for proper fuel delivery.
- Use an Oscilloscope: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the ignition coil’s firing pattern.
By combining these techniques, technicians can accurately diagnose the cause of the misfire and recommend the appropriate repair.
Mastering advanced diagnostic techniques requires specialized training and experience. However, these techniques are essential for accurately diagnosing and addressing complex vehicle issues and ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
9. CAN OBD2 Scanner Code FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about CAN OBD2 scanner codes:
-
What is the difference between a generic and a manufacturer-specific code?
- Generic codes are standardized codes that apply to all vehicles. Manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information about the problem.
-
Can I drive my car with a “Check Engine” light on?
- It depends on the severity of the problem. If the light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that requires immediate attention. If the light is solid, you can usually drive the car for a short period, but it’s important to diagnose and address the problem as soon as possible.
-
Will clearing the codes fix the problem?
- No, clearing the codes only turns off the “Check Engine” light. It does not fix the underlying problem. The codes will likely return if the issue is not addressed.
-
How do I know which OBD2 scanner is right for my car?
- Check the scanner’s compatibility list to ensure it supports your vehicle’s make and model. Also, consider the features you need, such as live data, system tests, and code definitions.
-
Can I use my smartphone as an OBD2 scanner?
- Yes, there are OBD2 adapters that connect to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and communicate with your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. You’ll also need to download an OBD2 app to read and interpret the codes.
-
How often should I scan my car for OBD2 codes?
- You should scan your car for OBD2 codes whenever the “Check Engine” light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms. Regular maintenance checks can also help identify potential problems before they trigger OBD2 codes.
-
Are OBD2 codes the same for all cars?
- Yes, generic OBD2 codes are the same for all cars. However, manufacturer-specific codes vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
-
What does it mean when my car fails an emissions test due to OBD2 codes?
- It means that the vehicle’s emissions control systems are not functioning properly. You’ll need to diagnose and address the underlying problems before the vehicle can pass the emissions test.
-
Can I fix OBD2 code issues myself, or should I take it to a mechanic?
- It depends on your mechanical skills and experience. Simple issues, such as replacing a spark plug or tightening a gas cap, can often be fixed yourself. However, more complex issues require specialized tools and expertise and should be handled by a qualified mechanic.
-
Where can I find more information about OBD2 codes and vehicle diagnostics?
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and diagnostic tools to help you decode CAN OBD2 scanner codes and ensure your Mercedes-Benz vehicle is running smoothly and reliably.
10. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Expert Assistance
Don’t let CAN OBD2 scanner codes leave you in the dark. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert assistance to help you diagnose and resolve any issues your Mercedes-Benz vehicle may be experiencing.
Here’s how we can help:
- Expert Diagnostics: Our team of certified Mercedes-Benz technicians can accurately diagnose the cause of your OBD2 codes using advanced diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Remote Support: We offer remote diagnostic services to help you troubleshoot issues from the comfort of your own home or shop.
- Parts and Accessories: We provide access to high-quality Mercedes-Benz parts and accessories to ensure your repairs are done right.
- Unlock Hidden Features: Discover the untapped potential of your Mercedes-Benz with our feature unlocking services. From enhanced performance to added convenience, we tailor your vehicle to your unique preferences.
- Maintenance and Repair Guides: Access our extensive library of maintenance and repair guides to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz in top condition.
Contact us today:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in decoding CAN OBD2 scanner codes and ensuring your Mercedes-Benz vehicle is running at its best. Reach out now to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a smoother, more reliable driving experience.