Can Obd2 Scanner Instructions are essential for diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed guides on how to effectively use these scanners to identify and resolve car issues, including interpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring live data. Our platform assists you in understanding automotive diagnostics, troubleshooting common issues, and unlocking advanced features, ensuring optimal vehicle performance with diagnostic tools, car diagnostic tools, and automotive diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of Can OBD2 Scanners
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.3 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 1.4 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2. Step-by-Step Instructions for Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2.1 Preparing to Use the Scanner
- 2.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- 2.3 Navigating the Scanner Menu
- 2.4 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.5 Using Live Data for Diagnostics
- 2.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.7 Tips for Effective OBD2 Scanning
- 3. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.1 Structure of a DTC
- 3.2 Common DTC Categories
- 3.3 Interpreting DTCs
- 3.4 Resources for DTC Information
- 3.5 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 4. Advanced Features of Can OBD2 Scanners
- 4.1 Live Data Streaming
- 4.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 4.3 Bi-Directional Control
- 4.4 Onboard Monitoring Tests
- 4.5 Advanced Coding and Programming
- 4.6 Choosing the Right Scanner
- 5. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz with an OBD2 Scanner
- 5.1 Common Mercedes-Benz Issues
- 5.2 Using an OBD2 Scanner for Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
- 5.3 Mercedes-Benz Specific Features
- 5.4 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz
- 5.5 Routine Maintenance Tips
- 6. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Mercedes-Benz
- 6.1 What are Hidden Features?
- 6.2 Common Hidden Features on Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 6.3 Tools Needed to Unlock Hidden Features
- 6.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Hidden Features
- 6.5 Risks and Precautions
- 7. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 7.1 Scanner Won’t Connect to Vehicle
- 7.2 Scanner Won’t Power On
- 7.3 Inaccurate or Missing Data
- 7.4 Scanner Freezes or Crashes
- 7.5 Common Error Messages
- 8. Choosing the Right Can OBD2 Scanner
- 8.1 Consider Your Needs
- 8.2 Key Features to Look For
- 8.3 Types of Scanners
- 8.4 Budget
- 8.5 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 8.6 User Reviews
- 9. The Future of Can OBD2 Scanners
- 9.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 9.2 Enhanced Connectivity
- 9.3 Expansion of Diagnostic Capabilities
- 9.4 User-Friendly Interfaces
- 9.5 Impact on Automotive Maintenance
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Can OBD2 Scanners
- 10.1 What is a Can OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2 How Do I Connect an OBD2 Scanner to My Car?
- 10.3 Will an OBD2 Scanner Work on Any Car?
- 10.4 Can an OBD2 Scanner Clear My Check Engine Light?
- 10.5 Do I Need a Professional-Grade Scanner, or Will a Basic One Suffice?
- 10.6 How Often Should I Use an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.7 What Do the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Mean?
- 10.8 Can I Unlock Hidden Features on My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.9 Are There Any Risks to Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.10 Where Can I Purchase a Reliable Can OBD2 Scanner?
1. Understanding the Basics of Can OBD2 Scanners
Can OBD2 scanners are essential tools for modern vehicle diagnostics. These devices allow you to communicate with your car’s onboard computer, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, and perform various diagnostic tests. Understanding the fundamentals of these scanners is the first step toward effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
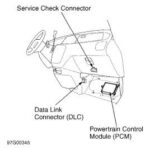
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a device used to access the diagnostic information stored in a vehicle’s computer system. These scanners connect to the car’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and provide access to a wealth of data about the vehicle’s performance and health. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been standardized in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models.
1.2 Key Components of an OBD2 Scanner
An OBD2 scanner typically consists of the following key components:
- Connector: This is the physical interface that plugs into the vehicle’s OBD2 port. The connector is standardized with a 16-pin configuration, ensuring compatibility across different vehicles.
- Display Screen: The display screen shows the diagnostic information, such as DTCs, sensor readings, and test results. Some scanners have simple LCD screens, while others feature color displays with advanced graphics.
- Buttons or Touchscreen: These controls allow you to navigate the scanner’s menu, select different functions, and input data.
- Processing Unit: The processing unit is the brain of the scanner, responsible for communicating with the vehicle’s computer, retrieving diagnostic data, and displaying it on the screen.
- Software: The software provides the interface for interacting with the scanner and interpreting the diagnostic information. Advanced scanners may include features like code definitions, repair tips, and data logging capabilities.
1.3 Types of OBD2 Scanners
OBD2 scanners come in various types, each offering different features and capabilities. Here are some common types:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, inexpensive scanners that can read and clear DTCs. They are suitable for basic troubleshooting and identifying common issues.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data monitoring, freeze frame data, and I/M readiness testing. They are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and car owners who want to perform more in-depth diagnostics.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are high-end scanners used by professional mechanics and technicians. They offer advanced features like bi-directional control, advanced coding, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic information.
- Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters: These adapters plug into the OBD2 port and communicate with a smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth. They require a compatible app to display diagnostic information and offer a convenient, portable solution.
1.4 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner offers several benefits for vehicle owners and enthusiasts:
- Early Issue Detection: OBD2 scanners allow you to detect potential problems early, preventing costly repairs down the road.
- Cost Savings: By diagnosing and fixing issues yourself, you can save money on mechanic fees.
- Emission Test Readiness: Scanners check your vehicle’s readiness for emissions tests, avoiding failures.
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time data monitoring helps you track your vehicle’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Informed Decisions: With accurate diagnostic information, you can make informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repairs.
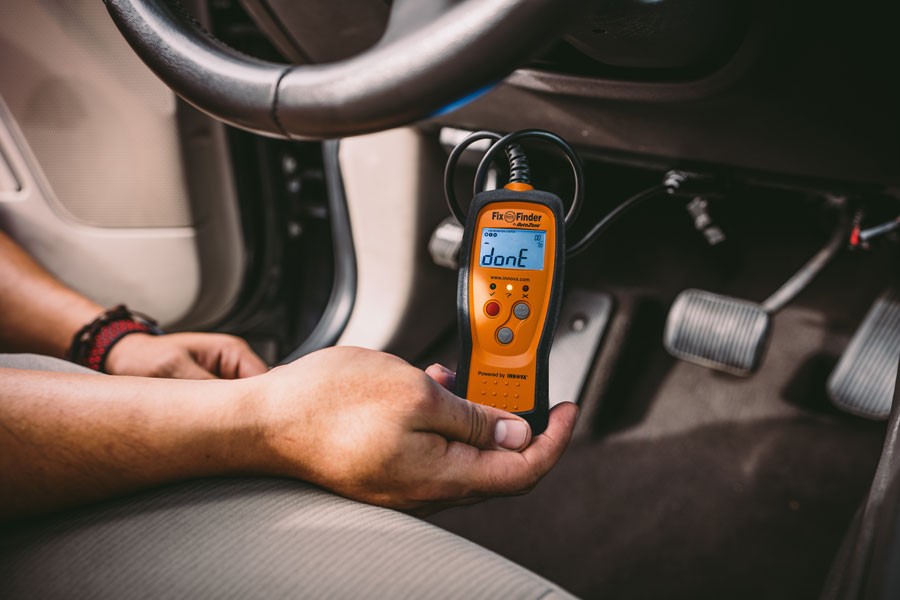 OBD-II scanner displaying trouble codes
OBD-II scanner displaying trouble codes
2. Step-by-Step Instructions for Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner might seem daunting at first, but with the right guidance, it can be a straightforward process. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to use an OBD2 scanner effectively.
2.1 Preparing to Use the Scanner
Before you start, gather necessary equipment and information to ensure a smooth diagnostic process.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the car’s ignition is off to prevent electrical issues during connection.
- Consult the Vehicle’s Manual: Refer to your vehicle’s manual for specific instructions or warnings related to OBD2 scanning.
- Gather Vehicle Information: Note the make, model, year, and VIN of your vehicle for accurate diagnostics.
2.2 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Match the trapezoidal shape of the scanner’s connector with the OBD2 port and gently push them together.
- Ensure a Secure Connection: Wiggle the connector slightly to ensure it is fully seated.
- Turn the Ignition On: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power Up the Scanner: The OBD2 port will power up your scanner; wait for it to boot up.
2.3 Navigating the Scanner Menu
Once the scanner is powered up, navigate the menu to access diagnostic functions.
- Read Codes: Select “Read Codes” to view diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Erase Codes: Choose “Erase Codes” to clear stored DTCs after repairs. Be cautious, as this clears all codes.
- Live Data: Use “Live Data” to monitor real-time sensor readings and performance data.
- Freeze Frame: Access “Freeze Frame” data to see parameters recorded when a DTC was set.
- Vehicle Info: Check “Vehicle Info” for details about your vehicle’s build.
- I/M Readiness: Use “I/M Readiness” to check emissions and smog test readiness.
2.4 Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When you select “Read Codes,” the scanner will display any stored DTCs. Each code consists of a letter followed by four numbers, such as P0301.
-
Identify the System: The letter indicates the system with the fault:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, emissions)
- B: Body (airbag, interior)
- C: Chassis (suspension, power steering)
- U: Network (communication issues)
-
Understand the Numbers:
- First Number: 0 (generic code) or 1 (manufacturer-specific code)
- Second Number: Indicates the system component (e.g., fuel and air metering, ignition system)
- Third and Fourth Numbers: Provide further detail about the specific fault
2.5 Using Live Data for Diagnostics
Live data monitoring allows you to observe real-time sensor readings and performance parameters.
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the “Live Data” option in the scanner menu.
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Observe Readings: Watch the readings as the engine runs to identify any unusual or out-of-range values.
- Analyze Data: Use the data to diagnose issues and verify the performance of various components.
2.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After addressing the issues indicated by the DTCs, you can clear the codes from the vehicle’s computer.
- Select “Erase Codes”: Navigate to the “Erase Codes” option in the scanner menu.
- Confirm Selection: Confirm your selection to clear the codes; the scanner may ask for confirmation to prevent accidental clearing.
- Verify Clearance: After clearing the codes, restart the vehicle and rescan to ensure the codes do not reappear.
2.7 Tips for Effective OBD2 Scanning
- Check the Battery: Low battery voltage can cause inaccurate readings; ensure the battery is fully charged.
- Update the Scanner: Keep your scanner’s software updated to access the latest code definitions and features.
- Refer to Repair Manuals: Use repair manuals and online resources for detailed information on DTCs and troubleshooting procedures.
- Document Your Findings: Keep a record of DTCs, live data readings, and repairs performed for future reference.
3. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in your car’s computer that help identify specific issues. Each code points to a particular problem area, making it easier to diagnose and repair your vehicle. Understanding DTCs is crucial for effective OBD2 scanning.
3.1 Structure of a DTC
A DTC typically consists of a five-character code, such as P0301. The structure of the code provides valuable information about the nature and location of the fault.
-
First Character: Indicates the system with the fault:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, emissions)
- B: Body (airbag, interior)
- C: Chassis (suspension, power steering)
- U: Network (communication issues)
-
Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code, applicable to all vehicles
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code, unique to a particular make or model
-
Third Character: Indicates the subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control or idle system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7, 8, 9: Transmission
- A, B, C: Hybrid propulsion system
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide further details about the specific fault within the subsystem.
3.2 Common DTC Categories
DTCs are categorized based on the system they relate to. Here are some common categories:
- Powertrain Codes (P Codes): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, fuel system, and emissions control system. Examples include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) and P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1).
- Body Codes (B Codes): These codes relate to the vehicle’s body control systems, such as airbags, power windows, and door locks. Examples include B1000 (ECU Internal Failure) and B1001 (ECU Configuration Error).
- Chassis Codes (C Codes): These codes relate to the vehicle’s chassis systems, such as ABS, traction control, and suspension. Examples include C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit) and C0040 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit).
- Network Codes (U Codes): These codes relate to the vehicle’s communication network, such as CAN bus and other communication protocols. Examples include U0100 (Lost Communication with ECM/PCM) and U0155 (Lost Communication with Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) Control Module).
3.3 Interpreting DTCs
Interpreting DTCs involves understanding the meaning of each code and using that information to diagnose the underlying issue.
- Record the Code: Write down the exact DTC displayed by the scanner.
- Look Up the Definition: Use a reliable source, such as a repair manual or online database, to look up the definition of the code.
- Gather Additional Information: Collect information about the vehicle’s symptoms, recent repairs, and any other relevant details.
- Analyze the Data: Use the code definition and additional information to analyze the potential causes of the issue.
- Perform Further Testing: Conduct additional tests, such as visual inspections, sensor testing, and circuit testing, to confirm the diagnosis.
3.4 Resources for DTC Information
Several resources can help you find DTC definitions and troubleshooting information:
- Repair Manuals: Vehicle-specific repair manuals provide detailed information on DTCs and repair procedures.
- Online Databases: Websites like OBD-Codes.com and Autozone.com offer free DTC lookups and troubleshooting tips.
- Scanner Software: Advanced OBD2 scanners often include built-in DTC definitions and troubleshooting information.
- Online Forums: Automotive forums can be a valuable resource for sharing information and getting advice from other enthusiasts and professionals.
3.5 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming the Code is the Solution: A DTC points to a potential problem area but doesn’t always identify the exact cause.
- Ignoring Symptoms: Pay attention to the vehicle’s symptoms, as they can provide valuable clues about the underlying issue.
- Failing to Perform Further Testing: Conduct additional tests to confirm the diagnosis and identify the root cause of the problem.
- Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Issue: Clearing codes without addressing the underlying issue will only result in the code reappearing.
4. Advanced Features of Can OBD2 Scanners
Modern OBD2 scanners offer a range of advanced features that go beyond basic code reading. These features can help you perform more in-depth diagnostics, monitor vehicle performance, and even perform certain repairs.
4.1 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings and performance parameters as the vehicle is running. This feature can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues and identifying problems that don’t trigger a DTC.
-
Key Parameters to Monitor:
- Engine RPM
- Coolant Temperature
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trims
- Mass Airflow (MAF)
- Throttle Position
-
Benefits:
- Identify abnormal sensor readings
- Diagnose performance issues
- Monitor engine health
- Verify repairs
4.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of sensor readings and operating conditions at the moment a DTC was set. This information can help you understand the circumstances that led to the fault and narrow down the potential causes.
-
Key Data Points:
- Engine RPM
- Vehicle Speed
- Engine Load
- Coolant Temperature
- Fuel Trims
-
Benefits:
- Understand conditions when DTC was set
- Identify potential causes of the fault
- Troubleshoot intermittent issues
4.3 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer and activate certain components for testing purposes. This feature can be used to perform tests such as:
- Activating fuel injectors
- Cycling the ABS pump
- Controlling the cooling fans
- Operating the throttle
- Benefits
- Verify component functionality
- Perform diagnostic tests
- Calibrate systems
4.4 Onboard Monitoring Tests
Onboard monitoring tests are diagnostic routines performed by the vehicle’s computer to monitor the performance of various systems. OBD2 scanners can access the results of these tests, providing valuable insights into the health of the vehicle.
-
Common Tests:
- Catalyst Efficiency Test
- Oxygen Sensor Heater Test
- Evaporative System Test
- EGR System Test
-
Benefits:
- Monitor system performance
- Identify potential issues
- Ensure compliance with emissions standards
4.5 Advanced Coding and Programming
Some professional-grade OBD2 scanners offer advanced coding and programming capabilities, allowing you to:
- Reprogram control modules
- Customize vehicle settings
- Enable or disable certain features
- Perform security functions
4.6 Choosing the Right Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner with advanced features, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Features: Choose a scanner with the features you need for your diagnostic and repair needs.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and easy-to-use controls.
- Updates: Check if the scanner receives regular software updates to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and diagnostic protocols.
- Support: Consider the level of support offered by the manufacturer, including documentation, online resources, and customer service.
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz with an OBD2 Scanner
Maintaining a Mercedes-Benz requires specialized tools and knowledge. An OBD2 scanner can be a valuable asset for Mercedes-Benz owners, allowing them to monitor their vehicle’s health, diagnose issues, and perform certain repairs.
5.1 Common Mercedes-Benz Issues
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are known for their luxury and performance, but they are also prone to certain common issues:
- Oil Leaks: Mercedes-Benz engines are notorious for oil leaks, particularly from the valve cover gaskets, oil filter housing, and rear main seal.
- Electrical Problems: Electrical issues are common in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including problems with the SRS (airbag) system, ABS, and various sensors.
- Suspension Issues: The air suspension systems in many Mercedes-Benz models are prone to leaks and failures, leading to ride height problems and suspension malfunctions.
- Transmission Problems: Some Mercedes-Benz transmissions are known for issues such as rough shifting, slipping, and delayed engagement.
- Engine Misfires: Engine misfires can occur due to faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
5.2 Using an OBD2 Scanner for Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
An OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose these and other issues in your Mercedes-Benz.
- Read DTCs: Use the scanner to read any stored DTCs and identify potential problems.
- Monitor Live Data: Monitor live data to observe sensor readings and performance parameters, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Perform Onboard Monitoring Tests: Access the results of onboard monitoring tests to assess the performance of various systems, such as the catalyst and oxygen sensors.
- Use Mercedes-Specific Codes: Mercedes-Benz uses some manufacturer-specific DTCs. Refer to a Mercedes-Benz repair manual or online database for definitions.
5.3 Mercedes-Benz Specific Features
Some advanced OBD2 scanners offer Mercedes-Benz specific features, such as:
- Access to Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Protocols: These scanners can communicate with Mercedes-Benz vehicles using the proprietary diagnostic protocols, providing access to more detailed diagnostic information.
- Coding and Programming Functions: Some scanners can perform coding and programming functions, such as resetting adaptations and programming control modules.
- Access to Mercedes-Benz Service Information: Some scanners provide access to Mercedes-Benz service information, such as repair procedures, wiring diagrams, and technical service bulletins.
5.4 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz
- iCarsoft MB V3.0: This scanner is specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles and offers a wide range of diagnostic and service functions.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: This scanner is a versatile tool that supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models, including Mercedes-Benz.
- LAUNCH X431 V+: This scanner is a professional-grade tool that offers advanced diagnostic and coding capabilities for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
5.5 Routine Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly. Here are some routine maintenance tips:
- Change Oil Regularly: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals.
- Check Fluid Levels: Regularly check and top off fluid levels, including coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid.
- Inspect Brakes: Inspect the brakes regularly and replace worn brake pads and rotors.
- Check Tires: Check tire pressure and tread depth regularly and rotate the tires as needed.
- Replace Air Filters: Replace the engine air filter and cabin air filter regularly.
6. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Mercedes-Benz
Many modern vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz models, have hidden features that can be unlocked or customized using specialized OBD2 scanners and coding tools. These features can enhance your driving experience, improve vehicle functionality, and personalize your car to your liking.
6.1 What are Hidden Features?
Hidden features are functions or settings that are present in the vehicle’s computer system but are not enabled by default. These features may be disabled for various reasons, such as regulatory requirements, market segmentation, or simply because they were not deemed necessary for the base model.
6.2 Common Hidden Features on Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- Cornering Lights: Activate the fog lights to illuminate the corner when turning.
- Coming Home Lights: Set the headlights to stay on for a period after the car is turned off.
- Increased Sensitivity of Rain Sensor: Adjust the sensitivity of the automatic rain sensor.
- AMG Menu in Instrument Cluster: Display AMG-specific information in the instrument cluster.
- Adjustable Ambient Lighting: Customize the colors and intensity of the ambient lighting system.
6.3 Tools Needed to Unlock Hidden Features
Unlocking hidden features typically requires a specialized OBD2 scanner or coding tool, as well as knowledge of the vehicle’s coding parameters.
- OBD2 Scanner with Coding Capabilities: Choose a scanner that supports advanced coding and programming functions.
- Coding Software: Some scanners require specific coding software to access and modify the vehicle’s settings.
- Vehicle-Specific Coding Data: You may need access to vehicle-specific coding data, such as parameter values and coding instructions.
6.4 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Hidden Features
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Access Coding Menu: Navigate to the coding or programming menu in the scanner’s software.
- Identify the Feature: Locate the hidden feature you want to unlock or customize.
- Modify the Coding Parameters: Change the coding parameters according to the desired settings.
- Save the Changes: Save the changes to the vehicle’s computer system.
- Test the Feature: Test the newly unlocked feature to ensure it is functioning correctly.
6.5 Risks and Precautions
Unlocking hidden features can be risky if not done properly. It is essential to proceed with caution and follow these precautions:
- Research Thoroughly: Research the hidden feature and the coding process before attempting to unlock it.
- Use Reliable Tools: Use a reputable OBD2 scanner and coding software.
- Back Up Original Settings: Back up the vehicle’s original coding settings before making any changes.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the coding instructions carefully and avoid making any unauthorized modifications.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are unsure about the coding process, seek help from a qualified technician.
7. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
While OBD2 scanners are reliable tools, you may encounter issues. This section provides troubleshooting tips for common problems.
7.1 Scanner Won’t Connect to Vehicle
If your scanner won’t connect to the vehicle, try these steps:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Vehicle Compatibility: Confirm the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Check the Ignition: Make sure the ignition is turned to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Test with Another Vehicle: Try connecting the scanner to another vehicle to rule out a scanner issue.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Check the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
7.2 Scanner Won’t Power On
If the scanner won’t power on, try these steps:
- Check the Power Source: Ensure the OBD2 port is providing power to the scanner.
- Test with Another Vehicle: Connect the scanner to another vehicle to see if it powers on.
- Check the Scanner’s Battery: If the scanner has a battery, make sure it is charged or replace it.
7.3 Inaccurate or Missing Data
If the scanner is displaying inaccurate or missing data, try these steps:
- Update the Scanner: Ensure the scanner’s software is up to date.
- Verify the Vehicle Information: Double-check that the vehicle’s make, model, and year are correctly entered into the scanner.
- Check Sensor Connections: Inspect the sensor connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
- Test the Sensors: Use a multimeter to test the sensors and verify they are functioning correctly.
7.4 Scanner Freezes or Crashes
If the scanner freezes or crashes, try these steps:
- Restart the Scanner: Restart the scanner and try again.
- Update the Software: Ensure the scanner’s software is up to date.
- Clear the Memory: Clear the scanner’s memory to free up resources.
- Contact Support: Contact the scanner manufacturer for assistance.
7.5 Common Error Messages
- “Link Error”: This message indicates a communication problem. Check the connection, verify vehicle compatibility, and ensure the ignition is on.
- “No Data”: This message means the scanner is not receiving data. Verify the vehicle information and check the sensor connections.
- “Code Not Found”: This message indicates the scanner does not have a definition for the DTC. Update the software or consult a repair manual.
8. Choosing the Right Can OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. Several factors should be considered to ensure that the scanner meets your needs and provides accurate, reliable results.
8.1 Consider Your Needs
- DIY Enthusiast: A mid-range scanner is adequate for reading and clearing codes.
- Professional Technician: A professional-grade scanner is needed for advanced diagnostics.
8.2 Key Features to Look For
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and easy-to-use controls.
- Features: Select a scanner with the features you need, such as live data, freeze frame, and bi-directional control.
- Updates: Check if the scanner receives regular software updates.
- Support: Consider the level of support offered by the manufacturer.
8.3 Types of Scanners
- Basic Code Readers: Simple and inexpensive scanners for basic troubleshooting.
- Mid-Range Scanners: More advanced features, such as live data and freeze frame.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: Advanced features like bi-directional control and coding.
- Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters: Adapters that connect to a smartphone or tablet.
8.4 Budget
- Basic Code Readers: $20 – $50
- Mid-Range Scanners: $100 – $300
- Professional-Grade Scanners: $500 – $2000+
8.5 Top OBD2 Scanner Brands
- Autel: Offers a wide range of scanners.
- LAUNCH: Known for professional-grade scanners with advanced features.
- iCarsoft: Scanners specifically designed for certain car brands.
- BlueDriver: Bluetooth adapters for smartphone connectivity.
8.6 User Reviews
- Read Reviews: Research user reviews.
- Check Ratings: Check ratings and feedback on websites like Amazon and automotive forums.
9. The Future of Can OBD2 Scanners
The future of Can OBD2 scanners is evolving with advancements in automotive technology and connectivity. As vehicles become more complex and connected, OBD2 scanners will continue to adapt and offer more sophisticated diagnostic and maintenance capabilities.
9.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI-powered scanners can predict potential issues.
- Automated Troubleshooting: Machine learning can suggest repairs.
9.2 Enhanced Connectivity
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Scanners connect to the cloud for real-time data and updates.
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians can remotely diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues.
9.3 Expansion of Diagnostic Capabilities
- Cybersecurity Diagnostics: Scanners can detect and address cybersecurity threats.
- ADAS Calibration: Support calibration.
9.4 User-Friendly Interfaces
- Intuitive Design: Streamlined interfaces simplify navigation and enhance user experience.
- Augmented Reality: AR displays diagnostic information.
9.5 Impact on Automotive Maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance: OBD2 scanners will play a key role in proactive maintenance.
- Remote Assistance: Remote assistance.
- Data-Driven Insights: Maintenance decisions will be based on real-time vehicle data.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Can OBD2 Scanners
10.1 What is a Can OBD2 Scanner?
A Can OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests.
10.2 How Do I Connect an OBD2 Scanner to My Car?
Locate the OBD2 port under the dashboard, turn off the ignition, and plug the scanner. Turn the ignition to the “ON” position to power the scanner.
10.3 Will an OBD2 Scanner Work on Any Car?
OBD2 scanners are standardized for vehicles sold in the United States since 1996, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models.
10.4 Can an OBD2 Scanner Clear My Check Engine Light?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can clear the check engine light by erasing the stored DTCs.
10.5 Do I Need a Professional-Grade Scanner, or Will a Basic One Suffice?
Depends on your needs. A basic scanner works.
10.6 How Often Should I Use an OBD2 Scanner?
Use an OBD2 scanner whenever you notice a problem or when the check engine light comes on.
10.7 What Do the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Mean?
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in your car’s computer that help identify specific issues.
10.8 Can I Unlock Hidden Features on My Car with an OBD2 Scanner?
Yes, you can unlock them by using specialized features.
10.9 Are There Any Risks to Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner is safe, but incorrect coding can be risky.
10.10 Where Can I Purchase a Reliable Can OBD2 Scanner?
You can find reliable Can OBD2 scanners at auto parts stores, online retailers, and directly from scanner manufacturers.
By using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can properly diagnose, repair, unlock and keep your mercedes benz working smoothly and with no problems
For expert guidance on selecting the right diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and performing essential maintenance on your Mercedes-Benz, contact us today. Our team at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is ready to assist you with top-tier solutions and support. Reach out now for personalized assistance! Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Trang web: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN