Does my car have an OBD2 port? Yes, most modern cars do, and this port is crucial for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance, and at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you understand and utilize it effectively. Understanding the OBD2 port empowers you to monitor your vehicle’s health, troubleshoot issues, and even unlock hidden features, leading to improved vehicle performance and longevity. Explore our resources for in-depth insights into automotive diagnostics and ECU programming.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Port and What Does It Do?
- 1.1. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port:
- 1.2. Why is the OBD2 Port Important for Car Owners?
- 1.3. The Evolution from OBD1 to OBD2
- 2. Where to Find the OBD2 Port in Your Mercedes-Benz
- 2.1. Locating the OBD2 Port:
- 2.2. Common Locations in Mercedes-Benz Models:
- 2.3. What If You Still Can’t Find the OBD2 Port?
- 3. Understanding the OBD2 Connector and Pinout
- 3.1. OBD2 Pinout Diagram:
- 3.2. Common Communication Protocols:
- 3.3. The Role of the CAN Bus in Modern Vehicles
- 4. Why the OBD2 Port is Essential for Modern Car Diagnostics
- 4.1. Comprehensive Vehicle Health Monitoring
- 4.2. Streamlined Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
- 4.3. Ensuring Compliance with Emissions Standards
- 5. How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 5.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner:
- 5.2. Types of OBD2 Scanners and Diagnostic Tools:
- 5.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6. Advanced Diagnostics with AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- 6.1. Benefits of Using AutoPi CAN-FD Pro:
- 6.2. Key Features of AutoPi CAN-FD Pro:
- 6.3. How AutoPi CAN-FD Pro Enhances Vehicle Performance Monitoring
- 7. Unlocking Hidden Features with OBD2 Programming
- 7.1. Examples of Hidden Features in Mercedes-Benz
- 7.2. The Process of OBD2 Programming
- 7.3. Risks and Precautions
- 8. Regular Maintenance and the Role of the OBD2 Port
- 8.1. Recommended Maintenance Schedule for Mercedes-Benz
- 8.2. How the OBD2 Port Helps in Identifying Maintenance Needs
- 8.3. Resetting Service Indicators with an OBD2 Scanner
- 9. FAQs About OBD2 Ports and Vehicle Diagnostics
- 9.1. Common Questions About OBD2 Ports
- 9.2. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues
- 9.3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Tool for Your Needs
- 10. Conclusion: Empowering You with OBD2 Knowledge
1. What is an OBD2 Port and What Does It Do?
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface in your car that provides access to the vehicle’s computer system. This allows technicians and car owners to diagnose problems, monitor performance, and access various data points.
The OBD2 port acts as a gateway to your vehicle’s data, facilitating communication between diagnostic tools and the car’s internal systems. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996 are required to have an OBD2 port. This standardization ensures that any compatible scanner can retrieve valuable information about the vehicle’s health and performance. This includes reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitoring engine parameters, and accessing emissions-related data. The OBD2 port also plays a crucial role in vehicle inspections, allowing technicians to quickly assess whether a car meets emissions standards.
1.1. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifying the source of a problem indicated by the check engine light.
- Monitoring Engine Performance: Tracking parameters like engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel efficiency.
- Emissions Testing: Ensuring the vehicle complies with environmental regulations.
- Data Logging: Recording vehicle data for analysis and performance tuning.
- Accessing Vehicle Information: Retrieving VIN, calibration IDs, and other vehicle-specific information.
1.2. Why is the OBD2 Port Important for Car Owners?
The OBD2 port empowers car owners to take a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance. By using a compatible scanner, you can:
- Identify Minor Issues Early: Catch potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
- Make Informed Repair Decisions: Understand the nature of the issue and avoid unnecessary repairs.
- Monitor Vehicle Performance: Track fuel efficiency, engine health, and other parameters to optimize performance.
- Save Money on Diagnostics: Avoid expensive diagnostic fees at dealerships or repair shops.
- Verify Repairs: Ensure that repairs have been performed correctly by clearing DTCs and monitoring system performance.
1.3. The Evolution from OBD1 to OBD2
The OBD2 system is a significant upgrade from its predecessor, OBD1. While OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization, OBD2 provides a universal interface and a more comprehensive set of diagnostic capabilities.
Prior to OBD2, each car manufacturer used its own proprietary diagnostic connector and communication protocols. This made it difficult for independent repair shops and car owners to diagnose and repair vehicles from different manufacturers. The OBD2 standard, introduced in the mid-1990s, addressed these issues by mandating a standardized connector, a common set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and a uniform communication protocol. This standardization has made vehicle diagnostics more accessible and affordable for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
2. Where to Find the OBD2 Port in Your Mercedes-Benz
Locating the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz is typically a straightforward process. While the exact location may vary slightly depending on the model and year, it is usually found in the driver’s side footwell, under the dashboard.
The OBD2 port is usually located within easy reach of the driver’s seat. Here’s a step-by-step guide to finding it:
2.1. Locating the OBD2 Port:
- Check Under the Dashboard: Look for a 16-pin connector located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Search Near the Steering Wheel: The port is often found near the steering column or in the vicinity of the pedals.
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: If you’re having trouble finding it, refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
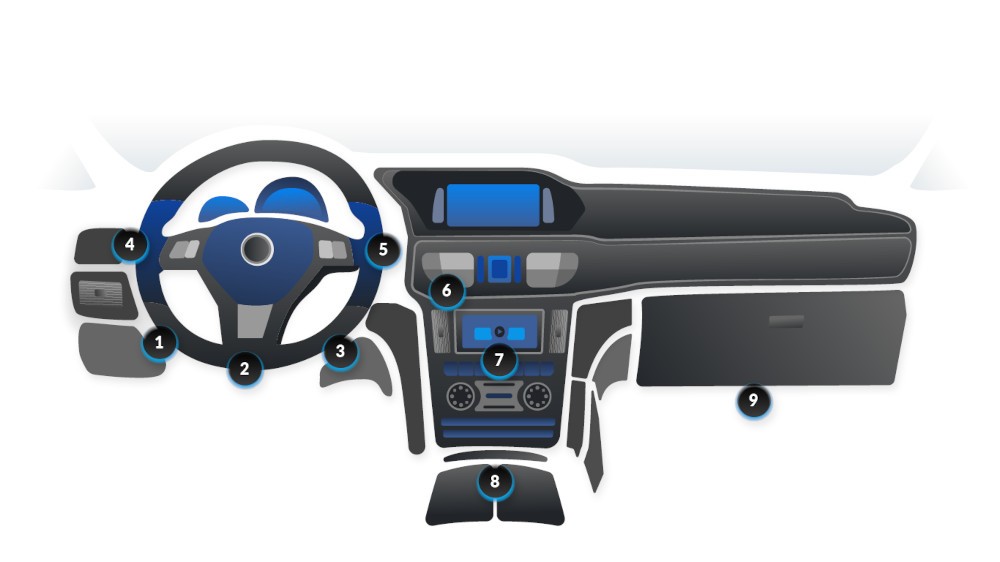 OBD2 port location under the steering wheel
OBD2 port location under the steering wheel
2.2. Common Locations in Mercedes-Benz Models:
- C-Class: Under the dashboard, to the left of the steering column.
- E-Class: Under the dashboard, above the driver’s side footwell.
- S-Class: Under the dashboard, on the left side of the steering column.
- GLC: Under the dashboard, near the center console on the driver’s side.
- GLE: Under the dashboard, to the left of the steering column.
2.3. What If You Still Can’t Find the OBD2 Port?
If you’ve checked the common locations and consulted your owner’s manual but still can’t find the OBD2 port, here are a few additional tips:
- Use a Flashlight: A flashlight can help you see into dark or hard-to-reach areas.
- Feel Around: Sometimes the port is hidden behind a panel or trim piece.
- Ask a Mechanic: If all else fails, consult a qualified mechanic for assistance.
3. Understanding the OBD2 Connector and Pinout
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin interface that allows communication between diagnostic tools and the vehicle’s computer system. Each pin serves a specific purpose, carrying different signals and data.
The OBD2 connector follows the SAE J1962 standard, which defines the physical characteristics of the connector, the pin assignments, and the communication protocols used. This standardization ensures that any compliant diagnostic tool can communicate with any OBD2-equipped vehicle.
3.1. OBD2 Pinout Diagram:
The OBD2 connector has a specific pinout, with each pin assigned to a particular function. Here’s a simplified overview of the most important pins:
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a common ground for the vehicle’s electrical system. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a ground reference for the diagnostic tool. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | Carries the CAN (Controller Area Network) high signal. |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | Used for communication with ISO 9141-2 compliant vehicles. |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus + | Used for communication with SAE J1850 compliant vehicles. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Carries the CAN (Controller Area Network) low signal. |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | Used for communication with ISO 9141-2 compliant vehicles. |
| 16 | Battery Power | Provides power to the diagnostic tool. |
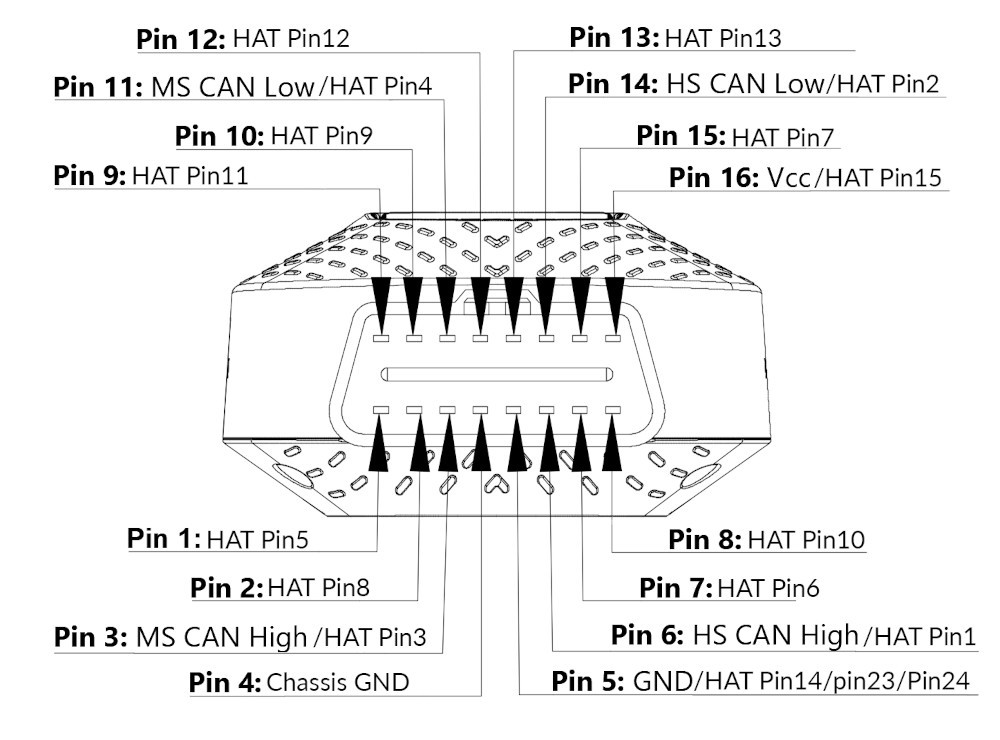 OBD2 connector pinout diagram
OBD2 connector pinout diagram
3.2. Common Communication Protocols:
The OBD2 standard supports several communication protocols, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are some of the most common protocols:
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used by General Motors vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used by Ford vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): Used by all vehicles sold in the United States since 2008.
3.3. The Role of the CAN Bus in Modern Vehicles
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) in a vehicle to communicate with each other. The CAN bus is used to transmit data between the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), anti-lock braking system (ABS), and other systems. The OBD2 port uses the CAN bus to access data from these ECUs for diagnostic purposes. As stated by Bosch, a pioneer in CAN technology, the CAN bus “enables microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in applications without a host computer.”
4. Why the OBD2 Port is Essential for Modern Car Diagnostics
The OBD2 port is essential for modern car diagnostics because it provides a standardized interface for accessing a wealth of information about the vehicle’s health and performance. It allows technicians and car owners to quickly and accurately diagnose problems, monitor system performance, and ensure compliance with emissions standards.
The OBD2 port has revolutionized the way cars are diagnosed and repaired. Prior to OBD2, diagnosing a car problem often required specialized tools and knowledge, and could be a time-consuming and expensive process. The OBD2 port has made vehicle diagnostics more accessible and affordable for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
4.1. Comprehensive Vehicle Health Monitoring
The OBD2 port provides access to a wide range of data points that can be used to monitor the vehicle’s health. These data points include:
- Engine Parameters: Engine speed, coolant temperature, fuel consumption, and more.
- Emissions Data: Oxygen sensor readings, catalytic converter efficiency, and more.
- Transmission Data: Transmission temperature, gear position, and more.
- ABS Data: Wheel speed, brake pressure, and more.
- Airbag Data: Airbag deployment status, sensor readings, and more.
By monitoring these data points, technicians and car owners can identify potential problems early on and take corrective action before they escalate into major repairs.
 Keywords about the OBD2 connector
Keywords about the OBD2 connector
4.2. Streamlined Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
The OBD2 port streamlines the diagnostic process by providing a standardized way to access diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). DTCs are codes that are stored in the vehicle’s computer system when a problem is detected. Each DTC corresponds to a specific fault or malfunction. By reading the DTCs, technicians and car owners can quickly identify the source of the problem and take appropriate action.
4.3. Ensuring Compliance with Emissions Standards
The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with emissions standards. The OBD2 system monitors the vehicle’s emissions control systems and stores DTCs when a problem is detected. During vehicle inspections, technicians can use the OBD2 port to verify that the vehicle meets emissions standards.
5. How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
Using the OBD2 port for vehicle diagnostics is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with a compatible scanner or diagnostic tool. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
5.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD2 Scanner:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and follow the instructions on the screen.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Select the option to read DTCs and wait for the scanner to retrieve the codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Consult a repair manual or online database to interpret the meaning of the DTCs.
- Take Corrective Action: Based on the DTCs, take appropriate action to repair the problem.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After repairing the problem, you can clear the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer system.
5.2. Types of OBD2 Scanners and Diagnostic Tools:
There are several types of OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools available, each with its own features and capabilities. Here are some of the most common types:
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, inexpensive scanners that can read and clear DTCs.
- Enhanced Scanners: These scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bi-directional control.
- Professional Scan Tools: These are high-end diagnostic tools used by professional mechanics. They offer the most comprehensive set of features and capabilities.
- Smartphone Apps and Adapters: These apps and adapters allow you to use your smartphone or tablet as an OBD2 scanner.
5.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are alphanumeric codes that are stored in the vehicle’s computer system when a problem is detected. Each DTC corresponds to a specific fault or malfunction. Understanding how to interpret DTCs is essential for diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems.
DTCs are typically five characters long and consist of a letter followed by four numbers. The letter indicates the system that is affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows, etc.)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension, etc.)
- U: Network (communication systems)
The numbers provide more specific information about the fault. For example, a DTC of P0300 indicates a random misfire in the engine.
6. Advanced Diagnostics with AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
While the standard OBD2 port provides valuable diagnostic information, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro takes vehicle diagnostics to the next level by offering faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance.
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is an advanced diagnostic tool that connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and provides access to a wealth of data and features that are not available with a standard OBD2 scanner.
6.1. Benefits of Using AutoPi CAN-FD Pro:
- Faster Data Acquisition: The CAN-FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-Rate) protocol allows for faster data transfer rates than the standard CAN protocol, providing real-time insights into your vehicle’s performance.
- More Detailed Data: The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro provides access to a wider range of data points, including proprietary data that is not available with a standard OBD2 scanner.
- Advanced Features: The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro offers advanced features such as remote diagnostics, data logging, and custom dashboards.
- Cloud Connectivity: The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro connects to the cloud, allowing you to access your vehicle’s data from anywhere in the world.
6.2. Key Features of AutoPi CAN-FD Pro:
- CAN-FD Support: Supports the latest CAN-FD protocol for faster data transfer rates.
- Data Logging: Allows you to record vehicle data for analysis and performance tuning.
- Remote Diagnostics: Allows you to diagnose your vehicle remotely.
- Custom Dashboards: Allows you to create custom dashboards to monitor your vehicle’s performance.
- Cloud Connectivity: Connects to the cloud for remote access to your vehicle’s data.
6.3. How AutoPi CAN-FD Pro Enhances Vehicle Performance Monitoring
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro enhances vehicle performance monitoring by providing access to a wider range of data points, faster data acquisition rates, and advanced features such as data logging and custom dashboards. This allows you to gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
For example, you can use the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to monitor your engine’s performance in real-time, track your fuel efficiency, and identify potential problems before they escalate into major repairs. You can also use the data logging feature to record vehicle data during track days or road trips and analyze the data later to identify areas for improvement.
 The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
7. Unlocking Hidden Features with OBD2 Programming
In addition to diagnostics and performance monitoring, the OBD2 port can also be used to unlock hidden features in your Mercedes-Benz. This process, known as OBD2 programming or coding, involves modifying the vehicle’s software to enable features that were not originally activated.
OBD2 programming can be used to customize various aspects of your vehicle, such as:
- Lighting: Activating cornering lights, adjusting daytime running lights, and more.
- Convenience Features: Enabling automatic folding mirrors, activating comfort access, and more.
- Performance Enhancements: Adjusting throttle response, increasing horsepower, and more.
- Safety Features: Activating lane departure warning, enabling blind spot monitoring, and more.
7.1. Examples of Hidden Features in Mercedes-Benz
Here are some examples of hidden features that can be unlocked in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- Cornering Lights: These lights illuminate the side of the road when turning, providing better visibility.
- Automatic Folding Mirrors: These mirrors automatically fold in when the vehicle is parked, preventing damage in tight spaces.
- Comfort Access: This feature allows you to unlock and start the vehicle without using the key fob.
- Lane Departure Warning: This system warns you if you are drifting out of your lane.
- Blind Spot Monitoring: This system alerts you to vehicles in your blind spot.
7.2. The Process of OBD2 Programming
OBD2 programming typically involves using a specialized software and an OBD2 adapter to connect to the vehicle’s computer system. The software allows you to modify the vehicle’s software and enable or disable various features.
It is important to note that OBD2 programming can be complex and requires specialized knowledge. It is recommended to consult with a qualified technician or use a reputable OBD2 programming service like MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to ensure that the programming is done correctly and safely.
7.3. Risks and Precautions
While OBD2 programming can be a great way to customize your vehicle, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and take appropriate precautions. Some of the risks associated with OBD2 programming include:
- Voiding the Warranty: Modifying the vehicle’s software may void the warranty.
- Damaging the Vehicle: Incorrect programming can damage the vehicle’s computer system.
- Malfunctioning Systems: Enabling or disabling certain features can cause other systems to malfunction.
To minimize these risks, it is important to:
- Consult with a Qualified Technician: Before attempting any OBD2 programming, consult with a qualified technician or use a reputable OBD2 programming service.
- Use Reputable Software and Hardware: Use only reputable software and hardware from trusted sources.
- Back Up the Original Software: Before making any changes, back up the original software in case you need to restore it later.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the instructions carefully and do not deviate from the recommended procedures.
8. Regular Maintenance and the Role of the OBD2 Port
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and reliably. The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in regular maintenance by providing access to data that can be used to monitor the vehicle’s health and identify potential problems early on.
8.1. Recommended Maintenance Schedule for Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz recommends following a specific maintenance schedule to ensure that your vehicle is properly maintained. The maintenance schedule typically includes:
- Oil Changes: Every 10,000 miles or 12 months.
- Filter Replacements: Air filter, fuel filter, and cabin filter.
- Fluid Checks: Coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Every 60,000 miles.
- Brake Inspections: Check brake pads, rotors, and calipers.
- Tire Rotations: Every 5,000 miles.
8.2. How the OBD2 Port Helps in Identifying Maintenance Needs
The OBD2 port can be used to identify maintenance needs by monitoring various data points, such as:
- Engine Oil Life: The OBD2 system can estimate the remaining life of the engine oil based on driving conditions and other factors.
- Brake Pad Wear: The OBD2 system can monitor the wear of the brake pads and alert you when they need to be replaced.
- Tire Pressure: The OBD2 system can monitor the tire pressure and alert you if the pressure is too low.
- Battery Health: The OBD2 system can monitor the health of the battery and alert you if it is weak.
By monitoring these data points, you can identify maintenance needs early on and take corrective action before they lead to more serious problems.
8.3. Resetting Service Indicators with an OBD2 Scanner
After performing maintenance, it is often necessary to reset the service indicators in the vehicle’s computer system. This can be done with an OBD2 scanner that has the ability to reset service indicators.
The process for resetting service indicators varies depending on the vehicle model and the OBD2 scanner being used. However, it typically involves selecting the “service reset” or “maintenance reset” option in the scanner’s menu and following the instructions on the screen.
9. FAQs About OBD2 Ports and Vehicle Diagnostics
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 ports and vehicle diagnostics:
9.1. Common Questions About OBD2 Ports
- Q: What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
- A: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location. You can also check our documentation at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for detailed guides.
- Q: Are all OBD2 ports the same?
- A: Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization.
- Q: How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
- A: Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
- Q: Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
- A: Yes, as long as the scanner supports the communication protocol used by your vehicle. Most modern scanners support all common protocols.
- Q: Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
- A: It is generally not recommended to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time, as it can drain the battery.
9.2. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues
- Q: My OBD2 scanner won’t connect to my car. What should I do?
- A: First, make sure that the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on. Then, check the scanner’s settings to ensure that it is configured to communicate with your vehicle. If the problem persists, try a different scanner or consult a qualified technician.
- Q: I’m getting a DTC that I don’t understand. Where can I find more information?
- A: You can find more information about DTCs in your vehicle’s repair manual or online databases such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) website. You can also consult with a qualified technician.
- Q: Can I clear DTCs myself, or do I need to take my car to a mechanic?
- A: You can clear DTCs yourself with an OBD2 scanner. However, it is important to understand the cause of the DTC before clearing it. If the problem is not resolved, the DTC will likely return.
9.3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Tool for Your Needs
- Q: What type of OBD2 scanner should I buy?
- A: The type of OBD2 scanner you should buy depends on your needs and budget. If you are a DIY enthusiast who wants to perform basic diagnostics and maintenance, a basic code reader or enhanced scanner may be sufficient. If you are a professional mechanic, you will need a professional scan tool with more advanced features and capabilities. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for personalized recommendations.
- Q: Are smartphone apps and adapters a good option for OBD2 diagnostics?
- A: Smartphone apps and adapters can be a convenient and affordable option for OBD2 diagnostics. However, it is important to choose a reputable app and adapter from a trusted source.
- Q: Where can I buy OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools?
- A: OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools are available from a variety of sources, including auto parts stores, online retailers, and tool suppliers.
10. Conclusion: Empowering You with OBD2 Knowledge
The OBD2 port is a powerful tool that can empower you to take control of your vehicle’s health and performance. By understanding how the OBD2 port works and how to use it effectively, you can save money on diagnostics and repairs, monitor your vehicle’s performance, and even unlock hidden features.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to make the most of your OBD2 port. Explore our website for in-depth articles, tutorials, and product reviews to help you master the art of vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. Remember the power of the OBD2 port at your fingertips. Embrace the capabilities of the OBD2 port to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz with our expert OBD2 diagnostic and programming services. Contact us today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to schedule a consultation and discover how we can help you optimize your vehicle’s performance and unlock its hidden features.