The Ford Obd2 Cat Cycle is a diagnostic procedure that ensures your vehicle’s catalytic converter is functioning correctly, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide expert guidance. Successfully completing this cycle is crucial for passing emissions tests and maintaining optimal engine performance. This article delves into the intricacies of the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle, offering solutions and insights to help you navigate this process smoothly, also enlisting the assistance of specialized tools and advanced vehicle diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. What Is the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle?
- 1.1 Why Is the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle Important?
- 1.1.1 Passing Emissions Tests
- 1.1.2 Optimal Engine Performance
- 1.1.3 Identifying Potential Issues
- 1.2 Key Components Involved in the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle
- 2. Understanding the Ford OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- 2.1 Common OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- 2.2 Why Readiness Monitors Are Important
- 2.3 How to Check Readiness Monitor Status
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle
- 3.1 Prerequisites
- 3.2 Step-by-Step Instructions
- 3.3 Tips for Successful Completion
- 3.4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 4. Common Issues Preventing CAT Cycle Completion
- 4.1 Faulty Oxygen Sensors
- 4.2 Catalytic Converter Problems
- 4.3 Exhaust Leaks
- 4.4 Engine Misfires
- 4.5 Fuel System Issues
- 4.6 Software or ECU Problems
- 5. Ford Specific Drive Cycle Tips
- 5.1 Ford’s Recommended Drive Cycle
- 5.2 Ford-Specific Considerations
- 5.3 Resources for Ford-Specific Information
- 6. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in the CAT Cycle
- 6.1 How Oxygen Sensors Work
- 6.2 Types of Oxygen Sensors
- 6.3 Symptoms of Faulty Oxygen Sensors
- 6.4 Testing and Replacing Oxygen Sensors
- 7. Catalytic Converter Efficiency and Diagnosis
- 7.1 How Catalytic Converters Work
- 7.2 Factors Affecting Catalytic Converter Efficiency
- 7.3 Symptoms of a Failing Catalytic Converter
- 7.4 Diagnosing Catalytic Converter Issues
- 8. Using OBD2 Scanners for CAT Cycle Monitoring
- 8.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 8.2 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- 8.3 How to Use an OBD2 Scanner for CAT Cycle Monitoring
- 8.4 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Ford Vehicles
- 9. Addressing Trouble Codes Related to the CAT Cycle
- 9.1 Common Trouble Codes Related to the CAT Cycle
- 9.2 Steps to Diagnose Trouble Codes
- 9.3 When to Seek Professional Help
- 10. Maintaining Your Ford’s Emissions System for Optimal Performance
- 10.1 Regular Maintenance Tasks
- 10.2 Tips for Extending Catalytic Converter Life
- 10.3 The Importance of Professional Inspections
- 11. Force Ready Mode: What It Is and How It Works
- 11.1 Understanding Force Ready Mode
- 11.2 How Force Ready Mode Works
- 11.3 Limitations of Force Ready Mode
- 11.4 Alternatives to Force Ready Mode
- 12. Battery Disconnection and Its Impact on OBD2 Readiness
- 12.1 Why Battery Disconnection Resets OBD2 Monitors
- 12.2 Steps to Take After Battery Disconnection
- 12.3 Tips for a Smooth Reset Process
- 13. Legal Considerations for Emissions Testing
- 13.1 State Emissions Testing Requirements
- 13.2 Exemptions and Waivers
- 13.3 Penalties for Non-Compliance
- 13.4 Resources for Emissions Testing Information
- 14. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
- 14.1 Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
- 14.2 Expert Guidance and Support
- 14.3 Step-by-Step Tutorials and Resources
- 14.4 Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
- 15. Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle FAQs
- 15.1 How long does it take for the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle to complete?
- 15.2 Can I complete the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle on a dynamometer?
- 15.3 What should I do if the CAT cycle won’t complete after multiple attempts?
- 15.4 Can I use a scan tool to force the CAT cycle to complete?
- 15.5 What are the common reasons for CAT cycle failure on Ford vehicles?
- 15.6 How often should I check my Ford’s OBD2 readiness monitors?
- 15.7 Does disconnecting the battery affect the OBD2 readiness monitors?
- 15.8 What is the difference between upstream and downstream oxygen sensors?
- 15.9 How can I find the specific drive cycle for my Ford vehicle?
- 15.10 Are there any special considerations for completing the CAT cycle on a hybrid Ford vehicle?
1. What Is the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle?
The Ford OBD2 CAT (Catalytic Converter) cycle, also known as the catalyst monitor, is an essential diagnostic routine performed by your vehicle’s onboard computer (OBD2 system). This cycle evaluates the efficiency and performance of the catalytic converter, a critical component in your car’s exhaust system responsible for reducing harmful emissions. When the CAT cycle runs and completes successfully, it indicates that the catalytic converter is functioning within the manufacturer’s specified parameters.
1.1 Why Is the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle Important?
1.1.1 Passing Emissions Tests
Many states and regions require vehicles to pass emissions tests to ensure they meet environmental standards. The CAT cycle must be complete and show a “ready” status for your vehicle to pass these tests.
1.1.2 Optimal Engine Performance
A properly functioning catalytic converter ensures that your engine runs efficiently and produces fewer harmful emissions.
1.1.3 Identifying Potential Issues
If the CAT cycle fails to complete or shows a “not ready” status, it may indicate underlying issues with the catalytic converter or related components.
1.2 Key Components Involved in the Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle
Several components play a crucial role in the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle, including:
- Catalytic Converter: The primary component responsible for reducing emissions.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): These sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust stream, providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The vehicle’s computer that controls and monitors various engine functions, including the CAT cycle.
- Exhaust System: The entire system that carries exhaust gases away from the engine.
- Fuel System: Proper fuel delivery is essential for the CAT cycle to run correctly.
2. Understanding the Ford OBD2 Readiness Monitors
OBD2 readiness monitors are diagnostic tests that your vehicle’s onboard computer performs to ensure that various systems are functioning correctly. These monitors must be in a “ready” or “complete” state for your vehicle to pass an emissions test. The CAT monitor is just one of several readiness monitors.
2.1 Common OBD2 Readiness Monitors
- Catalyst Monitor (CAT): Checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor (O2S): Evaluates the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Evaporative System Monitor (EVAP): Tests the integrity of the fuel vapor recovery system.
- EGR System Monitor (EGR): Monitors the exhaust gas recirculation system.
- Secondary Air System Monitor (AIR): Checks the secondary air injection system.
- Heated Catalyst Monitor (H/C): Tests the functionality of the heated catalytic converter.
- Comprehensive Components Monitor (CCM): Assesses various engine components.
2.2 Why Readiness Monitors Are Important
Readiness monitors ensure that all critical systems are functioning correctly, reducing emissions and optimizing engine performance. If any of these monitors are “not ready,” it can prevent your vehicle from passing an emissions test.
2.3 How to Check Readiness Monitor Status
You can check the status of your vehicle’s readiness monitors using an OBD2 scanner. Simply plug the scanner into the OBD2 port (usually located under the dashboard) and follow the instructions to retrieve the readiness monitor status. Modern scanners, like those supported by MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, provide user-friendly interfaces and detailed explanations of the monitor statuses.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle
Completing the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle requires following a specific drive cycle pattern. A drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that allow the vehicle’s computer to run all the necessary diagnostic tests. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
3.1 Prerequisites
- OBD2 Scanner: To monitor the readiness status.
- Vehicle Manual: Consult your vehicle’s manual for specific drive cycle instructions.
- Safe Driving Environment: Choose a route with minimal traffic and opportunities to maintain consistent speeds.
3.2 Step-by-Step Instructions
- Start with a Cold Start: Ensure the engine has been off for at least eight hours.
- Idle for Two Minutes: Start the engine and let it idle for two minutes without touching the accelerator.
- Accelerate to 45-50 mph: Drive at a steady speed of 45-50 mph for about five minutes.
- Decelerate Without Braking: Release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph without applying the brakes.
- Accelerate to 55-60 mph: Drive at a steady speed of 55-60 mph for about five minutes.
- Decelerate Without Braking: Release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph without applying the brakes.
- Repeat as Needed: Repeat steps 3-6 several times, checking the readiness monitor status with your OBD2 scanner after each cycle.
3.3 Tips for Successful Completion
- Follow the Instructions Precisely: Adhere to the specified speeds and durations to ensure the test runs correctly.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Smooth and consistent driving is essential.
- Monitor Readiness Status: Use an OBD2 scanner to check the readiness status after each cycle.
- Address Any Trouble Codes: If any trouble codes appear, address them before continuing the drive cycle.
3.4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inconsistent Speeds: Maintaining consistent speeds is crucial for the CAT cycle to run correctly.
- Aggressive Braking: Avoid hard braking, as it can disrupt the test.
- Ignoring Trouble Codes: Address any trouble codes before attempting the drive cycle.
- Not Allowing Enough Time: The CAT cycle may take multiple attempts to complete.
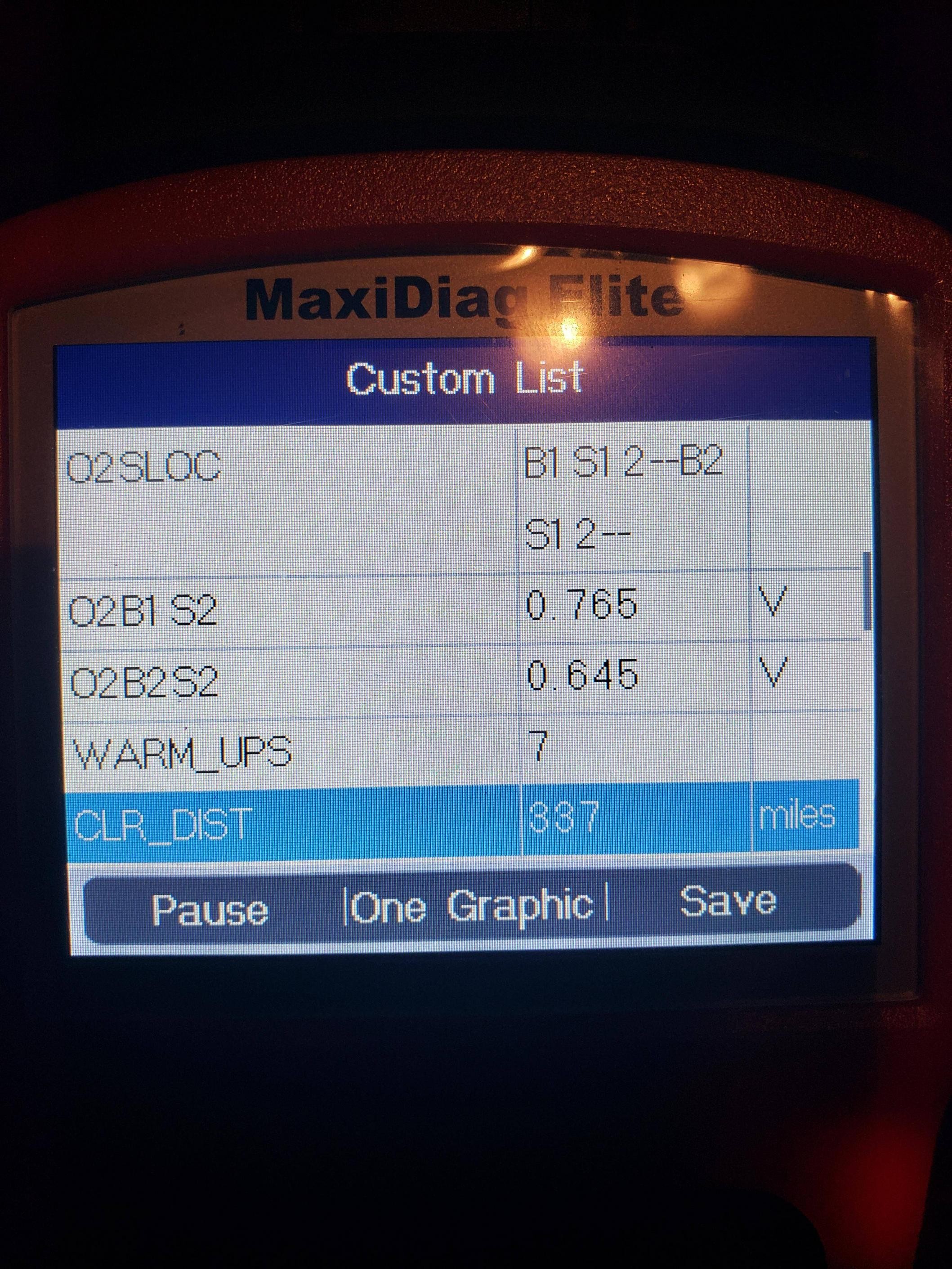 Ford OBD2 Scanner Diagnostic Tool
Ford OBD2 Scanner Diagnostic Tool
4. Common Issues Preventing CAT Cycle Completion
Several issues can prevent the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle from completing. Understanding these issues can help you troubleshoot and resolve them effectively.
4.1 Faulty Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors play a critical role in monitoring the exhaust stream and providing feedback to the ECU. Faulty or degraded oxygen sensors can disrupt the CAT cycle.
Solution: Test and replace any faulty oxygen sensors.
4.2 Catalytic Converter Problems
A damaged or inefficient catalytic converter will prevent the CAT cycle from completing.
Solution: Inspect the catalytic converter for damage and consider replacement if necessary.
4.3 Exhaust Leaks
Exhaust leaks can affect the accuracy of the oxygen sensors and disrupt the CAT cycle.
Solution: Inspect the exhaust system for leaks and repair any identified issues.
4.4 Engine Misfires
Engine misfires can introduce unburned fuel into the exhaust system, affecting the catalytic converter’s performance.
Solution: Identify and repair any engine misfires.
4.5 Fuel System Issues
Problems with the fuel system, such as incorrect fuel pressure or faulty injectors, can disrupt the CAT cycle.
Solution: Inspect and repair any fuel system issues.
4.6 Software or ECU Problems
In some cases, software glitches or ECU problems can prevent the CAT cycle from completing.
Solution: Consult a qualified technician for ECU diagnostics and potential reprogramming.
5. Ford Specific Drive Cycle Tips
Ford vehicles may have specific drive cycle requirements that differ slightly from the general OBD2 drive cycle. Consulting your vehicle’s manual is crucial for accurate instructions.
5.1 Ford’s Recommended Drive Cycle
- Cold Start: Ensure the engine has been off for at least eight hours.
- Idle for Two Minutes: Start the engine and let it idle for two minutes without touching the accelerator.
- Accelerate to 45 mph: Drive at a steady speed of 45 mph for about four minutes.
- Decelerate Without Braking: Release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph without applying the brakes.
- Accelerate to 55 mph: Drive at a steady speed of 55 mph for about three minutes.
- Decelerate Without Braking: Release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph without applying the brakes.
- Repeat as Needed: Repeat steps 3-6 several times, checking the readiness monitor status with your OBD2 scanner after each cycle.
5.2 Ford-Specific Considerations
- Transmission Type: The drive cycle may vary slightly depending on whether your vehicle has an automatic or manual transmission.
- Engine Type: Different engine types may have specific drive cycle requirements.
- Model Year: Newer models may have updated drive cycle procedures.
5.3 Resources for Ford-Specific Information
- Vehicle Manual: Your vehicle’s manual is the best source of information for Ford-specific drive cycle instructions.
- Ford Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): TSBs may provide additional information or updates on drive cycle procedures.
- Online Forums: Ford owner forums can be a valuable resource for tips and advice from other owners.
6. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in the CAT Cycle
Oxygen sensors (O2 sensors) are critical components in the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle. They monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream, providing feedback to the ECU. This feedback helps the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture and optimize the catalytic converter’s performance.
6.1 How Oxygen Sensors Work
Oxygen sensors measure the difference in oxygen levels between the exhaust gas and the outside air. This information is used to determine whether the air-fuel mixture is rich (too much fuel) or lean (too little fuel).
6.2 Types of Oxygen Sensors
- Upstream Oxygen Sensors: Located before the catalytic converter, these sensors provide feedback on the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
- Downstream Oxygen Sensors: Located after the catalytic converter, these sensors monitor the converter’s efficiency.
6.3 Symptoms of Faulty Oxygen Sensors
- Check Engine Light: A faulty oxygen sensor will often trigger the check engine light.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Inaccurate readings from the oxygen sensors can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Rough Idling: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to idle roughly.
- Failed Emissions Test: Faulty oxygen sensors can prevent the CAT cycle from completing, leading to a failed emissions test.
6.4 Testing and Replacing Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors can be tested using a multimeter or an OBD2 scanner. If a sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced promptly.
7. Catalytic Converter Efficiency and Diagnosis
The catalytic converter is a vital component in reducing harmful emissions. Its efficiency is crucial for passing emissions tests and maintaining environmental standards.
7.1 How Catalytic Converters Work
Catalytic converters use a chemical process to convert harmful pollutants, such as hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2).
7.2 Factors Affecting Catalytic Converter Efficiency
- Age: Catalytic converters can degrade over time, reducing their efficiency.
- Contamination: Oil, coolant, or excessive fuel can contaminate the catalytic converter, reducing its effectiveness.
- Damage: Physical damage to the catalytic converter can impair its function.
7.3 Symptoms of a Failing Catalytic Converter
- Check Engine Light: A failing catalytic converter will often trigger the check engine light.
- Poor Engine Performance: A clogged or inefficient catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, reducing engine power.
- Rattling Noises: Internal damage to the catalytic converter can cause rattling noises.
- Failed Emissions Test: A failing catalytic converter will prevent the CAT cycle from completing, leading to a failed emissions test.
7.4 Diagnosing Catalytic Converter Issues
Catalytic converter issues can be diagnosed using an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor readings before and after the converter. Significant differences in the readings can indicate a problem.
8. Using OBD2 Scanners for CAT Cycle Monitoring
OBD2 scanners are invaluable tools for monitoring the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle. They allow you to check the readiness status, retrieve trouble codes, and monitor sensor data.
8.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These scanners provide basic functionality, such as reading and clearing trouble codes and checking readiness monitor status.
- Advanced OBD2 Scanners: These scanners offer advanced features, such as live data streaming, bidirectional controls, and enhanced diagnostics.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These scanners are designed for professional technicians and offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
8.2 Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner
- Readiness Monitor Status: The ability to check the status of the readiness monitors.
- Trouble Code Retrieval: The ability to read and clear trouble codes.
- Live Data Streaming: The ability to monitor sensor data in real-time.
- Bidirectional Controls: The ability to control and test various vehicle systems.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface that is easy to navigate.
8.3 How to Use an OBD2 Scanner for CAT Cycle Monitoring
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port (usually located under the dashboard).
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Navigate to Readiness Monitors: Follow the scanner’s instructions to navigate to the readiness monitors menu.
- Check the CAT Monitor Status: Check the status of the CAT monitor. It should display “ready” or “complete” if the cycle has run successfully.
- Retrieve Trouble Codes: If the CAT monitor is “not ready,” retrieve any trouble codes that may be present.
8.4 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Ford Vehicles
- FORScan: A powerful scanner specifically designed for Ford vehicles.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: An advanced scanner with comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A user-friendly scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet.
9. Addressing Trouble Codes Related to the CAT Cycle
Trouble codes can provide valuable information about issues that may be preventing the CAT cycle from completing. Addressing these codes is essential for resolving the underlying problems.
9.1 Common Trouble Codes Related to the CAT Cycle
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0430: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0130-P0155: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunctions
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
9.2 Steps to Diagnose Trouble Codes
- Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the trouble code.
- Research the Code: Research the code to understand its potential causes and symptoms.
- Inspect Related Components: Inspect the components related to the code, such as oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and fuel system.
- Test Components: Test the components using a multimeter or other diagnostic tools.
- Repair or Replace Faulty Components: Repair or replace any faulty components.
- Clear the Code: Clear the trouble code using an OBD2 scanner.
- Run the CAT Cycle: Run the CAT cycle to verify that the issue has been resolved.
9.3 When to Seek Professional Help
If you are unable to diagnose or resolve the trouble codes, it is best to seek professional help from a qualified technician.
10. Maintaining Your Ford’s Emissions System for Optimal Performance
Proper maintenance of your Ford’s emissions system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance can prevent issues that may prevent the CAT cycle from completing.
10.1 Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential for maintaining engine health and preventing oil contamination of the catalytic converter.
- Air Filter Replacement: A clean air filter ensures proper airflow to the engine, optimizing combustion and reducing emissions.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Properly functioning spark plugs are essential for efficient combustion and reducing misfires.
- Fuel System Cleaning: Cleaning the fuel system can help prevent fuel injector clogs and ensure proper fuel delivery.
- Exhaust System Inspection: Regularly inspect the exhaust system for leaks and damage.
10.2 Tips for Extending Catalytic Converter Life
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips can prevent the catalytic converter from reaching its optimal operating temperature.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: High-quality fuel can help prevent fuel injector clogs and reduce emissions.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: Address any engine issues, such as misfires or leaks, promptly to prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
- Avoid Overloading the Engine: Avoid overloading the engine, as this can increase emissions and stress the catalytic converter.
10.3 The Importance of Professional Inspections
Regular professional inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems. A qualified technician can inspect the emissions system and provide recommendations for maintenance and repairs.
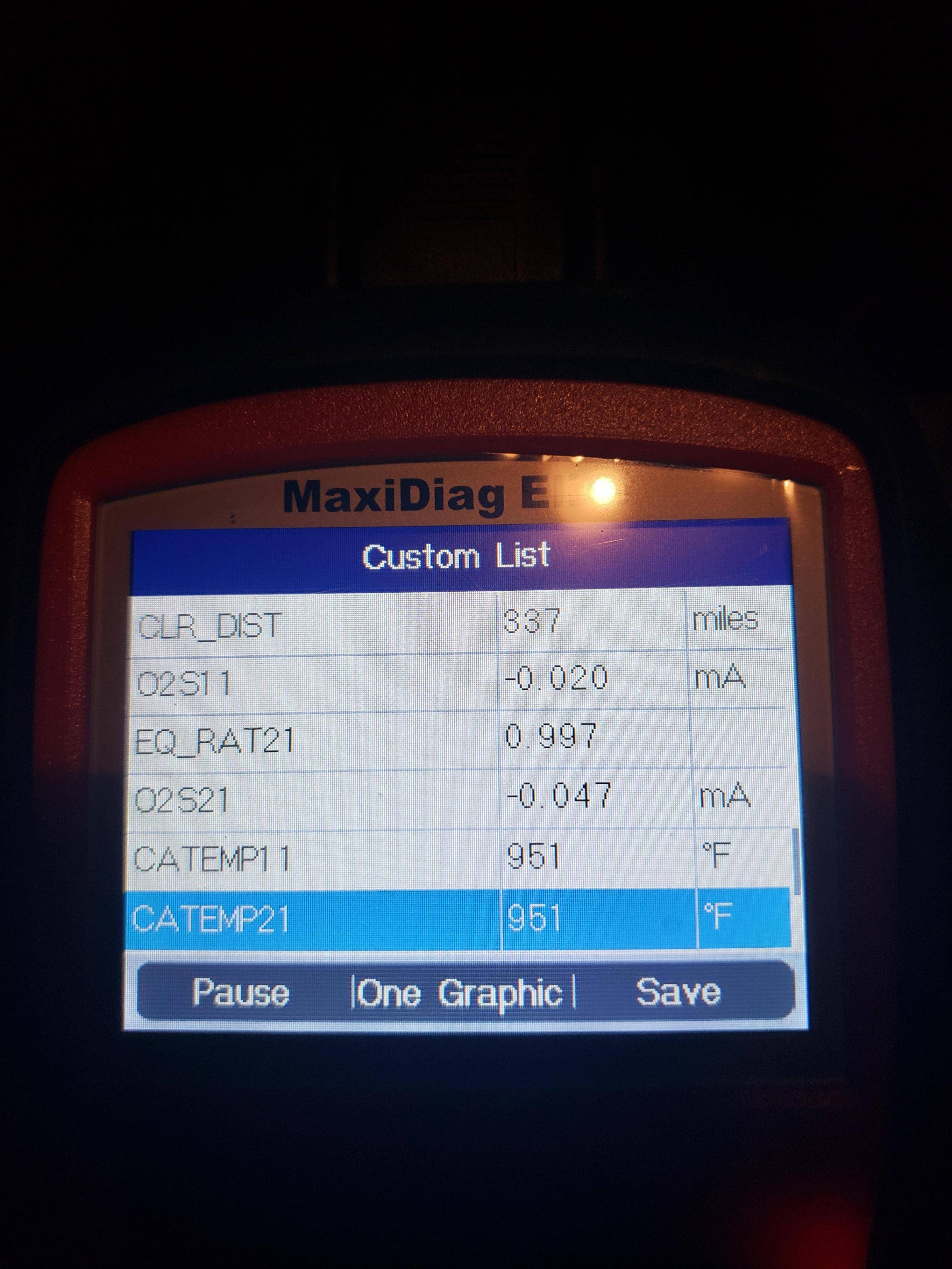 Ford O2 Sensor Diagnostic
Ford O2 Sensor Diagnostic
11. Force Ready Mode: What It Is and How It Works
Force Ready Mode is a feature available on some advanced OBD2 scanners, like the Ford IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System), that attempts to force the readiness monitors to complete without performing a traditional drive cycle. It’s designed to expedite the emissions testing process, but its effectiveness can vary.
11.1 Understanding Force Ready Mode
Force Ready Mode works by simulating the conditions required for each readiness monitor to run and complete. It attempts to bypass the need for a specific drive cycle by using the scanner to manipulate certain parameters and trigger the necessary tests.
11.2 How Force Ready Mode Works
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Access Force Ready Mode: Navigate to the Force Ready Mode option in the scanner’s menu.
- Follow the Instructions: Follow the scanner’s instructions to initiate the Force Ready Mode process.
- Monitor the Results: Monitor the readiness monitor status to see if the monitors have completed.
11.3 Limitations of Force Ready Mode
- Not Always Effective: Force Ready Mode is not always effective, and some monitors may still require a traditional drive cycle to complete.
- Potential for Inaccurate Results: In some cases, Force Ready Mode may produce inaccurate results, leading to false positives or negatives.
- Requires Specialized Equipment: Force Ready Mode is typically only available on advanced, professional-grade scanners.
11.4 Alternatives to Force Ready Mode
If Force Ready Mode is not effective, the best alternative is to perform a traditional drive cycle, ensuring that all the necessary conditions are met for each readiness monitor to run and complete.
12. Battery Disconnection and Its Impact on OBD2 Readiness
Disconnecting the battery can reset the vehicle’s computer and clear the OBD2 readiness monitors. This means that after reconnecting the battery, you will need to perform a drive cycle to reset the monitors and prepare the vehicle for an emissions test.
12.1 Why Battery Disconnection Resets OBD2 Monitors
Disconnecting the battery removes power from the vehicle’s computer, causing it to lose its stored data, including the readiness monitor status.
12.2 Steps to Take After Battery Disconnection
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery securely.
- Check for Trouble Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any trouble codes that may have been triggered by the battery disconnection.
- Perform a Drive Cycle: Perform a drive cycle to reset the OBD2 readiness monitors.
- Monitor the Readiness Status: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the readiness status and ensure that all monitors have completed.
12.3 Tips for a Smooth Reset Process
- Record Radio Presets: Before disconnecting the battery, record your radio presets, as they may be lost during the reset process.
- Allow Time for the ECU to Relearn: After reconnecting the battery, allow the ECU some time to relearn the engine’s operating parameters.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Avoid aggressive driving during the initial relearning period, as this can disrupt the process.
13. Legal Considerations for Emissions Testing
Emissions testing requirements vary by state and region. Understanding the legal considerations for emissions testing is essential for ensuring compliance.
13.1 State Emissions Testing Requirements
Many states require vehicles to pass emissions tests to ensure they meet environmental standards. These tests typically involve checking the OBD2 readiness monitors and measuring the levels of pollutants in the exhaust.
13.2 Exemptions and Waivers
Some vehicles may be exempt from emissions testing, such as classic cars or vehicles registered in rural areas. Waivers may also be available for vehicles that fail emissions tests but have undergone significant repairs.
13.3 Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with emissions testing requirements can result in penalties, such as fines or suspension of vehicle registration.
13.4 Resources for Emissions Testing Information
- State Environmental Protection Agencies: State environmental protection agencies provide information on emissions testing requirements and regulations.
- Local Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV): The DMV can provide information on emissions testing locations and procedures.
- Online Forums: Online forums can be a valuable resource for tips and advice from other vehicle owners.
14. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of vehicle diagnostics and emissions testing. We offer a range of services and resources to help you navigate these challenges successfully.
14.1 Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
We provide access to high-quality OBD2 scanners and diagnostic equipment that can help you monitor the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle, retrieve trouble codes, and diagnose emissions-related issues.
14.2 Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert guidance and support. Whether you need help understanding trouble codes or performing a drive cycle, we are here to assist you.
14.3 Step-by-Step Tutorials and Resources
We offer a library of step-by-step tutorials and resources that can help you troubleshoot emissions-related issues and perform necessary repairs.
14.4 Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
If you need personalized assistance, don’t hesitate to contact us. We are here to help you resolve your emissions testing challenges and keep your vehicle running smoothly. Reach out to us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or give us a call on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. You can also visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
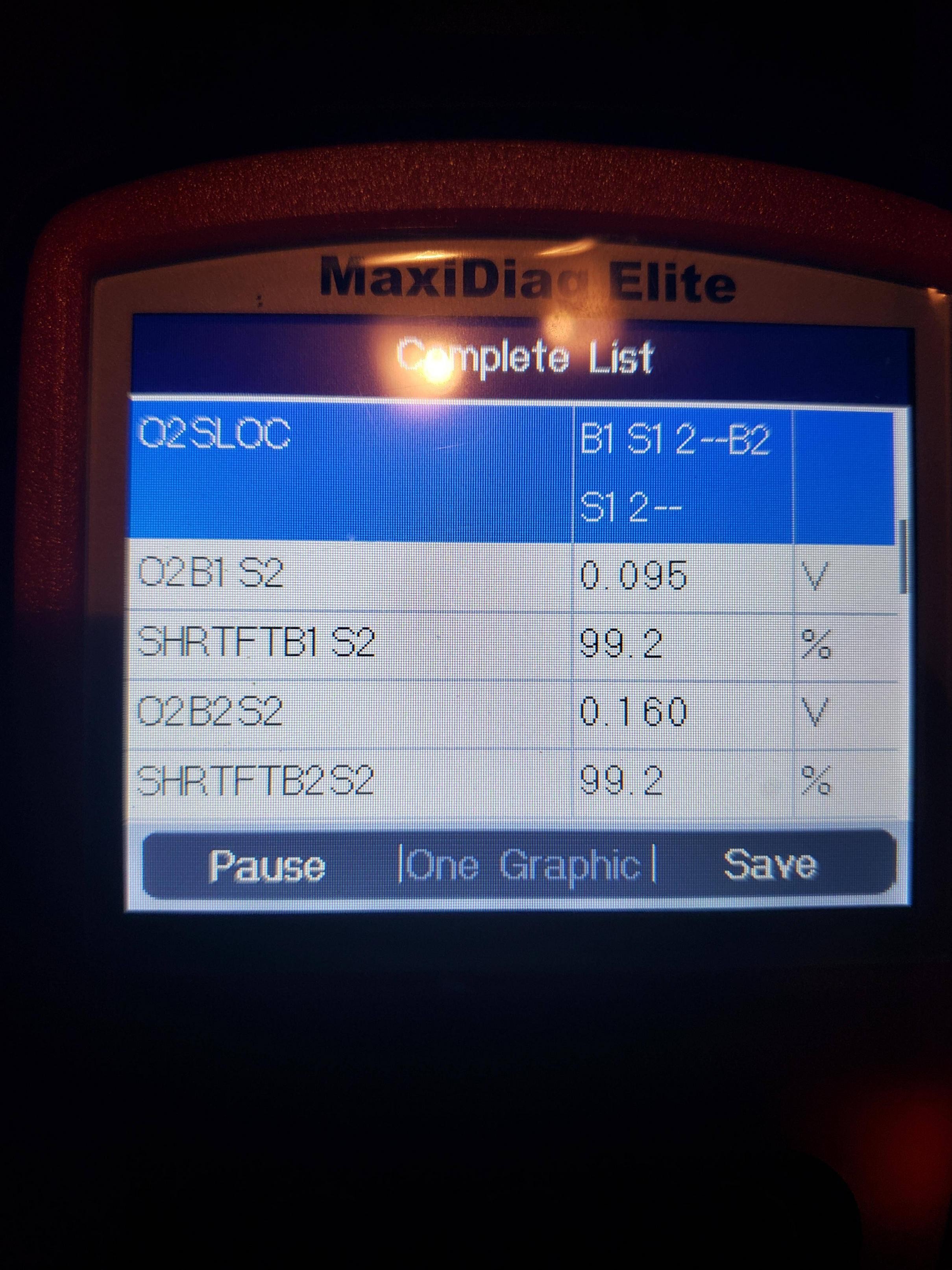 Ford OBD2 Monitor Data
Ford OBD2 Monitor Data
15. Ford OBD2 CAT Cycle FAQs
15.1 How long does it take for the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle to complete?
The time it takes for the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle to complete can vary depending on several factors, including the vehicle’s condition, driving conditions, and the specific drive cycle being performed. It may take multiple attempts and several days of driving to complete the cycle.
15.2 Can I complete the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle on a dynamometer?
While it is possible to complete the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle on a dynamometer, it is not recommended. Dynamometers simulate real-world driving conditions, but they may not accurately replicate the specific conditions required for the CAT cycle to run correctly.
15.3 What should I do if the CAT cycle won’t complete after multiple attempts?
If the CAT cycle won’t complete after multiple attempts, it is likely that there is an underlying issue with the vehicle’s emissions system. You should consult a qualified technician to diagnose and repair the problem.
15.4 Can I use a scan tool to force the CAT cycle to complete?
Some advanced scan tools offer a “Force Ready” mode that attempts to force the readiness monitors to complete without performing a traditional drive cycle. However, this feature is not always effective, and it may not be available on all scan tools.
15.5 What are the common reasons for CAT cycle failure on Ford vehicles?
Common reasons for CAT cycle failure on Ford vehicles include faulty oxygen sensors, a damaged catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, engine misfires, and fuel system issues.
15.6 How often should I check my Ford’s OBD2 readiness monitors?
You should check your Ford’s OBD2 readiness monitors before any emissions test to ensure that all monitors are in a “ready” state. It is also a good idea to check the monitors periodically to identify any potential issues early on.
15.7 Does disconnecting the battery affect the OBD2 readiness monitors?
Yes, disconnecting the battery will reset the vehicle’s computer and clear the OBD2 readiness monitors. After reconnecting the battery, you will need to perform a drive cycle to reset the monitors.
15.8 What is the difference between upstream and downstream oxygen sensors?
Upstream oxygen sensors are located before the catalytic converter and provide feedback on the engine’s air-fuel mixture. Downstream oxygen sensors are located after the catalytic converter and monitor the converter’s efficiency.
15.9 How can I find the specific drive cycle for my Ford vehicle?
The specific drive cycle for your Ford vehicle can be found in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or by consulting a qualified technician. You can also find information on online forums and in Ford technical service bulletins (TSBs).
15.10 Are there any special considerations for completing the CAT cycle on a hybrid Ford vehicle?
Yes, hybrid Ford vehicles may have specific drive cycle requirements that differ from non-hybrid vehicles. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a qualified technician for instructions specific to your vehicle.
Conclusion
Successfully completing the Ford OBD2 CAT cycle is essential for passing emissions tests and maintaining optimal engine performance. By understanding the process, addressing potential issues, and utilizing the right tools and resources, you can ensure that your vehicle meets environmental standards and runs smoothly. Remember, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide expert guidance and support every step of the way. Contact us today to learn more about our diagnostic tools and services. Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Don’t let emissions testing be a headache. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance and ensure your Ford passes with flying colors!
