Are you curious about how OBD2 scanners work and how they can help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz? This guide from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN will provide a comprehensive explanation of OBD2 scanner functionality, empowering you to diagnose issues, unlock hidden features, and perform routine maintenance. Understand the power of diagnostic tools, and explore advanced diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 2. How Do OBD2 Scanners Work: The Core Functionality
- 3. Understanding the Role of OBD2 Protocols
- 4. What Data Can OBD2 Scanners Access?
- 5. Types of OBD2 Scanners: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
- 6. The Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 7. OBD2 Scanners and Mercedes-Benz: What You Need to Know
- 8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Mercedes-Benz
- 9. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 10. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 11. Clearing DTCs: When and How
- 12. Live Data Streaming: Monitoring Your Vehicle’s Performance in Real-Time
- 13. Bi-Directional Control: Taking Control of Your Vehicle’s Systems
- 14. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Scanners
- 15. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
- 16. Using OBD2 Scanners for Routine Maintenance
- 17. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 18. OBD2 vs. OBD1: Understanding the Differences
- 19. CAN Bus and OBD2: How They Work Together
- 20. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 21. Legal Considerations and OBD2 Scanners
- 22. Resources for Learning More About OBD2 Scanners
- 23. Demystifying Myths About OBD2 Scanners
- 24. Optimizing Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2 Data
- 25. Essential Accessories for Your OBD2 Scanner
- 26. How To Read OBD2 Codes
- 27. Connecting OBD2 and CAN bus
- 28. The OBD2 Signal Protocols
- 29. Timeline of OBD2
- 30. FAQ: Your Questions About How OBD2 Scanners Work Answered
- Conclusion
1. What is an OBD2 Scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system, specifically the OBD2 port. It is used to read and interpret data from the vehicle’s computer, including Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), and monitor various parameters related to engine performance, emissions, and other critical systems. These scanners help technicians and vehicle owners identify and address potential issues, ensuring optimal vehicle operation and longevity. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), early detection of vehicle problems through OBD2 scanning can significantly reduce repair costs and downtime.
2. How Do OBD2 Scanners Work: The Core Functionality
OBD2 scanners work by tapping into a vehicle’s central computer system via the standardized OBD2 port, usually found under the dashboard. These scanners then communicate with the car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) to retrieve diagnostic information. Let’s break down the process:
- Connection: The scanner is physically connected to the OBD2 port.
- Communication: The scanner sends a request to the ECU for data.
- Data Retrieval: The ECU responds with data, including DTCs, sensor readings, and other diagnostic information.
- Interpretation: The scanner translates this data into a human-readable format, displaying error codes and parameter values on its screen.
- Action: Based on the information gathered, the user can then take appropriate action, such as clearing codes or further diagnosing the issue.
The OBD2 system utilizes a standardized set of DTCs, ensuring that a P0300 code, for example, always refers to a “Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected,” regardless of the vehicle’s make or model. This standardization makes OBD2 scanners incredibly versatile tools for diagnosing a wide range of automotive issues.
 OBD-II systems
OBD-II systems
3. Understanding the Role of OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 scanners communicate with vehicles using different protocols, which are like different languages that the scanner and the car’s computer must understand to exchange information. There are five main OBD2 protocols:
- SAE J1850 PWM: Primarily used in older Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Commonly found in older General Motors vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used in Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230 KWP2000: Also used in Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 15765 CAN: The current standard, mandatory for all vehicles sold in the US since 2008.
Modern OBD2 scanners are typically multi-protocol, meaning they can automatically detect and communicate using the correct protocol for the vehicle they are connected to.
4. What Data Can OBD2 Scanners Access?
OBD2 scanners can access a wealth of information about your vehicle’s operation, including:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s computer.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- Live Data Streams: Real-time readings from various sensors, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor voltage.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): A unique identifier for the vehicle.
- Readiness Monitors: Indicators of whether the vehicle’s emissions systems have completed their self-tests.
This data can be invaluable for diagnosing issues, monitoring performance, and ensuring your vehicle is operating efficiently.
5. Types of OBD2 Scanners: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
There are many types of OBD2 scanners available on the market, ranging from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
| Type of Scanner | Features | Target User |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Code Readers | Reads and clears DTCs | DIYers, vehicle owners looking for basic diagnostics |
| Enhanced OBD2 Scanners | Reads and clears DTCs, live data streams, freeze frame data | DIYers, enthusiasts, and technicians needing more detailed information |
| Professional Scanners | Advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, programming capabilities | Professional technicians, repair shops |
| Smartphone Adapters | Wireless connectivity, data logging, customizable dashboards | Tech-savvy users, performance enthusiasts |
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and skill level. Basic code readers are suitable for simple tasks like reading and clearing DTCs, while professional scanners offer advanced capabilities for in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
6. The Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner offers numerous benefits, including:
- Early Problem Detection: Identify issues before they become major problems, saving you time and money.
- Informed Repairs: Gain insight into the cause of vehicle problems, allowing you to make informed repair decisions.
- Cost Savings: Avoid unnecessary repairs by accurately diagnosing the problem yourself.
- Performance Monitoring: Track your vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues before they affect drivability.
- Emissions Compliance: Ensure your vehicle is running efficiently and meeting emissions standards.
According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), regular OBD2 scanning can help vehicle owners maintain optimal fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
7. OBD2 Scanners and Mercedes-Benz: What You Need to Know
Mercedes-Benz vehicles utilize the OBD2 system, but they also incorporate proprietary diagnostic systems that require specialized tools to access. While a generic OBD2 scanner can read basic DTCs and monitor some engine parameters, it may not be able to access all the diagnostic information available on a Mercedes-Benz.
For comprehensive diagnostics on a Mercedes-Benz, it is recommended to use a scanner that supports Mercedes-Benz specific protocols and functions. These scanners can access advanced systems like the transmission, ABS, and SRS, and perform functions like module programming and adaptation.
8. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Mercedes-Benz
When choosing an OBD2 scanner for your Mercedes-Benz, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports Mercedes-Benz specific protocols and functions.
- Features: Determine which features are important to you, such as live data streaming, bi-directional control, and module programming.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and easy-to-understand menus.
- Price: Balance your needs with your budget, considering that professional-grade scanners can be expensive.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of OBD2 scanners specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, providing comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and ease of use.
9. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, near the steering column.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, press the power button.
- Navigate the Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to select the desired function, such as reading DTCs or viewing live data.
- Interpret the Results: The scanner will display the results on its screen. Refer to the scanner’s manual for information on interpreting the data.
- Take Action: Based on the results, take appropriate action, such as clearing codes or performing repairs.
Always consult your vehicle’s repair manual before performing any repairs.
 Showcase of how OBD-II works
Showcase of how OBD-II works
10. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that indicate specific problems detected by the vehicle’s computer. Each code consists of five characters:
- The first character indicates the system:
- P = Powertrain
- B = Body
- C = Chassis
- U = Network
- The second character indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0 = Generic (SAE)
- 1 = Manufacturer-specific
- The third character indicates the subsystem:
- 1 = Fuel and air metering
- 2 = Fuel and air metering – Injector circuit
- 3 = Ignition system or misfire
- 4 = Auxiliary emission controls
- 5 = Vehicle speed controls and idle control system
- 6 = Computer output circuit
- 7 = Transmission
- 8 = Transmission
- The fourth and fifth characters indicate the specific fault.
For example, a P0300 code indicates a “Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected.” Understanding DTCs is crucial for accurately diagnosing vehicle problems.
11. Clearing DTCs: When and How
Clearing DTCs should only be done after you have diagnosed and repaired the underlying problem. Clearing codes without addressing the root cause will only result in the codes returning.
To clear DTCs, use the OBD2 scanner’s menu to select the “Clear Codes” function. The scanner will then send a command to the ECU to erase the stored codes.
Keep in mind that clearing codes may also reset the vehicle’s readiness monitors, which are indicators of whether the emissions systems have completed their self-tests. If you need to have your vehicle inspected for emissions, you may need to drive it for a period of time to allow the monitors to reset.
12. Live Data Streaming: Monitoring Your Vehicle’s Performance in Real-Time
Live data streaming allows you to monitor various parameters related to your vehicle’s operation in real-time. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or monitoring performance after repairs.
Common live data parameters include:
- Engine speed (RPM)
- Coolant temperature
- Oxygen sensor voltage
- Fuel trim
- Mass airflow (MAF)
- Throttle position
By monitoring these parameters, you can gain insight into how your vehicle is operating and identify potential issues before they trigger DTCs.
13. Bi-Directional Control: Taking Control of Your Vehicle’s Systems
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate or deactivate certain systems or components. This can be useful for testing components, performing calibrations, or troubleshooting complex problems.
Examples of bi-directional control functions include:
- Activating the fuel pump
- Cycling the ABS pump
- Adjusting idle speed
- Performing a cylinder balance test
Bi-directional control is typically found on professional-grade OBD2 scanners.
14. Unlocking Hidden Features on Your Mercedes-Benz with OBD2 Scanners
Some OBD2 scanners offer the ability to unlock hidden features on your Mercedes-Benz, such as:
- Activating cornering lights
- Enabling ambient lighting
- Adjusting instrument cluster settings
- Disabling seatbelt chimes
These features are often disabled by the manufacturer for various reasons, but they can be unlocked using an OBD2 scanner with the appropriate programming capabilities.
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides information and services related to unlocking hidden features on Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
 The five dialects under the OBD2 umbrella
The five dialects under the OBD2 umbrella
15. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Regular vehicle maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. By following a regular maintenance schedule, you can:
- Prevent major problems
- Extend the life of your vehicle
- Improve fuel efficiency
- Maintain vehicle safety
- Comply with warranty requirements
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides information and resources to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
16. Using OBD2 Scanners for Routine Maintenance
OBD2 scanners can be used for routine maintenance tasks, such as:
- Checking for DTCs
- Monitoring live data parameters
- Resetting service reminders
- Performing basic system tests
By incorporating OBD2 scanning into your routine maintenance, you can identify potential issues early and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
17. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added all the time. Some of the trends in OBD2 technology include:
- Increased integration with smartphones and cloud-based services
- Advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities
- Improved data logging and analysis
- Enhanced security features
- Greater focus on emissions compliance
As OBD2 technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in vehicle maintenance and repair.
18. OBD2 vs. OBD1: Understanding the Differences
OBD1 was an earlier version of the on-board diagnostic system, and it had several limitations compared to OBD2:
- Standardization: OBD1 was not standardized, meaning that each manufacturer used its own diagnostic connectors, protocols, and DTCs. OBD2 is fully standardized, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models.
- Coverage: OBD1 only monitored a limited number of systems, primarily related to emissions control. OBD2 monitors a wide range of systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, and SRS.
- Data Availability: OBD1 provided limited data compared to OBD2, making it more difficult to diagnose problems accurately.
- Accessibility: OBD1 systems were often difficult to access and required specialized tools and knowledge. OBD2 systems are easily accessible via the standardized OBD2 port.
OBD2 offers significant improvements over OBD1 in terms of standardization, coverage, data availability, and accessibility.
 OBD-II vehicle compatibility
OBD-II vehicle compatibility
19. CAN Bus and OBD2: How They Work Together
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a communication system used in modern vehicles to allow different electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other. The OBD2 system utilizes the CAN bus to access data from the various ECUs in the vehicle.
The CAN bus allows for high-speed, reliable communication between the ECUs, enabling advanced diagnostic and control capabilities. Without the CAN bus, the OBD2 system would be severely limited in its ability to access and interpret data.
20. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
While OBD2 scanners are generally reliable, they can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- Scanner Won’t Connect: Ensure the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on. Check the scanner’s power source and try a different OBD2 port if available.
- Scanner Won’t Read Codes: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Try updating the scanner’s software or contacting the manufacturer for support.
- Inaccurate Readings: Ensure that the scanner is properly calibrated and that the sensors it is reading from are functioning correctly.
- Scanner Freezes or Crashes: Try restarting the scanner or updating its software. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can resolve most common OBD2 scanner issues.
21. Legal Considerations and OBD2 Scanners
In many jurisdictions, it is illegal to tamper with or disable a vehicle’s OBD2 system. This is because the OBD2 system is essential for monitoring emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Tampering with the OBD2 system can result in fines, penalties, and even vehicle impoundment. It is important to be aware of the legal considerations related to OBD2 scanners before using them.
22. Resources for Learning More About OBD2 Scanners
There are many resources available for learning more about OBD2 scanners, including:
- Online forums and communities
- Technical articles and publications
- Training courses and workshops
- Manufacturer websites
- MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
By taking advantage of these resources, you can expand your knowledge of OBD2 scanners and become a more informed vehicle owner or technician.
23. Demystifying Myths About OBD2 Scanners
There are several common myths about OBD2 scanners that need to be debunked:
- Myth: OBD2 scanners can fix your car for you.
- Reality: OBD2 scanners can only diagnose problems; they cannot perform repairs.
- Myth: All OBD2 scanners are the same.
- Reality: OBD2 scanners vary widely in terms of features, capabilities, and price.
- Myth: You need to be a mechanic to use an OBD2 scanner.
- Reality: Basic OBD2 scanners are easy to use and can be used by anyone with a basic understanding of vehicle systems.
- Myth: OBD2 scanners can damage your car.
- Reality: When used properly, OBD2 scanners are safe and will not damage your car.
By understanding the reality behind these myths, you can make informed decisions about using OBD2 scanners.
24. Optimizing Your Vehicle’s Performance with OBD2 Data
The data provided by OBD2 scanners can be used to optimize your vehicle’s performance in several ways:
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: By monitoring fuel trim and other parameters, you can identify and address issues that are affecting fuel economy.
- Increasing Horsepower: By monitoring engine speed, throttle position, and other parameters, you can identify and address issues that are limiting horsepower.
- Reducing Emissions: By monitoring emissions-related parameters, you can ensure that your vehicle is running cleanly and meeting emissions standards.
- Extending Engine Life: By monitoring engine temperature, oil pressure, and other parameters, you can identify and address issues that are contributing to engine wear.
By using OBD2 data to optimize your vehicle’s performance, you can improve its efficiency, power, and longevity.
25. Essential Accessories for Your OBD2 Scanner
Several accessories can enhance the functionality and usability of your OBD2 scanner:
- OBD2 Extension Cable: Allows you to connect the scanner to the OBD2 port in hard-to-reach locations.
- OBD2 Adapter: Adapts the scanner to different OBD2 connector types.
- Carrying Case: Protects the scanner from damage during storage and transport.
- Software Updates: Keeps the scanner up-to-date with the latest features and bug fixes.
- Repair Manual: Provides detailed information on diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems.
By investing in these essential accessories, you can get the most out of your OBD2 scanner.
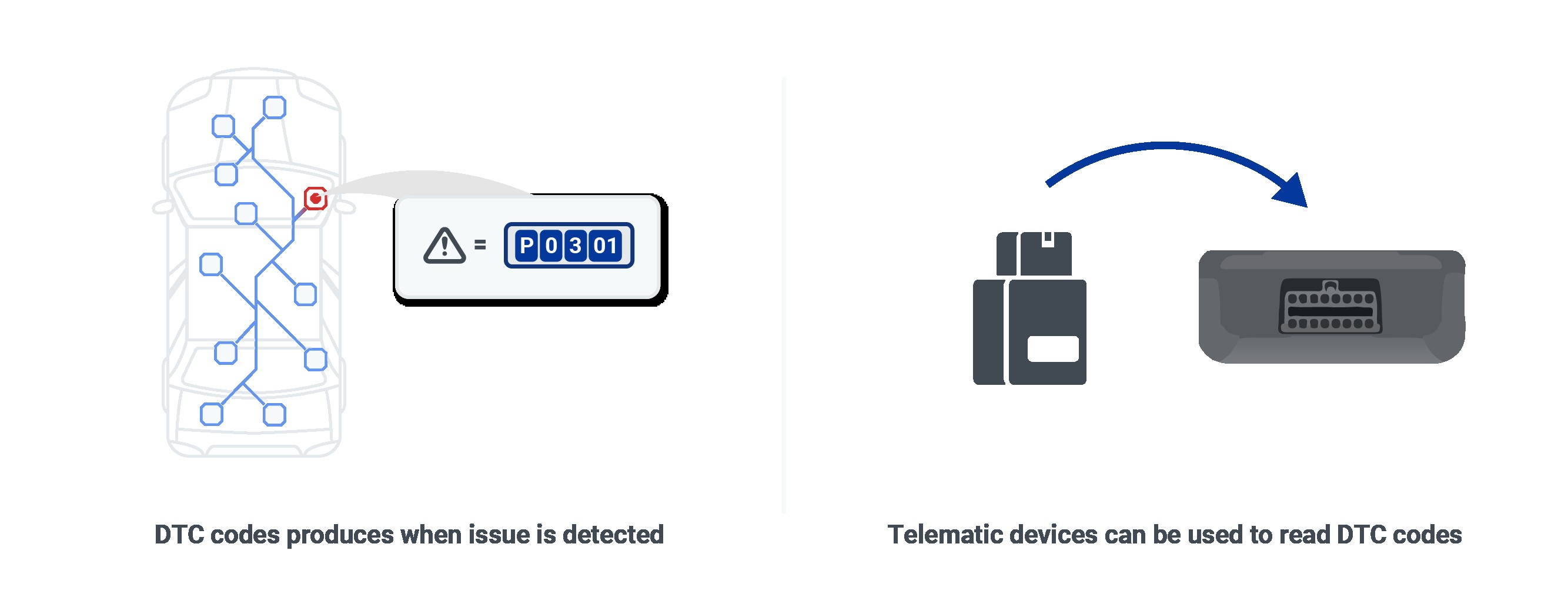
26. How To Read OBD2 Codes
Reading OBD2 codes involves a straightforward process using an OBD2 scanner. Start by plugging the scanner into your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine, and power on the scanner. Navigate to the section that reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The scanner will display any stored codes, which are alphanumeric identifiers indicating specific issues detected by the vehicle’s computer. For example, a code like “P0300” indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or a reliable online database to understand the meaning of each code and proceed with appropriate diagnostic and repair steps.
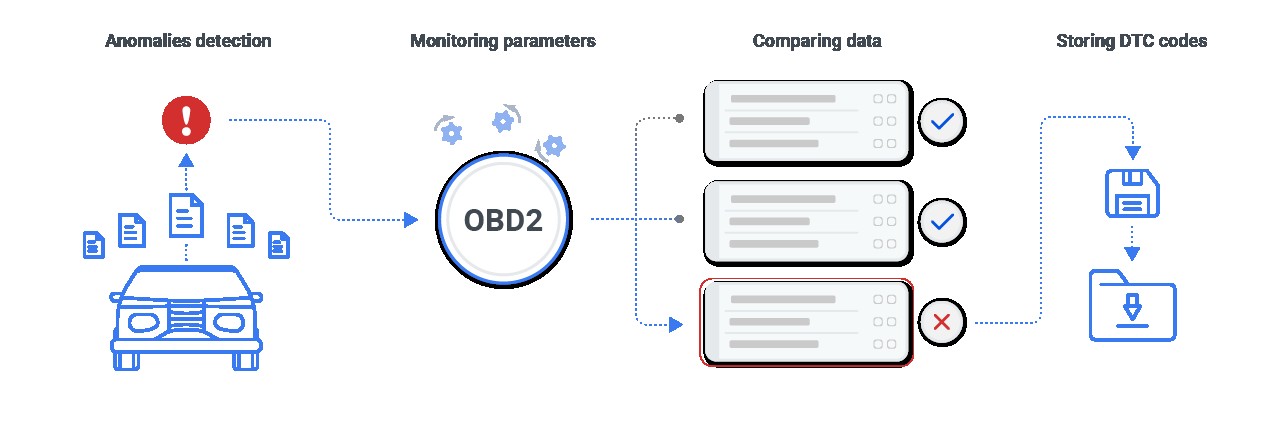 Showcase of how OBD-II logs data
Showcase of how OBD-II logs data
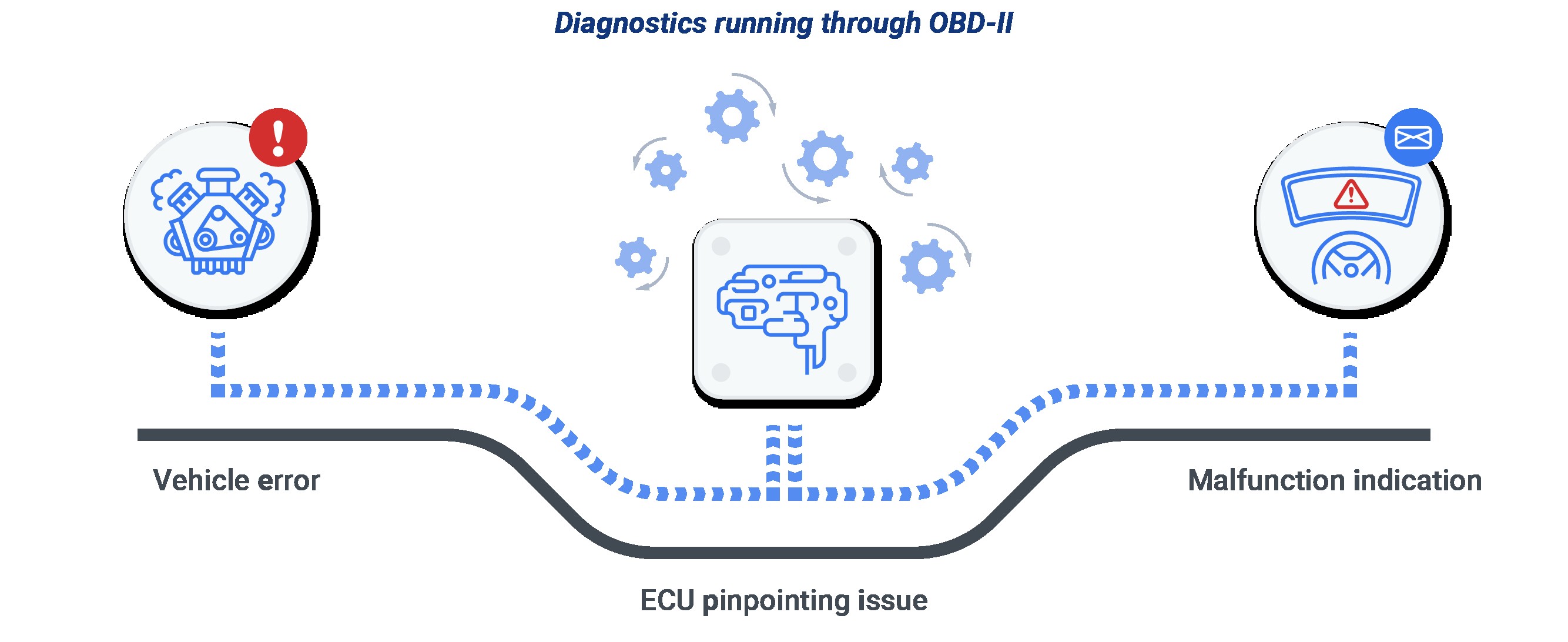
27. Connecting OBD2 and CAN bus
Connecting OBD2 and CAN bus involves understanding how these two systems interact within a vehicle. The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) system is a standardized interface used to access diagnostic information from a vehicle’s computer. The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication protocol that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other.
The OBD2 system uses the CAN bus to retrieve diagnostic data from different ECUs. To connect them, an OBD2 scanner is plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port, which is connected to the CAN bus. The scanner sends requests for specific data, and the ECUs respond via the CAN bus with the requested information, such as sensor readings and diagnostic trouble codes. This connection enables technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle issues effectively.
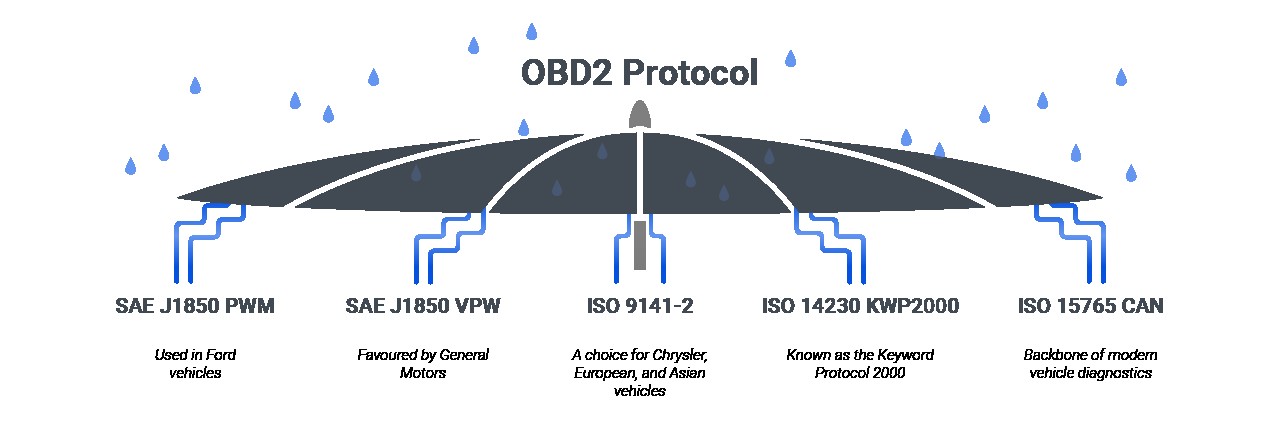
28. The OBD2 Signal Protocols
The five OBD2 signal protocols are essential for vehicle diagnostics, each serving as a specific communication method between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer. These protocols ensure that different vehicle makes and models can be effectively diagnosed. The main protocols include:
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Primarily used in older Ford vehicles, employing a variable pulse width for data transmission.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Mainly used in older General Motors vehicles, also utilizing pulse width modulation for communication.
- ISO 9141-2: Common in Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles, using asynchronous serial communication.
- ISO 14230 KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000): An extension of ISO 9141-2, offering enhanced diagnostic capabilities for Chrysler, European, and Asian models.
- ISO 15765 CAN (Controller Area Network): Mandatory for all vehicles sold in the US from 2008 onwards, providing high-speed data communication across the vehicle’s network.
Understanding these protocols is crucial for technicians to select the correct diagnostic tools and interpret the data accurately.
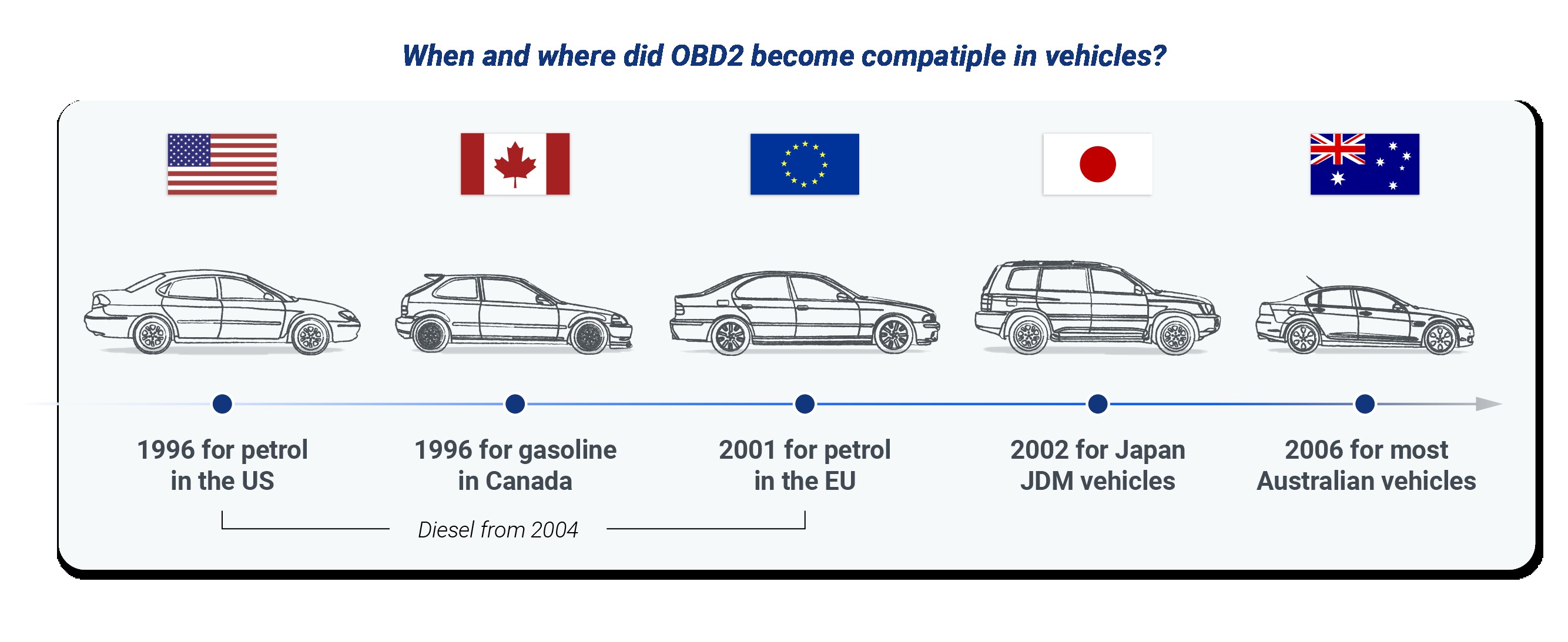
29. Timeline of OBD2
The timeline of OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) highlights key milestones in the development and implementation of this standardized vehicle diagnostic system. Originating in the 1960s with basic on-board diagnostic systems, significant advancements occurred in the early 1990s with OBD1, which offered manufacturer-specific diagnostics for emissions control.
The game-changing shift to OBD2 took place in 1996, mandating a standardized, comprehensive system across all vehicles sold in the United States. This system tracked a wide array of vehicle functions, enhanced compatibility between manufacturers, and facilitated precise real-time troubleshooting. By the early 2000s, Europe and other regions adopted OBD2, further solidifying its global presence. Continuous advancements in OBD2 technology have integrated more sophisticated features, enhancing vehicle diagnostics and contributing to improved fuel efficiency, early malfunction detection, and enhanced vehicle safety.
30. FAQ: Your Questions About How OBD2 Scanners Work Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 scanners:
- Q: What is the best OBD2 scanner for my Mercedes-Benz?
- A: The best OBD2 scanner for your Mercedes-Benz depends on your needs and budget. For basic diagnostics, a basic code reader may suffice. For more comprehensive diagnostics, consider a scanner that supports Mercedes-Benz specific protocols and functions.
- Q: How do I know if my car is OBD2 compliant?
- A: All vehicles sold in the US since 1996 are required to be OBD2 compliant.
- Q: Can an OBD2 scanner unlock hidden features on my car?
- A: Some OBD2 scanners offer the ability to unlock hidden features, but this depends on the scanner and the vehicle.
- Q: How often should I scan my car with an OBD2 scanner?
- A: You should scan your car with an OBD2 scanner whenever you suspect a problem or as part of your routine maintenance.
- Q: Can I clear DTCs without repairing the problem?
- A: Clearing DTCs without repairing the underlying problem will only result in the codes returning.
- Q: Are OBD2 scanners easy to use?
- A: Basic OBD2 scanners are easy to use, but advanced scanners may require more technical knowledge.
- Q: Where can I buy an OBD2 scanner?
- A: OBD2 scanners are available from auto parts stores, online retailers, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
- Q: How much do OBD2 scanners cost?
- A: OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 for basic code readers to several thousand dollars for professional-grade tools.
- Q: What is live data streaming?
- A: Live data streaming allows you to monitor various parameters related to your vehicle’s operation in real-time.
- Q: What is bi-directional control?
- A: Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate or deactivate certain systems or components.
Conclusion
Understanding how OBD2 scanners work can empower you to take control of your Mercedes-Benz maintenance and diagnostics. By using an OBD2 scanner, you can identify problems early, make informed repair decisions, and optimize your vehicle’s performance. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for OBD2 scanners, diagnostic information, and expert advice.
Ready to take the next step in understanding and maintaining your Mercedes-Benz? Contact us today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to explore our range of OBD2 tools and services. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with any questions about diagnostic tools, hidden feature unlocking, and Mercedes-Benz repair and maintenance. Don’t wait—empower yourself with the knowledge and tools to keep your Mercedes-Benz running at its best.