Rewiring your OBD2 port can seem daunting, but it’s often a necessary repair. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we simplify the process by providing expert guidance and resources to help you tackle this task effectively. Learn how to identify damaged terminals, source quality replacements, and perform a proper rewire, ensuring your diagnostic tools connect seamlessly. This guide covers everything from pin identification to choosing the right tools, empowering you to maintain your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
Contents
- 1. What Is the Purpose of Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 2. What are the Common Causes of OBD2 Port Wiring Issues?
- 3. How Do I Diagnose OBD2 Port Wiring Problems?
- 4. What Tools and Materials are Required for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 5. How Can I Identify the Correct OBD2 Pinout Diagram for My Mercedes-Benz?
- 6. What are the Step-by-Step Instructions for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 7. How Do I Choose the Right Replacement OBD2 Connector and Terminals?
- 8. What are the Best Practices for Crimping and Soldering OBD2 Wires?
- 9. How Can I Protect the Rewired OBD2 Port from Future Damage?
- 10. What are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 11. How Does Rewiring an OBD2 Port Affect Vehicle Diagnostics?
- 12. Can Rewiring an OBD2 Port Fix Communication Errors?
- 13. What are the Safety Precautions to Take When Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 14. How Often Should I Inspect My OBD2 Port Wiring?
- 15. What is the Cost of Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 16. Are There Any Common Issues with Aftermarket OBD2 Connectors?
- 17. How Does Temperature Affect OBD2 Port Wiring?
- 18. What Role Does the OBD2 Port Play in Vehicle Emissions Testing?
- 19. How Can I Test the Voltage at the OBD2 Port?
- 20. What are the Potential Risks of an Improperly Wired OBD2 Port?
- 21. How Do I Remove a Damaged Terminal from an OBD2 Connector?
- 22. Can I Use a Scan Tool with a Rewired OBD2 Port?
- 23. What Type of Wire Should I Use for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
- 24. How Do I Troubleshoot a Rewired OBD2 Port That Isn’t Working?
- 25. What are the Benefits of a Properly Functioning OBD2 Port?
- 26. How Do I Know If My OBD2 Port Needs to Be Rewired?
- 27. Can a Faulty OBD2 Port Cause Other Electrical Problems?
- 28. What Should I Do If I’m Not Comfortable Rewiring the OBD2 Port Myself?
- 29. What is the Role of the CAN Bus in the OBD2 System?
- 30. Where Can I Find Reliable OBD2 Wiring Diagrams for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles?
1. What Is the Purpose of Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
Rewiring an OBD2 port is necessary to restore proper communication between your vehicle’s computer and diagnostic tools. A damaged or improperly wired OBD2 port can prevent you from accessing vital diagnostic information, impacting your ability to troubleshoot and maintain your Mercedes-Benz. By rewiring, you ensure accurate data retrieval for effective vehicle maintenance and repairs.
The OBD2 port, or On-Board Diagnostics II port, acts as a gateway to your car’s computer system. It allows mechanics and car owners to access a wealth of information about the vehicle’s health and performance. Rewiring this port is crucial when the existing wiring is damaged, corroded, or incorrectly configured, leading to communication errors or complete failure of diagnostic tools. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), a properly functioning OBD2 port is essential for accurate emissions testing and diagnostics. Rewiring ensures compliance with these standards, maintaining the integrity of your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
2. What are the Common Causes of OBD2 Port Wiring Issues?
Common causes of OBD2 port wiring issues include physical damage, corrosion, incorrect aftermarket installations, and wear and tear. Identifying these causes is the first step in effectively rewiring the port.
Several factors can lead to OBD2 port wiring problems. Physical damage, such as bent or broken pins, often results from the improper insertion or removal of diagnostic tools. Corrosion, especially in humid environments, can degrade the wiring and terminals, disrupting electrical conductivity. Incorrect aftermarket installations, like poorly designed accessories or incorrectly wired devices, can overload the system and damage the wiring. General wear and tear over time can also cause wires to fray or disconnect. According to research published in the SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars – Electronic and Electrical Systems, understanding these failure modes is critical for effective OBD2 port maintenance and repair. Regular inspection and preventative measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of wiring issues.
3. How Do I Diagnose OBD2 Port Wiring Problems?
Diagnosing OBD2 port wiring problems involves visually inspecting the port, testing for power and ground, and checking continuity of the wiring. Use a multimeter to confirm proper voltage and identify any shorts or open circuits.
To accurately diagnose OBD2 port wiring issues, start with a thorough visual inspection. Look for bent, broken, or corroded pins. Next, use a multimeter to test for proper power and ground at the appropriate pins. Pin 16 should have battery voltage, while pins 4 and 5 should provide a solid ground. If these are not present, trace the wiring back to the power source or ground point to identify any breaks or shorts. Additionally, check the continuity of each wire from the OBD2 port to the corresponding connector at the vehicle’s computer using the multimeter. This ensures that the wires are intact and not broken internally. Consulting the vehicle’s wiring diagram is crucial for accurate testing. A study by the Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) emphasizes the importance of precise diagnostic procedures to prevent further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
4. What Tools and Materials are Required for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
Rewiring an OBD2 port requires tools like a multimeter, wire crimpers, soldering iron, wire stripper, and heat shrink tubing. Essential materials include replacement OBD2 connectors, terminals, and wiring.
To effectively rewire an OBD2 port, you’ll need a specific set of tools and materials. A multimeter is essential for testing voltage, ground, and continuity. High-quality wire crimpers are necessary for securely attaching terminals to the wires. A soldering iron and solder are required for making permanent, reliable connections. Use a wire stripper to remove insulation without damaging the wire. Heat shrink tubing provides insulation and protection for the soldered connections. You’ll also need replacement OBD2 connectors and terminals that match the original specifications of your Mercedes-Benz. Finally, ensure you have appropriately gauged wiring to replace any damaged sections. Research from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) highlights the importance of using the correct tools and materials to ensure a safe and effective repair, preventing future electrical issues.
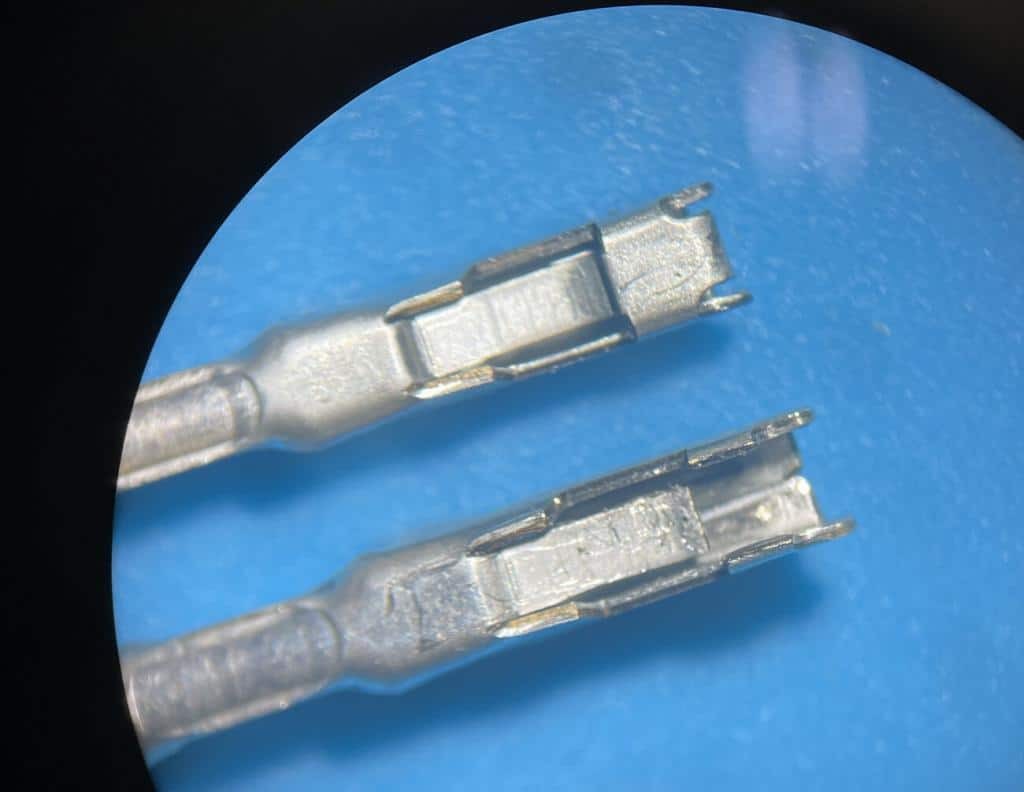 Damaged OBD2 terminal next to a new terminal under a microscope
Damaged OBD2 terminal next to a new terminal under a microscope
5. How Can I Identify the Correct OBD2 Pinout Diagram for My Mercedes-Benz?
Identify the correct OBD2 pinout diagram for your Mercedes-Benz by consulting the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database. These diagrams specify the function of each pin, ensuring correct wiring.
Locating the correct OBD2 pinout diagram is crucial for successful rewiring. The service manual for your specific Mercedes-Benz model contains detailed wiring diagrams, including the OBD2 port pinout. Alternatively, reputable online databases, such as ALLDATA or Mitchell OnDemand, provide access to vehicle-specific information. These diagrams illustrate the function of each pin, such as power, ground, CAN bus lines, and other diagnostic communication lines. Incorrect wiring can lead to communication errors or damage to the vehicle’s computer system. According to guidelines from the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA), always verify the pinout diagram against the vehicle’s documentation to ensure accuracy. Using the correct diagram ensures proper communication between the diagnostic tools and the vehicle’s systems.
6. What are the Step-by-Step Instructions for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
To rewire an OBD2 port, first disconnect the battery. Then, remove the old connector, strip the wire ends, crimp or solder new terminals, insert wires into the new connector according to the pinout diagram, and test the connection.
Here are detailed step-by-step instructions for rewiring an OBD2 port:
-
Disconnect the Battery: Start by disconnecting the negative terminal of your vehicle’s battery to prevent electrical shorts and ensure safety.
-
Remove the Old Connector: Carefully remove the damaged OBD2 connector from its mounting location. If necessary, use a small screwdriver to release any retaining clips.
-
Strip the Wire Ends: Use a wire stripper to carefully remove about 1/4 inch of insulation from the ends of the wires. Be careful not to nick or cut the wire strands.
-
Crimp or Solder New Terminals: Crimp new terminals onto the stripped wire ends using a high-quality wire crimper. For a more secure connection, you can solder the terminals to the wires and then apply heat shrink tubing for insulation.
-
Insert Wires into the New Connector: Refer to the OBD2 pinout diagram for your Mercedes-Benz model. Insert each wire into the corresponding pin location in the new connector. Ensure that the terminals are fully seated and locked into place.
-
Test the Connection: After all the wires are connected, use a multimeter to test the continuity between each pin on the OBD2 connector and the corresponding wire at the vehicle’s computer. Verify that there are no shorts or open circuits.
-
Reassemble and Test: Reconnect the battery, mount the new OBD2 connector in its original location, and use a diagnostic tool to ensure proper communication with the vehicle’s computer.
Following these steps ensures a successful and reliable rewiring of your OBD2 port. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), proper wiring techniques are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
7. How Do I Choose the Right Replacement OBD2 Connector and Terminals?
Choose the right replacement OBD2 connector and terminals by matching the part number and specifications to your vehicle’s original components. Consider factors like material quality, pin type, and compatibility.
Selecting the correct replacement OBD2 connector and terminals is essential for a successful repair. Start by identifying the part number of the original connector, which can often be found in the vehicle’s service manual or by contacting a Mercedes-Benz parts dealer. Ensure that the replacement connector matches the original in terms of pin configuration, size, and mounting style. When choosing terminals, consider the material quality. High-quality terminals are typically made of brass or copper alloy, providing good conductivity and corrosion resistance. Match the pin type to the original, whether they are crimp-on or solder-type terminals. Compatibility is key, so verify that the replacement parts are specifically designed for your Mercedes-Benz model. Research from the International Automotive Task Force (IATF) emphasizes the importance of using OEM-quality replacement parts to maintain the vehicle’s original performance and safety standards.
8. What are the Best Practices for Crimping and Soldering OBD2 Wires?
Best practices for crimping OBD2 wires include using the correct crimping tool, ensuring a tight and secure connection, and inspecting the crimp for proper form. For soldering, use a quality soldering iron, apply heat evenly, and use the correct type of solder.
When crimping OBD2 wires, using the correct crimping tool is paramount. The tool should match the size and type of terminal being used. Ensure that the wire is properly stripped, with no strands frayed or damaged. Insert the wire fully into the terminal and crimp firmly, creating a tight and secure connection. Inspect the crimp to ensure that it is properly formed and that the terminal is securely attached to the wire. For soldering, use a quality soldering iron with a fine tip. Apply heat evenly to the terminal and wire, and use a rosin-core solder specifically designed for electronics. Avoid using acid-core solder, as it can cause corrosion. Ensure that the solder flows smoothly and creates a shiny, solid connection. After soldering, allow the connection to cool before applying heat shrink tubing for insulation. According to the American Welding Society (AWS), proper soldering and crimping techniques are essential for creating reliable electrical connections that can withstand the harsh conditions in an automotive environment.
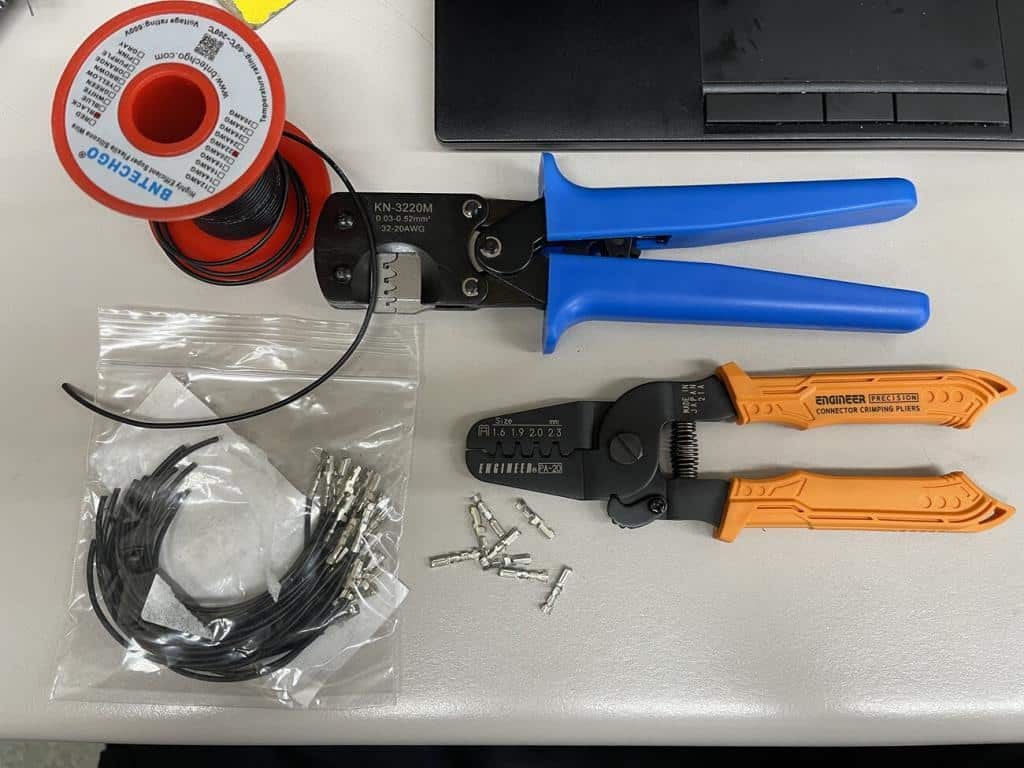 Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
9. How Can I Protect the Rewired OBD2 Port from Future Damage?
Protect the rewired OBD2 port from future damage by using a protective cover, avoiding excessive force when plugging in diagnostic tools, and regularly inspecting the port for corrosion or damage.
To safeguard your rewired OBD2 port, consider using a protective cover when the port is not in use. This can prevent dust, moisture, and debris from entering and causing corrosion or damage. When plugging in diagnostic tools, avoid using excessive force. Gently insert the tool and ensure it is properly aligned before pushing it in. Regularly inspect the OBD2 port for signs of corrosion, bent pins, or other damage. If you notice any issues, address them promptly to prevent further problems. Additionally, avoid using aftermarket accessories that draw excessive current from the OBD2 port, as this can overload the circuit and damage the wiring. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), proper maintenance and care of the OBD2 port can help ensure accurate and reliable diagnostic information, contributing to overall vehicle safety.
10. What are the Common Mistakes to Avoid When Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
Common mistakes to avoid when rewiring an OBD2 port include incorrect wiring, using low-quality parts, neglecting to disconnect the battery, and improper crimping or soldering.
When rewiring an OBD2 port, several common mistakes can lead to further issues. Incorrect wiring is a primary concern. Always double-check the pinout diagram for your specific Mercedes-Benz model to ensure each wire is connected to the correct pin. Using low-quality replacement parts, such as cheap connectors or terminals, can result in poor connections and premature failure. Neglecting to disconnect the battery before starting the rewiring process can lead to electrical shorts and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. Improper crimping or soldering can create weak connections that are prone to failure. Always use the correct crimping tool and soldering techniques to ensure secure and reliable connections. Research from the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA) emphasizes the importance of using high-quality parts and following proper procedures to ensure a successful and long-lasting repair.
11. How Does Rewiring an OBD2 Port Affect Vehicle Diagnostics?
Rewiring an OBD2 port correctly restores proper communication with diagnostic tools, allowing for accurate readings of vehicle systems. Incorrect rewiring can lead to inaccurate data or complete diagnostic failure.
The primary function of the OBD2 port is to facilitate communication between diagnostic tools and the vehicle’s computer. When the port is correctly rewired, it ensures that all data transmitted is accurate and reliable. This allows technicians and vehicle owners to properly diagnose issues, monitor performance, and perform necessary maintenance. Conversely, incorrect rewiring can lead to a range of problems, including inaccurate readings, communication errors, or a complete failure of the diagnostic system. This can hinder the ability to diagnose problems effectively and potentially lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs. According to a study by the Equipment and Tool Institute (ETI), a properly functioning OBD2 port is essential for accessing the full range of diagnostic information available from modern vehicles.
12. Can Rewiring an OBD2 Port Fix Communication Errors?
Yes, rewiring an OBD2 port can often fix communication errors by correcting faulty connections, damaged wiring, or corroded terminals that disrupt the diagnostic signal.
Communication errors with diagnostic tools are often caused by issues within the OBD2 port itself. Faulty connections, damaged wiring, or corroded terminals can disrupt the signal, preventing the diagnostic tool from communicating with the vehicle’s computer. Rewiring the OBD2 port addresses these issues by replacing damaged components and ensuring secure, reliable connections. By correcting these faults, rewiring can restore proper communication and resolve the communication errors. According to the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), a properly functioning OBD2 port is crucial for accessing and interpreting diagnostic data accurately.
13. What are the Safety Precautions to Take When Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
Safety precautions when rewiring an OBD2 port include disconnecting the battery, using insulated tools, wearing safety glasses, and ensuring proper ventilation to avoid exposure to fumes from soldering.
When rewiring an OBD2 port, safety should be a top priority. Always start by disconnecting the negative terminal of the vehicle’s battery to prevent electrical shorts and potential injuries. Use insulated tools to minimize the risk of electric shock. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris or solder splatters. If soldering is required, ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Additionally, take care when handling wires and terminals to avoid cuts or punctures. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), following these safety precautions can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries when working on vehicle electrical systems.
14. How Often Should I Inspect My OBD2 Port Wiring?
Inspect your OBD2 port wiring at least annually or whenever you experience diagnostic issues. Regular inspections can identify potential problems early, preventing more extensive damage.
Regular inspection of your OBD2 port wiring can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. At a minimum, inspect the port annually, looking for signs of corrosion, bent pins, or loose connections. If you experience any diagnostic issues, such as communication errors or an inability to connect with diagnostic tools, inspect the OBD2 port immediately. Early detection of problems can prevent more extensive damage to the wiring and ensure that your vehicle’s diagnostic system remains reliable. According to recommendations from the Vehicle Maintenance Council (VMC), proactive maintenance, including regular inspections, is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability of vehicle electrical systems.
15. What is the Cost of Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
The cost of rewiring an OBD2 port can vary, depending on the extent of the damage and whether you hire a professional. DIY rewiring can cost between $20 and $50 for parts, while professional service may range from $100 to $300.
The cost of rewiring an OBD2 port can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the damage, the cost of replacement parts, and whether you choose to perform the repair yourself or hire a professional. If you opt for a DIY approach, the cost will primarily be for replacement parts, such as a new OBD2 connector, terminals, and wiring, which can range from $20 to $50. However, if you choose to hire a professional mechanic, the cost will include labor charges, which can significantly increase the overall expense. Professional rewiring services can range from $100 to $300, depending on the complexity of the job and the labor rates in your area. According to data from RepairPal, the average cost for diagnosing and repairing electrical issues in a vehicle can vary widely, highlighting the importance of obtaining an estimate before proceeding with the repair.
16. Are There Any Common Issues with Aftermarket OBD2 Connectors?
Yes, common issues with aftermarket OBD2 connectors include poor build quality, incorrect pin alignment, and incompatibility with certain diagnostic tools, leading to unreliable connections.
Aftermarket OBD2 connectors can present several issues that may affect their performance and reliability. One common problem is poor build quality, where the materials used are not as durable or resistant to corrosion as the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. Incorrect pin alignment can also be an issue, leading to improper connections and communication errors. Additionally, some aftermarket connectors may not be fully compatible with certain diagnostic tools, resulting in unreliable or intermittent connections. It’s important to choose reputable brands and ensure that the connector is specifically designed for your vehicle model. According to a report by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), using high-quality replacement parts is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of vehicle systems and avoiding potential safety issues.
17. How Does Temperature Affect OBD2 Port Wiring?
Extreme temperatures can affect OBD2 port wiring by causing the insulation to become brittle and crack in cold conditions, or to soften and degrade in hot conditions, leading to potential shorts and connection failures.
Temperature extremes can significantly impact the integrity of OBD2 port wiring. In cold conditions, the insulation around the wires can become brittle and crack, exposing the conductors and increasing the risk of shorts. In hot conditions, the insulation can soften and degrade, leading to similar problems. These temperature-related issues can cause connection failures and communication errors with diagnostic tools. It’s important to protect the OBD2 port and its wiring from extreme temperatures whenever possible. According to research from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), automotive wiring and connectors are designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, but prolonged exposure to extreme conditions can still lead to degradation and failure.
18. What Role Does the OBD2 Port Play in Vehicle Emissions Testing?
The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in vehicle emissions testing by allowing technicians to access and monitor the vehicle’s emissions control systems, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
The OBD2 port is a critical component in vehicle emissions testing. It provides technicians with access to the vehicle’s computer, allowing them to monitor the performance of various emissions control systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and fuel system. The data obtained from the OBD2 port is used to verify that the vehicle is operating within the limits set by environmental regulations. If any issues are detected, the vehicle may fail the emissions test, requiring repairs to bring it into compliance. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the OBD2 system is designed to detect malfunctions that can increase emissions, helping to protect air quality and public health.
19. How Can I Test the Voltage at the OBD2 Port?
Test the voltage at the OBD2 port using a multimeter set to the DC voltage setting. Connect the positive lead to pin 16 (battery positive) and the negative lead to pin 4 or 5 (ground) to verify the presence of battery voltage.
To test the voltage at the OBD2 port, you will need a multimeter set to the DC voltage setting. First, locate pin 16, which is the battery positive terminal. Then, locate pin 4 or 5, which are the ground terminals. Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to pin 16 and the negative lead to either pin 4 or 5. The multimeter should display a voltage reading close to the vehicle’s battery voltage, typically around 12 to 14 volts. If the voltage reading is significantly lower or zero, it indicates a problem with the power supply to the OBD2 port, which may require further investigation. According to Fluke Corporation, a leading manufacturer of multimeters, accurate voltage testing is essential for diagnosing electrical issues in automotive systems.
20. What are the Potential Risks of an Improperly Wired OBD2 Port?
Potential risks of an improperly wired OBD2 port include inaccurate diagnostic readings, damage to the vehicle’s computer, communication errors, and potential safety hazards due to electrical shorts.
An improperly wired OBD2 port can pose several risks to both the vehicle and the user. Inaccurate diagnostic readings can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs, wasting time and money. Damage to the vehicle’s computer is another potential risk, as incorrect wiring can cause electrical surges that harm sensitive electronic components. Communication errors with diagnostic tools can prevent proper monitoring of vehicle systems, hindering the ability to identify and address issues. Additionally, electrical shorts caused by improper wiring can create safety hazards, such as fires or electrical shocks. It’s crucial to ensure that the OBD2 port is wired correctly to avoid these potential risks. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical malfunctions are a leading cause of vehicle fires, highlighting the importance of proper wiring and maintenance.
21. How Do I Remove a Damaged Terminal from an OBD2 Connector?
Remove a damaged terminal from an OBD2 connector using a terminal removal tool or a small pick to release the retaining clip while gently pulling the wire from the back of the connector.
Removing a damaged terminal from an OBD2 connector requires care to avoid further damage to the connector housing. The best approach is to use a terminal removal tool specifically designed for this purpose. Insert the tool into the connector to release the retaining clip that holds the terminal in place, then gently pull the wire from the back of the connector. If a terminal removal tool is not available, a small pick or thin screwdriver can be used to carefully push the retaining clip while pulling the wire. Be sure to avoid excessive force, which can break the clip or damage the connector. According to industry experts, using the correct tools and techniques is essential for safely and effectively removing terminals from automotive connectors.
22. Can I Use a Scan Tool with a Rewired OBD2 Port?
Yes, you can use a scan tool with a rewired OBD2 port, provided the rewiring was done correctly and the port now meets the necessary electrical and communication standards for diagnostic tools.
After rewiring an OBD2 port, it is essential to verify that it functions correctly with a scan tool. If the rewiring was performed accurately, ensuring proper pin connections and electrical continuity, the scan tool should be able to communicate with the vehicle’s computer and retrieve diagnostic data. However, if there are any errors in the rewiring, the scan tool may not be able to connect or may provide inaccurate information. It is recommended to test the rewired OBD2 port with a scan tool to confirm its functionality and ensure that it meets the necessary electrical and communication standards for diagnostic purposes. According to Bosch Automotive, a leading manufacturer of diagnostic tools, a properly functioning OBD2 port is crucial for accurate and reliable vehicle diagnostics.
23. What Type of Wire Should I Use for Rewiring an OBD2 Port?
Use automotive-grade wire, typically 18 or 20 gauge, for rewiring an OBD2 port. Automotive wire is designed to withstand the harsh conditions in a vehicle, including temperature variations and exposure to chemicals.
When rewiring an OBD2 port, it is important to use the correct type of wire to ensure a reliable and long-lasting repair. Automotive-grade wire is specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions found in a vehicle, including temperature variations, exposure to chemicals, and constant vibration. Typically, 18 or 20 gauge wire is used for OBD2 port wiring, as it is sufficient to carry the necessary current and fits properly into the connector terminals. Avoid using standard household wire, as it is not designed for automotive applications and may not hold up over time. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), using the correct type of wire is essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of automotive electrical systems.
24. How Do I Troubleshoot a Rewired OBD2 Port That Isn’t Working?
Troubleshoot a rewired OBD2 port that isn’t working by checking the wiring connections, testing for power and ground, verifying continuity, and ensuring the correct pinout configuration.
If you’ve rewired an OBD2 port and it’s not working, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take. First, double-check all of the wiring connections to ensure they are secure and properly inserted into the connector terminals. Next, use a multimeter to test for power and ground at the appropriate pins. Pin 16 should have battery voltage, while pins 4 and 5 should have a solid ground connection. Verify continuity between the OBD2 port and the vehicle’s computer to ensure there are no breaks in the wiring. Finally, double-check the pinout configuration to ensure that each wire is connected to the correct pin. If you’ve followed these steps and the OBD2 port still isn’t working, there may be an issue with the vehicle’s computer or another part of the electrical system. According to the Automotive Aftermarket Industry Association (AAIA), systematic troubleshooting is essential for accurately diagnosing and repairing electrical issues in vehicles.
25. What are the Benefits of a Properly Functioning OBD2 Port?
The benefits of a properly functioning OBD2 port include accurate diagnostics, improved vehicle maintenance, compliance with emissions testing, and enhanced resale value of the vehicle.
A properly functioning OBD2 port provides numerous benefits for vehicle owners and technicians. Accurate diagnostics allow for quick and efficient identification of vehicle issues, reducing repair time and costs. Improved vehicle maintenance is another benefit, as the OBD2 port provides valuable data for monitoring vehicle performance and identifying potential problems before they become major issues. Compliance with emissions testing is essential for meeting environmental regulations, and a properly functioning OBD2 port ensures that the vehicle can be tested accurately. Finally, a vehicle with a properly functioning OBD2 port is more attractive to potential buyers, enhancing its resale value. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the OBD2 system is designed to improve vehicle performance, reduce emissions, and facilitate accurate diagnostics, all of which contribute to the overall value and reliability of the vehicle.
26. How Do I Know If My OBD2 Port Needs to Be Rewired?
You know your OBD2 port needs to be rewired if you experience communication errors with diagnostic tools, visible damage to the connector, or a failure to pass emissions testing due to OBD2 port issues.
Several signs indicate that your OBD2 port may need to be rewired. One of the most common is experiencing communication errors when trying to connect with diagnostic tools. If the scan tool is unable to establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer, it may be due to faulty wiring in the OBD2 port. Visible damage to the connector, such as bent or broken pins, is another clear indication that rewiring may be necessary. Additionally, if your vehicle fails an emissions test due to OBD2 port issues, rewiring may be required to restore proper functionality. According to automotive diagnostic experts, addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system and ensure accurate diagnostic capabilities.
27. Can a Faulty OBD2 Port Cause Other Electrical Problems?
Yes, a faulty OBD2 port can cause other electrical problems by creating shorts, interfering with communication signals, and potentially damaging other electronic components in the vehicle.
A faulty OBD2 port can have far-reaching effects on a vehicle’s electrical system. Shorts within the port can cause power surges or drains, affecting other electronic components. Interference with communication signals can disrupt the proper functioning of various systems, leading to performance issues or malfunctions. In some cases, a faulty OBD2 port can even damage the vehicle’s computer or other sensitive electronic modules. It’s important to address any issues with the OBD2 port promptly to prevent these potential problems. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper diagnosis and repair of electrical issues is crucial for maintaining the overall health and reliability of a vehicle.
28. What Should I Do If I’m Not Comfortable Rewiring the OBD2 Port Myself?
If you’re not comfortable rewiring the OBD2 port yourself, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic who has experience with automotive electrical systems and diagnostic procedures.
Rewiring an OBD2 port can be a complex task that requires a good understanding of automotive electrical systems. If you’re not comfortable performing the repair yourself, it’s best to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic. Look for a mechanic who has experience with automotive electrical systems and diagnostic procedures. They will have the necessary tools and expertise to properly diagnose the issue and perform the rewiring safely and effectively. According to the Automotive Service Association (ASA), choosing a qualified and reputable mechanic is essential for ensuring that your vehicle is repaired correctly and to avoid potential safety issues.
29. What is the Role of the CAN Bus in the OBD2 System?
The CAN bus (Controller Area Network) plays a critical role in the OBD2 system by facilitating communication between the vehicle’s various electronic control units (ECUs) and the diagnostic tools connected to the OBD2 port.
The CAN bus is a communication network that allows the various electronic control units (ECUs) in a vehicle to communicate with each other. In the OBD2 system, the CAN bus is used to transmit diagnostic data from the vehicle’s computer to the diagnostic tools connected to the OBD2 port. This allows technicians to access a wealth of information about the vehicle’s performance and identify any potential issues. The CAN bus is a critical component of the OBD2 system, and any problems with the CAN bus can affect the ability to diagnose and repair the vehicle. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the CAN bus has become the industry standard for automotive communication networks due to its reliability and efficiency.
30. Where Can I Find Reliable OBD2 Wiring Diagrams for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles?
Find reliable OBD2 wiring diagrams for Mercedes-Benz vehicles in the vehicle’s service manual, online databases like ALLDATA and Mitchell OnDemand, or through Mercedes-Benz’s official technical information portal.
Locating reliable OBD2 wiring diagrams is crucial for performing accurate rewiring. The best source is the vehicle’s service manual, which contains detailed wiring diagrams specific to your Mercedes-Benz model. Online databases like ALLDATA and Mitchell OnDemand also provide access to vehicle-specific wiring diagrams. Additionally, Mercedes-Benz’s official technical information portal may offer wiring diagrams for authorized technicians. Always verify the wiring diagram against the vehicle’s documentation to ensure accuracy. According to automotive repair experts, using the correct wiring diagram is essential for avoiding mistakes and ensuring a successful repair.
Don’t let a faulty OBD2 port keep you in the dark about your Mercedes-Benz’s health. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on rewiring your OBD2 port, selecting the right diagnostic tools, and unlocking hidden features. Reach us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or WhatsApp +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and efficiently.