Are you wondering how to test your car’s alternator using an OBD2 scanner? With an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT1009, you can efficiently diagnose alternator issues by reading trouble codes and monitoring live data. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive insights and tools to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz’s electrical system and avoid unexpected breakdowns; this guide will explore using an OBD2 scanner for alternator diagnostics and other methods to ensure accurate results. Use our car diagnostic tools and automotive diagnostic tools to protect your vehicle.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Alternator’s Role in Your Mercedes-Benz
- 2. Can You Diagnose Alternator Problems with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner to Check Your Alternator
- 3.1. Prepare Your Vehicle and Scanner
- 3.2. Connect the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
- 3.3. Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
- 3.4. Check Error Codes
- 3.5. Check Live Data for Voltage Output
- 3.6. Perform a Load Test
- 3.7. Take Advantage of Special Testing Functions
- 3.8. Analyze and Respond
- 3.9. Clear Error Codes (If Applicable)
- 3.10. Unplug and Store the Scanner Properly
- 4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Mercedes-Benz’s Alternator
- 4.1. Multimeter Testing
- 4.2. Load Testing
- 4.3. Battery Terminal Inspection
- 4.4. Professional Diagnostic Services
- 5. Interpreting OBD2 Scanner Results and Alternator Health
- 5.1. Normal Voltage Readings
- 5.2. Low Voltage Readings
- 5.3. High Voltage Readings
- 5.4. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.5. Voltage Drop Under Load
- 5.6. Intermittent Issues
- 6. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Alternator Diagnostics
- 7. Addressing Common Alternator Issues in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 7.1. Voltage Regulator Failure
- 7.2. Worn Brushes
- 7.3. Faulty Diode Trio
- 7.4. Slipping Belt
- 7.5. Corroded Connections
- 8. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Alternator for Longevity
- 9. Latest Innovations in Alternator Technology
- 9.1. Smart Alternators
- 9.2. Integrated Starter-Generator (ISG) Systems
- 9.3. High-Efficiency Alternators
- 9.4. Solid-State Alternators
- 10. Why Regular Alternator Testing is Crucial for Mercedes-Benz Owners
- 11. Conclusion: Empowering Mercedes-Benz Owners with Diagnostic Knowledge
- 12. FAQs About Testing Alternators with OBD2 Scanners
- 12.1. Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 12.2. Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
- 12.3. Is there an OBD code for alternator?
- 12.4. What voltage should I see when testing my alternator?
- 12.5. How do I know if my alternator is bad?
- 12.6. Can a faulty alternator cause other electrical problems?
- 12.7. How often should I test my alternator?
- 12.8. Is it safe to drive with a bad alternator?
- 12.9. Can I replace the alternator myself?
- 12.10. How much does it cost to replace an alternator?
1. Understanding the Alternator’s Role in Your Mercedes-Benz
Your Mercedes-Benz’s alternator is a critical component of its electrical system. It is responsible for charging the battery and powering the electrical components while the engine is running. Without a functioning alternator, your vehicle will eventually drain the battery and stop running.
The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This process involves a rotating magnetic field interacting with a set of stationary coils, producing an alternating current (AC) that is then converted to direct current (DC) to power the car’s systems and charge the battery. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Energy and Resources Group, alternators play a vital role in maintaining the overall energy efficiency of vehicles.
Common signs of a failing alternator include:
- Dimming headlights
- Slow engine start
- Dead battery
- Warning lights on the dashboard (e.g., battery light)
- Unusual noises from the engine
Recognizing these symptoms early can save you from more significant issues and costly repairs down the road.
2. Can You Diagnose Alternator Problems with an OBD2 Scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can be a valuable tool for diagnosing alternator issues, but it’s essential to understand its capabilities and limitations. An OBD2 scanner reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in your car’s computer, providing insights into potential problems.
However, an OBD2 scanner won’t directly tell you, “Your alternator is faulty.” Instead, it identifies related electrical issues, such as low voltage or problems in the alternator’s control circuit. These clues can guide you toward determining if the alternator is the primary cause or if further investigation is needed.
According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 systems are designed to monitor various vehicle systems, including the charging system, and report any detected anomalies through specific diagnostic codes. The key is interpreting these codes correctly.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner to Check Your Alternator
Follow these steps to effectively use an OBD2 scanner, such as the Foxwell NT1009, to check for alternator problems in your Mercedes-Benz.
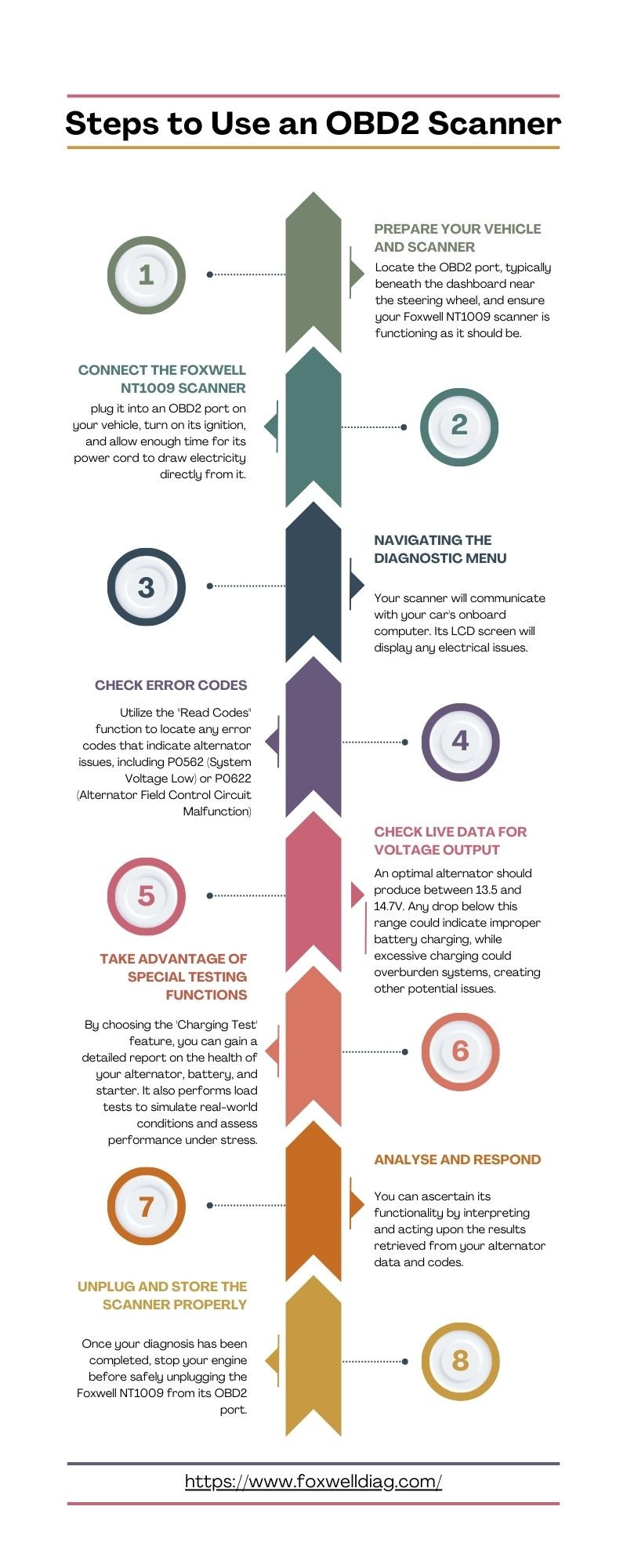
3.1. Prepare Your Vehicle and Scanner
First, ensure your vehicle is parked in a safe location and turn off all unnecessary electrical loads, such as headlights, radio, and air conditioning. This minimizes electrical interference during the diagnostic process.
Locate the OBD2 port, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Ensure your Foxwell NT1009 scanner is in good working condition with a fully charged battery or connected to a power source.
3.2. Connect the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
Plug the Foxwell NT1009 scanner into the OBD2 port. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This allows the scanner to draw power and establish communication with your vehicle’s computer.
3.3. Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
Turn on the scanner and navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Troubleshooting” menu. Select your vehicle’s make, model, and year for accurate data retrieval. The scanner will then communicate with your Mercedes-Benz’s onboard computer.
3.4. Check Error Codes
Use the “Read Codes” or “Retrieve Codes” function to check for any stored diagnostic trouble codes. Pay close attention to codes related to the electrical system, such as:
- P0562: System Voltage Low
- P0620: Generator Control Circuit Malfunction
- P0621: Generator Lamp Control Circuit Malfunction
- P0622: Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction
These codes indicate potential issues with the alternator or its control circuits.
 OBD2 Scanner Connection | Foxwell
OBD2 Scanner Connection | Foxwell
3.5. Check Live Data for Voltage Output
One of the most valuable features of the Foxwell NT1009 is its ability to monitor live data. Start the engine and navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” menu. Look for parameters such as “Battery Voltage,” “Alternator Voltage,” or “Charging System Voltage.”
An optimal alternator should produce a voltage between 13.5 and 14.7 volts. A voltage reading below this range indicates the battery is not charging correctly, while a voltage above this range suggests overcharging, which can damage the battery and other electrical components.
3.6. Perform a Load Test
To further assess the alternator’s performance, turn on various electrical accessories, such as headlights, air conditioning, and the radio. Observe the voltage readings while these accessories are running. A significant drop in voltage under load indicates the alternator is struggling to meet the electrical demands of the vehicle.
3.7. Take Advantage of Special Testing Functions
The Foxwell NT1009 may also offer specific testing functions for the charging system. Look for options like “Charging System Test” or “Alternator Test.” These tests provide a more detailed analysis of the alternator’s health, battery condition, and starter performance.
3.8. Analyze and Respond
Carefully analyze the data retrieved from the OBD2 scanner. If the voltage readings are within the normal range and there are no relevant error codes, the alternator is likely functioning correctly. However, if you observe abnormal voltage readings or relevant error codes, further investigation is necessary.
3.9. Clear Error Codes (If Applicable)
If you have made repairs or replaced the alternator, use the scanner to clear any stored error codes. This ensures the vehicle’s computer recognizes the changes and resets the diagnostic system.
3.10. Unplug and Store the Scanner Properly
Once the diagnosis is complete, turn off the engine and safely unplug the Foxwell NT1009 scanner from the OBD2 port. Store it in a safe place, ready for future use.
4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Mercedes-Benz’s Alternator
While an OBD2 scanner is a useful tool, it’s not the only method for testing your alternator. Here are some alternative approaches:
4.1. Multimeter Testing
A multimeter is a simple and effective tool for testing alternator voltage. Here’s how to do it:
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode.
- Connect the red lead to the positive (+) terminal of the battery and the black lead to the negative (-) terminal.
- Start the engine.
- Observe the voltage reading on the multimeter.
A healthy alternator should produce a voltage between 13.5 and 14.7 volts. Readings outside this range indicate a potential problem with the alternator.
4.2. Load Testing
A load test provides a more in-depth assessment of the alternator’s ability to handle electrical loads. This test can be performed using a dedicated load testing tool or by a professional mechanic.
The load test measures the alternator’s output under different electrical loads, simulating real-world driving conditions. It assesses whether the alternator can maintain a consistent voltage output when various electrical components are in use.
According to research from the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), load testing is a reliable method for evaluating the performance and durability of automotive alternators.
4.3. Battery Terminal Inspection
Visually inspect the battery terminals and connections for corrosion or damage. Clean the terminals with a wire brush and ensure the connections are tight. Corroded or loose connections can interfere with the alternator’s ability to charge the battery.
4.4. Professional Diagnostic Services
If you are unsure about performing these tests yourself, consider taking your Mercedes-Benz to a qualified mechanic for a professional diagnostic service. They have the expertise and equipment to accurately diagnose alternator issues and recommend the appropriate repairs.
 Full System Car Scanner | Foxwell
Full System Car Scanner | Foxwell
5. Interpreting OBD2 Scanner Results and Alternator Health
Understanding how to interpret the results from an OBD2 scanner is crucial for effectively diagnosing alternator issues. Here are some key points to consider:
5.1. Normal Voltage Readings
If the OBD2 scanner shows voltage readings between 13.5 and 14.7 volts while the engine is running, the alternator is likely functioning correctly. This indicates the alternator can adequately charge the battery and supply power to the vehicle’s electrical components.
5.2. Low Voltage Readings
If the voltage readings are consistently below 13.5 volts, it suggests the alternator is not producing enough power to charge the battery. This can lead to a discharged battery and potential electrical problems.
5.3. High Voltage Readings
Voltage readings above 14.7 volts indicate the alternator is overcharging the battery. Overcharging can damage the battery and other electrical components, leading to premature failure.
5.4. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Pay attention to any diagnostic trouble codes related to the charging system. Codes such as P0562 (System Voltage Low) or P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction) indicate specific issues with the alternator or its control circuits.
5.5. Voltage Drop Under Load
Observe the voltage readings while turning on various electrical accessories. A significant drop in voltage under load suggests the alternator is struggling to meet the electrical demands of the vehicle.
5.6. Intermittent Issues
Sometimes, alternator problems can be intermittent, making them challenging to diagnose. If you suspect an intermittent issue, monitor the voltage readings over time and during different driving conditions.
6. Benefits of Using MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Alternator Diagnostics
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information, tools, and support to help you diagnose and maintain your Mercedes-Benz’s electrical system. Here are some of the benefits of using our resources:
- Expert Guidance: Our website offers detailed guides and tutorials on using OBD2 scanners, multimeters, and other diagnostic tools.
- Accurate Information: We provide accurate and up-to-date information on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic trouble codes, voltage specifications, and testing procedures.
- Recommended Tools: We recommend high-quality OBD2 scanners, such as the Foxwell NT1009, and other diagnostic tools that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Our website offers troubleshooting tips and advice for diagnosing and resolving alternator issues, helping you save time and money on repairs.
- Community Support: Join our online community to connect with other Mercedes-Benz owners and share your experiences and knowledge.
7. Addressing Common Alternator Issues in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are known for their sophisticated electrical systems, which can be prone to certain alternator issues. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
7.1. Voltage Regulator Failure
The voltage regulator controls the alternator’s output voltage to prevent overcharging or undercharging the battery. If the voltage regulator fails, it can lead to unstable voltage readings and potential damage to the battery and electrical components.
7.2. Worn Brushes
The brushes are components that make contact with the rotating part of the alternator to transfer electricity. Over time, the brushes can wear down, leading to reduced alternator output and eventual failure.
7.3. Faulty Diode Trio
The diode trio converts the alternator’s AC output to DC. If one or more diodes fail, it can result in reduced alternator output and potential electrical problems.
7.4. Slipping Belt
The alternator is driven by a belt connected to the engine. If the belt is loose or worn, it can slip, causing reduced alternator output and potential damage to the belt and pulleys.
7.5. Corroded Connections
Corrosion on the alternator’s electrical connections can interfere with its ability to function properly. Clean the connections with a wire brush and apply a corrosion inhibitor to prevent future problems.
8. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Alternator for Longevity
Proper maintenance is essential for extending the life of your Mercedes-Benz alternator and preventing unexpected failures. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the alternator for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
- Belt Maintenance: Check the alternator belt for proper tension and condition. Replace the belt if it is cracked, worn, or loose.
- Electrical Connections: Clean and tighten the alternator’s electrical connections to ensure proper conductivity.
- Battery Maintenance: Maintain the battery’s health by keeping it charged and free of corrosion.
- Professional Service: Have the alternator and charging system inspected by a qualified mechanic during routine maintenance visits.
9. Latest Innovations in Alternator Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and alternator technology is no exception. Here are some of the latest innovations in alternator technology:
9.1. Smart Alternators
Smart alternators use sophisticated electronic controls to optimize their output based on the vehicle’s electrical demands. They can communicate with the vehicle’s computer to adjust the charging voltage and current, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
9.2. Integrated Starter-Generator (ISG) Systems
ISG systems combine the functions of the starter and alternator into a single unit. They provide smooth and seamless engine starting and stopping, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
9.3. High-Efficiency Alternators
High-efficiency alternators use advanced materials and designs to reduce energy losses and improve their overall efficiency. They can generate more power with less energy input, improving fuel economy and reducing emissions.
9.4. Solid-State Alternators
Solid-state alternators use electronic components instead of traditional brushes and mechanical parts. This improves their reliability, durability, and efficiency.
10. Why Regular Alternator Testing is Crucial for Mercedes-Benz Owners
Regular alternator testing is crucial for Mercedes-Benz owners for several reasons:
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular testing can identify potential alternator problems early, before they lead to a breakdown.
- Cost Savings: Early detection and repair of alternator issues can prevent more costly repairs down the road.
- Safety: A malfunctioning alternator can lead to a dead battery and a stalled vehicle, which can be dangerous, especially in high-traffic areas.
- Performance: A healthy alternator ensures the vehicle’s electrical components function properly, maintaining optimal performance.
- Longevity: Regular maintenance and testing can extend the life of the alternator, saving you money on replacements.
11. Conclusion: Empowering Mercedes-Benz Owners with Diagnostic Knowledge
Diagnosing alternator issues with an OBD2 scanner is a practical skill for any Mercedes-Benz owner. While the OBD2 scanner offers valuable insights, combining it with other testing methods, such as multimeter testing and load testing, ensures a comprehensive diagnosis.
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to maintain your Mercedes-Benz’s electrical system and avoid unexpected breakdowns. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently test your alternator and ensure your vehicle remains in top condition.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz’s health? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance on selecting the right diagnostic tools and accessing detailed repair information. Our team is here to help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
12. FAQs About Testing Alternators with OBD2 Scanners
12.1. Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can help you test an alternator by reading trouble codes and monitoring live voltage data. However, it may not give a direct diagnosis, so you might need to combine it with other testing methods for a complete assessment.
12.2. Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
A bad alternator can trigger related trouble codes on a scan, such as low system voltage or issues with the alternator’s circuit. While it won’t specifically say “bad alternator,” the codes can indicate a problem that requires further investigation.
12.3. Is there an OBD code for alternator?
Yes, there are OBD codes that relate to alternator issues. Common ones include P0562 (System Voltage Low) and P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction), which can signal that your alternator isn’t working properly.
12.4. What voltage should I see when testing my alternator?
When testing your alternator with a multimeter or OBD2 scanner, you should typically see a voltage between 13.5 and 14.7 volts while the engine is running. This range indicates that the alternator is charging the battery correctly.
12.5. How do I know if my alternator is bad?
Common signs of a bad alternator include dimming headlights, a slow engine start, a dead battery, warning lights on the dashboard, and unusual noises from the engine. Testing the alternator with an OBD2 scanner or multimeter can help confirm the diagnosis.
12.6. Can a faulty alternator cause other electrical problems?
Yes, a faulty alternator can cause a variety of electrical problems, including a dead battery, malfunctioning electrical components, and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
12.7. How often should I test my alternator?
It’s a good idea to test your alternator as part of your routine maintenance schedule, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles. Regular testing can help identify potential problems early, before they lead to a breakdown.
12.8. Is it safe to drive with a bad alternator?
Driving with a bad alternator is not recommended, as it can lead to a dead battery and a stalled vehicle, which can be dangerous, especially in high-traffic areas.
12.9. Can I replace the alternator myself?
Replacing the alternator can be a DIY project for experienced mechanics. However, if you are not comfortable working on your vehicle’s electrical system, it’s best to have the alternator replaced by a qualified mechanic.
12.10. How much does it cost to replace an alternator?
The cost to replace an alternator can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model, the type of alternator, and the labor costs. On average, you can expect to pay between $300 and $800 for an alternator replacement.
