K-Line OBD2 is a single-wire communication protocol that allows diagnostic tools to communicate with a vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit), and understanding it is crucial for Mercedes diagnostics; MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert insights and tools to streamline this process. Utilizing K-Line effectively enables precise troubleshooting, unlocking hidden features, and optimizing your Mercedes-Benz’s performance. Discover how to harness advanced diagnostic capabilities and maintenance solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the K-Line Protocol in OBD2 for Mercedes
- 1.1 What is K-Line in OBD2?
- 1.2 How Does K-Line Work in Mercedes Vehicles?
- 1.3 Key Features of K-Line Protocol
- 2. Advantages of Using K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes Diagnostics
- 2.1 Cost-Effectiveness
- 2.2 Simplicity
- 2.3 Wide Compatibility
- 2.4 Ease of Use
- 2.5 Basic Diagnostics
- 3. Limitations of K-Line OBD2
- 3.1 Slower Data Transfer Rates
- 3.2 Limited Functionality
- 3.3 Single Point of Failure
- 3.4 Susceptibility to Noise
- 3.5 Lack of Standardization
- 4. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- 4.1 Communication Errors
- 4.2 Data Corruption
- 4.3 Slow Data Transfer
- 4.4 Incompatible Tools
- 5. Choosing the Right K-Line OBD2 Tool for Your Mercedes
- 5.1 Compatibility
- 5.2 Functionality
- 5.3 Ease of Use
- 5.4 Updates and Support
- 5.5 Price
- 5.6 Professional Reviews
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide to Using a K-Line OBD2 Tool
- 6.1 Connect the Tool
- 6.2 Power On
- 6.3 Select Vehicle
- 6.4 Read DTCs
- 6.5 Access Live Data
- 6.6 Perform Tests
- 6.7 Interpret Results
- 6.8 Clear DTCs
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures with K-Line OBD2
- 7.1 ECU Reprogramming
- 7.2 Key Programming
- 7.3 Airbag Reset
- 7.4 ABS Diagnostics
- 8. K-Line OBD2 vs. CAN Bus: Which is Better for Mercedes?
- 8.1 Overview of CAN Bus
- 8.2 Key Differences
- 8.3 Which One to Choose?
- 8.4 Hybrid Solutions
- 9. Future Trends in Mercedes Diagnostics
- 9.1 Wireless Diagnostics
- 9.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 9.3 Artificial Intelligence
- 9.4 Augmented Reality
- 9.5 Remote Diagnostics
- 10. FAQ About K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes
- 10.1 What is K-Line OBD2?
- 10.2 How does K-Line OBD2 work?
- 10.3 What are the advantages of using K-Line OBD2?
- 10.4 What are the limitations of K-Line OBD2?
- 10.5 Which Mercedes models use K-Line OBD2?
- 10.6 Can I use a K-Line OBD2 tool on a newer Mercedes?
- 10.7 What types of diagnostic functions can I perform with K-Line OBD2?
- 10.8 How do I troubleshoot communication errors with K-Line OBD2?
- 10.9 What is the difference between K-Line OBD2 and CAN bus?
- 10.10 Where can I find reliable K-Line OBD2 tools and resources?
- Conclusion
1. Understanding the K-Line Protocol in OBD2 for Mercedes
The K-Line protocol is a single-wire communication system utilized in OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, which facilitates communication between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit). This protocol is essential for reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), accessing live data, and performing various diagnostic and maintenance functions.
1.1 What is K-Line in OBD2?
K-Line, short for Keyword Line 2000, is a communication protocol used in automotive diagnostics. According to the Robert Bosch GmbH’s “Bosch Automotive Handbook,” the K-Line is a single-wire, bidirectional communication line. It allows a diagnostic tool to interface with the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) for diagnostics and reprogramming. In OBD2, K-Line is one of the physical layers used for communication.
1.2 How Does K-Line Work in Mercedes Vehicles?
In Mercedes vehicles, the K-Line operates by transmitting data as voltage pulses over a single wire. The ECU and diagnostic tool communicate using a master-slave configuration, where the diagnostic tool (master) sends requests, and the ECU (slave) responds with data.
The K-Line communication process involves the following steps:
- Initialization: The diagnostic tool sends an initialization sequence to the ECU.
- Request: The diagnostic tool sends a request for specific data or functions.
- Response: The ECU processes the request and sends back the requested data or executes the function.
- Data Transmission: Data is transmitted serially using specific timing and voltage levels.
1.3 Key Features of K-Line Protocol
The K-Line protocol has several key features:
- Single-Wire Communication: Reduces wiring complexity and cost.
- Bidirectional Communication: Allows both sending and receiving data over the same wire.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: Enables reading DTCs, accessing live data, and performing diagnostic tests.
- Reprogramming Capabilities: Supports ECU reprogramming and software updates.
2. Advantages of Using K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes Diagnostics
Utilizing K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes diagnostics offers several notable advantages, which make it a valuable tool for both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
2.1 Cost-Effectiveness
K-Line interfaces are generally more cost-effective compared to other diagnostic interfaces like CAN (Controller Area Network). The simplicity of the single-wire system reduces the cost of the interface hardware.
2.2 Simplicity
The K-Line protocol is relatively simple to implement, making it easier to develop diagnostic tools and software. According to “Automotive Ethernet” by Kirsten Matheus and Thomas Königseder, the K-Line’s straightforward nature simplifies the development and maintenance of diagnostic systems.
2.3 Wide Compatibility
K-Line is supported by a wide range of Mercedes-Benz models, especially older vehicles. This broad compatibility ensures that a single K-Line interface can be used across multiple vehicle models.
2.4 Ease of Use
Many diagnostic tools that use K-Line are user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces that make it easy to read diagnostic codes and access live data. This ease of use makes K-Line tools accessible to both professional technicians and DIY users.
2.5 Basic Diagnostics
K-Line OBD2 is proficient at performing basic diagnostics. With K-Line, one can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view real-time data, and perform basic tests, making it a practical tool for troubleshooting common issues.
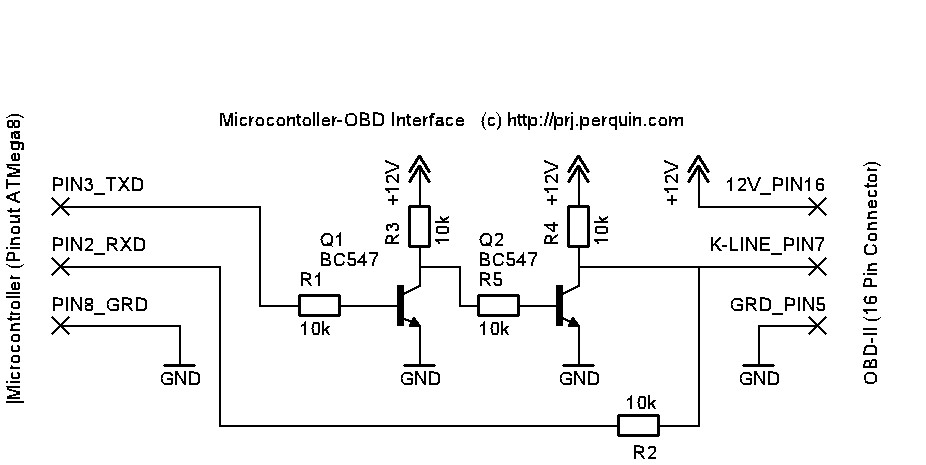 Mercedes K-Line OBD2 Connection
Mercedes K-Line OBD2 Connection
3. Limitations of K-Line OBD2
Despite its advantages, K-Line OBD2 also has several limitations that users should be aware of.
3.1 Slower Data Transfer Rates
K-Line has slower data transfer rates compared to newer protocols like CAN. This can be a limitation when dealing with large amounts of data or performing real-time diagnostics.
3.2 Limited Functionality
K-Line has limited functionality compared to CAN. It may not support advanced diagnostic functions or ECU reprogramming on newer Mercedes models.
3.3 Single Point of Failure
Because K-Line uses a single wire for communication, a fault in the wire can disrupt the entire communication, leading to diagnostic failures.
3.4 Susceptibility to Noise
The single-wire design makes K-Line more susceptible to electrical noise and interference, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic data.
3.5 Lack of Standardization
While OBD2 provides a standard interface, the implementation of K-Line can vary between manufacturers, leading to compatibility issues with some diagnostic tools.
4. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
When using K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes diagnostics, you may encounter several common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help resolve these issues:
4.1 Communication Errors
Issue: The diagnostic tool fails to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the OBD2 connector is securely plugged into the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Verify Power Supply: Ensure the diagnostic tool has a stable power supply.
- Inspect the K-Line Wiring: Check the K-Line wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Use Compatible Software: Ensure the diagnostic software is compatible with the vehicle model and K-Line protocol.
4.2 Data Corruption
Issue: The diagnostic tool displays incorrect or corrupted data.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for Interference: Identify and eliminate any sources of electrical noise or interference.
- Use Shielded Cables: Use shielded OBD2 cables to minimize interference.
- Update Software: Ensure the diagnostic software is up to date with the latest bug fixes and improvements.
- Verify ECU Firmware: Check if the vehicle’s ECU firmware is up to date and compatible with the diagnostic tool.
4.3 Slow Data Transfer
Issue: The diagnostic tool takes a long time to retrieve data or perform diagnostic tests.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Minimize Background Processes: Close any unnecessary applications or processes running on the diagnostic tool.
- Use a Faster Interface: If possible, use a diagnostic tool with a faster communication interface, such as CAN.
- Optimize Software Settings: Adjust the diagnostic software settings to optimize data transfer rates.
4.4 Incompatible Tools
Issue: The diagnostic tool is not compatible with the Mercedes vehicle.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Compatibility Lists: Verify that the diagnostic tool is compatible with the specific Mercedes model and year.
- Use a Universal Tool: Consider using a universal OBD2 tool that supports multiple protocols, including K-Line and CAN.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the diagnostic tool’s documentation for compatibility information and troubleshooting tips.
5. Choosing the Right K-Line OBD2 Tool for Your Mercedes
Selecting the appropriate K-Line OBD2 tool is critical for effective diagnostics of your Mercedes-Benz. Consider the factors when making your choice:
5.1 Compatibility
Ensure the tool supports the K-Line protocol and is compatible with your Mercedes model and year.
5.2 Functionality
Determine the functions you need, such as reading DTCs, accessing live data, or performing specific diagnostic tests. Choose a tool that offers the required functionality.
5.3 Ease of Use
Look for a tool with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions. A simple interface will make it easier to navigate and use the tool effectively.
5.4 Updates and Support
Check if the tool receives regular software updates and has good customer support. Regular updates ensure the tool remains compatible with newer vehicles and includes the latest features and bug fixes.
5.5 Price
Consider your budget and choose a tool that offers the best value for your money. Compare the features and functionality of different tools within your price range.
5.6 Professional Reviews
Research on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools can be found in “OBD2 Diagnostics” by Steven T. Gary, which offers detailed reviews and comparisons of various tools, which helps in making an informed decision.
6. Step-by-Step Guide to Using a K-Line OBD2 Tool
To effectively use a K-Line OBD2 tool for Mercedes diagnostics, follow these steps:
6.1 Connect the Tool
Plug the OBD2 connector into the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard.
6.2 Power On
Turn on the diagnostic tool and follow the on-screen instructions to establish a connection with the vehicle’s ECU.
6.3 Select Vehicle
Select the correct vehicle model, year, and engine type from the tool’s menu.
6.4 Read DTCs
Choose the option to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The tool will display any stored DTCs along with descriptions.
6.5 Access Live Data
Select the option to access live data. The tool will display real-time data from various sensors and systems in the vehicle.
6.6 Perform Tests
Choose the option to perform diagnostic tests. The tool may offer various tests, such as actuator tests, sensor tests, and system tests.
6.7 Interpret Results
Analyze the DTCs, live data, and test results to diagnose the issue and identify the necessary repairs.
6.8 Clear DTCs
After performing repairs, clear the DTCs from the ECU to reset the check engine light.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures with K-Line OBD2
K-Line OBD2 tools can also be used for advanced diagnostic procedures.
7.1 ECU Reprogramming
Some K-Line tools support ECU reprogramming, allowing you to update the vehicle’s software or install custom firmware. However, ECU reprogramming should only be performed by experienced technicians.
7.2 Key Programming
Some K-Line tools can be used to program new keys or immobilizer systems. This requires specialized software and knowledge of the vehicle’s security systems.
7.3 Airbag Reset
K-Line tools can be used to reset the airbag control module after an accident. This should only be done after verifying that all airbag components are functioning correctly.
7.4 ABS Diagnostics
K-Line tools can perform diagnostics on the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), including reading ABS codes, accessing live data, and performing ABS tests.
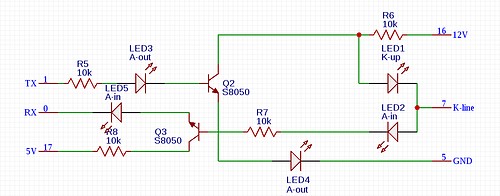 K-Line OBD2 Connection Diagram
K-Line OBD2 Connection Diagram
8. K-Line OBD2 vs. CAN Bus: Which is Better for Mercedes?
When it comes to Mercedes diagnostics, understanding the differences between K-Line OBD2 and CAN Bus is essential. Each protocol has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and capabilities required.
8.1 Overview of CAN Bus
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a more advanced communication protocol widely used in modern vehicles. It allows multiple ECUs to communicate with each other without a central host computer. According to “Understanding Modern контроллеры” by Gianluca Cena and Adriano Valenzano, CAN Bus is a high-speed, reliable communication system that enables advanced vehicle functions.
8.2 Key Differences
The following table highlights the key differences between K-Line OBD2 and CAN Bus:
| Feature | K-Line OBD2 | CAN Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Single-wire, bidirectional | Two-wire, differential |
| Data Transfer Rate | Slower | Faster |
| Complexity | Simpler | More Complex |
| Functionality | Limited | Advanced |
| Noise Susceptibility | Higher | Lower |
| Compatibility | Older Vehicles | Newer Vehicles |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| ECU Communication | Point-to-point | Multi-point, networked |
8.3 Which One to Choose?
- Choose K-Line OBD2 if you are working on older Mercedes models and need basic diagnostic functions at a lower cost.
- Choose CAN Bus if you are working on newer Mercedes models and need advanced diagnostic functions, faster data transfer rates, and more reliable communication.
8.4 Hybrid Solutions
Some diagnostic tools support both K-Line OBD2 and CAN Bus, providing versatility for working on a wide range of Mercedes vehicles. These hybrid tools can automatically detect the communication protocol and switch accordingly.
9. Future Trends in Mercedes Diagnostics
The field of Mercedes diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging. Here are some future trends to watch for:
9.1 Wireless Diagnostics
Wireless diagnostic tools that communicate with the vehicle’s ECU via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi are becoming increasingly popular. These tools offer greater flexibility and convenience compared to wired tools.
9.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms allow technicians to access diagnostic data, software updates, and technical support remotely. This can improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
9.3 Artificial Intelligence
AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze diagnostic data and provide intelligent recommendations for repairs. AI can also help predict potential issues and prevent breakdowns.
9.4 Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) applications can overlay diagnostic information onto the vehicle, providing technicians with a visual guide to troubleshooting and repair procedures.
9.5 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostic services allow technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, using telematics data and remote access tools. This can be useful for diagnosing issues in remote locations or providing support to DIY users.
10. FAQ About K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes
Here are some frequently asked questions about K-Line OBD2 for Mercedes:
10.1 What is K-Line OBD2?
K-Line OBD2 is a single-wire communication protocol used in older Mercedes-Benz vehicles for diagnostic purposes, allowing tools to interface with the vehicle’s computer system.
10.2 How does K-Line OBD2 work?
K-Line OBD2 operates through a single wire that transmits voltage pulses, enabling bidirectional communication between a diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s ECU for data exchange.
10.3 What are the advantages of using K-Line OBD2?
Advantages include cost-effectiveness, simplicity, wide compatibility with older models, and ease of use for basic diagnostic tasks such as reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes.
10.4 What are the limitations of K-Line OBD2?
Limitations include slower data transfer rates, limited functionality compared to CAN bus systems, susceptibility to noise, and a single point of failure due to its single-wire design.
10.5 Which Mercedes models use K-Line OBD2?
K-Line OBD2 is commonly found in older Mercedes-Benz models manufactured before the widespread adoption of CAN bus systems, typically pre-2008 vehicles.
10.6 Can I use a K-Line OBD2 tool on a newer Mercedes?
No, newer Mercedes models use CAN bus systems, which are not compatible with K-Line OBD2 tools. You will need a CAN bus-compatible diagnostic tool for these vehicles.
10.7 What types of diagnostic functions can I perform with K-Line OBD2?
You can perform basic diagnostic functions such as reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), accessing live data, performing basic tests, and clearing DTCs.
10.8 How do I troubleshoot communication errors with K-Line OBD2?
Check the OBD2 connector, verify the power supply, inspect the K-Line wiring for damage, and ensure the diagnostic software is compatible with the vehicle model and K-Line protocol.
10.9 What is the difference between K-Line OBD2 and CAN bus?
K-Line OBD2 is a single-wire, slower communication protocol used in older vehicles, while CAN bus is a two-wire, faster, and more complex protocol used in newer vehicles.
10.10 Where can I find reliable K-Line OBD2 tools and resources?
Reliable tools and resources can be found at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, which offers expert insights, tools, and support for Mercedes diagnostics.
Conclusion
K-Line OBD2 is a valuable tool for diagnosing older Mercedes-Benz vehicles, offering cost-effective and straightforward diagnostic capabilities. While it has limitations compared to newer protocols like CAN Bus, understanding its features and troubleshooting tips can help you effectively diagnose and maintain your Mercedes. For advanced diagnostics, newer models, and comprehensive solutions, consider exploring CAN Bus tools and resources available at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance, tools, and services tailored to your needs. Whether you need help choosing the right diagnostic tool, unlocking hidden features, or troubleshooting complex issues, our team is here to assist you. Reach out today and experience the difference!
Contact Information:
- Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
