An OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector is a diagnostic tool designed to read data from older vehicles (OBD1) while utilizing the physical connector shape of the newer OBD2 standard. These scanners bridge the gap, allowing technicians and car enthusiasts to diagnose a wider range of vehicles with a single device. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information and expert guidance on selecting and using these versatile tools, and help you unlock advanced features, repair guides and maintenance tips. We also offer support to ensure you find the best solutions for your diagnostic needs. Let us help you find the correct automotive diagnostic tools, mercedes hidden features, and Mercedes-Benz repair procedures.
1. Understanding OBD1 and OBD2 Standards
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) was the early generation of automotive diagnostic systems, primarily used in vehicles manufactured before 1996. It lacked standardization, meaning each car manufacturer used their own unique connectors, communication protocols, and diagnostic codes. This made diagnosing issues a cumbersome process, often requiring specialized tools for each make and model.
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics 2) is the standardized system introduced in 1996 in the United States (and later adopted worldwide) to provide a more uniform approach to vehicle diagnostics. OBD2 mandates a standard 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC), a common set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and standardized communication protocols. This standardization simplified vehicle diagnostics, allowing a single scanner to interface with a wide range of vehicles.
2. The Role of an Obd1 Scanner With Obd2 Connector
An OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector is designed to address the challenges of diagnosing older OBD1 vehicles. It typically consists of:
- An OBD1 interface: This includes the necessary hardware and software to communicate with the specific protocols used by different OBD1 vehicle manufacturers.
- An OBD2 connector: This allows the scanner to physically connect to the standard 16-pin DLC found in newer vehicles.
- Adapter cables (optional): Some scanners may include adapter cables to connect to the proprietary connectors used in specific OBD1 vehicles.
3. Why Use an OBD1 Scanner with OBD2 Connector?
There are several compelling reasons to use an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector:
- Versatility: These scanners can diagnose both older OBD1 vehicles and newer OBD2 vehicles, making them a versatile tool for mechanics and car enthusiasts who work on a variety of cars.
- Convenience: Instead of needing separate scanners for OBD1 and OBD2 vehicles, a single scanner can handle both, saving time, money, and storage space.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Purchasing a single scanner that supports both OBD1 and OBD2 is often more cost-effective than buying separate scanners.
- Ease of Use: Many modern OBD1 scanners with OBD2 connectors come with user-friendly interfaces and software, making them easier to use than older, specialized OBD1 scanners.
4. Identifying Your Vehicle’s Diagnostic Standard
Before using any scanner, it’s crucial to identify whether your vehicle uses the OBD1 or OBD2 standard. Here’s how to determine this:
- Model Year: Vehicles manufactured in 1996 and later in the United States are typically OBD2 compliant. Vehicles made before 1996 are usually OBD1. However, some vehicles manufactured in 1994 and 1995 may have implemented OBD2 features ahead of the mandate.
- Data Link Connector (DLC) Location: OBD2 vehicles have a standard 16-pin DLC, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. The location may be different across brands. Consult your owner’s manual.
- Check the Vehicle’s Documentation: Your vehicle’s owner’s manual or service manual should specify whether it is OBD1 or OBD2 compliant.
5. Key Features to Look for in an OBD1 Scanner with OBD2 Connector
When selecting an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports the specific OBD1 protocols used by the vehicles you intend to diagnose. Check the manufacturer’s compatibility list carefully.
- OBD2 Functionality: Verify that the scanner supports all five OBD2 protocols (SAE J1850 VPW, SAE J1850 PWM, ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000), and ISO 15765-4 (CAN)).
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with a user-friendly interface, clear display, and intuitive menu navigation.
- Data Logging and Reporting: Choose a scanner that allows you to record diagnostic data for later analysis and generate reports for customers or your own records.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner manufacturer provides regular software updates to support new vehicles and protocols.
- Bi-Directional Control: Some advanced scanners offer bi-directional control, allowing you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to test components and systems.
- Live Data Streaming: Live data streaming allows you to view real-time sensor data, which can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems.
- Adapter Cables: Check if the scanner includes the necessary adapter cables for the specific OBD1 vehicles you plan to work on. If not, you may need to purchase them separately.
6. Top OBD1 Scanner with OBD2 Connector Brands
Several reputable brands offer OBD1 scanners with OBD2 connectors. Here are a few of the top contenders:
- Launch: Launch Tech offers a wide range of diagnostic tools, including several that support both OBD1 and OBD2.
- Autel: Autel is another leading manufacturer of diagnostic equipment, known for their comprehensive coverage and advanced features.
- Snap-on: Snap-on is a well-respected brand among professional mechanics, offering high-quality scanners with extensive capabilities.
- Actron: Actron (now part of Bosch) provides a range of affordable OBD1 and OBD2 scanners for DIYers and professional technicians.
- Innova: Innova offers a variety of scanners, including some that support both OBD1 and OBD2, with a focus on user-friendliness.
7. Step-by-Step Guide to Using an OBD1 Scanner with OBD2 Connector
Here’s a general guide to using an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector:
- Connect the Scanner:
- For OBD2 vehicles, simply plug the scanner’s OBD2 connector into the vehicle’s DLC.
- For OBD1 vehicles, you may need to use an adapter cable to connect the scanner to the vehicle’s proprietary connector.
- Turn on the Vehicle’s Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the scanner and wait for it to boot up.
- Select the Vehicle Make and Model: Use the scanner’s menu to select the make, model, and year of the vehicle you are diagnosing.
- Choose the Diagnostic Function: Select the diagnostic function you want to perform, such as reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), viewing live data, or performing bi-directional tests.
- Follow the Scanner’s Instructions: The scanner will guide you through the diagnostic process. Follow the on-screen instructions carefully.
- Interpret the Results: Once the scanner has completed the diagnostic test, it will display the results. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource to interpret the results and determine the appropriate course of action.
8. Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and Their Meanings
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are codes stored in the vehicle’s computer that indicate a problem with a specific system or component. Here are some common DTCs and their meanings:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction
- P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
- P0113: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input
- P0122: Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Circuit Low Input
- P0505: Idle Air Control (IAC) System Malfunction
9. Tips for Effective Vehicle Diagnostics
Here are some tips for effective vehicle diagnostics using an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector:
- Read the Vehicle’s Service Manual: The vehicle’s service manual is an invaluable resource for understanding the vehicle’s systems and components.
- Start with the Basics: Before diving into advanced diagnostics, check the basics, such as fluid levels, wiring connections, and vacuum lines.
- Verify the DTC: Before replacing any parts, verify that the DTC is accurate by performing additional tests and inspections.
- Use a Reliable Resource: Refer to a reliable online resource or database to research DTCs and their potential causes.
- Don’t Guess: Avoid guessing at the cause of a problem. Instead, use a systematic approach to diagnosis, following the steps outlined in the vehicle’s service manual.
- Document Your Work: Keep a record of the diagnostic tests you perform, the results you obtain, and the repairs you make.
10. Unlocking Hidden Features in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Many modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles have hidden features that can be unlocked using diagnostic tools and specialized software. These features can enhance the vehicle’s functionality, appearance, or comfort. Here are a few examples of hidden features that can be unlocked:
- AMG Menu in Instrument Cluster: Display additional performance data, such as engine oil temperature, coolant temperature, and battery voltage, in the instrument cluster.
- Cornering Lights: Activate the fog lights to illuminate the side of the road when turning at low speeds.
- Enhanced Ambient Lighting: Customize the color and intensity of the ambient lighting in the cabin.
- Sport Display: Change the appearance of the instrument cluster to a sportier design.
- Acoustic Lock Confirmation: Enable an audible beep when locking or unlocking the vehicle.
- Video in Motion: Allow the DVD player or other video sources to play while the vehicle is in motion (may be restricted by law in some areas).
- Comfort Closing: Enable the ability to close the windows and sunroof by holding the lock button on the key fob.
- Automatic High Beams: Automatically switch between high beams and low beams based on the presence of other vehicles.
- Changing the Instrument Cluster Theme: Alter the look of your instrument panel to suit your preferences.
11. Legal and Ethical Considerations
When using an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector, it’s important to be aware of the following legal and ethical considerations:
- Warranty Implications: Modifying a vehicle’s software or systems may void the warranty. Check with the vehicle manufacturer or your warranty provider before making any modifications.
- Emissions Regulations: Tampering with emissions control systems is illegal in many jurisdictions. Ensure that any modifications you make comply with local emissions regulations.
- Safety: Some modifications may affect the safety of the vehicle. Ensure that any modifications you make are safe and do not compromise the vehicle’s handling or braking performance.
- Privacy: Some diagnostic tools may collect and transmit vehicle data to the manufacturer or other third parties. Be aware of the privacy implications of using these tools.
12. The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving. Here are some of the trends shaping the future of vehicle diagnostics:
- Wireless Diagnostics: Wireless OBD2 adapters and smartphone apps are becoming increasingly popular, allowing users to diagnose their vehicles from the convenience of their mobile devices.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are emerging, providing access to a wealth of diagnostic data, repair information, and expert support.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to develop more advanced diagnostic algorithms that can identify problems more quickly and accurately.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic services are becoming more common, allowing technicians to diagnose vehicles remotely, reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems use data from vehicle sensors to predict when maintenance will be required, helping to prevent breakdowns and reduce downtime.
13. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz: Essential Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and reliably. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Follow the Recommended Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the maintenance schedule outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Change the Oil Regularly: Change the engine oil and filter at the intervals recommended by the manufacturer.
- Check Fluid Levels: Regularly check and top off all fluid levels, including coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Inspect the Brakes: Inspect the brakes regularly for wear and tear. Replace brake pads and rotors as needed.
- Check the Tires: Check the tires for proper inflation and wear. Rotate the tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Replace Air Filters: Replace the engine air filter and cabin air filter at the recommended intervals.
- Inspect Belts and Hoses: Inspect belts and hoses for cracks, leaks, or other damage. Replace them as needed.
- Keep the Vehicle Clean: Wash and wax the vehicle regularly to protect the paint and prevent rust.
14. Resources for Mercedes-Benz Owners
Here are some helpful resources for Mercedes-Benz owners:
- Mercedes-Benz Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual contains valuable information about the vehicle’s systems, features, and maintenance requirements.
- Mercedes-Benz Service Manual: The service manual provides detailed information about how to diagnose and repair the vehicle.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles can be a great resource for troubleshooting problems and sharing information with other owners.
- Mercedes-Benz Dealership: Your local Mercedes-Benz dealership can provide expert service and support.
15. The Benefits of Choosing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing Mercedes-Benz owners and enthusiasts with the knowledge, tools, and support they need to keep their vehicles running at their best. Here are some of the benefits of choosing us:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of experienced technicians and Mercedes-Benz specialists can provide expert guidance on selecting the right diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and performing repairs and maintenance.
- Comprehensive Information: We offer a wealth of information on Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including diagnostic trouble codes, repair procedures, and maintenance schedules.
- High-Quality Products: We offer a curated selection of high-quality diagnostic tools and accessories from leading brands.
- Exceptional Customer Service: We are committed to providing exceptional customer service and support. Our team is always available to answer your questions and help you find the solutions you need.
- Community: We foster a community of Mercedes-Benz owners and enthusiasts where you can connect with other like-minded individuals, share information, and get support.
We invite you to explore our website, browse our products, and contact us with any questions you may have. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your Mercedes-Benz.
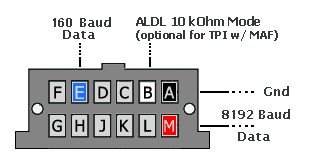 OBD1 ALDL Connector Pinouts
OBD1 ALDL Connector Pinouts
16. Understanding the Limitations
While OBD1 scanners with OBD2 connectors offer increased versatility, it’s vital to understand their limitations:
- Not a Universal Solution: Due to the vast differences in OBD1 systems across manufacturers, a single scanner might not cover every vehicle. Always verify compatibility before purchase.
- Complexity: Diagnosing OBD1 vehicles often requires specialized knowledge and a deeper understanding of vehicle-specific systems.
- Data Interpretation: The diagnostic codes and data provided by OBD1 systems can be less specific and more challenging to interpret compared to OBD2.
17. Essential Accessories for OBD1 Scanning
To maximize the effectiveness of your OBD1 scanner, consider these accessories:
- Adapter Cables: As mentioned earlier, these are crucial for connecting to the diverse range of OBD1 connectors.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for electrical testing, verifying sensor signals, and troubleshooting wiring issues.
- Wiring Diagrams: Access to accurate wiring diagrams for the specific vehicle you’re diagnosing is invaluable for tracing circuits and identifying faults.
- Diagnostic Software: Some scanners work with specialized software that provides enhanced diagnostic capabilities, data analysis, and repair information.
18. Choosing the Right Adapter Cables
Selecting the correct adapter cables is crucial for successful OBD1 diagnostics. Here’s what to consider:
- Vehicle Make and Model: Identify the specific connector type used by the vehicle you’re diagnosing.
- Pin Configuration: Ensure the adapter cable has the correct pin configuration to match the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Quality: Invest in high-quality adapter cables to ensure reliable connections and prevent damage to the scanner or vehicle.
- Compatibility: Verify that the adapter cable is compatible with your OBD1 scanner.
19. Alternative Diagnostic Methods for Older Vehicles
While OBD1 scanners are helpful, consider these alternative diagnostic methods for older vehicles:
- Visual Inspection: A thorough visual inspection can often reveal obvious problems, such as damaged wiring, leaking fluids, or worn components.
- Manual Testing: Use a multimeter, vacuum gauge, and other tools to manually test sensors, actuators, and other components.
- Listening for Unusual Noises: Pay attention to unusual noises, such as squeals, rattles, or knocks, which can indicate specific problems.
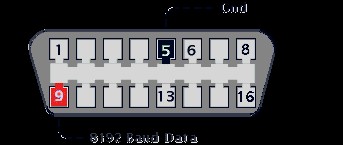 OBD2 Connector Pinouts
OBD2 Connector Pinouts
20. Safety Precautions When Working with Automotive Electronics
When working with automotive electronics, always follow these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks, debris, and chemicals.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shock.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Avoid working on electrical components in wet conditions.
- Follow Proper Procedures: Follow the proper diagnostic and repair procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual.
21. Understanding OBD1 Communication Protocols
Understanding the communication protocols used by OBD1 systems is essential for effective diagnostics. Here are some common protocols:
- ALDL (Assembly Line Diagnostic Link): Used by General Motors vehicles.
- EEC-IV (Electronic Engine Control IV): Used by Ford vehicles.
- OBD-I: Used by Chrysler vehicles.
- Motronic: Used by BMW and other European vehicles.
22. Common Issues Diagnosed with an OBD1 Scanner
An OBD1 scanner can help diagnose a wide range of issues, including:
- Engine Misfires: Identify the cylinder that is misfiring and the cause of the misfire.
- Sensor Failures: Detect faulty sensors, such as oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensors, and throttle position sensors.
- Fuel System Problems: Diagnose issues with fuel injectors, fuel pumps, and fuel pressure regulators.
- Emissions Control Problems: Identify problems with the catalytic converter, evaporative emissions system, and other emissions control components.
- Ignition System Problems: Diagnose issues with spark plugs, ignition coils, and distributors.
23. Resources for Learning More About OBD1 Diagnostics
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to specific vehicle makes and models can provide valuable information about OBD1 diagnostics.
- Service Manuals: The vehicle’s service manual is an invaluable resource for understanding the vehicle’s systems and diagnostic procedures.
- Training Courses: Consider taking a training course on automotive diagnostics to improve your skills and knowledge.
24. The Importance of Regular Vehicle Inspections
Regular vehicle inspections are essential for identifying potential problems early on and preventing costly repairs. During a vehicle inspection, a technician will typically check:
- Fluid Levels: Check all fluid levels, including engine oil, coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Tires: Check the tires for proper inflation and wear.
- Brakes: Inspect the brakes for wear and tear.
- Suspension: Inspect the suspension components for damage or wear.
- Lights: Check all lights to ensure they are working properly.
- Belts and Hoses: Inspect belts and hoses for cracks, leaks, or other damage.
25. Understanding Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the time a DTC was set. This data can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or understanding the circumstances that led to a particular DTC. Freeze frame data typically includes:
- Engine Speed: The engine speed (RPM) at the time the DTC was set.
- Engine Load: The engine load at the time the DTC was set.
- Coolant Temperature: The engine coolant temperature at the time the DTC was set.
- Fuel Trim: The fuel trim values at the time the DTC was set.
- Vehicle Speed: The vehicle speed at the time the DTC was set.
26. How to Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After repairing a problem, it’s important to clear the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer. Here’s how to clear DTCs using an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector:
- Connect the Scanner: Connect the scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
- Select the Clear Codes Function: Use the scanner’s menu to select the “Clear Codes” function.
- Confirm the Clear Codes Request: The scanner may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Wait for Confirmation: Wait for the scanner to confirm that the codes have been cleared.
27. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- Waveform Analysis: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the waveforms of sensor signals.
- Fuel Injector Testing: Use a fuel injector tester to check the operation of fuel injectors.
- Compression Testing: Perform a compression test to check the condition of the engine’s cylinders.
- Leak Down Testing: Perform a leak down test to identify leaks in the cylinders.
28. Resources for Mercedes-Benz Enthusiasts
- Mercedes-Benz Club of America: Join the Mercedes-Benz Club of America to connect with other enthusiasts, attend events, and learn more about Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles can be a great resource for troubleshooting problems and sharing information with other owners.
- Mercedes-Benz Museums: Visit a Mercedes-Benz museum to learn about the history of the brand and see some of the most iconic Mercedes-Benz vehicles ever built.
29. Maximizing the Lifespan of Your Mercedes-Benz
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Proper Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive driving habits, such as hard acceleration and braking.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any problems promptly to prevent them from escalating into more serious issues.
- Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts to ensure the longevity of your vehicle.
- Protect from the Elements: Protect your vehicle from the elements by parking it in a garage or using a car cover.
30. Why Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs?
Navigating the complexities of OBD1 and OBD2 diagnostics, especially for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, can be challenging. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer the expertise and support you need to confidently diagnose and maintain your vehicle.
Our Services Include:
- Expert Consultation: We can help you select the right OBD1 scanner with OBD2 connector for your specific needs and budget.
- Diagnostic Support: Our experienced technicians can provide guidance on interpreting diagnostic codes and troubleshooting problems.
- Hidden Feature Unlocking: We offer services to unlock hidden features in your Mercedes-Benz, enhancing its functionality and personalization.
- Repair and Maintenance Advice: We can provide advice on performing repairs and maintenance, helping you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Don’t struggle with your Mercedes-Benz diagnostics alone. Contact MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance!
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
FAQ Section
Q1: What is an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector, and why would I need one?
An OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector is a diagnostic tool that can read trouble codes and data from both older (OBD1) and newer (OBD2) vehicles. You would need one if you work on a variety of cars, including those made before and after the 1996 OBD2 standardization.
Q2: Will an OBD2 scanner work on an OBD1 car?
No, an OBD2 scanner will not work on an OBD1 car without an adapter and the ability to read the older protocols. OBD1 systems used different connectors and communication protocols than OBD2.
Q3: How do I know if my car is OBD1 or OBD2?
Cars manufactured in 1996 and later in the United States are typically OBD2. OBD1 vehicles were made before 1996. Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or look for the standard 16-pin OBD2 connector under the dashboard.
Q4: What are some common problems I can diagnose with an OBD1 scanner?
You can diagnose engine misfires, sensor failures (like O2 sensors or MAF sensors), fuel system problems, emissions control issues, and ignition system problems.
Q5: Are adapter cables always necessary when using an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector on an older vehicle?
Yes, adapter cables are typically necessary because OBD1 vehicles used a variety of proprietary connectors that are different from the standard OBD2 connector.
Q6: What is freeze frame data, and why is it useful?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions (like engine speed, coolant temperature, etc.) at the moment a diagnostic trouble code was set. This helps you understand the conditions that caused the problem.
Q7: Can I clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) with an OBD1 scanner with an OBD2 connector?
Yes, after repairing the issue, you can usually clear the DTCs using the scanner. The process involves connecting the scanner, turning on the ignition, and selecting the “Clear Codes” function.
Q8: What are some safety precautions I should take when working with automotive electronics?
Always disconnect the negative battery cable, wear safety glasses, use insulated tools, avoid working in wet conditions, and follow proper diagnostic procedures.
Q9: Where can I find more information about OBD1 diagnostics and repair procedures?
Consult your vehicle’s service manual, online forums dedicated to your car’s make and model, and consider taking automotive diagnostic training courses. You can also consult with MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert support.
Q10: What are the benefits of contacting MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for my Mercedes-Benz diagnostic needs?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert consultation to select the right scanner, diagnostic support, services to unlock hidden features, and advice on repairs and maintenance specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.